|
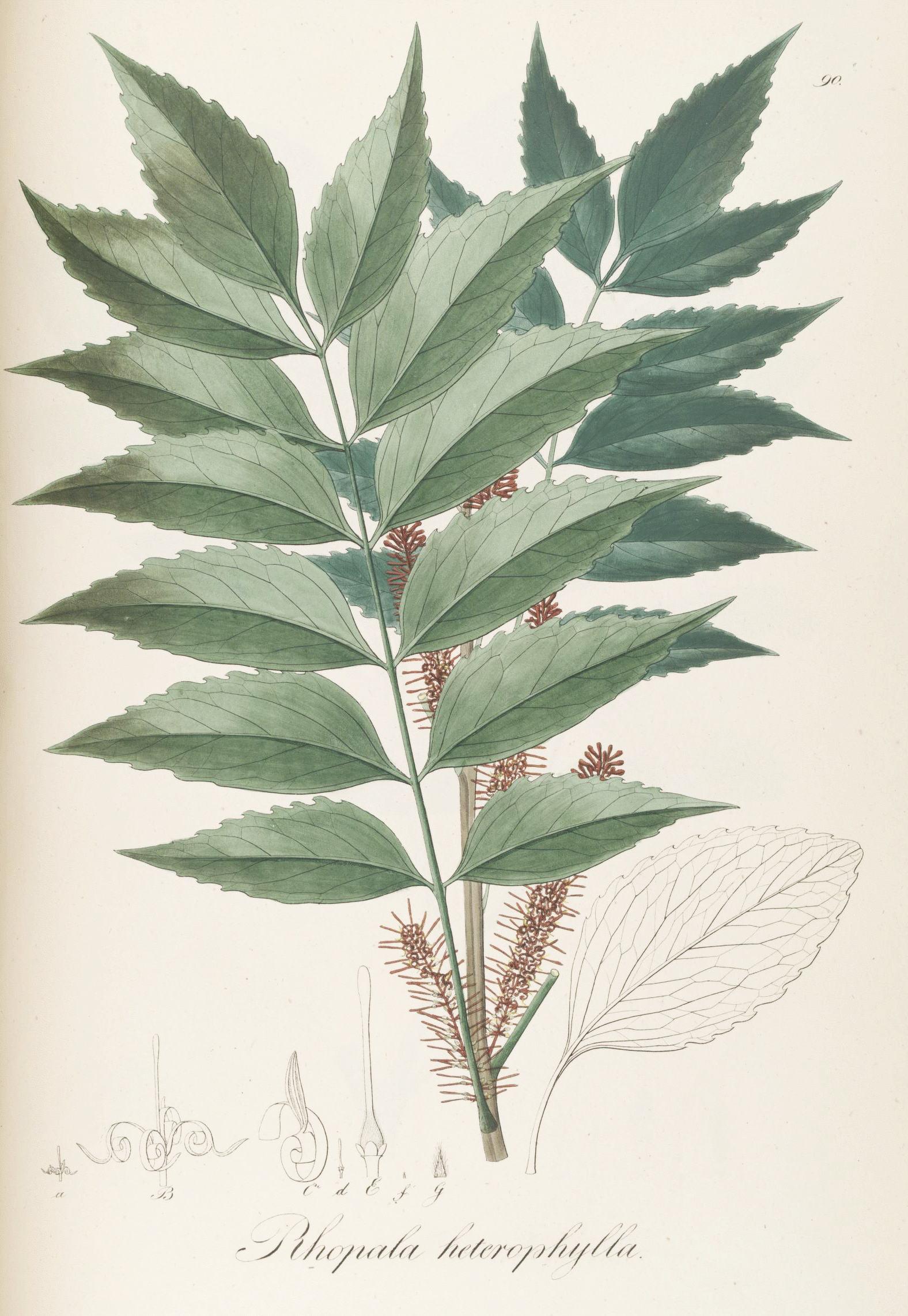
Darlingia Ferruginea
''Darlingia ferruginea'', commonly known as the brown silky oak, is a rainforest tree of the family Proteaceae from Northern Queensland. Taxonomy and naming Queensland botanist John Frederick Bailey described ''Darlingia ferruginea'' in 1899. The species name is the Latin adjective ''ferruginea'' "rusty", and refers to the rust-coloured fur on the stems and leaves. Molecular analysis indicates ''Darlingia ferruginea'' and its relative '' D. darlingiana'' join '' Floydia prealta'' as members of the subtribe Floydiinae within the subfamily Grevilleoideae in the family Proteaceae. Common names include brown silky oak, rose silky oak, and rusty silky oak. Its everyday name in the local Dyirbal language was , though a more general word "oak tree" (also applied to '' Cardwellia sublimis'' and ''Helicia australasica'') was used in the taboo yalŋuyvocabulary. Description ''Darlingia ferruginea'' grows as a tall tree in its native rainforest habitat, forming part of the canopy and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Frederick Bailey
John Frederick Bailey (5 August 1866 – 19 May 1938) was a botanist and horticulturist active in Australia in the late 19th and early 20th century. Bailey became Director of the Botanic Gardens of Brisbane in 1905. He succeeded his father, Frederick Manson Bailey, as state botanist of Queensland for 18 months in 1915–1916. He was subsequently the Director of the Botanic Gardens of Adelaide from 1917 to 1932. Memberships * ''Royal Society of Queensland The Royal Society of Queensland was formed in Queensland, Australia in 1884 from the Queensland Philosophical Society, Queensland's oldest scientific institution, with royal patronage granted in 1885. The aim of the Society is "Progressing scie ...'', Secretary from 1893 to 1905, President in 1909 * ''Horticultural Society'' Publications * 1896: ''Report on the timber trees of Herberton District, North Queensland''. 15 pages. * 1906: ''A Selection of Flowering Climbers''. 15 pages. * 1910: ''Introduction of economic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteaceae
The Proteaceae form a family of flowering plants predominantly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises 83 genera with about 1,660 known species. Together with the Platanaceae and Nelumbonaceae, they make up the order Proteales. Well-known genera include ''Protea'', ''Banksia'', ''Embothrium'', ''Grevillea'', ''Hakea'' and ''Macadamia''. Species such as the New South Wales waratah (''Telopea speciosissima''), king protea (''Protea cynaroides''), and various species of ''Banksia'', ''soman'', and ''Leucadendron'' are popular cut flowers. The nuts of ''Macadamia integrifolia'' are widely grown commercially and consumed, as are those of Gevuina avellana on a smaller scale. Australia and South Africa have the greatest concentrations of diversity. Etymology The name Proteaceae was adapted by Robert Brown from the name Proteae coined in 1789 for the family by Antoine Laurent de Jussieu, based on the genus ''Protea'', which in 1767 Carl Linnaeus derived from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darlingia Darlingiana
''Darlingia darlingiana'' is a rainforest tree of the family Proteaceae from Northern Queensland. It was described by Ferdinand von Mueller Baron Sir Ferdinand Jacob Heinrich von Mueller, (german: Müller; 30 June 1825 – 10 October 1896) was a German-Australian physician, geographer, and most notably, a botanist. He was appointed government botanist for the then colony of Vict ... in 1865 as ''Helicia darlingiana''. References Roupaleae Endemic flora of Queensland Taxa named by Ferdinand von Mueller {{Australia-eudicot-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floydia
