|
Deltabot
A delta robot is a type of parallel robot that consists of three arms connected to universal joints at the base. The key design feature is the use of parallelograms in the arms, which maintains the orientation of the end effector. In contrast, Stewart platform can change the orientation of its end effector.Bonev, I. The True Origins of Parallel Robots. Online article available at http://www.parallemic.org/Reviews/Review007.html Delta robots have popular usage in picking and packaging in factories because they can be quite fast, some executing up to 300 picks per minute. History The delta robot (a parallel arm robot) was invented in the early 1980s by a research team led by professor Reymond Clavel at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL, Switzerland). After a visit to a chocolate maker, a team member wanted to develop a robot to place pralines in their packages. The purpose of this new type of robot was to manipulate light and small objects at a very hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adept Technology
Omron Adept Technology, Inc. is a multinational corporation with headquarters in Pleasanton, California (San Francisco Bay Area). The company focus on industrial automation and robotics, including software and vision guidance. Adept has offices throughout the United States as well as in Dortmund, Germany, Paris, France, and Singapore. Adept was acquired by Omron in October 2015. Company history Adept was founded in 1983, having formerly been the West Coast Division of Unimation, which became part of Westinghouse after being a division of Consolidated Diesel Electronic (Condec) for many years. However, Adept's roots go back almost 10 years earlier, when company founders Bruce Shimano and Brian Carlisle, both Stanford graduate students, started to work with Victor Scheinman at Stanford's AI lab. In 2000, Adept Technology acquired Pensar Tucson Inc. In 2015, Omron acquired Adept Technology. Today, the company is active in a variety of industries requiring high speed, precision p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fanuc
FANUC ( or ; often styled Fanuc) is a Japanese group of companies that provide automation products and services such as robotics and computer numerical control wireless systems. These companies are principally of Japan, Fanuc America Corporation of Rochester Hills, Michigan, USA, and FANUC Europe Corporation S.A. of Luxembourg. FANUC is the largest maker of industrial robots in the world. FANUC had its beginnings as part of Fujitsu developing early numerical control (NC) and servo systems. FANUC is acronym for Fuji Automatic NUmerical Control. History In 1955, Fujitsu Ltd. approached Seiuemon Inaba( :ja:稲葉清右衛門), who was then a young engineer, to lead a new subsidiary purposed to make the field of numerical control. This nascent form of automation involved sending instructions encoded into punched cards or magnetic tape to motors that controlled the movement of tools, effectively creating programmable versions of the lathes, presses, and milling machines. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degrees Of Freedom (engineering)
In physics, the degrees of freedom (DOF) of a mechanical system is the number of independent parameters that define its configuration or state. It is important in the analysis of systems of bodies in mechanical engineering, structural engineering, aerospace engineering, robotics, and other fields. The position of a single railcar (engine) moving along a track has one degree of freedom because the position of the car is defined by the distance along the track. A train of rigid cars connected by hinges to an engine still has only one degree of freedom because the positions of the cars behind the engine are constrained by the shape of the track. An automobile with highly stiff suspension can be considered to be a rigid body traveling on a plane (a flat, two-dimensional space). This body has three independent degrees of freedom consisting of two components of translation and one angle of rotation. Skidding or drifting is a good example of an automobile's three independent degrees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the ''net'' force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's Second Law, is the combined effect of two causes: * the net balance of all external forces acting onto that object — magnitude is directly proportional to this net resulting force; * that object's mass, depending on the materials out of which it is made — magnitude is inversely proportional to the object's mass. The SI unit for acceleration is metre per second squared (, \mathrm). For example, when a vehicle starts from a standstill (zero velocity, in an inertial frame of reference) and travels in a straight line at increasing speeds, it is accelerating in the direction of travel. If the vehicle turns, an acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertia
Inertia is the idea that an object will continue its current motion until some force causes its speed or direction to change. The term is properly understood as shorthand for "the principle of inertia" as described by Newton in his first law of motion. After some other definitions, Newton states in his first law of motion: The word "perseveres" is a direct translation from Newton's Latin. Other, less forceful terms such as "to continue" or "to remain" are commonly found in modern textbooks. The modern use follows from some changes in Newton's original mechanics (as stated in the ''Principia'') made by Euler, d'Alembert, and other Cartesians. The term inertia comes from the Latin word ''iners'', meaning idle, sluggish. The term inertia may also refer to the resistance of any physical object to a change in its velocity. This includes changes to the object's speed or direction of motion. An aspect of this property is the tendency of objects to keep moving in a straight li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Material
A composite material (also called a composition material or shortened to composite, which is the common name) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions. Typical engineered composite materials include: *Reinforced concrete and masonry *Composite wood such as plywood *Reinforced plastics, such as fibre-reinforced polymer or fiberglass *Ceramic matrix composites ( composite ceramic and metal matrices) *Metal matrix composites *and other advanced composite materials There are various reasons where new material can be favoured. Typical examples include materials which are less expensive, lighter, stronger or more durable when compared with commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Drive Mechanism
A direct-drive mechanism is a mechanism design where the force or torque from a prime mover is transmitted directly to the effector device (such as the drive wheels of a vehicle) without involving any intermediate couplings such as a gear train or a belt.Asada, H., & Kanade, T. (1983) Design of direct-drive mechanical arms' in ''Journal of Vibration, Acoustics, Stress, and Reliability in Design'', Volume 105, Issue 3, pp.312-316 History In the late 19th century and early 20th century, some of the earliest locomotives and cars used direct drive transmissions at higher speeds. Direct-drive mechanisms for industrial arms began to be possible in the 1980s, with the use of rare-earth magnetic materials. The first direct-drive arm was built in 1981 at Carnegie Mellon University. Today the most commonly used magnets are neodymium magnets. Design Direct-drive systems are characterized by smooth torque transmission, and nearly-zero backlash.Bruno Siciliano, Oussama Khatib (Eds., 2008) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
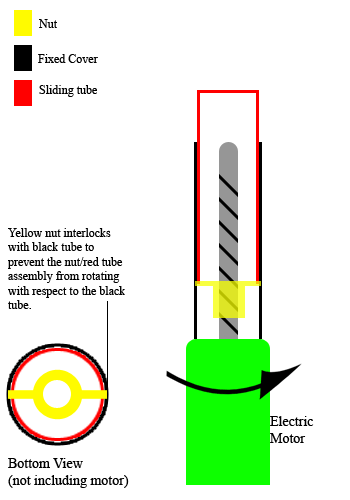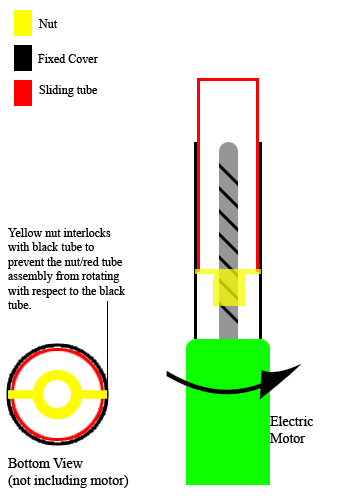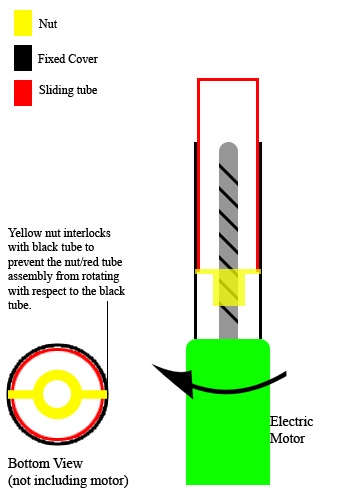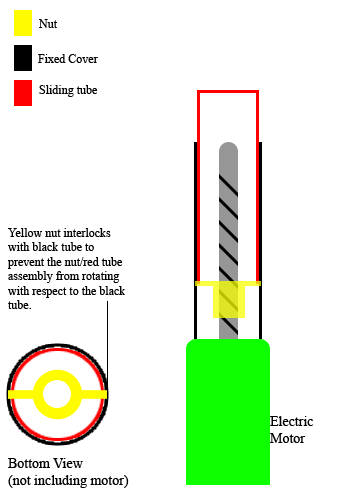
Linear Actuator
A linear actuator is an actuator that creates motion in a straight line, in contrast to the circular motion of a conventional electric motor. Linear actuators are used in machine tools and industrial machinery, in computer Peripheral, peripherals such as disk drives and printers, in Valve, valves and Damper (flow), dampers, and in many other places where linear motion is required. Hydraulics, Hydraulic or Pneumatics, pneumatic cylinders inherently produce linear motion. Many other mechanisms are used to generate linear motion from a rotating motor. Types Mechanical actuators Machine, Mechanical linear actuators typically operate by conversion of rotary motion into linear motion. Conversion is commonly made via a few simple types of mechanism: * Screw (simple machine), Screw: leadscrew, screw jack, ball screw and roller screw actuators all operate on the principle of the simple machine known as the screw. By rotating the actuator's nut, the screw shaft moves in a line. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actuator
An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving and controlling a mechanism or system, for example by opening a valve. In simple terms, it is a "mover". An actuator requires a control device (controlled by control signal) and a source of energy. The control signal is relatively low energy and may be electric voltage or current, pneumatic, or hydraulic fluid pressure, or even human power. Its main energy source may be an electric current, hydraulic pressure, or pneumatic pressure. The Control device is usually a valve. When it receives a control signal, an actuator responds by converting the source's energy into mechanical motion. In the ''electric'', ''hydraulic'', and ''pneumatic'' sense, it is a form of automation or automatic control. History The history of the pneumatic actuation system and the hydraulic actuation system dates to around the time of World War II (1938). It was first created by Xhiter Anckeleman who used his knowledge of engines and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four-bar Linkage
In the study of mechanisms, a four-bar linkage, also called a four-bar, is the simplest closed- chain movable linkage. It consists of four bodies, called ''bars'' or ''links'', connected in a loop by four joints. Generally, the joints are configured so the links move in parallel planes, and the assembly is called a ''planar four-bar linkage''. Spherical and spatial four-bar linkages also exist and are used in practice. Planar four-bar linkage Planar four-bar linkages are constructed from four links connected in a loop by four one- degree-of-freedom joints. A joint may be either a revolute joint – also known as a pin joint or hinged joint – denoted by R, or a prismatic joint – also known as a sliding pair – denoted by P. A link that are fixed in place relative to the viewer is called a ''ground link.'' A link connecting to the ground by a revolute joint that can perform a complete revolution is called a '' crank link.'' A link connecting to the ground by a revolute join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |