|
Daguerrotypes
Daguerreotype (; french: daguerréotype) was the first publicly available photographic process; it was widely used during the 1840s and 1850s. "Daguerreotype" also refers to an image created through this process. Invented by Louis Daguerre and introduced worldwide in 1839, the daguerreotype was almost completely superseded by 1860 with new, less expensive processes, such as ambrotype (collodion process), that yield more readily viewable images. There has been a revival of the daguerreotype since the late 20th century by a small number of photographers interested in making artistic use of early photographic processes. To make the image, a daguerreotypist polished a sheet of silver-plated copper to a mirror finish; treated it with fumes that made its surface light-sensitive; exposed it in a camera for as long as was judged to be necessary, which could be as little as a few seconds for brightly sunlit subjects or much longer with less intense lighting; made the resulting laten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Daguerre 2 , names sometimes translated to English as "Louis"
{{disambiguation ...
Louis may refer to: * Louis (coin) * Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name * Louis (surname) * Louis (singer), Serbian singer * HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy See also Derived or associated terms * Lewis (other) * Louie (other) * Luis (other) * Louise (other) * Louisville (other) * Louis Cruise Lines * Louis dressing, for salad * Louis Quinze, design style Associated names * * Chlodwig, the origin of the name Ludwig, which is translated to English as "Louis" * Ladislav and László - names sometimes erroneously associated with "Louis" * Ludovic, Ludwig, Ludwick, Ludwik Ludwik () is a Polish given name. Notable people with the name include: * Ludwik Czyżewski, Polish WWII general * Ludwik Fleck (1896–1961), Polish medical doctor and biologist * Ludwik Gintel (1899–1973), Polish-Israeli Olympic soccer player ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
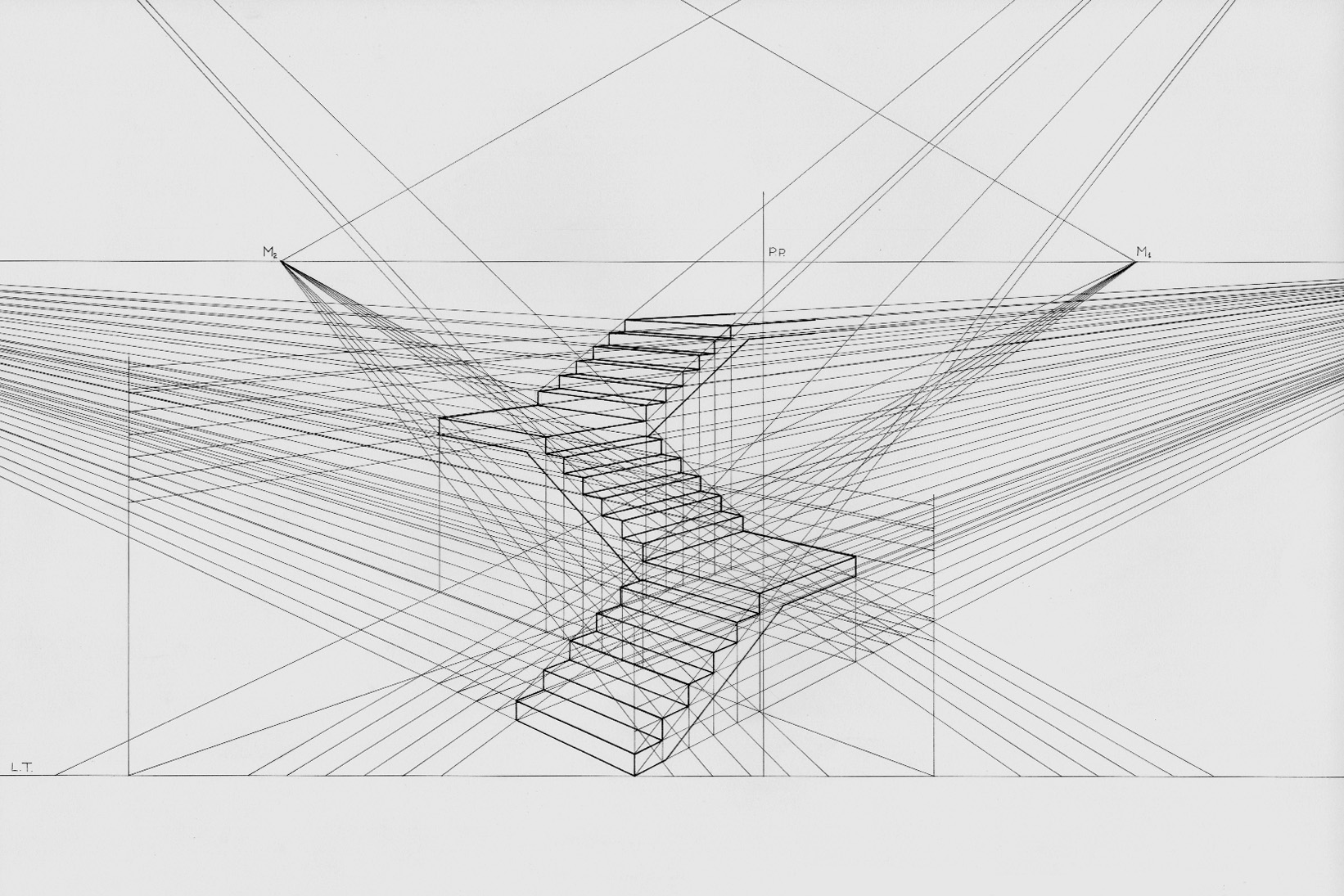
Perspective (graphical)
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of 3D projection, graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table (halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig (in 1825) and Antoine Jérôme Balard (in 1826), its name was derived from the Ancient Greek (bromos) meaning "stench", referring to its sharp and pungent smell. Elemental bromine is very reactive and thus does not occur as a native element in nature but it occurs in colourless soluble crystalline mineral halide salts, analogous to table salt. In fact, bromine and all the halogens are so reactive that they form bonds in pairs—never in single atoms. While it is rather rare in the Earth's crust, the high solubility of the bromide ion (Br) has caused its accumulation in the oceans. Commercial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek 'violet-coloured'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. It is the least abundant of the stable halogens, being the sixty-first most abundant element. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angelo Sala
Angelo Sala (Latin: Angelus Sala) (21 March 1576, Vicenza – 2 October 1637, Bützow) was an Italian doctor and early iatrochemist. He promoted chemical remedies and, drawing on the relative merits of the conflicting chemical and Galenical systems of medicine, dismissed alchemical transmutation and 'universal medicine'; objected to tartar which had deliquesced being called an 'oil'; observed that metals reacted differently with acids; that sulphur extracted something from the air in order to burn; that silver nitrate darkened on exposure to light; surmised the existence of elementary (atomic) particles; and described newly discovered compounds and methods of preparation. Sala made the first studies on the formation of alcohol from fermenting musts and so is regarded as the founder of sugar chemistry. Biography Sala was the son of the spinner Bernardino Sala. He probably first learned the profession of pharmacy in Venice. A Calvinist, he left Italy and his career as a docto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Miniature
A Persian miniature (Persian: نگارگری ایرانی ''negârgari Irâni'') is a small Persian painting on paper, whether a book illustration or a separate work of art intended to be kept in an album of such works called a ''muraqqa''. The techniques are broadly comparable to the Western Medieval and Byzantine traditions of miniatures in illuminated manuscripts. Although there is an equally well-established Persian tradition of wall-painting, the survival rate and state of preservation of miniatures is better, and miniatures are much the best-known form of Persian painting in the West, and many of the most important examples are in Western, or Turkish, museums. Miniature painting became a significant genre in Persian art in the 13th century, receiving Chinese influence after the Mongol conquests, and the highest point in the tradition was reached in the 15th and 16th centuries. The tradition continued, under some Western influence, after this, and has many modern exponent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Eastern Art
The history of Asian art includes a vast range of arts from various cultures, regions, and religions across the continent of Asia. The major regions of Asia include Central, East, South, Southeast, and West Asia. Central Asian art primarily consists of works by the Turkic peoples of the Eurasian Steppe, while East Asian art includes works from China, Japan, and Korea. South Asian art encompasses the arts of the Indian subcontinent, with Southeast Asian art including the arts of Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, Singapore, Indonesia, and the Philippines. West Asian art encompasses the arts of the Near East, including the ancient art of Mesopotamia, and more recently becoming dominated by Islamic art. In many ways, the history of art in Asia parallels the development of Western art. The art histories of Asia and Europe are greatly intertwined, with Asian art greatly influencing European art, and vice versa; the cultures mixed through methods such as the Silk Road transmission of art, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perspective (graphical)
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of 3D projection, graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modernism
Modernism is both a philosophy, philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western world, Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new forms of art, philosophy, and social organization which reflected the newly emerging industrial society, industrial world, including features such as urbanization, architecture, new technologies, and war. Artists attempted to depart from traditional forms of art, which they considered outdated or obsolete. The poet Ezra Pound's 1934 injunction to "Make it New" was the touchstone of the movement's approach. Modernist innovations included abstract art, the stream-of-consciousness novel, montage (filmmaking), montage cinema, atonal and twelve-tone music, divisionist painting and modern architecture. Modernism explicitly rejected the ideology of Realism (arts), realism and made use of the works of the past by the employment of reprise, incorpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Art History
The art of Europe, or Western art, encompasses the history of visual art in Europe. European prehistoric art started as mobile Upper Paleolithic rock and cave painting and petroglyph art and was characteristic of the period between the Paleolithic and the Iron Age. Written histories of European art often begin with the art of Ancient Israel and the Ancient Aegean civilizations, dating from the 3rd millennium BC. Parallel with these significant cultures, art of one form or another existed all over Europe, wherever there were people, leaving signs such as carvings, decorated artifacts and huge standing stones. However a consistent pattern of artistic development within Europe becomes clear only with the art of Ancient Greece, adopted and transformed by Rome and carried; with the Roman Empire, across much of Europe, North Africa and Western Asia. The influence of the art of the Classical period waxed and waned throughout the next two thousand years, seeming to slip into a dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_001.jpg)


_-_Apelles_painting_Campaspe_-_2.jpg)