''Floydia'' is a monotypic species of tree in the family Proteaceae native to Australia. It is a somewhat rare tree found only growing in the rainforests of southeastern Queensland and northern New South Wales. The sole species is ''Floydia praealta'' which is commonly known as the ball nut or possum nut. The tree has a superficial resemblance to the closely related ''Macadamia'' and could be confused with them. The fruit of ''F. praealta'' is poisonous. The species was formally described in 1862 by Victorian Government Botanist Ferdinand von Mueller based on plant material collected near the Clarence River in northern New South Wales and the Brisbane River in Queensland. In his publication '' Fragmenta Phytographiae Australiae '' Mueller named the plant ''Helicia praealta''. The species was transferred to the genus ''Macadamia'' in 1901 by Queensland Colonial Botanist Frederick Manson Bailey and then to ''Floydia'' in 1975 by Lawrie Johnson Lawrence Alexander Sidney Johns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floydiinae
The Grevilleoideae are a subfamily of the plant family Proteaceae. Mainly restricted to the Southern Hemisphere, it contains around 46 genera and about 950 species. Genera include ''Banksia'', ''Grevillea'', and ''Macadamia''. Description The Grevilleoideae grow as trees, shrubs, or subshrubs. They are highly variable, making a simple, diagnostic identification key for the subfamily essentially impossible to provide. One common and fairly diagnostic characteristic is the occurrence of flowers in pairs that share a common bract. However, a few Grevilleoideae taxa do not have this property, having solitary flowers or inflorescences of unpaired flowers. In most taxa, the flowers occur in densely packed heads or spikes, and the fruit is a follicle. Distribution and habitat Grevilleoideae are mainly a Southern Hemisphere family. The main centre of diversity is Australia, with around 700 of 950 species occurring there, and South America also contains taxa. However, the Grevilleoidea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grevilleoideae
The Grevilleoideae are a subfamily of the plant family Proteaceae. Mainly restricted to the Southern Hemisphere, it contains around 46 genera and about 950 species. Genera include ''Banksia'', ''Grevillea'', and ''Macadamia''. Description The Grevilleoideae grow as trees, shrubs, or subshrubs. They are highly variable, making a simple, diagnostic identification key for the subfamily essentially impossible to provide. One common and fairly diagnostic characteristic is the occurrence of flowers in pairs that share a common bract. However, a few Grevilleoideae taxa do not have this property, having solitary flowers or inflorescences of unpaired flowers. In most taxa, the flowers occur in densely packed heads or spikes, and the fruit is a follicle. Distribution and habitat Grevilleoideae are mainly a Southern Hemisphere family. The main centre of diversity is Australia, with around 700 of 950 species occurring there, and South America also contains taxa. However, the Grevilleoidea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Tropical Rainforest Plants
Australian Tropical Rainforest Plants, also known as RFK, is an identification key giving details—including images, taxonomy, descriptions, range, habitat, and other information—of almost all species of flowering plants (i.e. trees, shrubs, vines, forbs, grasses and sedges, epiphytes, palms and pandans) found in tropical rainforests of Australia, with the exception of most orchids which are treated in a separate key called Australian Tropical Rainforest Orchids (see External links section). A key for ferns is under development. RFK is a project initiated by the Australian botanist Bernie Hyland. History The information system had its beginnings when Hyland started working for the Queensland Department of Forestry in the 1960s. It was during this time that he was tasked with the creation of an identification system for rainforest trees, but given no direction as to its format. Having little belief in single-access keys, he began work on creating a multi-access key (or polyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Scientific And Industrial Research Organisation
