|
Daufuskie Island, South Carolina
Daufuskie Island, located between Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, Hilton Head Island and Savannah, Georgia, Savannah, is the southernmost inhabited Sea Islands, sea island in South Carolina. It is long by almost wide – approximate surface area of (5,000 acres). With over of beachfront, Daufuskie is surrounded by the waters of Calibogue Sound, the Intracoastal Waterway and the Atlantic Ocean. It was listed as a census-designated place in the 2020 United States census, 2020 census with a population of 557. Accessible only by ferry or barge, and with a full-time population of just over 400, Daufuskie Island contains environmental preserves, private communities, resorts, Gullah houses, diverse art galleries and history. The island was named a Historic districts in the United States, historic district on the National Register of Historic Places due to its Gullah and American Civil War, Civil War history. The island is also the setting of Pat Conroy's memoir ''The Water Is Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilton Head, South Carolina
Hilton Head Island, often referred to as simply Hilton Head, is a Lowcountry resort town and barrier island in Beaufort County, South Carolina, United States. It is northeast of Savannah, Georgia (as the crow flies), and southwest of Charleston. The year-round population was 37,661 at the 2020 census, although during the peak of summer vacation season the population can swell to 150,000."Consolidated Municipal Budget Fiscal Year July 1, 2016 – June 30, 2017," ''Town of Hilton Head Island'', Accessed August 22, 2017. It is the principal city of the Hilton Head Island� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muskogean
Muskogean ( ; also Muskhogean) is a language family spoken in the Southeastern United States. Members of the family are Indigenous Languages of the Americas. Typologically, Muskogean languages are highly synthetic and agglutinative. One documented language, Apalachee, is no longer spoken, and the remaining languages are critically endangered. Genetic relationships Family division The Muskogean family consists of Alabama, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Muscogee (or Creek), Koasati, Apalachee, and Hitchiti-Mikasuki. Hitchiti is generally considered a dialect of Mikasuki. "Seminole" is sometimes used for a dialect of Muscogee spoken in Oklahoma. The major subdivisions of the family have long been controversial, but the following lower-level groups are universally accepted: Choctaw–Chickasaw, Alabama–Koasati, Hitchiti–Mikasuki, and Muscogee. Apalachee is no longer spoken; its precise relationship to the other languages is uncertain, but Mary Haas and Pamela Munro both classify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which American Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot forces organized as the Continental Army and commanded by George Washington defeated the British Army during the American Revolutionary War, British Army. The conflict was fought in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. The war's outcome seemed uncertain for most of the war. However, Washington and the Continental Army's decisive victory in the Siege of Yorktown in 1781 led King George III and the Kingdom of Great Britain to negotiate an end to the war in the Treaty of Paris (1783), Treaty of Paris two years later, in 1783, in which the British monarchy acknowledged the independence of the Thirteen Colonies, leading to the establishment of the United States as an independent and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inquisition
The Inquisition was a Catholic Inquisitorial system#History, judicial procedure where the Ecclesiastical court, ecclesiastical judges could initiate, investigate and try cases in their jurisdiction. Popularly it became the name for various medieval and reformation-era state-organized tribunals whose aim was to combat Christian heresy, heresy, apostasy, blasphemy, witchcraft, and customs considered to be Deviance (sociology), deviant, using this procedure. Violence, isolation, torture or the threat of its application, have been used by the Inquisition to extract confessions and denunciations. Studies of the records have found that the overwhelming majority of sentences consisted of penances, but convictions of unrepentant heresy were handed over to the secular courts for the application of local law, which generally resulted in execution or life imprisonment. Inquisitions with the aim of combatting religious sedition (e.g. apostasy or heresy) had their start in the Christianity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Besançon Hugues, was in common use by the mid-16th century. ''Huguenot'' was frequently used in reference to those of the Reformed Church of France from the time of the Protestant Reformation. By contrast, the Protestant populations of eastern France, in Alsace, Moselle (department), Moselle, and Montbéliard, were mainly Lutheranism, Lutherans. In his ''Encyclopedia of Protestantism'', Hans Hillerbrand wrote that on the eve of the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572, the Huguenot community made up as much as 10% of the French population. By 1600, it had declined to 7–8%, and was reduced further late in the century after the return of persecution under Louis XIV, who instituted the ''dragonnades'' to forcibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloody Point, South Carolina
Bloody Point is a residential community on the southernmost tip of Daufuskie Island, South Carolina, United States. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean on one side and the Mungen River on the other. History Bloody Point was a part of the land settled by European colonists in the late 17th and early 18th centuries. It was the site of a violent battle in 1715, during the Yemassee War. After the island had been divided up by Europeans in the 18th century, the Spanish began to grow uncomfortable having the English so close to their Florida settlements. As a result, they began to encourage and reward Yemassee Indians and other local tribes for undertaking raids on the Daufuskie colonists' settlements. During one such raid, the beaches on the southernmost tip of Daufuskie ran red with blood, earning it the title "Bloody Point". Bloody Point served as the battleground for three separate skirmishes before the American Revolutionary War. The Native Americans ultimately lost these bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
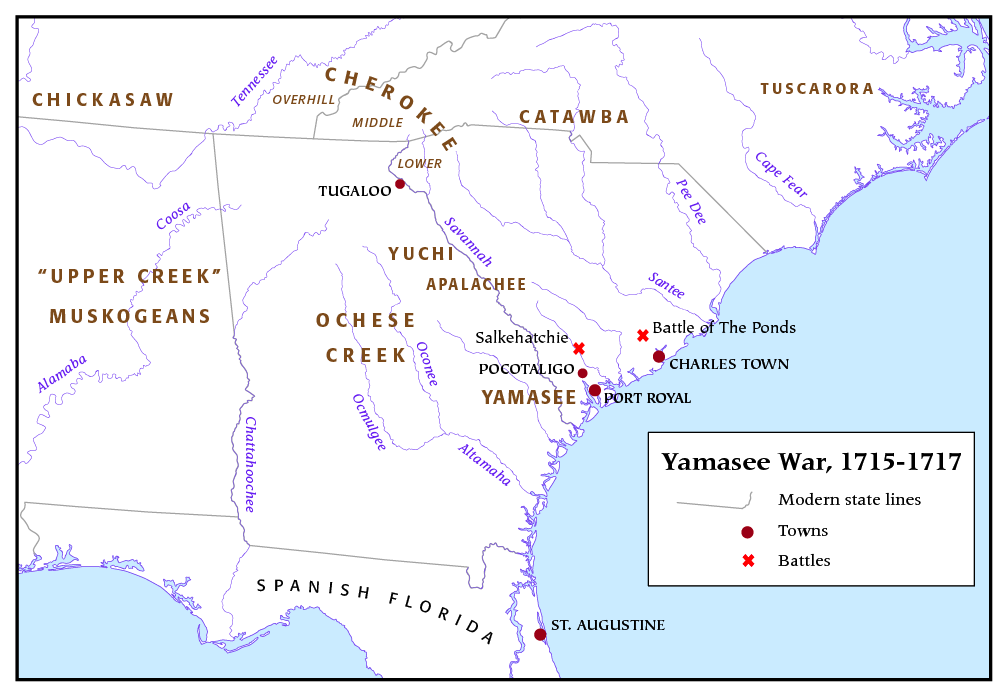
Yamasee War
The Yamasee War (also spelled Yamassee or Yemassee) was a conflict fought in South Carolina from 1715 to 1717 between British settlers from the Province of Carolina and the Yamasee, who were supported by a number of allied Native Americans in the United States, Native American peoples, including the Muscogee people, Muscogee, Cherokee, Catawba people, Catawba, Apalachee, Apalachicola Province, Apalachicola, Yuchi, Savannah River Shawnee, Congaree people, Congaree, Waxhaw people, Waxhaw, Pee Dee people, Pee Dee, Cape Fear Indians, Cape Fear, Cheraw people, Cheraw, and others. Some of the Native American groups played a minor role, while others launched attacks throughout South Carolina in an attempt to destroy the colony. Native Americans killed hundreds of colonists and destroyed many settlements, and they killed traders throughout the southeastern region. Colonists abandoned the frontiers and fled to Charleston, South Carolina, Charles Town, where starvation set in as supplie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Royal, South Carolina
Port Royal is a town on Port Royal Island in Beaufort County, South Carolina, United States. The population was 14,220 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Hilton Head Island–Bluffton metropolitan area. Port Royal is home to Marine Corps Recruit Depot Parris Island and United States Naval Hospital Beaufort. History Port Royal takes its name from the adjacent Port Royal Sound, which was explored and named by Frenchman Jean Ribault in 1562. Ribault founded the short-lived settlement of Charlesfort on Parris Island. The area later became the site of a Spanish and still later Scottish colony during the 17th century. Port Royal was the site of the Naval Battle of Port Royal during the Civil War. Later during the war, it was one of the sites of the Port Royal Experiment, which included most of the Sea Islands in Union hands. In 1863, the Emancipation Proclamation was first read at Christmas under the Proclamation tree in Port Royal. Due to the benefits of a large and shelt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolina Marsh Tacky
The Carolina Marsh Tacky or Marsh Tacky is a critically endangered breed of horse, native to South Carolina. It is a member of the Colonial Spanish group of horse breeds, which also include the Florida Cracker Horse and the Banker horse of North Carolina. It is a small horse, well-adapted for use in the lowland swamps of its native South Carolina. The Marsh Tacky developed from Spanish horses brought to the South Carolina coast by Spanish explorers, settlers and traders as early as the 16th century. The horses were used by the colonists during the American Revolution, and by settlers for farm work, herding cattle and hunting throughout the breed's history. The breed is considered to be critically endangered by both the Livestock Conservancy and the Equus Survival Trust, and there are only around 400 Marsh Tackies in existence today. In 2006 and 2007, the two organizations worked together to complete DNA testing on the breed, with the goals of mapping the Marsh Tacky's place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberian Horse
The Iberian horse is a designation given to a number of horse breeds native to the Iberian Peninsula. At present, some breeds are officially recognized by the FAO,'FAO breed list' accessed March 15, 2012, cites 3 Portuguese and 20 spanish breeds while other horses believed to be native to the peninsula are not. Likewise, some modern breeds are understood from to be descended from historic s, while others have origins outside the Iberian peninsula. The remaining FAO-recognized breeds are of well-known foreign blood, or are recently developed breeds. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Royal Sound
Port Royal Sound is a coastal sound, or inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, located in the Sea Islands region, in Beaufort County in the U.S. state of South Carolina. It is the estuary of several rivers, the largest of which is the Broad River. Geography Port Royal Sound is located between Hilton Head Island to the south and, to the north, Port Royal Island, Saint Helena Island, Parris Island, and other smaller islands. The Marine Corps Recruit Depot Parris Island facility is located on Parris Island. Several rivers flow into Port Royal Sound, most notably the Broad River. Other rivers that contribute to Port Royal sound include the Coosawhatchie River, Colleton River, Chechessee River, and Pocotaligo River, among others. Many waterways called rivers in the Sea Islands region are more akin to tidal straits, connecting bays and estuaries and separating islands. Port Royal Sound is connected to other coastal waterbodies via channels of this type. For example, the Beaufort River se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Sandford (explorer)
Robert Sandford was an English explorer of the Province of Carolina in the 17th century on behalf of the eight Lords Proprietor of the Province of Carolina. He followed Captain William Hilton in the search for sites on the Carolina coast for establishing English settlements after the charter of 1663. Both Sandford and Hilton's expeditions were based in Barbados, and Sandford was patronized by English planters in Barbados, including James Drax. Youth and early career Sandford was born in Hamburg in 1632, the son of merchant adventurer Thomas Sandford and his wife Elizabeth Kingsland. He and his brother, William, moved to Barbados as children around 1642, and Sandford stated he was ignorant of English ways in a pamphlet he wrote called ''Suriname Justice''. His uncle was Major Nathaniel Kingsland, settler of Barbados. In 1661-62 Robert Sandford ran afoul of Governor William Byam and was manacled, fined and exiled from Suriname without trial. Byam accused Sandford that under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |