|
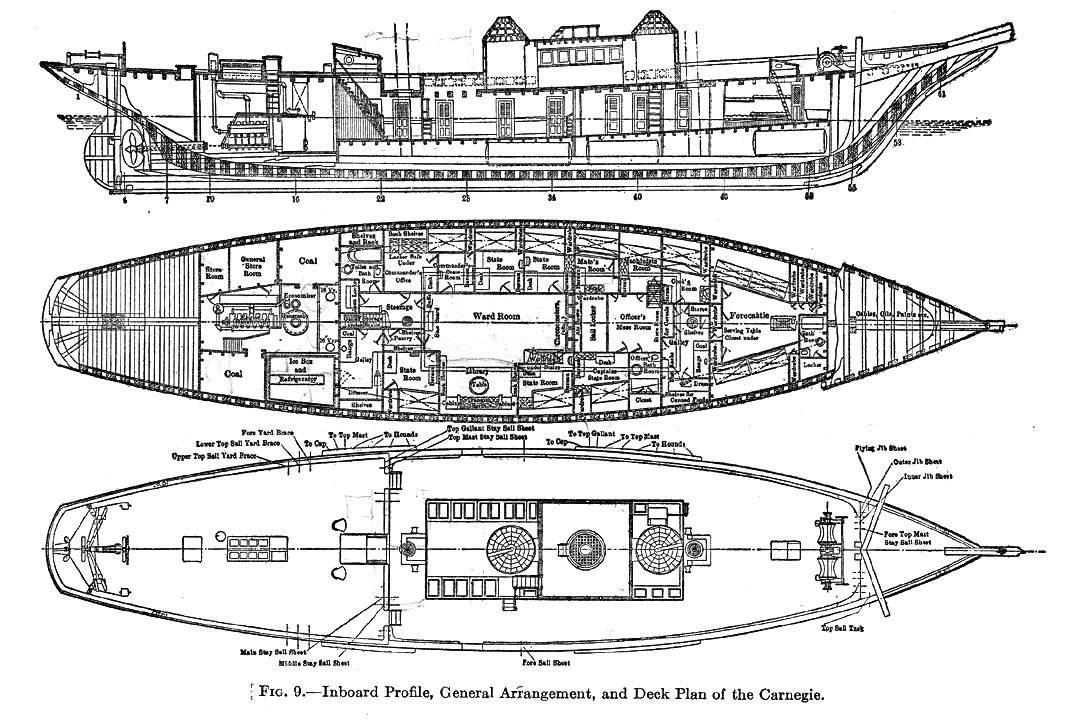
Carnegie (yacht)
''Carnegie'' was a brigantine yacht, equipped as a research vessel, constructed almost entirely from wood and other non-magnetic materials to allow sensitive magnetic measurements to be taken for the Carnegie Institution for Science, Carnegie Institution's Department of Terrestrial Magnetism. She carried out a series of cruises from her launch in 1909 to her destruction by an onboard explosion while in port in 1929. She covered almost in her twenty years at sea. The Carnegie Rupes on the planet Mercury are named after this research vessel. Construction Louis Agricola Bauer, the first director of the Department of Terrestrial Magnetism at the Carnegie Institution, wanted to focus on acquiring oceanic magnetic data to improve the understanding of the Earth's magnetic field. After an experiment in which the brigantine ''Galilee (ship), Galilee'' was adapted by removing as much magnetic material as possible, it became clear that a new entirely non-magnetic ship was needed. After conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Institution
The Carnegie Institution of Washington (the organization's legal name), known also for public purposes as the Carnegie Institution for Science (CIS), is an organization in the United States established to fund and perform scientific research. The institution is headquartered in Washington, D.C. , the Institution's endowment was valued at $926.9 million. In 2018 the expenses for scientific programs and administration were $96.6 million.Eric Isaacs is president of the institution. Name More than 20 independent organizations were established through the philanthropy of Andrew Carnegie and now feature his surname. They perform work involving topics as diverse as art, education, international affairs, world peace, and scientific research. In 2007, the Carnegie Institution of Washington adopted the public name "Carnegie Institution for Science" to distinguish itself from other organizations established by and named for Andrew Carnegie. The Institution remains officially and le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercus Alba
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably '' Lithocarpus'' (stone oaks), as well as in those of unrelated species such as '' Grevillea robusta'' (silky oaks) and the Casuarinaceae (she-oaks). The genus ''Quercus'' is native to the Northern Hemisphere, and includes deciduous and evergreen species extending from cool temperate to tropical latitudes in the Americas, Asia, Europe, and North Africa. North America has the largest number of oak species, with approximately 160 species in Mexico of which 109 are endemic and about 90 in the United States. The second greatest area of oak diversity is China, with approximately 100 species. Description Oaks have spirally arranged leaves, with lobate margins in many species; some have serrated leaves or entire leaves with smooth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Revelle
Roger Randall Dougan Revelle (March 7, 1909 – July 15, 1991) was a scientist and scholar who was instrumental in the formative years of the University of California, San Diego and was among the early scientists to study anthropogenic global warming, as well as the movement of Earth's tectonic plates. UC San Diego's first college is named Revelle College in his honor. Career Roger Revelle was born in Seattle to William Roger Revelle and Ella Dougan. He grew up in southern California. After graduating from Pomona College in 1929 with early studies in geology, he earned a PhD in oceanography from the University of California, Berkeley in 1936. While at Cal, he studied under George Louderback and was initiated into Theta Tau Professional Engineering Fraternity, which started as a mining engineering fraternity and maintained a strong affinity for geology and geological engineering students. Much of his early work in oceanography took place at the Scripps Institution of Oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harald Sverdrup (oceanographer)
Harald Ulrik Sverdrup (15 November 1888 – 21 August 1957) was a Norwegian oceanographer and meteorologist. He was director of Scripps Institution of Oceanography and director of the Norwegian Polar Institute. Background He was born at Sogndal in Sogn og Fjordane, Norway. He was the son of Lutheran theologian Edvard Sverdrup (1861–1923) and Maria Vollan (1865–1891). His sister Mimi Sverdrup Lunden (1894–1955) was an educator and author. His brother Leif Sverdrup (1898–1976) was a General with the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. His brother Einar Sverdrup (1895–1942) was CEO of Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani. Sverdrup was a student at Bergen Cathedral School in 1901 before graduating in 1906 at Kongsgård School in Stavanger. He graduated cand. real. in 1914 from University of Oslo. He studied under Vilhelm Bjerknes and earned his Dr. Philos. at the University of Leipzig in 1917. Career He was the scientific director of the North Polar expedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apia, Samoa
Apia () is the capital and largest city of Samoa, as well as the nation's only city. It is located on the central north coast of Upolu, Samoa's second-largest island. Apia falls within the political district (''itūmālō'') of Tuamasaga. The Apia Urban Area (generally known as the City of Apia) has a population of 37,391 (2016 census). Its geographic boundaries extend roughly from Letogo village to the newer, industrialized region of Apia known as "Vaitele". History Apia was originally a small village (the 1800 population was 304), from which the country's capital took its name. Apia Village still exists within the larger modern capital of Apia, which has grown into a sprawling urban area that encompasses many villages. Like every other settlement in the country, Apia Village has its own ''matai'' (leaders) and ''fa'alupega'' (genealogy and customary greetings) according to fa'a Samoa. The modern city of Apia was founded in the 1850s, and it has been the official capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ''Ekuatur Nunka''), is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. Ecuador also includes the Galápagos Islands in the Pacific, about west of the mainland. The country's capital and largest city is Quito. The territories of modern-day Ecuador were once home to a variety of Indigenous groups that were gradually incorporated into the Inca Empire during the 15th century. The territory was colonized by Spain during the 16th century, achieving independence in 1820 as part of Gran Colombia, from which it emerged as its own sovereign state in 1830. The legacy of both empires is reflected in Ecuador's ethnically diverse population, with most of its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Ridge
The Carnegie Ridge is an aseismic ridge on the Nazca Plate that is being subducted beneath the South American Plate. The ridge is thought to be a result of the passage of the Nazca Plate over the Galapagos hotspot. It is named for the research vessel '' Carnegie'', which discovered it in 1929. Extent The Carnegie Ridge is seen to extend eastwards over 1,000 km from the Galapagos islands to the Colombia-Ecuador trench and is interpreted to continue beneath northern Ecuador for about a further 700 km. The subducted extent is disputed, with some workers arguing that there is no evidence of a subducted ridge beneath Ecuador extending more than about 60 km from the trench. Structure The Carnegie Ridge consists of thickened oceanic crust. Wide-angle seismic reflection and refraction data acquired over the central and eastern part of the ridge give crustal thicknesses of 13 km and 19 km respectively for crust that has estimated ages of about 11 Ma and 20 Ma. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James P
James is a common English language surname and given name: *James (name), the typically masculine first name James * James (surname), various people with the last name James James or James City may also refer to: People * King James (other), various kings named James * Saint James (other) * James (musician) * James, brother of Jesus Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Arts, entertainment, and media * ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * James the Red Engine, a character in ''Thomas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William John Peters
William John Peters (February 5, 1863 – July 10, 1942) was an American explorer and scientist who worked extensively in the Arctic and tropics. His significant contributions the study of geomagnetism at sea in the early 1900s helped lay the foundation for the current scientific understanding of Earth's magnetism. Early life Born in Oakland, California, in 1863, Peters was son of William Bonaventure Peters and Margaret Major. He took courses in botany and chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley. Before obtaining his degree, he was recruited to conduct boundary surveys in some western states with his uncles, the Major brothers. From 1884 to 1898, Peters worked as a topographer for the United States Geological Survey, primarily in the western states, including California, the Dakotas, Iowa, Kansas, and Nebraska. Arctic exploration From 1898 to 1902, Peters continued his work for the United States Geological Survey, mostly in Alaska, where he worked with Alfred B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumnavigation
Circumnavigation is the complete navigation around an entire island, continent, or astronomical body (e.g. a planet or moon). This article focuses on the circumnavigation of Earth. The first recorded circumnavigation of the Earth was the Magellan–Elcano expedition, which sailed from Sanlucar de Barrameda, Spain in 1519 and returned in 1522, after crossing the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian oceans. Since the rise of commercial aviation in the late 20th century, circumnavigating Earth is straightforward, usually taking days instead of years. Today, the challenge of circumnavigating Earth has shifted towards human and technological endurance, speed, and less conventional methods. Etymology The word ''circumnavigation'' is a noun formed from the verb ''circumnavigate'', from the past participle of the Latin verb '' circumnavigare'', from ''circum'' "around" + ''navigare'' "to sail" (see further Navigation § Etymology). Definition A person walking completely around eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Producer Gas
Producer gas is fuel gas that is manufactured by blowing a coke or coal with air and steam simultaneously. It mainly consists of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), as well as substantial amounts of nitrogen (N2). The caloric value of the producer gas is low (mainly because of its high nitrogen content), and the technology is obsolete. Improvements over producer gas, also obsolete, include water gas where the solid fuel is treated intermittently with air and steam and, far more efficiently synthesis gas where the solid fuel is replaced with methane. In the USA, producer gas may also be referred to by other names based on the fuel used for production such as wood gas. Producer gas may also be referred to as suction gas. The term suction refers to the way the air was drawn into the gas generator by an internal combustion engine. Wood gas is produced in a gasifier Production Producer gas is generally made from coke, or other carbonaceous material such as anthracite. Air is pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doldrums
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal equator though its specific position varies seasonally. When it lies near the geographic Equator, it is called the near-equatorial trough. Where the ITCZ is drawn into and merges with a monsoonal circulation, it is sometimes referred to as a monsoon trough, a usage that is more common in Australia and parts of Asia. Meteorology The ITCZ was originally identified from the 1920s to the 1940s as the ''Intertropical Front'' (''ITF''), but after the recognition in the 1940s and the 1950s of the significance of wind field convergence in tropical weather production, the term ''Intertropical Convergence Zone'' (''ITCZ'') was then applied. The ITCZ appears as a band of clouds, usually thunderstorms, that encircle the globe near the Equator. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |