|
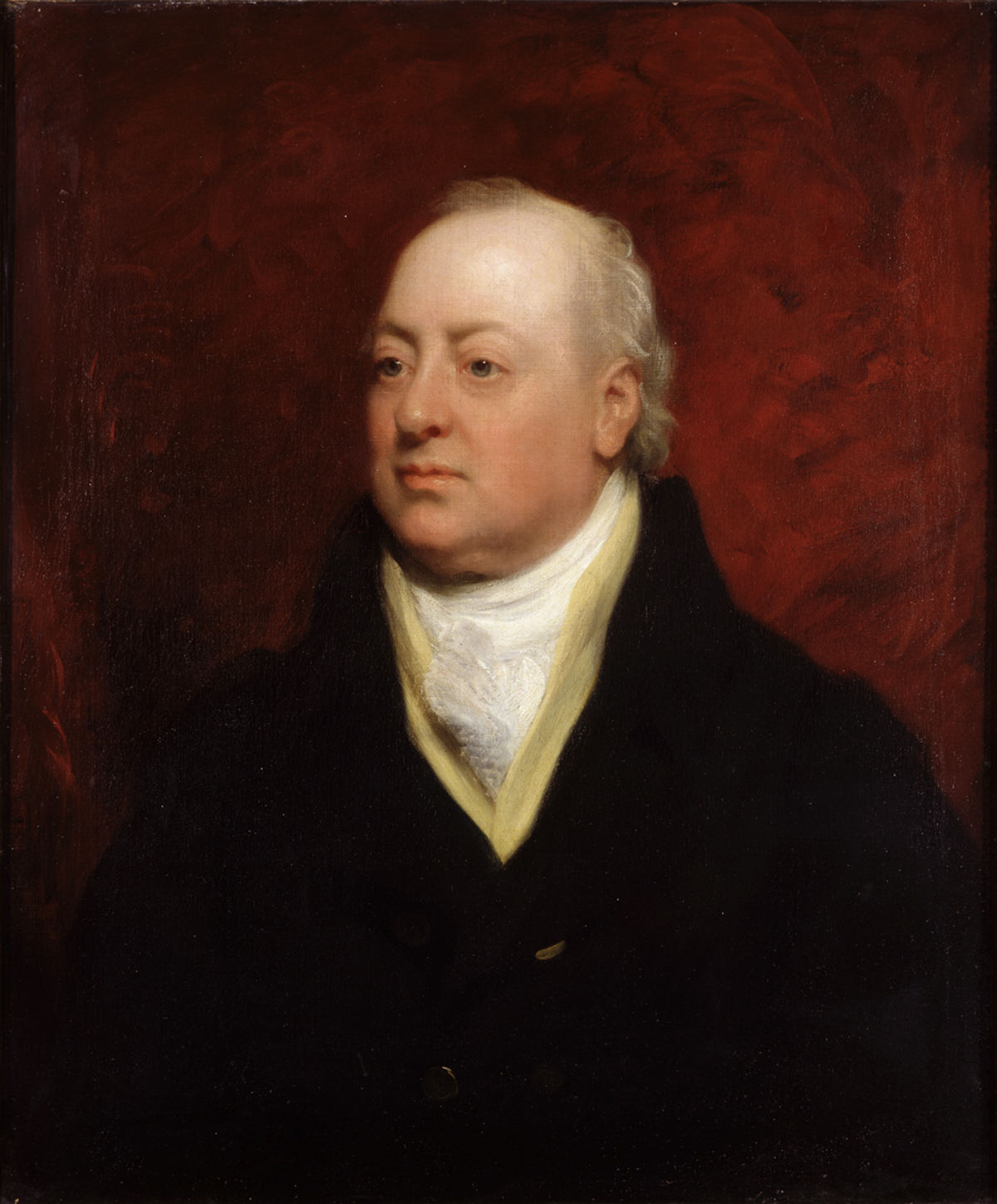
David Pitcairn
David Pitcairn M.D. (1749–1809) was a Scottish physician. Life Born on 1 May 1749 in Fife, he was eldest son of Major John Pitcairn, who was killed at the battle of Bunker's Hill; Robert Pitcairn (1752–) was his brother. He was sent to Edinburgh High School, the university of Glasgow, and then to the University of Edinburgh. He went on in 1773 to Corpus Christi College, Cambridge, where he graduated M.B. in 1779 and M.D. in 1784. In 1779 Pitcairn began practice in London, and was elected a fellow of the Royal College of Physicians on 15 Aug. 1785. He was five times censor, and in 1786 was also Gulstonian lecturer and Harveian orator. On the resignation of his uncle William Pitcairn, he was, on 10 February 1780, elected physician to St Bartholomew's Hospital, and held the post till 1793, when he resigned. He attained a large private practice. John Latham mentioned, in his treatise on gout and rheumatism, that David Pitcairn was the first to discover that valvular diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fife
Fife (, ; gd, Fìobha, ; sco, Fife) is a council area, historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. It is situated between the Firth of Tay and the Firth of Forth, with inland boundaries with Perth and Kinross (i.e. the historic counties of Perthshire and Kinross-shire) and Clackmannanshire. By custom it is widely held to have been one of the major Pictish kingdoms, known as ''Fib'', and is still commonly known as the Kingdom of Fife within Scotland. A person from Fife is known as a ''Fifer''. In older documents the county was very occasionally known by the anglicisation Fifeshire. Fife is Scotland's third largest local authority area by population. It has a resident population of just under 367,000, over a third of whom live in the three principal towns, Dunfermline, Kirkcaldy and Glenrothes. The historic town of St Andrews is located on the northeast coast of Fife. It is well known for the University of St Andrews, the most ancient univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valvular Disease Of The Heart
Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart (the aortic and mitral valves on the left side of heart and the pulmonic and tricuspid valves on the right side of heart). These conditions occur largely as a consequence of aging,Burden of valvular heart diseases: a population-based study. Nkomo VT, Gardin JM, Skelton TN, Gottdiener JS, Scott CG, Enriquez-Sarano. Lancet. 2006 Sep;368(9540):1005-11. but may also be the result of congenital (inborn) abnormalities or specific disease or physiologic processes including rheumatic heart disease and pregnancy. Anatomically, the valves are part of the dense connective tissue of the heart known as the cardiac skeleton and are responsible for the regulation of blood flow through the heart and great vessels. Valve failure or dysfunction can result in diminished heart functionality, though the particular consequences are dependent on the type and severity of valvular disease. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertfordshire
Hertfordshire ( or ; often abbreviated Herts) is one of the home counties in southern England. It borders Bedfordshire and Cambridgeshire to the north, Essex to the east, Greater London to the south, and Buckinghamshire to the west. For government statistical purposes, it forms part of the East of England region. Hertfordshire covers . It derives its name – via the name of the county town of Hertford – from a hart (stag) and a ford, as represented on the county's coat of arms and on the flag. Hertfordshire County Council is based in Hertford, once the main market town and the current county town. The largest settlement is Watford. Since 1903 Letchworth has served as the prototype garden city; Stevenage became the first town to expand under post-war Britain's New Towns Act of 1946. In 2013 Hertfordshire had a population of about 1,140,700, with Hemel Hempstead, Stevenage, Watford and St Albans (the county's only ''city'') each having between 50,000 and 100,000 r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadham Magna
Much Hadham, formerly known as Great Hadham, is a village and civil parish in the district of East Hertfordshire, Hertfordshire, England. The parish of Much Hadham contains the hamlets of Perry Green and Green Tye, as well as the village of Much Hadham itself and Hadham Cross. It covers . The village of Much Hadham is situated midway between Ware and Bishop's Stortford. The population of the parish was recorded as 2,087 in the 2011 census, an increase from 1,994 in 2001. History The name "Hadham" probably derives from Old English words meaning "Heath homestead". The affix "Much" comes from the Old English "mycel", meaning "great". The name changed around the time of the Civil War. The parish has been occupied since the Roman period. There were pottery kilns in the parish in the Roman period, and a Roman coin hoard has been found nearby. Written records of Much Hadham go back to the time of King Edgar. The village was a possession of the Bishops of London before the Norman C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Bartholomew The Less
St Bartholomew the Less is an Anglican church in the City of London, associated with St Bartholomew's Hospital, within whose precincts it stands. Once a parish church, it has, since 1 June 2015, been a chapel of ease in the parish of St Bartholomew the Great. History The present establishment is the latest in a series of churches and chapels associated with the hospital over the past 800 years. Its earliest predecessor, known as the Chapel of the Holy Cross, was founded nearby in 1123 (at the same time as the priory, now the Priory Church of St Bartholomew the Great) before moving to the present site in 1184. Along with most other religious foundations the hospital was dissolved by Henry VIII. It was then refounded by King Henry VIII, when the chapel became an Anglican parish church serving those living within its precincts. Its suffix, "the less", was given to distinguish it from its larger neighbour, St Bartholomew the Great (the former priory). The church's tower and wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Charles Wells
Dr William Charles Wells FRS FRSE FRCP (24 May 1757 – 18 September 1817) was a Scottish-American physician and printer. He lived a life of extraordinary variety, did some notable medical research, and made the first clear statement about natural selection. He applied the idea to the origin of different skin colours in human races, and from the context it seems he thought it might be applied more widely. Charles Darwin said: "''ellsdistinctly recognises the principle of natural selection, and this is the first recognition which has been indicated''".Darwin, Charles 1866. ''The origin of species by means of natural selection''. Murray, London, 4th and subsequent editions, in the preliminary 'Historical sketch'. Life Wells was born in Charleston on 24 May 1757, the second son of Mary and Robert Wells, a printer. His parents were Scots who had settled in South Carolina in 1753. He is the brother of Louisa Susannah Wells and Helena Wells. He was sent to school in Dumfries, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Everard Home
Sir Everard Home, 1st Baronet, FRS (6 May 1756, in Kingston upon Hull – 31 August 1832, in London) was a British surgeon. Home was born in Kingston-upon-Hull and educated at Westminster School. He gained a scholarship to Trinity College, Cambridge, but decided instead to become a pupil of his brother-in-law, John Hunter, at St George's Hospital. Hunter had married his sister, the poet and socialite Anne Home, in July 1771. He assisted Hunter in many of his anatomical investigations, and in the autumn of 1776 he partly described Hunter's collection. There is also considerable evidence that Home plagiarized Hunter's work, sometimes directly, sometimes indirectly; he also systematically destroyed his brother-in-law's papers in order to hide evidence of this plagiarism. It seems likely that the fire (in Home's apartments at Chelsea Hospital) which destroyed the Hunterian manuscripts in Home's possession also destroyed a precious collection of 26 microscopes originally made by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Collins Brodie The Elder
Sir Benjamin Collins Brodie, 1st Baronet, (9 June 178321 October 1862) was an English physiologist and surgeon who pioneered research into bone and joint disease. Biography Brodie was born in Winterslow, Wiltshire. He received his early education from his father, the Rev Peter Bellinger Brodie; then choosing medicine as his profession he went to London in 1801 and attended the lectures of John Abernethy and attended Charterhouse School. Two years later he became a pupil of Sir Everard Home at St George's Hospital, and in 1808 was appointed assistant surgeon at that institution, on the staff of which he served for over thirty years. In 1810 he was elected a fellow of the Royal Society, to which in the next four or five years he contributed several papers describing original investigations in physiology. In 1834, he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. At this period he also rapidly obtained a large and lucrative practice and from time to ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Macnamara Hayes
Sir John Macnamara Hayes, 1st Baronet ( – 19 July 1809) was a military physician who served as physician-extraordinary to the George, Prince of Wales, the future George IV of the United Kingdom. Early life Hayes was born in Limerick, Ireland. He was a son of John Hayes and Margaret ( Macnamara) Hayes. His grandfather, Daniel Hayes, of Mayvore, was a captain in the army at the Battle of the Boyne in the Nine Years' War. He became a doctor of medicine of Rheims on 20 March 1784 before being admitted a Licentiate of the College of Physicians on 26 June 1786. Career He was a British Army surgeon in the US from 1775 to 1783. In the 1790s, he served in the army in the French Revolutionary Wars. In 1784, Hayes was appointed physician-extraordinary to the George, Prince of Wales, the future George IV of the United Kingdom. He was also a physician at the Westminster Hospital from 1792 to 1794. For his medical service, he was awarded a baronetcy in 1797. In 1806, Hayes was appointed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew Baillie
Matthew Baillie FRS (27 October 1761 – 23 September 1823) was a British physician and pathologist, credited with first identifying transposition of the great vessels (TGV) and situs inversus. Early life and education He was born in the manse at Shotts in Lanarkshire, the son of Rev Prof James Baillie DD (1723-1778) and his wife, Dorothea Hunter (sister of Dr John Hunter and Dr William Hunter. His father was Professor of Divinity at Glasgow University. His sisters were centenarian Agnes Baillie (1760-1761) and poet/author Joanna Baillie. He was a pupil of his uncle, the anatomist John Hunter and his father-in-law, Dr. Thomas Denman, a pre-eminent obstetrician in London at the turn of the nineteenth century, whose textbook on childbirth had been first published in 1788. Baillie was educated at the Old Grammar School of Hamilton (renamed the Hamilton Academy in 1848), the University of Glasgow, and obtained his MD from the University of Oxford in 1789, having been named Snell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Clockwise from north these are: the east side of Trafalgar Square leading to St Martin's Place and then Charing Cross Road; the Strand leading to the City; Northumberland Avenue leading to the Thames Embankment; Whitehall leading to Parliament Square; The Mall leading to Admiralty Arch and Buckingham Palace; and two short roads leading to Pall Mall. The name also commonly refers to the Queen Eleanor Memorial Cross at Charing Cross station. A bronze equestrian statue of Charles I, erected in 1675, stands on a high plinth, situated roughly where a medieval monumental cross had previously stood for 353 years (since its construction in 1294) until destroyed in 1647 by Cromwell and his revolutionary government. The famously beheaded King, appearing ascendant, is the work of French sculptor Hubert Le Sueur. The aforementioned eponymous monument, the "Charing Cross", was the largest and most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hæmoptysis
Hemoptysis is the coughing up of blood or blood-stained mucus from the bronchi, larynx, trachea, or lungs. In other words, it is the airway bleeding. This can occur with lung cancer, infections such as tuberculosis, bronchitis, or pneumonia, and certain cardiovascular conditions. Hemoptysis is considered massive at . In such cases, there are always severe injuries. The primary danger comes from choking, rather than blood loss. Diagnosis * Past history, history of present illness, family history ** history of tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, chronic bronchitis, mitral stenosis, etc. ** history of cigarette smoking, occupational diseases by exposure to silica dust, etc. * Blood ** duration, frequency, amount ** Amounts of blood: large amounts of blood, or is there blood-streaked sputum ** Probable source of bleeding: Is the blood coughed up, or vomited? * Bloody sputum ** color, characters: blood-streaked, fresh blood, frothy pink, bloody gelatinous. * Accompanying symptoms ** fever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1.084_-_Old_Serjeants'_Inn.jpg)