|
COACH Syndrome
COACH syndrome, also known as Joubert syndrome with hepatic defect, is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disease. The name is an acronym of the defining signs: cerebellar vermis, cerebellar vermis aplasia, oligophrenia, oligophrenia, ataxia, congenital ataxia, coloboma, coloboma and hepatic fibrosis, hepatic fibrosis. The condition is associated with moderate intellectual disability. It falls under the category of a Joubert syndrome, Joubart Syndrome-related disorder (JSRD). The syndrome was first described in 1974 by Alasdair Hunter and his peers at the Montreal Children's Hospital. It was not until 1989 that it was labelled COACH syndrome, by Verloes and Lambotte, at the Sart Tilman University Hospital, Belgium. Signs and symptoms Signs of COACH syndrome tend to present from birth to early childhood. Facial abnormalities are a common symptom, with some characteristics being broadness of the forehead, Ptosis (eyelid), ptosis of either one or both eyes and misalignment of the ey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coloboma
A coloboma (from the Greek , meaning defect) is a hole in one of the structures of the eye, such as the iris, retina, choroid, or optic disc. The hole is present from birth and can be caused when a gap called the choroid fissure, which is present during early stages of prenatal development, fails to close up completely before a child is born. Ocular coloboma is relatively uncommon, affecting less than one in every 10,000 births. The classical description in medical literature is of a keyhole-shaped defect. A coloboma can occur in one eye (unilateral) or both eyes (bilateral). Most cases of coloboma affect only the iris. The level of vision impairment of those with a coloboma can range from having no vision problems to being able to see only light or dark, depending on the position and extent of the coloboma (or colobomata if more than one is present). Signs and symptoms Visual effects may be mild to more severe depending on the size and location of the coloboma. If, for exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascites
Ascites is the abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen. Technically, it is more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, although volumes greater than one liter may occur. Symptoms may include increased abdominal size, increased weight, abdominal discomfort, and shortness of breath. Complications can include spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. In the developed world, the most common cause is liver cirrhosis. Other causes include cancer, heart failure, tuberculosis, pancreatitis, and blockage of the hepatic vein. In cirrhosis, the underlying mechanism involves high blood pressure in the portal system and dysfunction of blood vessels. Diagnosis is typically based on an examination together with ultrasound or a CT scan. Testing the fluid can help in determining the underlying cause. Treatment often involves a low-salt diet, medication such as diuretics, and draining the fluid. A transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) may be placed but is associated with co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
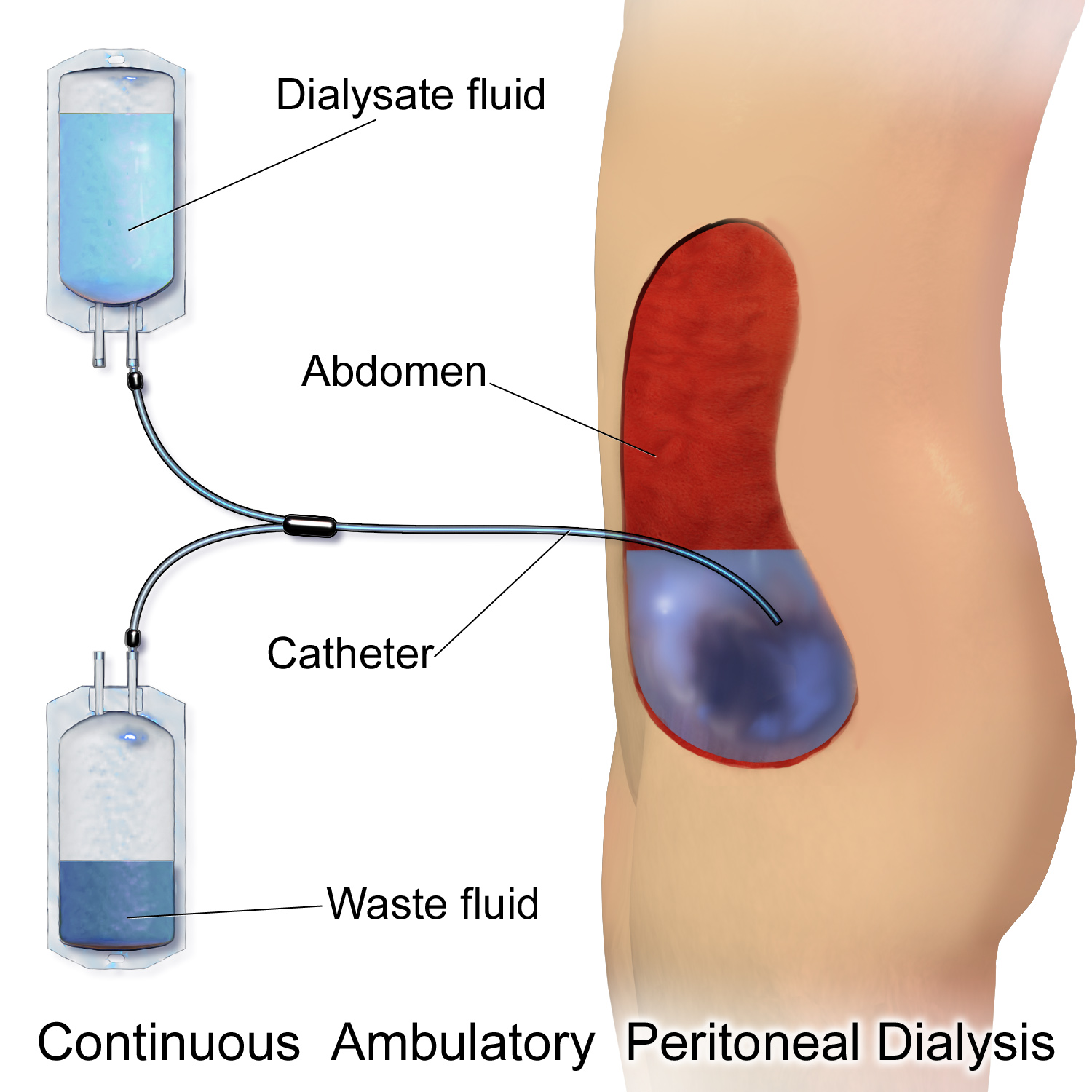
Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of dialysis which uses the peritoneum in a person's abdomen as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte problems, and remove toxins in those with kidney failure. Peritoneal dialysis has better outcomes than hemodialysis during the first couple of years. Other benefits include greater flexibility and better tolerability in those with significant heart disease. Complications may include infections within the abdomen, hernias, high blood sugar, bleeding in the abdomen, and blockage of the catheter. Use is not possible in those with significant prior abdominal surgery or inflammatory bowel disease. It requires some degree of technical skill to be done properly. In peritoneal dialysis, a specific solution is introduced through a permanent tube in the lower abdomen and then removed. This may either occur at regular intervals throughout the day, kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Ultrasound
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g. distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. Its aim is usually to find a source of disease or to exclude pathology. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequencies which are significantly higher than the range of human hearing (>20,000 Hz). Ultrasonic images, also known as sonograms, are created by sending pulses of ultrasound into tissue using a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpeduncular Fossa
The interpeduncular fossa is a deep depression of the ventral surface of the midbrain between the two crura cerebri. It has been found in humans and macaques, but not in rats or mice, showing that this is a relatively new evolutionary region. Anatomy The interpeduncular fossa is a somewhat rhomboid-shaped area of the base of the brain. Features The lateral wall of the interpeduncular fossa bears a groove - the oculomotor sulcus - from which rootlets of the oculomotor nerve emerge from the substance of the brainstem and aggregate into a single fascicle. Anatomical relations The ventral tegmental area lies at the depth of the interpeduncular fossa. Boundaries The interpeduncular fossa is in front by the optic chiasma, behind by the antero-superior surface of the pons, antero-laterally by the converging optic tracts, and postero-laterally by the diverging cerebral peduncles. The floor of interpeduncular fossa, from behind forward, are the posterior perforated substance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Cerebellar Peduncle
In the human brain, the superior cerebellar peduncle (brachium conjunctivum) is a paired structure of white matter that connects the cerebellum to the midbrain. It consists mainly of efferent fibers, the cerebellothalamic tract that runs from a cerebellar hemisphere to the contralateral thalamus, and the cerebellorubral tract that runs from a cerebellar hemisphere to the red nucleus. It also contains afferent tracts, most prominent of which is the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Other afferent tracts are the trigeminothalamic fibers, tectocerebellar fibers, and noradrenergic fibers from the locus coeruleus. The superior peduncle emerges from the upper and medial parts of the white matter of each hemisphere and is placed under cover of the upper part of the cerebellum. Structure Superior cerebellar peduncles are connected together by the anterior medullary velum, which can be followed upward as far as the inferior colliculi, under which they disappear. Below, they form the upper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RPGRIP1L
RPGRIP1L is a human gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is localized to primary cilia and centrosomes in ciliated human epithelial kidney cells and retinal pigment epithelial cells . RPGRIP1L colocalized at the basal body-centrosome complex with the proteins NPHP4, NPHP6, and TUBG1. Also, it can interact with MyosinVa Clinical significance Mutations in the RPGRIP1L gene are associated with Joubert syndrome and Meckel syndrome which belong to a group of developmental autosomal recessive disorders that are associated with cilium dysfunction. Mutations in this gene are also associated with nephronophthisis. Copy number variation affecting the gene was associated with schizophrenia in one study.Gene Overview of All Published Schizophrenia-As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RPGRIP1
X-linked retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator-interacting protein 1 is a protein in the ciliary transition zone that in humans is encoded by the ''RPGRIP1'' gene. RPGRIP1 is a multi-domain protein containing a coiled-coil domain at the N-terminus, two C2 domains and a C-terminal RPGR-interacting domain (RID). Defects in the gene result in the Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA) syndrome and in the eye disease glaucoma. Interactions RPGRIP1 has been shown to interact with Retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator. RPGRIP1 interacts with RPGR via its RPGR-interacting domain (RID), which folds into a C2 domain architecture and interacts with RPGR at three different locations: A β strand of the RID interacting with the large loop of RPGR, at a hydrophobic interaction In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CC2D2A
Coiled-coil and C2 domain-containing protein 2A that in humans is encoded by the ''CC2D2A'' gene. Function This gene encodes a coiled-coil and calcium binding domain protein that appears to play a critical role in cilia formation. Clinical significance Mutations in the CC2D2A gene are associated with Meckel syndrome as well as Joubert syndrome Joubert syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder that affects the cerebellum, an area of the brain that controls balance and coordination. Joubert syndrome is one of the many genetic syndromes associated with syndromic retinitis pi .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * {{gene-4-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TMEM67
Meckelin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TMEM67'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene localizes to the primary cilium The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike project ... and to the plasma membrane. The gene functions in centriole migration to the apical membrane and formation of the primary cilium. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Clinical significance Defects in this gene are a cause of Meckel syndrome type 3 (MKS3), nephronophthisis and Joubert syndrome type 6 (JBTS6). See also * Meckel syndrome References Further reading * * * * * * * {{gene-8-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliopathy
A ciliopathy is any genetic disorder that affects the cellular cilia or the cilia anchoring structures, the basal bodies, or ciliary function. Primary cilia are important in guiding the process of development, so abnormal ciliary function while an embryo is developing can lead to a set of malformations that can occur regardless of the particular genetic problem. The similarity of the clinical features of these developmental disorders means that they form a recognizable cluster of syndromes, loosely attributed to abnormal ciliary function and hence called ciliopathies. Regardless of the actual genetic cause, it is clustering of a set of characteristic physiological features which define whether a syndrome is a ciliopathy. Although ciliopathies are usually considered to involve proteins that localize to motile and/or immotile (primary) cilia or centrosomes, it is possible for ciliopathies to be associated with unexpected proteins such as XPNPEP3, which localizes to mitochondria bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |