COACH Syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
COACH syndrome, also known as Joubert syndrome with hepatic defect, is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disease. The name is an acronym of the defining signs: cerebellar vermis aplasia, oligophrenia, congenital ataxia, coloboma and hepatic fibrosis. The condition is associated with moderate intellectual disability. It falls under the category of a Joubart Syndrome-related disorder (JSRD).
The syndrome was first described in 1974 by Alasdair Hunter and his peers at the Montreal Children's Hospital. It was not until 1989 that it was labelled COACH syndrome, by Verloes and Lambotte, at the Sart Tilman University Hospital, Belgium.
 Due to generational familial linkage and the frequency of siblings sharing inheritance of COACH syndrome, it is classified as an autosomal recessive disorder. COACH syndrome is a ciliopathy, a group of diseases categorized by irregular behavior of the primary cilia, which are involved in cell division, transportation, communication and tissue differentiation. This leads to irregular tissue growth in organs and various other diseases. 83% of COACH syndrome carriers presented with either one or two mutations on the MKS3 gene, and findings suggest this is where most of the symptoms can be accredited.
Due to generational familial linkage and the frequency of siblings sharing inheritance of COACH syndrome, it is classified as an autosomal recessive disorder. COACH syndrome is a ciliopathy, a group of diseases categorized by irregular behavior of the primary cilia, which are involved in cell division, transportation, communication and tissue differentiation. This leads to irregular tissue growth in organs and various other diseases. 83% of COACH syndrome carriers presented with either one or two mutations on the MKS3 gene, and findings suggest this is where most of the symptoms can be accredited.
 There is no cure for COACH, syndrome, therefore treatment targets the various complications it implies and management of the disease and its symptoms.
Management includes monitoring patients' neurological activity, development patterns and renal and hepatic function annually. Programs for special education and
There is no cure for COACH, syndrome, therefore treatment targets the various complications it implies and management of the disease and its symptoms.
Management includes monitoring patients' neurological activity, development patterns and renal and hepatic function annually. Programs for special education and
Signs and symptoms
Signs of COACH syndrome tend to present from birth to early childhood. Facial abnormalities are a common symptom, with some characteristics being broadness of the forehead,ptosis
Ptosis (from the Greek: πτῶσις 'falling', 'a fall', 'dropped') refers to droopiness or abnormal downward displacement of a body part or organ. Particular cases include:
* Ptosis (eyelid)
* Ptosis (chin)
* Ptosis (breasts)
* Visceroptosis, ...
of either one or both eyes and misalignment of the eyes. Other cases also report a "carp" shaped mouth, flattened face and nose and hypertelorism
Hypertelorism is an abnormally increased distance between two organs or bodily parts, usually referring to an increased distance between the orbits (eyes), or orbital hypertelorism. In this condition the distance between the inner eye corners as ...
.
Patients are often within the lower percentiles for height and weight growth. Hypotonia is a possible sign of COACH syndrome. Infants with COACH syndrome may experience very categorical hyperventilation and complications with respiration, such as irregular breathing. It has been reported that as patients surpass infancy, these respiratory issues may disappear.
Behavioral and intellectual delays are symptoms caused by the hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis and oligophrenia. This implies delayed onset of speech and walking, along with learning and social issues. Poor motor skills and balance, speech impairment, mild gait or hand ataxia and irregular eye movement are symptoms of the disease attributed to congential ataxia.
Coloboma of the eye is visible in the retina as "hole" in its structure, and causes low vision, possible sensitivity to light and variance in size of the eyeball. The build-up of tissue in the liver, known as hepatic fibrosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repai ...
, may cause symptoms such as jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme meta ...
, ascites, abnormal bleeding and enlarged spleen. Kidney complications in the form of polycystic kidney
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD or PCKD, also known as polycystic kidney syndrome) is a genetic disorder in which the renal tubules become structurally abnormal, resulting in the development and growth of multiple cysts within the kidney. These cy ...
or nephronophthisis
Nephronophthisis is a genetic disorder of the kidneys which affects children. It is classified as a medullary cystic kidney disease. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion and, although rare, is the most common genetic cause o ...
is estimated to affect 77% of patients with COACH syndrome, and is therefore a highly significant symptom of the disease.
Genetics
CC2D2A
Coiled-coil and C2 domain-containing protein 2A that in humans is encoded by the ''CC2D2A'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a coiled-coil and calcium binding domain protein that appears to play a critical role in cilia formation.
Clinical s ...
and RPGRIP1
X-linked retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator-interacting protein 1 is a protein in the ciliary transition zone that in humans is encoded by the ''RPGRIP1'' gene. RPGRIP1 is a multi-domain protein containing a coiled-coil domain at the N-term ...
L genes may also have some minor contributions, with around 8.7% reporting a mutation on the CC2D2A
Coiled-coil and C2 domain-containing protein 2A that in humans is encoded by the ''CC2D2A'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a coiled-coil and calcium binding domain protein that appears to play a critical role in cilia formation.
Clinical s ...
gene and 4.3% on the RPGRIP1L
RPGRIP1L is a human gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is localized to primary cilia and centrosomes in ciliated human epithelial kidney cells and retinal pigment epithelial cells . RPGRIP1L colocalized at the basal body-centrosome ...
gene. These three genetic mutations reportedly cover 96% of families with COACH syndrome.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of COACH syndrome is based on the presence of all five categories; cerebellar vermis hypoplasia, oligophrenia, congenital ataxia, coloboma, andhepatic fibrosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repai ...
.
Detection of the hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis is achieved through a cranial magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI) scan. The presence of the 'molar tooth sign' (MTS) on the MRI scan, a mid- brain hind- brain malformation, confirms this condition and is a key indicator of COACH syndrome. The MTS's distinguished shape is attributed to the lengthened superior cerebellar peduncle
In the human brain, the superior cerebellar peduncle (brachium conjunctivum) is a paired structure of white matter that connects the cerebellum to the midbrain. It consists mainly of efferent fibers, the cerebellothalamic tract that runs from a cer ...
s and deepened interpeduncular fossa
The interpeduncular fossa is a deep depression of the ventral surface of the midbrain between the two crura cerebri.
It has been found in humans and macaques, but not in rats or mice, showing that this is a relatively new evolutionary region.
A ...
. To diagnose ataxia, both neurological assessment and physical examination are required. This can include MRI scans, study of behavior and motor skills in infancy and analysis of family history and genetics. In the case of congenital ataxia, patients are born with the condition and thus diagnosis is more difficult, therefore diagnosis of ataxia alone is not sufficient to indicate COACH syndrome, and must be used in conjunction with other symptoms. Oligophrenia, more commonly known as intellectual disability, is diagnosed using personalized testing to measure intelligence and physical examination for anomalies and facial dysmorphia. Hepatic fibrosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repai ...
has a range of diagnostic techniques, including invasive and non- invasive. Liver biopsy examination is an invasive technique, which uses liver tissue extracted from the patient to identify the degree and severity of the fibrosis, and may also provide insight on tumor growth. Ultrasonography- based tests use radiation waves to measure the stiffness of the tissue and are non- invasive. Serum tests are also non- invasive, and diagnose liver complications on the basis of the amount and presence of certain proteins and chemicals in the body. Kidney cysts can be discovered using ultrasound techniques, and monitoring of the patient's urine concentrating ability for any abnormalities can indicate other renal complications such as nephronophthisis
Nephronophthisis is a genetic disorder of the kidneys which affects children. It is classified as a medullary cystic kidney disease. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion and, although rare, is the most common genetic cause o ...
.
Management
 There is no cure for COACH, syndrome, therefore treatment targets the various complications it implies and management of the disease and its symptoms.
Management includes monitoring patients' neurological activity, development patterns and renal and hepatic function annually. Programs for special education and
There is no cure for COACH, syndrome, therefore treatment targets the various complications it implies and management of the disease and its symptoms.
Management includes monitoring patients' neurological activity, development patterns and renal and hepatic function annually. Programs for special education and occupational therapy
Occupational therapy (OT) is a global healthcare profession. It involves the use of assessment and intervention to develop, recover, or maintain the meaningful activities, or ''occupations'', of individuals, groups, or communities. The field of ...
for speech and motor impairment can improve symptoms of intellectual disability and quality of life for patients. Families and patients are offered ongoing psychological support and specialized care is provided to aid societal integration. In some cases, antiepileptic drugs or neuroleptics are prescribed to reduce anger and behavioral difficulties and improve mood. Some children with hypotonia and other motor skill complications may need a nasogastric feeding tube to ensure adequate nutrients are received and breathing is undisrupted.
Ophthalmological surgery may be used to treat coloboma and ptosis
Ptosis (from the Greek: πτῶσις 'falling', 'a fall', 'dropped') refers to droopiness or abnormal downward displacement of a body part or organ. Particular cases include:
* Ptosis (eyelid)
* Ptosis (chin)
* Ptosis (breasts)
* Visceroptosis, ...
of the eye to improve vision and appearance. A common technique to treat coloboma is intraocular lens (IOL) implantation, whereby a lens is surgically inserted and adhered to the iris to improve vision and appearance. In some severe cases, in conjunction with the IOL implantation, an artificial iris may be inserted into the lens capsule to treat this condition. To treat ptosis
Ptosis (from the Greek: πτῶσις 'falling', 'a fall', 'dropped') refers to droopiness or abnormal downward displacement of a body part or organ. Particular cases include:
* Ptosis (eyelid)
* Ptosis (chin)
* Ptosis (breasts)
* Visceroptosis, ...
, upper eyelid blepharoplasty
Blepharoplasty (Greek: ''blepharon'', "eyelid" + ''plassein'' "to form") is the plastic surgery operation for correcting defects, deformities, and disfigurations of the eyelids; and for aesthetically modifying the eye region of the face. With t ...
is used for both cosmetic and functional reasons. Excess muscle and fat is removed, and the lid is raised in this procedure, and it is considered a minor procedure.
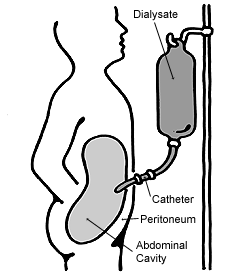
If kidney function is abnormal, dialysis Dialysis may refer to:
*Dialysis (chemistry), a process of separating molecules in solution
**Electrodialysis, used to transport salt ions from one solution to another through an ion-exchange membrane under the influence of an applied electric pote ...
is a viable method of management, though is not a cure. Dialysis involves the refiltering of the blood through an external dialyzer, and is done usually three times a week to improve quality of life. In most advanced cases, a kidney transplant will be required to ensure patient survival. Hepatic fibrosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repai ...
has a variety of treatment options, including anti-fibrotic methods, which aim to prevent the build-up of tissue in the liver. There are multiple methods, such as the targeting or clearance of collagen- generating cells, deactivation of receptors to certain cytokines and inhibition of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF). In cases of advanced fibrosis causing liver failure, liver transplant surgery is necessary to restore function.
Prognosis
COACH syndrome is categorized as a Jobert syndrome related disorder (JSRD).Joubert syndrome
Joubert syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder that affects the cerebellum, an area of the brain that controls balance and coordination.
Joubert syndrome is one of the many genetic syndromes associated with syndromic retinitis pig ...
affects approximately 1 in 80,000 to 1 in 100,000 live births, meaning it is a rare disease, while COACH syndrome is even more rare, with only 43 cases being reported from its discovery until 2010. It is estimated to occur in less than one in one million people. Due to this rarity, the prognosis of the disease is dealt with case- by- case. Survival depends on the severity of the symptoms, with most patients surviving infancy. The likely causes of death with the progression of time are a renal and hepatic failure in later stages of life.
History
The first official report of COACH syndrome was published in 1974 at the Montreal Children's Hospital, identifying two siblings, a brother and sister, presenting with all 5 components of the disorder. The report summarizes the family history and provides detailed case reports on the two siblings, analyzing all health abnormalities to reach a conclusion about the condition. The siblings both presented with the symptoms of congenitalhepatic fibrosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repai ...
, choroidal colobomata, dysmorphic feature
A dysmorphic feature is an abnormal difference in body structure. It can be an isolated finding in an otherwise normal individual, or it can be related to a congenital disorder, Genetics, genetic syndrome or birth defect. Dysmorphology is the stud ...
s, polycystic kidneys, encephalopathy causing intellectual disability and growth problems. The report concludes that the symptoms presented by the siblings are not completely consistent with any other existing disorders, and thus prompted further research into the official classification of COACH syndrome in 1989.
The official report classifying COACH syndrome in 1989 by Verloes and Lambotte assesses the disorder in two siblings and a third unrelated child, finding very similar symptoms to the initial report in 1974. The report concludes by suggesting that more cases of the disorder need to be reported to refine its definition, and assigns the name COACH syndrome as an acronym for the major symptoms.
References
{{Medical resources , ICD11 = , ICD10 = , ICD10CM = , ICD9 = , ICDO = , OMIM = 216360 , MeshID = C536430 , DiseasesDB = 34681 , SNOMED CT = 721847002 , Curlie = , MedlinePlus = , eMedicineSubj = , eMedicineTopic = , PatientUK = , NCI = , GeneReviewsNBK = , GeneReviewsName = , NORD = COACH syndrome , GARDNum = 1410 , GARDName = Joubert syndrome with hepatic defect , RP = 8239 , AO = , WO = , OrthoInfo = , Orphanet = 1454 , Scholia = Q25326623 , OB = Rare genetic syndromes