|
Dagistheus
Dagistheus ( 479) was an Ostrogothic chieftain. The name is Germanic. Theodoric the Great (r. 474–526) sent Dagistheus and Soas as hostages to Adamantius in Epirus in 479. He was presumably a leading Ostrogothic chieftain under Theodoric. The Roman baths in Constantinople were possibly named after him. He may have been an ancestor of the later Byzantine general Dagisthaeus Dagisthaeus (, ''Dagisthaîos'') was a 6th-century Eastern Roman military commander, probably of Gothic origin, in the service of the emperor Justinian I. Dagisthaeus was possibly a descendant of the Ostrogothic chieftain Dagistheus.* In 548, .... References Sources *{{cite book, first1=Arnold Hugh Martin, last1=Jones, first2=John Robert , last2=Martindale, first3=J. , last3=Morris, title=The Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire, url=https://books.google.com/books?id=G5W6vCO_pYUC&pg=PA341, year=1980, publisher=Cambridge University Press, isbn=978-0-521-20159-9, pages=341– 5th-century Ostrogothi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagisthaeus (general)
Dagisthaeus (, ''Dagisthaîos'') was a 6th-century Eastern Roman military commander, probably of Gothic origin, in the service of the emperor Justinian I. Dagisthaeus was possibly a descendant of the Ostrogothic chieftain Dagistheus.* In 548, Dagisthaeus, still a young officer, was ''magister militum per Armeniam'' and commanded a force of 7,000 Romans and 1,000 Tzani sent to recapture the Euxine fortress of Petra, in Lazica, from a Sassanid Persian force during the Lazic War. Dagisthaeus put Petra under siege, but, according to the contemporary historian Procopius, acted in an incompetent manner. He was so confident in victory that he wrote to Justinian, indicating what rewards he thought he and his brother deserved. Dagisthaeus failed in his task, however, and had to flee before a relieving Sassanid army towards the Phasis river, without giving orders to his men. After that, Dagisthaeus, joined by the Lazi under King Gubazes, was able to defeat two Persian field armies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
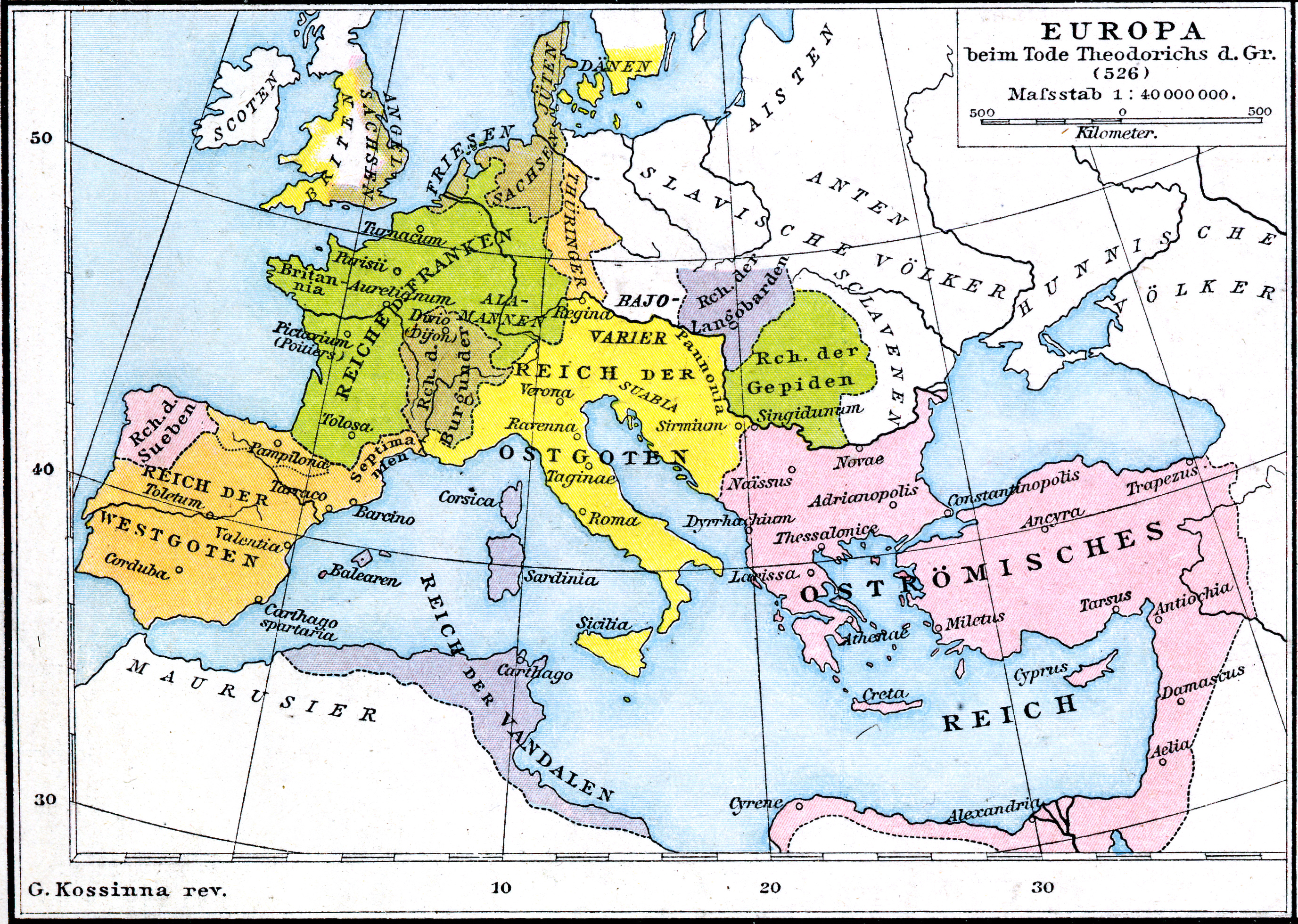
Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths () were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under Theodoric the Great. Theoderic's family, the Amal dynasty, accumulated royal power in Roman Pannonia after the death of Attila, and collapse of his Hunnic empire. Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Zeno (emperor), Emperor Zeno played these Pannonian Goths off against the Thracian Goths to their south. However, instead the two groups united after the death of the Thracian leader Theoderic Strabo and his son Recitach. Zeno then backed Theodoric to invade Italy and replace Odoacer there, whom he had previously supported as its king. In 493, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania, and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English language, English, is also the world's most List of languages by total number of speakers, widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia, History of Germany#Iron Age, Iron Age Northern Germany and along the North Sea and Baltic coasts. The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English language, English with around 360–400 million native speakers; German language, German, with over 100 million native speakers; and Dutch language, Dutch, with 24 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal, was king of the Ostrogoths (475–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician (ancient Rome)#Late Roman and Byzantine period, patrician of the Byzantine Empire#Loss of the Western Roman Empire, Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Roman Emperor#Later assertions to the title, Western Roman emperor in all but name, since he ruled a large part of the former Western Roman Empire described as a ''Res Publica'', had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497 which he used, was referred to by the imperial title ''princeps'' by the Italian aristocracy and exercised imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adamantius (praefectus Urbi)
Adamantius or Adamantios may refer to: People Only name * Adamantius (Pseudo-Origen), 4th-century Christian writer * Adamantius (physician), 5th-century Jewish physician from Alexandria * Adamantius (praefectus urbi), 5th-century politician of the Eastern Roman Empire Nickname * Origen Adamantius, 3rd century early Christian theologian First name * Adamantios Korais (1748–1833), humanist scholar credited with laying the foundations of Modern Greek literature * Adamantios Androutsopoulos (1919–2000), Prime Minister of Greece from 1973 to 1974 * Adamantios Sampson (fl. 1973–present), archaeologist from Rhodes Other * ''Adamantius'' (journal), academic journal of the Italian Research Group on Origen and the Alexandrian Tradition See also * Adeimantus (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay of Vlorë and the Ceraunian Mountains, Acroceraunian Mountains in the north to the Ambracian Gulf and the ruined Roman Empire, Roman city of Nicopolis in the south.. It is currently divided between the Modern regions of Greece, region of Epirus (region), Epirus in northwestern Greece and the counties of Gjirokastër County, Gjirokastër and Vlorë County, Vlorë in southern Albania. The largest city in Epirus is Ioannina, seat of the Greek region of Epirus, with Gjirokastër the largest city in the Albanian part of Epirus. A rugged and mountainous region, Epirus was the north-west area of ancient Greece. It was inhabited by the Greek tribes of the Chaonians, Molossians, and Thesprotians. It was home to the sanctuary of Dodona, the oldest o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empires between its consecration in 330 until 1930, when it was renamed to Istanbul. Initially as New Rome, Constantinople was founded in 324 during the reign of Constantine the Great on the site of the existing settlement of Byzantium, and shortly thereafter in 330 became the capital of the Roman Empire. Following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century, Constantinople remained the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire (also known as the Byzantine Empire; 330–1204 and 1261–1453), the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Although the city had been known as Istanbul since 1453, it was officially renamed as Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th-century Ostrogothic People
The 5th century is the time period from AD 401 (represented by the Roman numerals CDI) through AD 500 (D) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia. It saw the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire, which came to a formal end in 476 AD. This empire had been ruled by a succession of weak emperors, with the real political might being increasingly concentrated among military leaders. Internal instability allowed a Visigoth army to reach and Sack of Rome (410), ransack Rome in 410. Some recovery took place during the following decades, but the Western Empire received another serious blow when a second foreign group, the Vandals, occupied Carthage, capital of an extremely important province in Africa (Roman province), Africa. Attempts to retake the province were interrupted by the invasion of the Huns under Attila. After Attila's defeat, both Eastern and W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |