|
Cabbage Tactics
Cabbage tactics is a militarily swarming and overwhelming tactic used by the People's Liberation Army Navy to seize control of islands. It is a tactic to overwhelm and seize control of an island by surrounding and wrapping the island in successive layers of Chinese naval ships, China Coast Guard ships, and fishing boats and cut off the island from outside support. Definition Cabbage tactics were first named by Rear Admiral Zhang Zhaozhong of the People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN). It is a tactic to overwhelm and seize control of an island by surrounding and wrapping the island in successive layers of Chinese naval ships, China Coast Guard ships and fishing boats and cut-off the island from outside support. It has also been called small-stick diplomacy. According to '' The New York Times Magazine'', Zhang Zhaozhong "described a “cabbage strategy,” which entails surrounding a contested area with so many boats — fishermen, fishing administration ships, marine surveillanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swarming (military)
Military swarming is a battlefield tactic designed to maximize target saturation, and thereby overwhelm or saturate the defences of the principal target or objective. On the other-hand, defenders can overcome attempts at swarming, by launching counter-swarming measures that are designed to neutralize or otherwise repel such attacks. Military swarming is often encountered in asymmetric warfare where opposing forces are not of the same size, or capacity. In such situations, swarming involves the use of a decentralized force against an opponent, in a manner that emphasizes mobility, communication, unit autonomy and coordination or synchronization. Historically military forces have used the principles of swarming without really examining them explicitly, but there is now active research in consciously examining military doctrines that draw ideas from swarming. In nature and nonmilitary situations, there are other various forms of swarming. Biologically driven forms are often comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no), * bik, Republika kan Filipinas * ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas * cbk, República de Filipinas * hil, Republika sang Filipinas * ibg, Republika nat Filipinas * ilo, Republika ti Filipinas * ivv, Republika nu Filipinas * pam, Republika ning Filipinas * krj, Republika kang Pilipinas * mdh, Republika nu Pilipinas * mrw, Republika a Pilipinas * pag, Republika na Filipinas * xsb, Republika nin Pilipinas * sgd, Republika nan Pilipinas * tgl, Republika ng Pilipinas * tsg, Republika sin Pilipinas * war, Republika han Pilipinas * yka, Republika si Pilipinas In the recognized optional languages of the Philippines: * es, República de las Filipinas * ar, جمهورية الفلبين, Jumhūriyyat al-Filibbīn is an archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It is situated in the western Pacific Ocean and consists of aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Warfare Tactics
Naval tactics and doctrine is the collective name for methods of engaging and defeating an enemy ship or fleet in battle at sea during naval warfare, the naval equivalent of military tactics on land. Naval tactics are distinct from naval strategy. Naval tactics are concerned with the movements a commander makes in battle, typically in the presence of the enemy. Naval strategy concerns the overall strategy for achieving victory and the large movements by which a commandant or commander secures the advantage of fighting at a place convenient to himself. Modern naval tactics are based on tactical doctrines developed after World War II, following the obsolescence of the battleship and the development of long-range missiles. Since there has been no major naval conflict since World War II, apart from the Indo-Pakistani Naval War of 1971 and the Falklands War, many of these doctrines reflect scenarios developed for planning purposes. Critics argue that the collapse of the Sov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Warfare
Hybrid warfare is a theory of military strategy, first proposed by Frank Hoffman, which employs political warfare and blends conventional warfare, irregular warfare, and cyberwarfare with other influencing methods, such as fake news, diplomacy, lawfare and foreign electoral intervention. By combining kinetic operations with subversive efforts, the aggressor intends to avoid attribution or retribution. The concept of hybrid warfare has been criticized by a number of academics and practitioners due to its alleged vagueness, its disputed constitutive elements, and its alleged historical distortions. Definition There is no universally-accepted definition of hybrid warfare; some debate whether the term is useful at all. Some argue that the term is too abstract and only the latest term to refer to irregular methods to counter a conventionally superior force. The abstractness of the term means that it is often used as a catch-all term for all non-linear threats. Hybrid warfare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey-zone (international Relations)
The grey-zone (also grey zone, gray zone, and gray-zone) describes the space in between peace and war in which state and non-state actors engage in competition. Definition Use of the term ''grey-zone'' is widespread in national security circles, but there is no universal agreement on the definition of ''grey-zone'', or even whether it is a useful term, with views about the term ranging from "faddish" or "vague", to "useful" or "brilliant". The grey-zone is defined as "competitive interactions among and within state and non-state actors that fall between the traditional war and peace duality." by the United States Special Operations Command. A key element of operations within the grey-zone is that they remain below the threshold of an attack which could have a legitimate conventional military response (jus ad bellum). One paper defined it as "coercive statecraft actions short of war", and a "mainly non-military domain of human activity in which states use national resources to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China's Salami Slicing
China's salami slicing (; Robert BarnettChina Is Building Entire Villages in Another Country’s Territory Foreign Policy, 7 May 2021.) is a strategy by which the government of China uses small provocations, none of which would constitute a ''casus belli'' by itself, but cumulatively produce a much larger action or result in China's favor which would have been difficult or unlawful to perform all at once. In 1996, a United States Institute of Peace report on the territorial disputes in the South China Sea wrote, " ��analysts point to Chinese "salami tactics," in which China is said to test the other claimants through aggressive actions, then back off when it meets significant resistance." The term "salami slice strategy" has been used to describe policies that incrementally improve China's foreign policy position. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
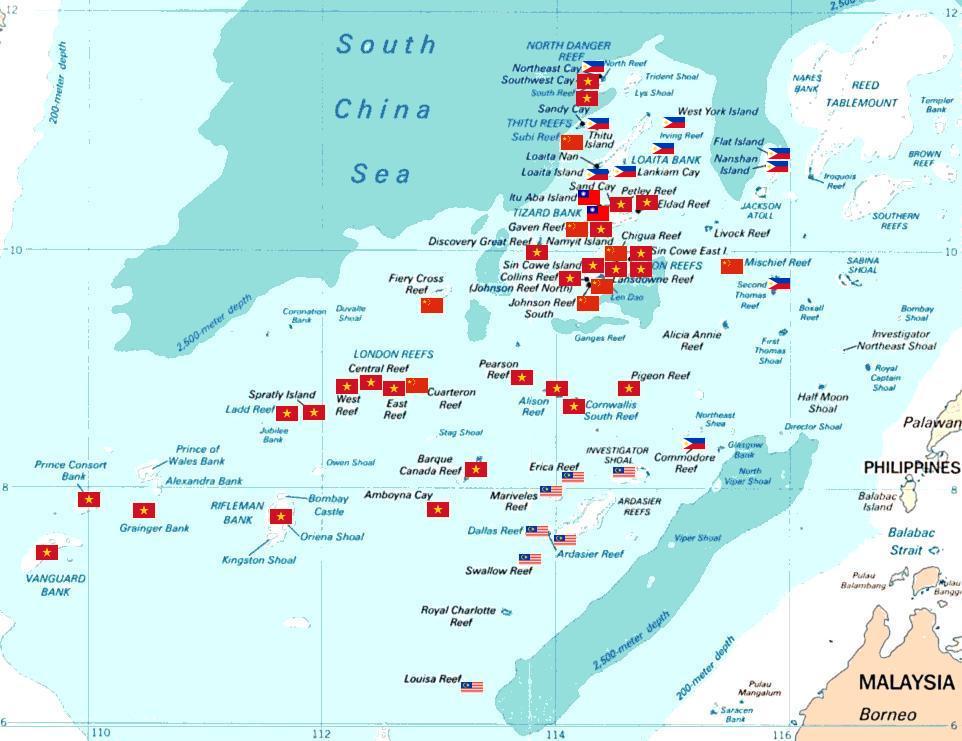
Thitu Island
Thitu Island, also known as Pag-asa Island ( tl, Pulo ng Pag-asa, lit=Island of Hope; pag, Ilalo, having an area of , is the second largest of the naturally occurringNote that in 2014 the PRC embarked on a number of reclamation projects in the Spratly Islands. It appears that the largest of these, at Fiery Cross Reef, is of at least 60 hectares, and according to some unverifiable sources, possibly as large as 150 hectares. Spratly Islands and the largest of the Philippine-administered islands. It lies about west of Puerto Princesa. Its neighbors are the North Danger Reef to the north, Subi Reef to the west, and the Loaita and Tizard Banks to the south. As the poblacion (administrative center) of the Kalayaan municipality of Palawan province in the Philippines, it also administers nearly a dozen other islets, cays and reefs in the Spratly Islands. Vietnam also claims the island. In 2019–20, the island's naval port and civilian-military airstrip were upgraded despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China National Offshore Oil Corporation
China National Offshore Oil Corporation, or CNOOC Group ( Chinese: 中国海洋石油总公司 Pinyin: ''Zhōngguó Háiyáng Shíyóu Zǒnggōngsī''), is one of the largest national oil companies in China, and the third-largest national oil company in China, after CNPC (parent of PetroChina) and China Petrochemical Corporation (parent of Sinopec). The CNOOC Group focuses on the exploitation, exploration and development of crude oil and natural gas in offshore China, along with its subsidiary COOEC. The company is owned by the government of the People's Republic of China, and the State-Owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council (SASAC) assumes shareholder rights and obligations on the government's behalf. One subsidiary, CNOOC Limited, is listed on the Hong Kong exchange; the other, China Oilfield Services, is listed on the Hong Kong and New York exchanges. In the 2020 Forbes Global 2000, CNOOC was ranked as the 126th largest public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exclusive Economic Zone Of Vietnam
Vietnam claims an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of with from its shores. Excluding all disputed waters, Vietnam has an undisputed exclusive economic zone of . This figure does not include the EEZ areas of the Paracel Islands and the Spratly Islands. Vietnam has disputes mainly with the People's Republic of China due to the nine-dash line. Vietnam has the 33rd longest coastline of . It includes much of the western area of the South China Sea and parts of the southern area bordering Malaysia and Brunei's EEZs. The total land area, including inland bodies of water, of Vietnam is . Vietnam has dozens of islands. Phú Quốc is the largest island with . Disputes Vietnam's disputes are mainly with the People's Republic of China. Vietnam rejects China's nine-dash line which extends much further than China's from its shores. The nine-dash line cuts straight through Vietnam's Exclusive Economic Zone in the South China Sea and would reduce Vietnam's EEZ by 3/4th. This lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
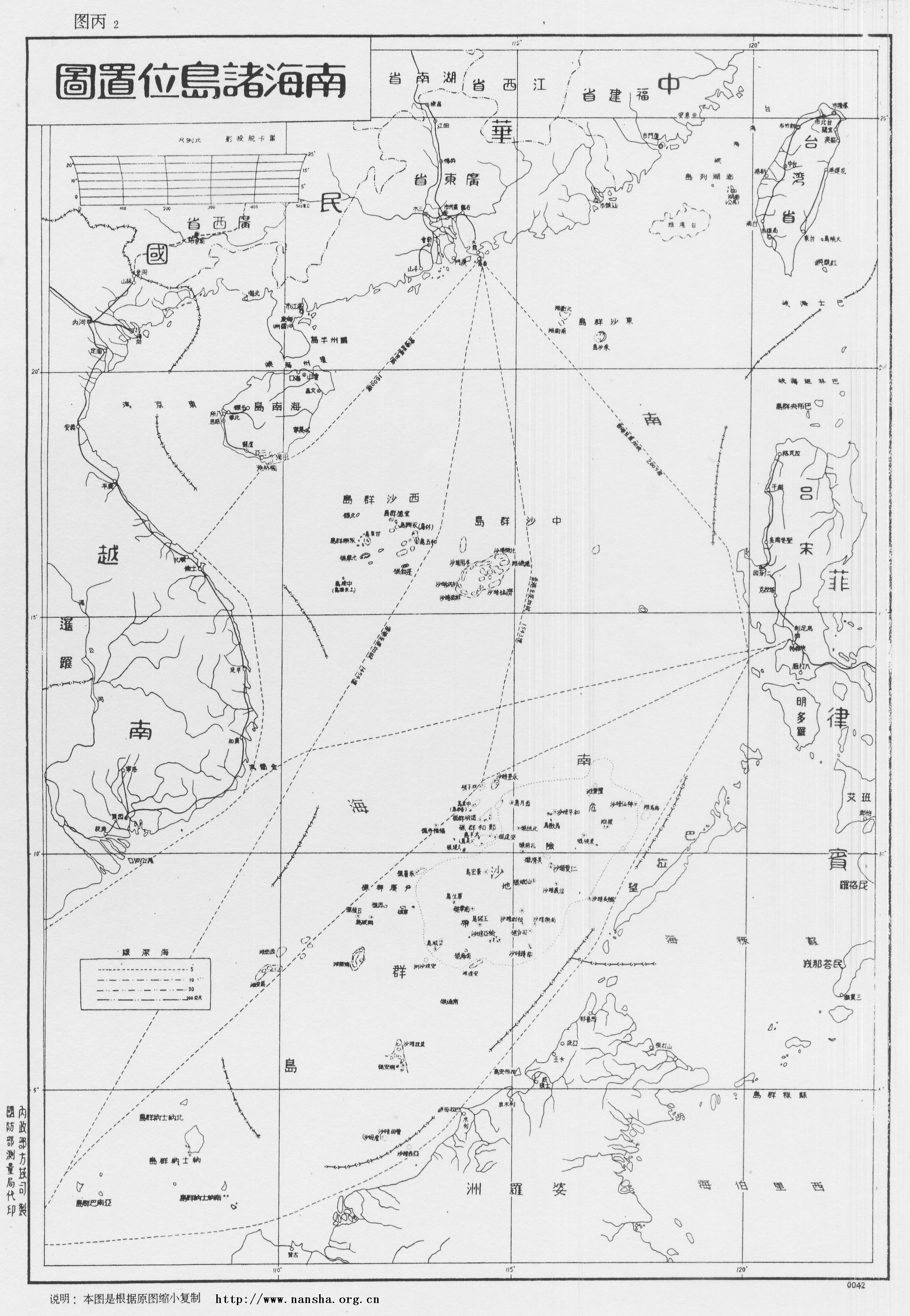
Spratly Islands
The Spratly Islands ( fil, Kapuluan ng Kalayaan; zh, c=南沙群島/南沙群岛, s=, t=, p=Nánshā Qúndǎo; Malay, id, Kepulauan Spratly; vi, Quần đảo Trường Sa) are a disputed archipelago in the South China Sea. Composed of islands, islets, cays, and more than 100 reefs, sometimes grouped in submerged old atolls, the archipelago lies off the coasts of the Philippines, Malaysia, and southern Vietnam. Named after the 19th-century British whaling captain Richard Spratly who sighted Spratly Island in 1843, the islands contain less than of naturally occurring land area, which is spread over an area of more than . The Spratly Islands are one of the major archipelagos in the South China Sea which complicate governance and economics in this part of Southeast Asia due to their location in strategic shipping lanes. The islands are largely uninhabited, but offer rich fishing grounds and may contain significant oil and natural gas reserves,Owen, N. A. and C. H. Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Thomas Shoal
Second Thomas Shoal, also known as Ayungin Shoal ( fil, Kulumpol ng Ayungin, lit=Cluster of hesilver perch; vi, Bãi Cỏ Mây; and Mandarin ), is a shoal or atoll in the Spratly Islands of the South China Sea, west of Palawan, Philippines. Claimed by several nations, the shoal is currently militarily occupied by the Philippines. History The shoal is one of three named after Thomas Gilbert, captain of the : *First Thomas Shoal – (South of Second Thomas Shoal)NGA Chart 93046 - SE Dangerous Ground * Second Thomas Shoal – (Southeast of ) * |
Scarborough Reef
Scarborough Shoal, also known as Bajo de Masinloc (in Spanish), Panatag Shoal ( fil, Kulumpol ng Panatag, lit=serene cluster), Huangyan Island (Mandarin zh, c=黄岩岛, p=Huáng Yán Dǎo, l=yellow rock island), and Democracy Reef, are two rocks in a shoal located between Luzon and Macclesfield Bank within the Philippine EEZ in the South China Sea. It is away from the nearest landmass of Luzon, the largest island of the Philippines. It is a disputed territory claimed by the Republic of the Philippines through the 1734 Velarde map, while the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China (Taiwan) claim it through the disputed nine-dash line (originally an eleven-dash line which included waters in the Gulf of Tonkin). The shoal's status is often discussed in conjunction with other territorial disputes in the South China Sea such as those involving the Spratly Islands, and the 2012 Scarborough Shoal standoff. It was administered by the Philippines as part of its Zambale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)