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government agency responsible for scientific research. CSIRO works with leading organisations around the world. From its headquarters in Canberra, CSIRO maintains more than 50 sites across Australia and in France, Chile and the United States, employing about 5,500 people. Federally funded scientific research began in Australia years ago. The Advisory Council of Science and Industry was established in 1916 but was hampered by insufficient available finance. In 1926 the research effort was reinvigorated by establishment of the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), which strengthened national science leadership and increased research funding. CSIR grew rapidly and achieved significant early successes. In 1949, further legislated changes included renaming the organisation as CSIRO. Notable developments by CSIRO have included the invention of atomic absorption spectroscopy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyirbal Language
Dyirbal (also ''Djirubal'') is an Australian Aboriginal language spoken in northeast Queensland by the Dyirbal people. In 2016, the Australian Bureau of Statistics reported that there were 8 speakers of the language. It is a member of the small Dyirbalic branch of the Pama–Nyungan family. It possesses many outstanding features that have made it well known among linguists. In the years since the Dyirbal grammar by Robert Dixon was published in 1972, Dyirbal has steadily moved closer to extinction as younger community members have failed to learn it. Dialects There are many different groups speaking dialects of Dyirbal language. Researcher Robert Dixon estimates that Dyirbal had, at its peak, 10 dialects. Dialects include: * Dyirbal (or Jirrbal) spoken by the Dyirbalŋan * Mamu, spoken by the Waɽibara, Dulgubara, Bagiɽgabara, Dyiɽibara, and Mandubara (There are also different types of Mamu spoken by individual groups, such as Warribara Mamu, and Dulgubara Mamu) * Gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardwellia
''Cardwellia'' is a genus of a sole described species of large trees in the plant family Proteaceae. The species ''Cardwellia sublimis'' (northern silky oak) is endemic to the rainforests of the wet tropics region of northeastern Queensland, Australia. Other common names include bull oak, golden spanglewood, lacewood, oak and oongaary. The compound leaves have up to 17 leaflets. It produces white inflorescences followed by woody fruits which are prominently displayed outside the canopy. Taxonomy and naming Ferdinand von Mueller named the genus in honour of Edward Cardwell, who had been Secretary of State for the Colonies from 1864 to 1866. The species name is the Latin adjective ''sublimis'' "lofty". The type specimen was collected by John Dallachy in Rockingham Bay. Its everyday name in the local Dyirbal language was ''jungan'', though a more general word ''gurruŋun'' "oak tree" (also applied to ''Darlingia ferruginea'' and ''Helicia australasica'') was used in the taboo yal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicia Australasica
''Helicia australasica'', also named Austral oak or creek silky oak, is a species of rainforest trees from the flowering plant family Proteaceae. Its everyday name in the local northeast Queensland Dyirbal language was ''miyabur'', though a more general word ''gurruŋun'' "oak tree" (also applied to ''Darlingia ferruginea'' and '' Cardwellia sublimis'') was used in the taboo yalŋuyvocabulary. They grow naturally through New Guinea and in Australia in central and northeastern Queensland, Cape York Peninsula and the Northern Territory, from about altitude. They are threatened by habitat loss Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby .... They have been recorded growing up to about tall. References australasica Proteales of Australia Flora of Papua New Guinea Vu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |