|
Climate Of Multan
Multan is a city located in the southern part of Punjab, province in Pakistan. Multan features an arid climate with very hot summers and cold winters. The city witnesses some of the most extreme temperatures in the country. Dust storms are a common occurrence within the city. The closest major city is Bahawalpur. The area around the city is a flat plain and is ideal for agriculture, with many citrus and mango farms. There are many canals that cut across the Multan District, providing water from nearby farms. This makes the land very fertile. However usually land close to the Chenab River are flooded in the monsoon season. Factors The monsoon and the Western Disturbance are the two main factors that affect the weather in Multan; otherwise, Continental air prevails for rest of the seasons. Following are the main factors that influence the weather over Multan. *Western Disturbances generally occur during the winter months and cause moderate rainfall. Hailstorms are also a common occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multan
Multan (; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, on the bank of the Chenab River. Multan is Pakistan's seventh largest city as per the 2017 census, and the major cultural, religious and economic centre of southern Punjab. Multan is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities#Asia, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Asia, with a history stretching deep into antiquity. The ancient city was the site of the renowned Multan Sun Temple, and was besieged by Alexander the Great during the Mallian Campaign. A historic cultural centre of the wider Punjab, it was conquered by the Ummayad military commander Muhammad bin qasim, Muhammad bin Qasim. The city later became independent as the capital of the Emirate of Multan in 855 A.D., before subsequently coming under the rule of empires such as the Ghaznavids, the Ghurids and the Mamluk Sultanate, Mamluks. In 1445, it became capital of the Langah Sultanate. In 1526, it was conquered by the Mughal Empire. Multan Subah would become o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Extreme Weather Records In Pakistan
The weather extremes in Pakistan include extremely high and extremely low temperatures, heaviest rainfalls and floodings. Pakistan has one of the highest temperature ranges in the world (temperature range refers to the difference between highest and lowest recorded temperatures ever) with proven weather conditions ranging from as high as like those in the Sahara desert, to as low as those like in Alaska making it one of the most climatically diverse countries in the world. The highest temperature ever recorded in Pakistan is which was recorded in Turbat, Balochistan on 28 May 2017. It was not only the hottest temperature ever recorded in Pakistan but also the hottest reliably measured temperature ever recorded on the continent of Asia and the fourth-highest temperature ever recorded on Earth. The second-highest temperature ever recorded in Pakistan is which was recorded in Moenjo Daro, Sindh on 26 May 2010. It is fifth-highest temperature ever recorded on Earth. The highest r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Of Lahore
Lahore features a five-season semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification ''BSh''), closely bordering a humid subtropical climate, with five seasons: foggy winter (10 Dec – 1 Feb) with few western disturbances causing rain; pleasant spring (16 Feb – 15 April); summer (15 April – 30 June) with dust, rain storms and heat wave periods; rainy monsoon (1 July – 16 September); and dry autumn (16 September –14 November). However, in some cases, it can be classified as being humid subtropical (Cwa), rather than semi-arid, since it has well defined seasons and an ample amount of rain. It occasionally has very prolonged and dense monsoons, typical of a humid subtropical climate. The hottest month is June, where average highs routinely exceed . The wettest month is July, with heavy rainfalls and evening thunderstorms with the possibility of cloudbursts. The coolest month is January with dense fog. The city's record high temperature was , recorded on 5 June 2003. On 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
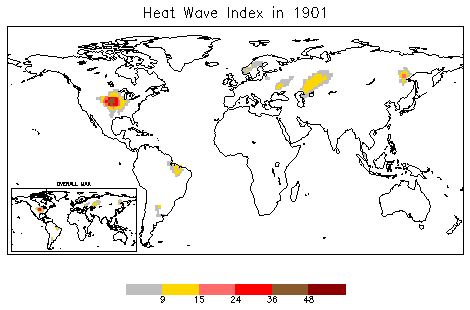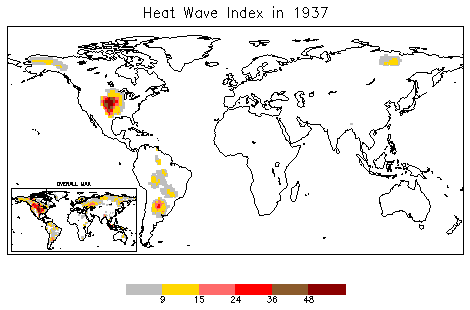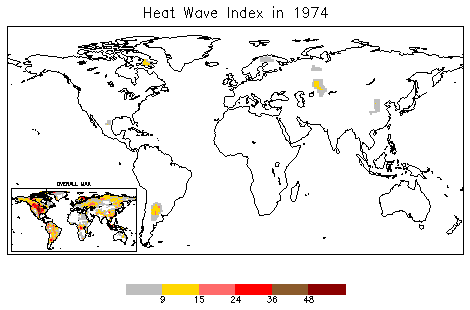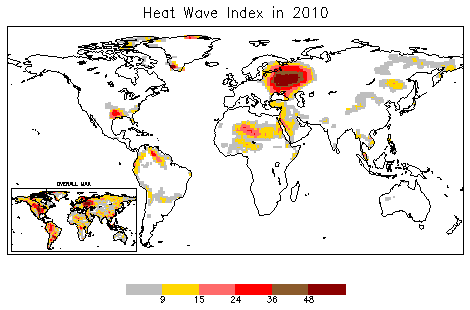
Heat Wave
A heat wave, or heatwave, is a period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity, especially in oceanic climate countries. While definitions vary, a heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the area and relative to normal temperatures for the season. Temperatures that people from a hotter climate consider normal can be called a heat wave in a cooler area if they are outside the normal climate pattern for that area. The term is applied both to hot weather variations and to extraordinary spells of hot weather which may occur only once a century. Severe heat waves have caused catastrophic crop failures, thousands of deaths from hyperthermia, increased risk of wildfires in areas with drought, and widespread power outages due to increased use of air conditioning. A heat wave is considered extreme weather, and poses danger to human health because heat and sunlight overwhelm the human body's cooling system. Heat waves can usually be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern side, where it comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert (also known as the Great Indian Desert) and shares a border with the Pakistani provinces of Punjab to the northwest and Sindh to the west, along the Sutlej- Indus River valley. It is bordered by five other Indian states: Punjab to the north; Haryana and Uttar Pradesh to the northeast; Madhya Pradesh to the southeast; and Gujarat to the southwest. Its geographical location is 23.3 to 30.12 North latitude and 69.30 to 78.17 East longitude, with the Tropic of Cancer passing through its southernmost tip. Its major features include the ruins of the Indus Valley civilisation at Kalibangan and Balathal, the Dilwara Temples, a Jain pilgrimage site at Rajasthan's only hill stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent, Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's List of deserts by area, 20th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-largest hot subtropical desert. About 85% of the Thar Desert is in India, and about 15% is in Pakistan. The Thar Desert is about 4.56% of the total geographical area of India. More than 60% of the desert lies in the Indian state of Rajasthan; the portion in India also extends into Gujarat, Punjab, India, Punjab, and Haryana. The portion in Pakistan extends into the provinces of Sindh and Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab (the portion in the latter province is referred to as the Cholistan Desert). History of desertification Ice-age desertification During the Last Glacial Maximum 20,000 before present, an approximately ice sheet covered the Tibetan Plateau#Glaciology, Tibetan P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan Meteorological Department
The Pakistan Meteorological Department (PMD) ( ur, , also known as Pakistan Met Office), is an autonomous and independent institution tasked with providing weather forecasts and public warnings concerning weather for protection, safety and general information. Apart from meteorology, it is also involved in monitoring as well as investigating Weather forecasting, weather phenomenons, Astrometeorology, astronomical events, hydrology and space research, research in astrophysics, climate changes and studies on Aerospace engineering, aeronautical engineering, Renewable energy in Pakistan, renewable energy resources across various parts of the country. Headquartered in Islamabad. Till 1991, PMD was providing Aviation Weather services to Defense Forces through regular deputation of meteorologists to PAF. However, in 1991, PAF formed its own Met branch and officers are now inducted on regular basis to meet Aviation requirements. The main training however is being imparted by PMD through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
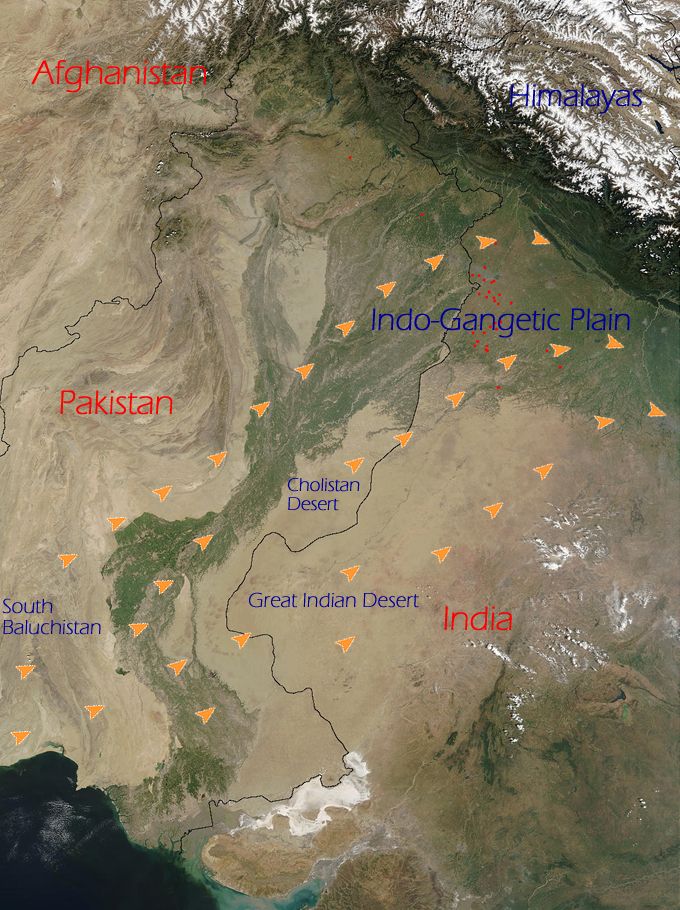
Loo (wind)
The Loo ( hi, लू, Urdu: لو) is a strong, dusty, gusty, hot and dry summer wind from the west which blows over the Indo-Gangetic Plain region of North India and Pakistan. It is especially strong in the months of May and June. Due to its very high temperatures (45 °C–50 °C or 115 °F–120 °F), exposure to it often leads to fatal heatstrokes. Since it causes extremely low humidity and high temperatures, the ''Loo'' also has a severe drying effect on vegetation leading to widespread browning in the areas affected by it during the months of May and June. Origin and ending The Loo mainly originates in the large desert regions of the northwestern Indian subcontinent: the Great Indian Desert, the Cholistan Desert and the desert areas of Southern Balochistan. The Loo ends in late summer, with the arrival of the Indian monsoon. In some areas of North India and Pakistan, there are brief, but violent, dust storms known as Kali Andhi (or ''black Storm'') b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not wholl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Rukhn-i-Alam Multan
Shah (; fa, شاه, , ) is a royal title that was historically used by the leading figures of Iranian monarchies.Yarshater, EhsaPersia or Iran, Persian or Farsi, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) It was also used by a variety of Persianate societies, such as the Ottoman Empire, the Kazakh Khanate, the Khanate of Bukhara, the Emirate of Bukhara, the Mughal Empire, the Bengal Sultanate, historical Afghan dynasties, and among Gurkhas. Rather than regarding himself as simply a king of the concurrent dynasty (i.e. European-style monarchies), each Iranian ruler regarded himself as the Shahanshah ( fa, شاهنشاه, translit=Šâhanšâh, label=none, ) or Padishah ( fa, پادشاه, translit=Pâdešâh, label=none, ) in the sense of a continuation of the original Persian Empire. Etymology The word descends from Old Persian ''xšāyaθiya'' "king", which used to be considered a borrowing from Median, as it was compared to Avestan ''xšaθra-'', "power" and "command" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hailstorms
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fall in cold weather, while hail growth is greatly inhibited during low surface temperatures. Unlike other forms of water ice precipitation, such as graupel (which is made of rime ice), ice pellets (which are smaller and translucent), and snow (which consists of tiny, delicately crystalline flakes or needles), hailstones usually measure between and in diameter. The METAR reporting code for hail or greater is GR, while smaller hailstones and graupel are coded GS. Hail is possible within most thunderstorms (as it is produced by cumulonimbus), as well as within of the parent storm. Hail formation requires environments of strong, upward motion of air within the parent thunderstorm (similar to tornadoes) and lowered heights of the freezing le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |