|
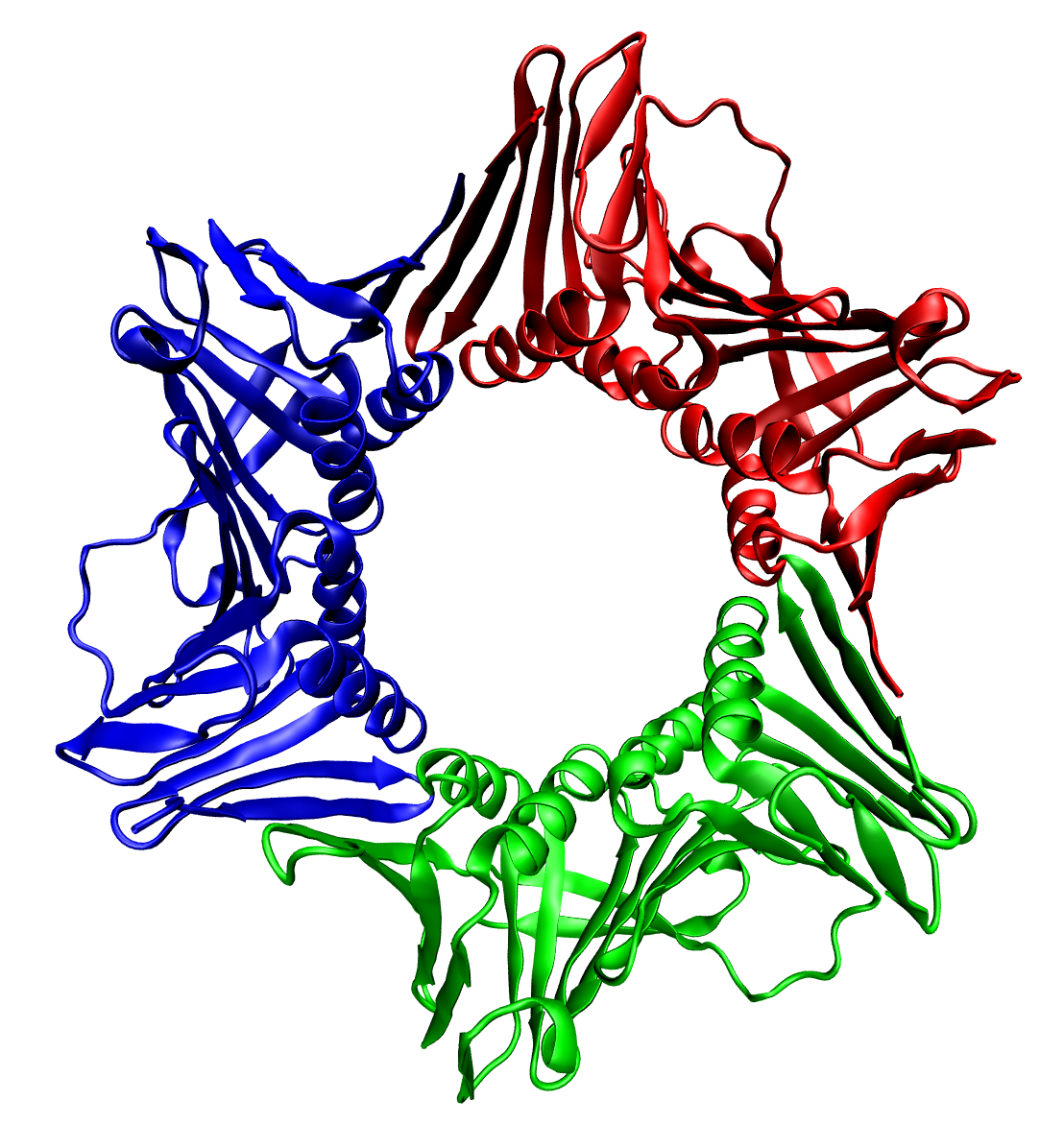
RPGRIP1
X-linked retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator-interacting protein 1 is a protein in the ciliary transition zone that in humans is encoded by the ''RPGRIP1'' gene. RPGRIP1 is a multi-domain protein containing a coiled-coil domain at the N-terminus, two C2 domains and a C-terminal RPGR-interacting domain (RID). Defects in the gene result in the Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA) syndrome and in the eye disease glaucoma. Interactions RPGRIP1 has been shown to interact with Retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator. RPGRIP1 interacts with RPGR via its RPGR-interacting domain (RID), which folds into a C2 domain architecture and interacts with RPGR at three different locations: A β strand of the RID interacting with the large loop of RPGR, at a hydrophobic interaction In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C2 Domain
A C2 domain is a protein structural domain involved in targeting proteins to cell membranes. The typical version (PKC-C2) has a beta-sandwich composed of 8 beta sheet, β-strands that co-ordinates two or three calcium ions, which bind in a cavity formed by the first and final loops of the domain, on the membrane binding face. Many other C2 domain families don't have calcium binding activity. Coupling with other domains C2 domains are frequently found coupled to enzyme, enzymatic domains; for example, the C2 domain in PTEN (gene), PTEN, brings the phosphatase domain into contact with the plasma membrane, where it can dephosphorylate its substrate, Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3), without removing it from the membrane - which would be energetically very costly. PTEN consists of two domains, a protein tyrosine phosphatase domain and a C2 domain. This domain pair constitutes a superdomain, a heritable unit that is found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye remains open, with less common types including closed-angle (narrow angle, acute congestive) glaucoma and normal-tension glaucoma. Open-angle glaucoma develops slowly over time and there is no pain. Peripheral vision may begin to decrease, followed by central vision, resulting in blindness if not treated. Closed-angle glaucoma can present gradually or suddenly. The sudden presentation may involve severe eye pain, blurred vision, mid-dilated pupil, redness of the eye, and nausea. Vision loss from glaucoma, once it has occurred, is permanent. Eyes affected by glaucoma are referred to as being glaucomatous. Risk factors for glaucoma include increasing age, high pressure in the eye, a family history of glaucoma, and use of steroid medication. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leber's Congenital Amaurosis
Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA) is a rare inherited eye disease that appears at birth or in the first few months of life. It affects about 1 in 40,000 newborns. LCA was first described by Theodor Leber in the 19th century. It should not be confused with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy, which is a different disease also described by Theodor Leber. One form of LCA was successfully treated with gene therapy in 2008. Signs and symptoms The term congenital refers to a condition present from birth (not acquired) and amaurosis refers to a loss of vision not associated with a lesion. However, beyond these general descriptions, the presentation of LCA can vary, because it is associated with multiple genes. LCA is typically characterized by nystagmus, sluggish or absent pupillary responses, and severe vision loss or blindness. Genetics It is usually autosomal recessive; however, importantly for family planning, it is sometimes autosomal dominant. It is a disorder thought to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinitis Pigmentosa GTPase Regulator
X-linked retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator is a GTPase-binding protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RPGR'' gene. The gene is located on the X-chromosome and is commonly associated with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP). In photoreceptor cells, RPGR is localized in the connecting cilium which connects the protein-synthesizing inner segment to the photosensitive outer segment and is involved in the modulation of cargo trafficked between the two segments. Function This gene encodes a protein with a series of six RCC1-like domains (RLDs), characteristic of the highly conserved guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Mutations in this gene have been associated with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different isoforms of this gene have been reported, but the full-length natures of only some have been determined. The two major isoforms are RPGRconst, the default isoform, composed of exons 1-19, and RPGRORF15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilium
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with a subtype, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core called the axoneme determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pair o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Quaternary Structure
Protein quaternary structure is the fourth (and highest) classification level of protein structure. Protein quaternary structure refers to the structure of proteins which are themselves composed of two or more smaller protein chains (also referred to as subunits). Protein quaternary structure describes the number and arrangement of multiple protein folding, folded protein subunits in a Multiprotein complex, multi-subunit complex. It includes organizations from simple protein dimer, dimers to large homooligomers and multiprotein complex, complexes with defined or variable numbers of subunits. In contrast to the first three levels of protein structure, not all proteins will have a quaternary structure since some proteins function as single units. Protein quaternary structure can also refer to biomolecular complexes of proteins with nucleic acids and other Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactors. Description and examples Many proteins are actually assemblies of multiple polypeptide c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coiled Coil
A coiled coil is a structural motif in proteins in which 2–7 alpha-helices are coiled together like the strands of a rope. (Dimers and trimers are the most common types.) Many coiled coil-type proteins are involved in important biological functions, such as the regulation of gene expression — e.g., transcription factors. Notable examples are the oncoproteins c-Fos and c-Jun, as well as the muscle protein tropomyosin. Discovery The possibility of coiled coils for α-keratin was initially somewhat controversial. Linus Pauling and Francis Crick independently came to the conclusion that this was possible at about the same time. In the summer of 1952, Pauling visited the laboratory in England where Crick worked. Pauling and Crick met and spoke about various topics; at one point, Crick asked whether Pauling had considered "coiled coils" (Crick came up with the term), to which Pauling said he had. Upon returning to the United States, Pauling resumed research on the topic. He conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |