|
Chōraku-ji
is a small Shingon sect Buddhist temple in Shimoda, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. It is noteworthy in that it was the location of the signing of the Treaty of Shimoda in 1855, which officially established diplomatic relations between Bakumatsu Japan and the Russian Empire. History Chōraku-ji was founded in 1555, but much of its subsequent history is uncertain. The temple was commandeered by the Tokugawa shogunate for use as a conference hall during negotiations to end Japan's national isolation policy. The Russian delegation under Vice-Admiral Euphimy Vasil'evich Putiatin, was trapped in Shimoda at the end of 1854 when a tsunami caused by the Ansei Tokai earthquake destroyed their fleet. While a new ship was being constructed in nearby Heda, negotiations proceeded towards a treaty, and on February 7, 1855, the Russo-Japanese treaty of friendship was signed at Chōraku-ji by Putiatin as Russian Imperial Ambassador and Japanese representative Kawaji Toshiakira. The treaty c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Shimoda
The Treaty of Shimoda (下田条約, ''Shimoda Jouyaku'') (formally Treaty of Commerce and Navigation between Japan and Russia 日露和親条約, ''Nichi-Ro Washin Jouyaku'') of February 7, 1855, was the first treaty between the Russian Empire, and the Empire of Japan, then under the administration of the Tokugawa shogunate. Following shortly after the Convention of Kanagawa signed between Japan and the United States, it effectively meant the end of Japan's 220-year-old policy of national seclusion (''sakoku''), by opening the ports of Nagasaki, Shimoda and Hakodate to Russian vessels and established the position of Russian consuls in Japan and defined the borders between Japan and Russia. The isolation of Japan Since the beginning of the seventeenth century, the Tokugawa shogunate pursued a policy of isolating the country from outside influences. Foreign trade was maintained only with the Dutch and the Chinese and was conducted exclusively at Nagasaki under a strict government m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimoda, Shizuoka
270px, Shimoda City Hall is a city and port located in Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 21,402 in 10,787 households, and a population density of 200 persons per km2. The total area of the city is . In the 1850s, Japan was in political crisis over its increasing inability to maintain its national seclusion policy and the issue of what relations, if any, it should have with foreign powers. For a few years, Shimoda was central to this debate. Geography Shimoda is located at the southern tip of the Izu Peninsula about 100 kilometres southwest of Tokyo. Shimoda's location, with the Amagi Mountains to the north, and the warm Kuroshio Current to the south give the city a humid, sub-tropical climate. Surrounding Municipalities *Shizuoka Prefecture **Minamiizu ** Kawazu ** Matsuzaki Demographics Per Japanese census data, the population of Shimoda has been in slow decline over the past 40 years. Climate The city has a climate characterized by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
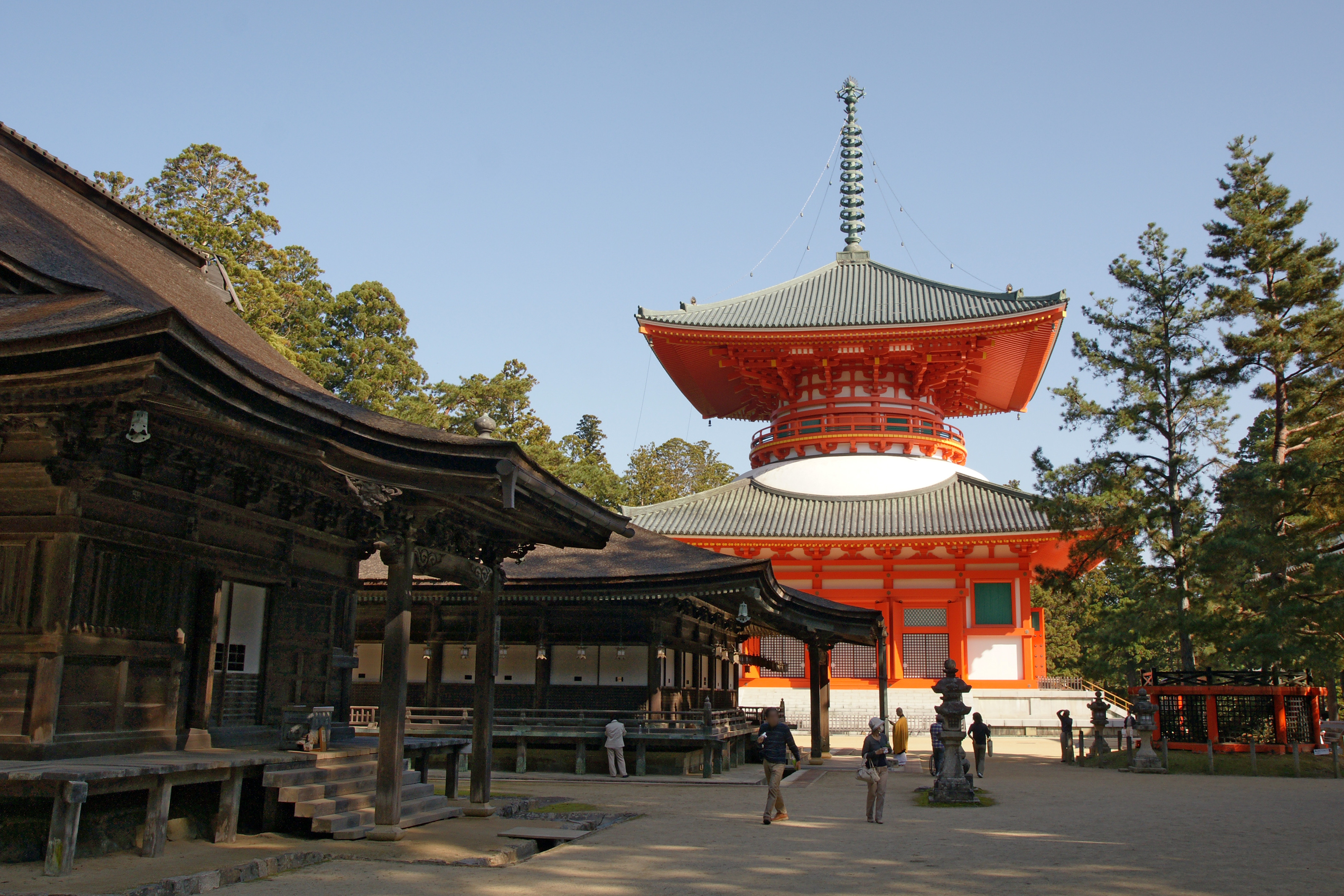
Shingon
file:Koyasan (Mount Koya) monks.jpg, Shingon monks at Mount Koya is one of the major schools of Buddhism in Japan and one of the few surviving Vajrayana lineages in East Asia, originally spread from India to China through traveling monks such as Vajrabodhi and Amoghavajra. Known in Chinese as the Tangmi (; the Esoteric School in Tang Dynasty of China), these esoteric teachings would later flourish in Japan under the auspices of a Buddhist monk named Kūkai (), who traveled to Tang China to acquire and request transmission of the esoteric teachings. For that reason, it is often called Japanese Esoteric Buddhism, or Orthodox Esoteric Buddhism. The word ''shingon'' is the Kan-on, Japanese reading of the Traditional Chinese characters, Chinese word ('), which is the translation of the Sanskrit word ("mantra"). History Shingon Buddhist doctrine and teachings arose during the Heian period (794-1185) after a Buddhist monk named Kūkai traveled to China in 804 to study Esote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yevfimy Putyatin
Yevfimiy Vasilyevich Putyatin (russian: Евфи́мий Васи́льевич Путя́тин; November 8, 1803 – October 16, 1883), also known as was an admiral in the Imperial Russian Navy. His diplomatic mission to Japan resulted in the signing of the Treaty of Shimoda in 1855, for which he was made a count. His mission to China in 1858 resulted in the Russian Treaty of Tianjin. Early life Putyatin was descended from a noble family in Novgorod. He entered the Naval Cadet Corps, graduating in 1822, and soon afterwards was appointed to the crew of Mikhail Petrovich Lazarev which circumnavigated the globe in a three-year voyage from 1822 to 1825. He subsequently participated in the Battle of Navarino during the Greek War of Independence on October 20, 1827 and was awarded the Order of St. Vladimir, 4th degree. From 1828 to 1832, the participated in numerous missions in the Mediterranean and in the Baltic, and was awarded the Order of St George, 4th class. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etorofu
, other_names = russian: Итуру́п; ja, 択捉島 , location = Sea of Okhotsk , coordinates = , archipelago = Kuril Islands , total_islands = , major_islands = , area_km2 = 3139 , length_km = 200 , width_km = 27 , coastline = , highest_mount = Stokap , elevation_m = 1634 , country_claim = , country_claim_divisions_title_1 = Prefecture , country_claim_divisions_1 = Hokkaido , country_claim_divisions_title_2 = Subprefecture , country_claim_divisions_2 = Nemuro , country = , country_admin_divisions_title_1 = Federal subject , country_admin_divisions_1 = Sakhalin Oblast , country_admin_divisions_title_2 = District , country_admin_divisions_2 = Kurilsky , population = 7,500 , population_as_of = 2003 , density = , ethnic_groups = , additional_info = Iturup (russian: Остров Итуру́п, Ostrov Iturúp; ain, エツ゚ヲロㇷ゚� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurile Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the Russian Far East. It stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaido in Japan to Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the north Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many minor rocks. The Kuril Islands consist of the Greater Kuril Chain and the Lesser Kuril Chain. They cover an area of around , with a population of roughly 20,000. The islands have been under Russian administration since their 1945 invasion as the Soviet Union towards the end of World War II. Japan claims the four southernmost islands, including two of the three largest ( Iturup and Kunashir), as part of its territory, as well as Shikotan and the Habomai islets, which has led to the ongoing Kuril Islands dispute. The disputed islands are kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan. It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the Nagasaki Region have been recognized and included in the UNESCO World Heritage List. Part of Nagasaki was home to a major Imperial Japanese Navy base during the First Sino-Japanese War and Russo-Japanese War. Near the end of World War II, the American atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki made Nagasaki the second and, to date, last city in the world to experience a nuclear attack (at 11:02 am, August 9, 1945 'Japan Standard Time (UTC+9)'). , the city has an estimated population of 407,624 and a population density of 1,004 people per km2. The total area is . History Nagasaki as a Jesuit port of call The first contact with Portuguese explorers occurred in 1543. An early visitor was Fernão Mendes Pinto, who came from Sagres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakodate
is a city and port located in Oshima Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital city of Oshima Subprefecture. As of July 31, 2011, the city has an estimated population of 279,851 with 143,221 households, and a population density of 412.83 persons per km2 (1,069.2 persons per sq. mi.). The total area is . The city is the third biggest in Hokkaido after Sapporo and Asahikawa. History Hakodate was Japan's first city whose port was opened to foreign trade in 1854, as a result of Convention of Kanagawa, and used to be the most important port in northern Japan. Also, the city had been the biggest city in Hokkaido before the Great Hakodate Fire of 1934. Pre-Meiji restoration Hakodate (like much of other parts of Hokkaido), was originally populated by the Ainu. They lived in the Oshima Peninsula. The name "Hakodate" may have originated from an Ainu word, "hak-casi" ("shallow fort"). Another possibility is that it means "box" or "building" in Japanese which refers to the castl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawaji Toshiakira
Kawaji (written: 川路) is a Japanese surname. Notable people with the surname include: *, Japanese politician *, pen name of Kawaki Makoto, Japanese poet and literary critic See also * Kawaji Station, a railway station in Iida, Nagano Prefecture, Japan {{surname Japanese-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansei Great Earthquakes
The Ansei great earthquakes (安政の大地震, ''Ansei no Dai Jishin'') were a series of major earthquakes that struck Japan during the Ansei era (1854–1860): * The Ansei Tōkai quake ( ja, 安政東海地震, Ansei Tōkai Jishin, label=none) was an 8.4 magnitude earthquake which struck on December 23, 1854. The epicenter ranged from Suruga Bay to the deep ocean, and struck primarily in the Tōkai region, but destroyed houses as far away as in Edo. The subsequent tsunami caused damage along the entire coast from the Bōsō Peninsula in modern-day Chiba prefecture to Tosa province (modern-day Kōchi Prefecture)_____. (2007). in , p. 253. * The Ansei Nankai quake ( ja, 安政南海地震, Ansei Nankai Jishin, label=none) was an 8.4 magnitude earthquake which struck on December 24, 1854. Over 10,000 people from the Tōkai region down to Kyushu were killed. * The ( ja, 豊予海峡地震, Hōyo Kaikyō Jishin, label=none) was an M7.4 intra-plate earthquake in Hōyo Strait affe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
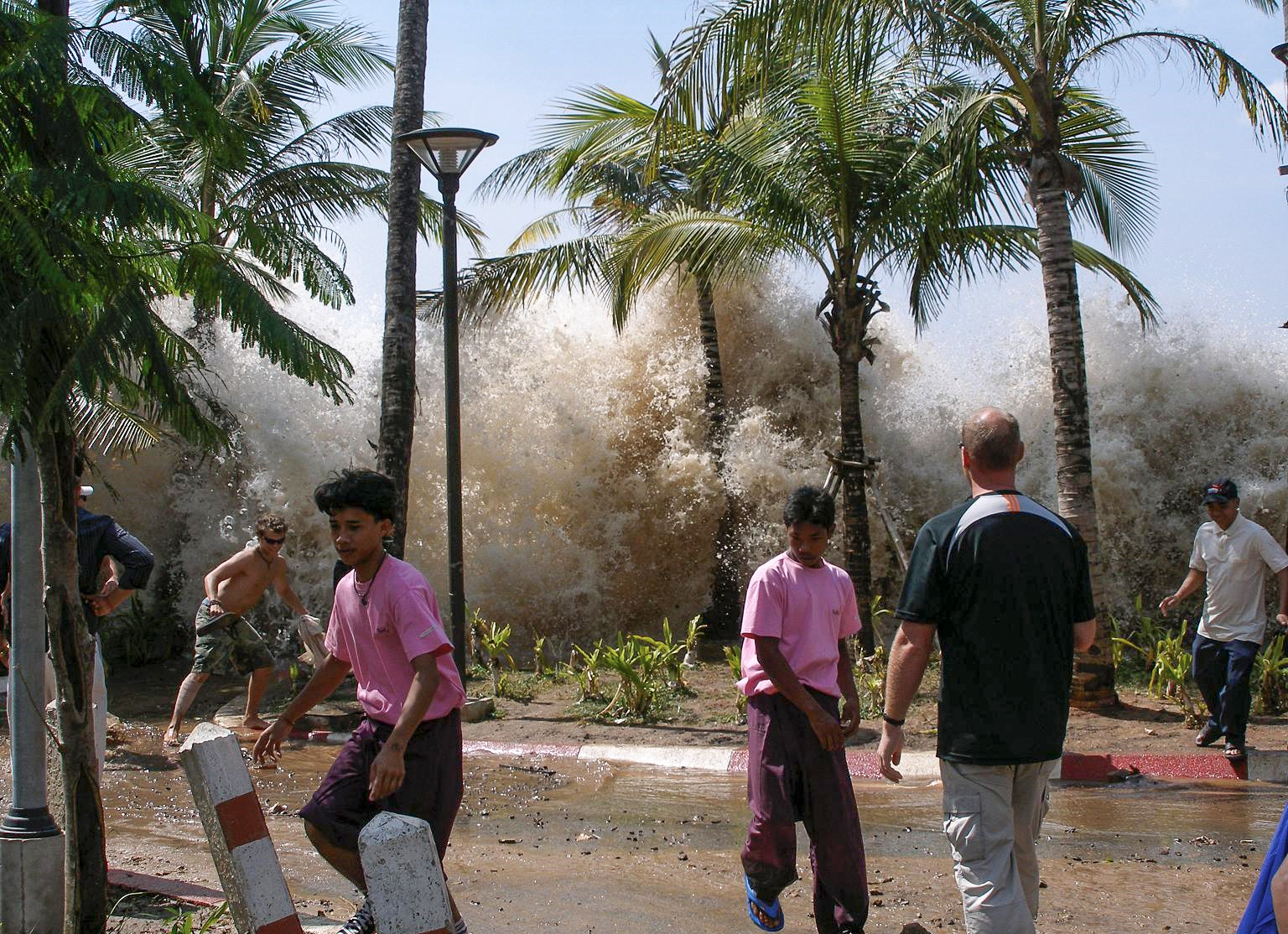
Tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations, landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances) above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event. Tsunami waves do not resemble normal undersea currents or sea waves because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide. For this reason, it is often referred to as a tidal wave, although this usage is not favoured by the scientific community because it might give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakoku
was the Isolationism, isolationist Foreign policy of Japan, foreign policy of the Japanese Tokugawa shogunate under which, for a period of 265 years during the Edo period (from 1603 to 1868), relations and trade between Japan and other countries were severely limited, and nearly all foreign nationals were banned from entering Japan, while common Japanese people were kept from leaving the country. The policy was enacted by the shogunate government (or ) under Tokugawa Iemitsu through a number of edicts and policies from 1633 to 1639, and ended after 1853 when the Perry Expedition commanded by Matthew C. Perry forced the opening of Japan to American (and, by extension, Western) trade through a series of Unequal treaty#Japan, treaties, called the Convention of Kanagawa. It was preceded by a period of largely unrestricted trade and widespread piracy. Japanese mariners and merchants traveled Asia, sometimes forming communities in certain cities, while official embassies and envoy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |