|
Carstensz Pyramid
Puncak Jaya (; literally "Glorious Peak") or Carstensz Pyramid, Mount Jayawijaya or Mount Carstensz () on the island of New Guinea, with an elevation of , is the highest mountain peak of an island on Earth. The mountain is located in the Sudirman Range of the highlands of Central Papua, Indonesia, in the southwest of Puncak Jaya Regency. The massive, open cut Grasberg gold and copper mine, the world's fifth-largest gold mine, is west of Puncak Jaya. Other summits are '' East Carstensz Peak'' (), ''Sumantri'' () and ''Ngga Pulu'' (). Other names include Nemangkawi in the Amungkal language, Carstensz Toppen and Gunung Soekarno.Greater Atlas of the World, Mladinska knjiga, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 1986. It is also the highest point between the Himalayas and the Andes. Some sources claim Papua New Guinea's Mount Wilhelm, , as the highest mountain peak in Oceania, on account of Indonesia being part of Asia (Southeast Asia). History The highlands surrounding the peak were inhabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Summits
The Seven Summits are the highest mountains of each of the seven traditional continents. Climbing to the summit of all of them is regarded as a mountaineering challenge, first achieved on 30 April 1985 by Richard Bass. Climbing the Seven Summits and additionally reaching the North Pole, North and South Pole, South poles has been dubbed the Explorers Grand Slam. Definition The Seven Summits are composed of each of the highest mountain peaks on each of the continents. Different lists include slight variations, but generally the same core is maintained. The seven summits depend on the definition used for a continent – in particular the location of the border of that continent. This results in two major points of variation. The first one is Mont Blanc versus Mount Elbrus for Europe, which depends on whether the crest of the Greater Caucasus, Greater Caucasus Mountains is taken to Boundaries between the continents of Earth#Modern definition, define the Greater Caucasus#Watershed, Grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngga Pulu
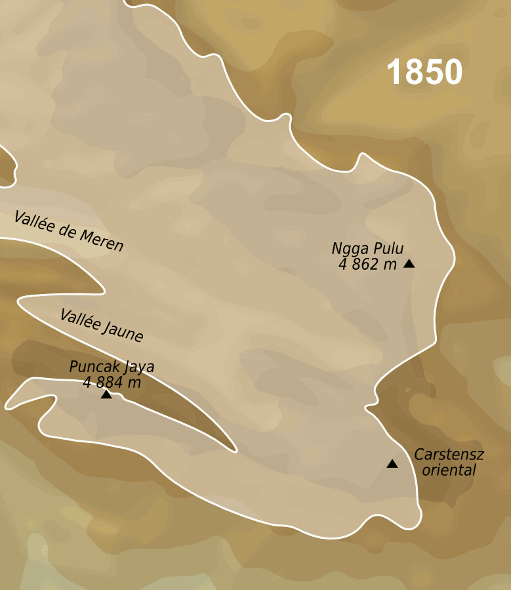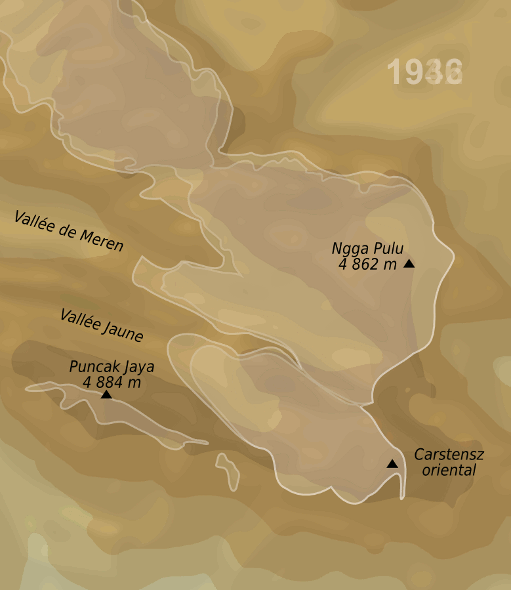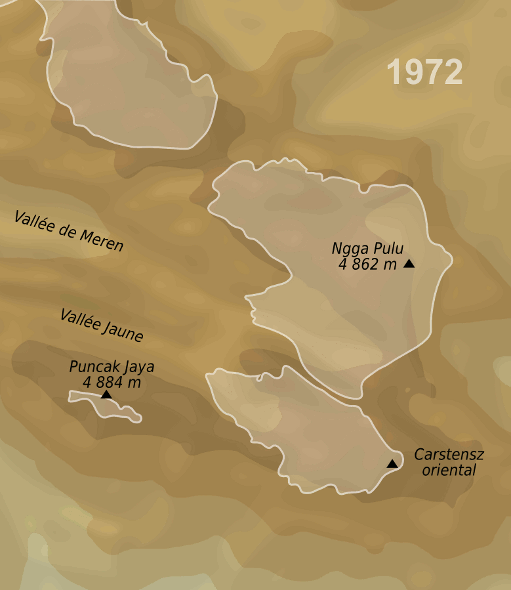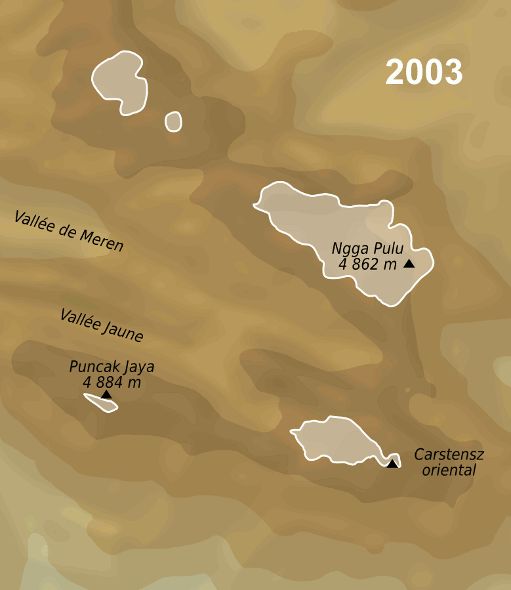
Ngga Pulu is a summit on the north rim of Mount Carstensz in the western part of the island of New Guinea rising . Trigonometric measurements showed that Ngga Pulu was (and had been for many centuries before) the highest mountain of New Guinea and also the highest summit of the Australia-New Guinea continent. The elevation of Ngga Pulu in 1936 was about , and it was the highest and most prominent peak between the Himalaya and the Andes. However, due to glacial melting, Ngga Pulu lost a lot of elevation in the 20th century. Name Ngga Pulu is the only summit of Mount Carstensz with a regular indigenous name. Sumantri and the current summit used to be called the NW and SE peaks of Ngga Pulu. Heinrich Harrer labeled the NW peak Ngapalu ohis map drawn in 1962 while calling the SE Peak (the current Ngga Pulu) ''Sunday Peak''. When Indonesia took control of Western New Guinea in 1963, the peaks were known as and until the Carstensz Pyramid was established as the highest summit. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dayak People
The Dayak (; older spelling: Dajak) or Dyak or Dayuh are one of the native groups of Borneo. It is a loose term for over 200 riverine and hill-dwelling ethnic groups, located principally in the central and southern interior of Borneo, each with its own dialect, customs, laws, territory, and culture, although common distinguishing traits are readily identifiable. Dayak languages are categorised as part of the Austronesian languages. The Dayak were animist ( Kaharingan and Folk Hindus) in belief; however, since the 19th century there has been mass conversion to Christianity as well as Islam due to the spreading of Abrahamic religions. Etymology It is commonly assumed that the name originates from the Bruneian and Melanau word for “interior people”, without any reference to an exact ethnic group. The term was adopted by Dutch and German authors as an umbrella term for any non-Muslim natives of Borneo. Thus, the difference between Dayaks and non-Dayaks natives could be unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
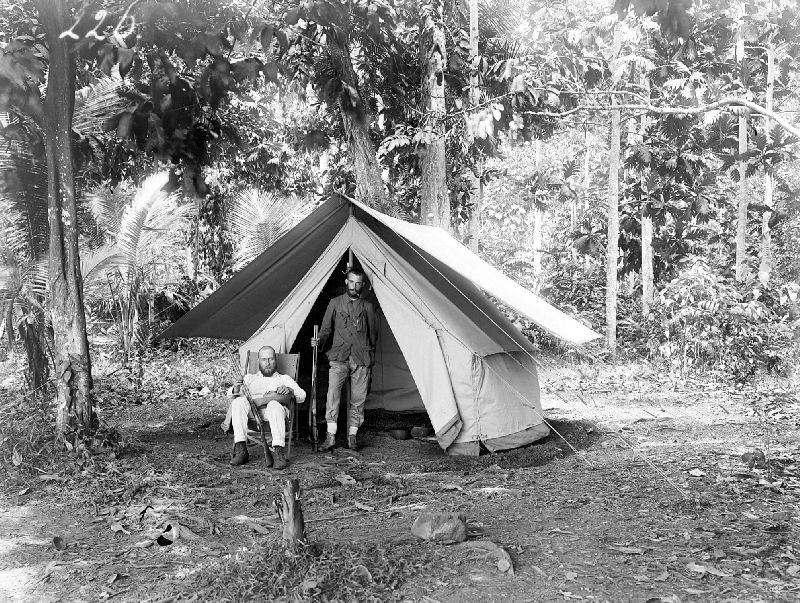
Hendrik Albert Lorentz
Hendrikus Albertus Lorentz (18 September 1871 – 2 September 1944) was a Dutch explorer in New Guinea and diplomat in South Africa. He was born to Theodorus Apolonius Ninus Lorentz, a tobacco grower in East Java who had returned to the Netherlands and Marie Soet in 1871. Lorentz studied law and biology at Utrecht University and married Marie Louise Clemence baroness Van Zuylen van Nievelt. Lorentz participated in three expeditions to Dutch New Guinea, the present-day Indonesian (western) portion of the island of New Guinea. The first was the North New Guinea Expedition in 1903, led by Arthur Wichmann. Lorentz himself led expeditions in 1907 and 1909–1910. Places and species named after Lorentz * Lorentz National Park and the Lorentz River (Undir or Unir in Indonesian) in southern New Guinea * Lorentz catfish and Lorentz's mosaic-tailed rat * The non-venomous Lorentz's tree snake ''Dendrelaphis lorentzii'' ( Van Lidth de Jeude, 1911). The holotype was collected at S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowfield
A snow field, snowfield or neve is an accumulation of permanent snow and ice, typically found above the snow line, normally in mountainous and glacial terrain. Glaciers originate in snowfields. The lower end of a glacier is usually free from snow and névé in summer. In the upper end and above the upper boundary of a glacier, the snow field is an ice field An ice field (also spelled icefield) is a mass of interconnected valley glaciers (also called mountain glaciers or alpine glaciers) on a mountain mass with protruding rock ridges or summits. They are often found in the colder climates and highe ... covered with snow. The glacier upper boundary, where it emerges from under a snow field, is ill-defined because of gradual transition.Thomas Chrowder Chamberlin, Rollin D. Salisbury (1904) "Geology"p. 258 References Bodies of ice Landforms {{glaciology-stub it:Formazioni nevose perenni#Nevaio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia University Press
Columbia University Press is a university press based in New York City, and affiliated with Columbia University. It is currently directed by Jennifer Crewe (2014–present) and publishes titles in the humanities and sciences, including the fields of literary and cultural studies, history, social work, sociology, religion, film, and international studies. History Founded in May 1893, In 1933 the first four volumes of the ''History of the State of New York'' were published. In early 1940s revenues rises, partially thanks to the ''Encyclopedia'' and the government's purchase of 12,500 copies for use by the military. Columbia University Press is notable for publishing reference works, such as ''The Columbia Encyclopedia The ''Columbia Encyclopedia'' is a one-volume encyclopedia produced by Columbia University Press and, in the last edition, sold by the Gale Group. First published in 1935, and continuing its relationship with Columbia University, the encyclopedi ...'' (1935� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between latitudes 35°N and 35°S, glaciers occur o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Carstenszoon
Jan Carstenszoon or more commonly Jan Carstensz In Dutch patronyms ending in -szoon were almost universally abbreviated to -sz was a 17th-century Dutch explorer. In 1623, Carstenszoon was commissioned by the Dutch East India Company to lead an expedition to the southern coast of New Guinea and beyond, to follow up the reports of land sighted further south in the 1606 voyages of Willem Janszoon in the ''Duyfken''. Setting sail from Ambon in the Dutch East Indies with two ships, the yacht ''Pera'' (captained by Carstenszoon) and ''Arnhem'' (captained by Willem Joosten van Colster), the ships travelled along the south coast of New Guinea, then headed south to Cape York Peninsula and the Gulf of Carpentaria. On 14 April 1623, Cape Keerweer was passed. Landing in search of fresh water for his stores, Carstenszoon encountered a party of the local indigenous Australian inhabitants. Carstenszoon described them as "poor and miserable looking people" who had "no knowledge of precious m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a federal republic that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795 (the Batavian Revolution). It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. The republic was established after seven Dutch provinces in the Spanish Netherlands revolted against rule by Spain. The provinces formed a mutual alliance against Spain in 1579 (the Union of Utrecht) and declared their independence in 1581 (the Act of Abjuration). It comprised Groningen, Frisia, Overijssel, Guelders, Utrecht, Holland and Zeeland. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. Through its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million as of 2021. When compared with (and sometimes described as being one of) the continents, the region of Oceania is the smallest in land area and the second least populated after Antarctica. Its major population centres are Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Auckland, Adelaide, Honolulu, and Christchurch. Oceania has a diverse mix of economies from the highly developed and globally competitive financial markets of Australia, French Polynesia, Hawaii, New Caledonia, and New Zealand, which rank high in quality of life and Human Development Index, to the much less developed economies of Kiribati, Papua New Guinea, Tuvalu, Vanuatu, and Western New Guinea, while also including medium-sized economies of Pacific islands such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Wilhelm
Mount Wilhelm (german: Wilhelmsberg) is the highest mountain in Papua New Guinea at . It is part of the Bismarck Range and the peak is the point where three provinces, Chimbu, Jiwaka and Madang, meet. The peak is also known as ''Enduwa Kombuglu'', or ''Kombugl'o Dimbin'', in the local Kuman. The mountain is on the island of New Guinea, which incorporates Papua New Guinea and the Indonesian province of Papua. It is surpassed by Puncak Jaya, , and several other peaks in Indonesian Papua. Mount Wilhelm may be considered the highest mountain in Oceania (including Australia and New Zealand). A Seven Summits list may therefore sometimes include Mount Wilhelm. History Discovery Mount Wilhelm received its name in 1888 when a German newspaper correspondent, Hugo Zöller, climbed the Finisterre Range, south-east of Madang, and named the Bismarck Range after the German Chancellor, Otto von Bismarck, and the four highest peaks of the range after him and his children: Ottoberg, Herb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
