|
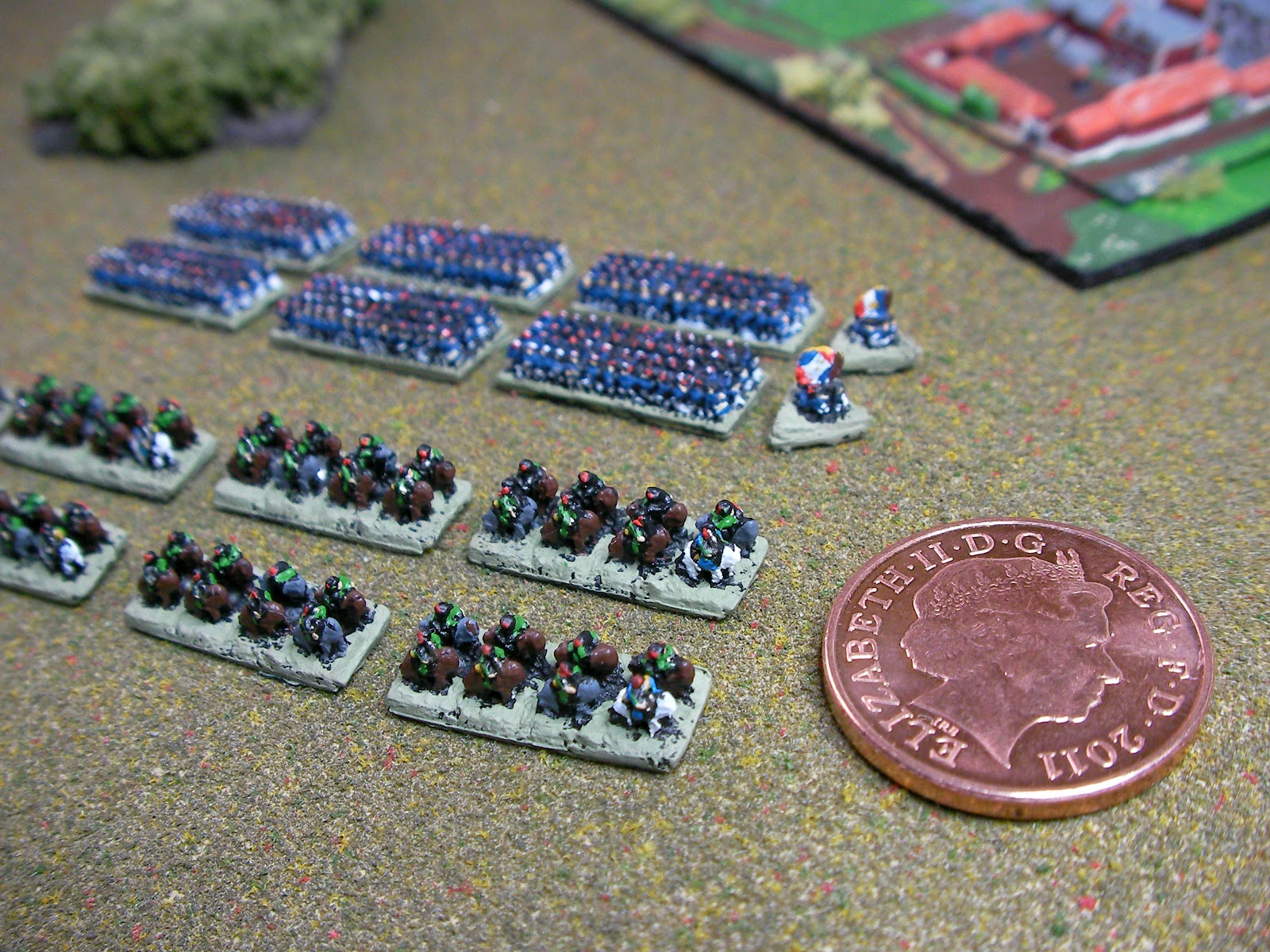
De Bellis Multitudinis
De Bellis Multitudinis (DBM) () is a ruleset for table-top miniatures wargames for the period 3000 BC to 1485 AD. It is the big battle development of De Bellis Antiquitatis. As its name implies, it is aimed primarily at simulating large battles. The rules allow armies to be chosen from published Army Lists (in 4 books, with about 250 different army lists in total - but many more once all the in-list variants are taken into account) using a points system to select roughly equal armies if required. History DBM was written by the UK based Wargames Research Group (WRG) team of Phil Barker, Richard Bodley Scott and Sue Laflin Barker. ( DBMM is Phil Barker's intended successor to DBM). First published in 1993, it went through a number of formal revisions with the last published version, DBM 3.0, coming out in 2000. Two unpublished, minor revisions have since been made, with the latest, DBM 3.2, coming into use in 2011 and available through WRG's website. DBM evolved from the ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miniature Wargaming
Miniature wargaming is a form of wargaming in which military units are represented by miniature physical models on a model battlefield. The use of physical models to represent military units is in contrast to other tabletop wargames that use abstract pieces such as counters or blocks, or computer wargames which use virtual models. The primary benefit of using models is aesthetics, though in certain wargames the size and shape of the models can have practical consequences on how the match plays out. Miniature wargaming is typically a recreational form of wargaming because issues concerning scale can compromise realism too much for most serious military applications. A historical exception to this is naval wargaming before the advent of computers. Overview A miniature wargame is played with miniature models of soldiers, artillery, and vehicles on a model of a battlefield. The benefit of using models as opposed to abstract pieces is primarily an aesthetic one. Models offer a vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Bellis Antiquitatis
''De Bellis Antiquitatis'' or ''DBA'' (English: Of the Wars of Antiquity) is a fast play set of rules for the hobby of historical miniature wargaming, particularly ancient and medieval wargaming in the period 3000 BC to 1520 AD. Now in 3rd edition. These rules allow entire armies to be represented by fewer than 50 figures. The rules also include diagrams and over 600 army lists. DBA is produced by the Wargames Research Group and was the first game in the DBx series, which now includes De Bellis Multitudinis (DBM), De Bellis Magistrorum Militum (DBMM, a successor or alternative to DBM), Hordes of the Things (a fantasy version), De Bellis Renationis (DBR, a Renaissance version). and for 1700-1920 Horse Foot and Guns (HFG) An online video game titled DBA Online' was also created. Scale and basing Scale: Each army is composed of 12 elements (stands), with several figures fixed upon each one. The number of men represented by an element varies according to the size of the army simulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wargames Research Group
The Wargames Research Group (WRG) is a British publisher of rules and reference material for miniature wargaming. Founded in 1969 they were the premier publisher of tabletop rules during the seventies and eighties, publishing rules for periods ranging from ancient times to modern armoured warfare, and reference books which are still considered standard works for amateur researchers and wargamers. They are best known for their seminal ancient and medieval period rules, and also for De Bellis Antiquitatis and Hordes of the Things fantasy rules. History WRG was founded by Phil Barker, Bob O'Brien, and Ed Smith in 1969, when they published ''War Game Rules: 1000 B.C. to 500 A.D.''. The rules quickly gained widespread acceptance through the miniature wargaming world, especially in the UK, and quickly became the acknowledged standard for ancient warfare.The Ancient Wargame Charles Grant p148 WRG followed with rules for other periods which gained similar widespread acceptance. Inno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phil Barker
Phil Barker (born 5 November 1932) is one of the major figures in the development of the modern hobby of miniatures wargaming, tabletop wargaming, particularly that of ancient warfare, and is a co-founder of the Wargames Research Group. In the 1960s he was a methods engineer at British Leyland. However, in the 1970s he took voluntary redundancy to become the first person in the UK to work full-time on wargames writing and rules design. At the time, he was also a keen horseman, a skill which he used to advantage in carrying out experiments in the use of cavalry weapons. Introduction to Wargaming Barker began wargaming as a boy using H.G. Wells Little Wars, though his interest lapsed during his time serving in the army. In the early 1960s he gamed alongside founders of the modern hobby such as Donald Featherstone (wargamer), Donald Featherstone, Tony Bath, and Charles Grant (game designer), Charles Grant. At the beginning he did not play ancients. His introduction to ancients was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Bellis Multitudinis
De Bellis Multitudinis (DBM) () is a ruleset for table-top miniatures wargames for the period 3000 BC to 1485 AD. It is the big battle development of De Bellis Antiquitatis. As its name implies, it is aimed primarily at simulating large battles. The rules allow armies to be chosen from published Army Lists (in 4 books, with about 250 different army lists in total - but many more once all the in-list variants are taken into account) using a points system to select roughly equal armies if required. History DBM was written by the UK based Wargames Research Group (WRG) team of Phil Barker, Richard Bodley Scott and Sue Laflin Barker. ( DBMM is Phil Barker's intended successor to DBM). First published in 1993, it went through a number of formal revisions with the last published version, DBM 3.0, coming out in 2000. Two unpublished, minor revisions have since been made, with the latest, DBM 3.2, coming into use in 2011 and available through WRG's website. DBM evolved from the ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skirmishers
Skirmishers are light infantry or light cavalry soldiers deployed as a vanguard, flank guard or rearguard to screen a tactical position or a larger body of friendly troops from enemy advances. They are usually deployed in a skirmish line, an irregular open formation that is much more spread out in depth and in breadth than a traditional line formation. Their purpose is to harass the enemy by engaging them in only light or sporadic combat to delay their movement, disrupt their attack, or weaken their morale. Such tactics are collectively called skirmishing. A battle with only light, relatively indecisive combat is often called a skirmish even if heavier troops are sometimes involved. Skirmishers can be either regular army units that are temporarily detached to perform skirmishing or specialty units that are specifically armed and trained for such low-level irregular warfare tactics. Light infantry, light cavalry, and irregular units often specialize in skirmishing. Skirmishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishigten, Khorch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened within Britain, and the identity was not merely imported. Anglo-Saxon identity arose from interaction between incoming groups from several Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes, both amongst themselves, and with Celtic Britons, indigenous Britons. Many of the natives, over time, adopted Anglo-Saxon culture and language and were assimilated. The Anglo-Saxons established the concept, and the Kingdom of England, Kingdom, of England, and though the modern English language owes somewhat less than 26% of its words to their language, this includes the vast majority of words used in everyday speech. Historically, the Anglo-Saxon period denotes the period in Britain between about 450 and 1066, after Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hastings
The Battle of Hastings nrf, Batâle dé Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William the Conqueror, William, the Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman Conquest of England. It took place approximately northwest of Hastings, close to the present-day town of Battle, East Sussex, and was a decisive Normans, Norman victory. The background to the battle was the death of the childless King Edward the Confessor in January 1066, which set up a succession struggle between several claimants to his throne. Harold was crowned king shortly after Edward's death, but faced invasions by William, his own brother Tostig Godwinson, Tostig, and the Norwegian King Harald Hardrada (Harold III of Norway). Hardrada and Tostig defeated a hastily gathered army of Englishmen at the Battle of Fulford on 20 September 1066, and were in turn defeated by Harold at the Battle of Stamford Brid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miniature Wargames
A miniature is a small-scale reproduction, or a small version. It may refer to: * Portrait miniature, a miniature portrait painting * Miniature art, miniature painting, engraving and sculpture * Miniature (chess), a masterful chess game or problem with very few pieces or moves, often comprising spectacular tactical combinations * Miniature (illuminated manuscript), a small painting in an illuminated text ** Arabic miniature, a small painting in an illuminated text ** Armenian miniature, a small painting in an illuminated text ** Persian miniature, a small painting in an illuminated text or album ** Ottoman miniature, a small painting in an illuminated text or album *** Contemporary Turkish Miniature, painting ** Mughal miniature, a small painting in an illuminated text or album * Scale model ** Room box ** Figurine ** Miniature figure (gaming), a small figurine used in role playing games and tabletop wargames * Miniature (alcohol), a very small bottle of an alcoholic drink * Mini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wargames Introduced In The 1990s
''WarGames'' is a 1983 American science fiction techno-thriller film written by Lawrence Lasker and Walter F. Parkes and directed by John Badham. The film, which stars Matthew Broderick, Dabney Coleman, John Wood, and Ally Sheedy, follows David Lightman (Broderick), a young hacker who unwittingly accesses a United States military supercomputer programmed to simulate, predict and execute nuclear war against the Soviet Union. ''WarGames'' was a critical and box-office success, costing $12 million and grossing $125 million worldwide. The film was nominated for three Academy Awards. Plot During a surprise nuclear attack drill, many United States Air Force Strategic Missile Wing controllers prove unwilling to turn the keys required to launch a missile strike. Such refusals convince John McKittrick and other NORAD systems engineers that missile launch control centers must be automated, without human intervention. Control is given to a NORAD supercomputer known as WOPR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |