peritoneal dialysis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of dialysis which uses the
File:DP branchement.svg, Hookup
File:DP infusion.svg, Infusion
File:DP stase.svg, Diffusion (fresh)
File:DP fin stase.svg, Diffusion (waste)
File:DP drainage.svg, Drainage
 The abdomen is cleaned in preparation for surgery and a
The abdomen is cleaned in preparation for surgery and a
Treatment Methods for Kidney Failure
-
peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesoth ...
in a person's abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. ...
as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the c ...
. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte problems
Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function, ...
, and remove toxins in those with kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
. Peritoneal dialysis has better outcomes than hemodialysis
Hemodialysis, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply dialysis, is a process of purifying the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of dialysis achieves the extracorporeal removal of waste products such as creatinin ...
during the first couple of years. Other benefits include greater flexibility and better tolerability in those with significant heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, hea ...
.
Complications may include infections within the abdomen, hernia
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ (anatomy), organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the gr ...
s, high blood sugar
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even ...
, bleeding in the abdomen, and blockage of the catheter. Use is not possible in those with significant prior abdominal surgery
The term abdominal surgery broadly covers Surgery, surgical procedures that involve opening the abdomen (laparotomy). Surgery of each abdominal organ is dealt with separately in connection with the description of that organ (see stomach, kidney, l ...
or inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammation, inflammatory conditions of the colon (anatomy), colon and small intestine, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine a ...
. It requires some degree of technical skill to be done properly.
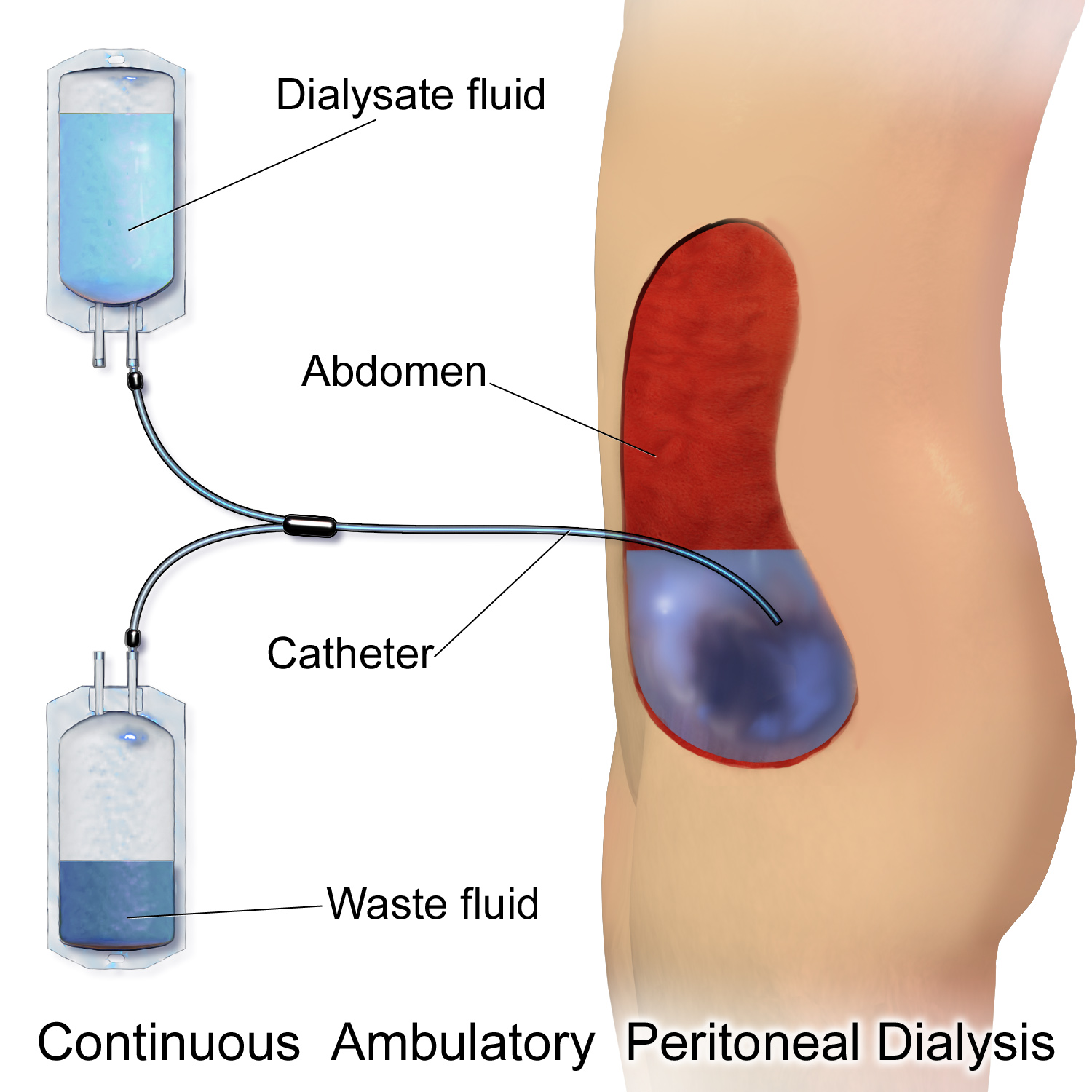
In peritoneal dialysis, a specific solution is introduced through a permanent tube in the lower abdomen and then removed. This may either occur at regular intervals throughout the day, known as continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD), or at night with the assistance of a machine, known as automated peritoneal dialysis (APD). The solution is typically made of sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g ...
, bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochemic ...
, and an osmotic agent such as glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
.
The solution used for peritoneal dialysis is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health ...
. As of 2009, peritoneal dialysis was available in 12 out of 53 African countries.
Medical uses
Peritoneal dialysis is a method ofrenal replacement therapy
Renal replacement therapy (RRT) is therapy that replaces the normal blood-filtering function of the kidneys. It is used when the kidneys are not working well, which is called kidney failure and includes acute kidney injury and chronic kidney dis ...
for needing maintenance therapy for late stage chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vo ...
. This is an alternative to the most common method hemodialysis
Hemodialysis, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply dialysis, is a process of purifying the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of dialysis achieves the extracorporeal removal of waste products such as creatinin ...
.
Complications
Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis
A common cause ofperitonitis
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part or ...
is touch contamination, e.g. insertion of catheter by un-sanitized hands, which potentially introduces bacteria to the abdomen; other causes include catheter complication, transplantation of bowel bacteria, and systemic infections. Most common type of PD-peritonitis infection (80%) are from bacterial sources. Infection rates are highly variable by region and within centers with estimated rates between 0.06 - 1.66 episodes per patient year. With recent technical advances peritonitis incidence has decreased overtime.
There is not sufficient evidence to be clear about the best treatment for PD-associated peritonitis, although direct infusion of antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s into the peritoneum appears to offer slight advantage over the intravenous route of administration; there is no clear advantage for other frequently used treatments such as routine peritoneal lavage or use of urokinase
Urokinase, also known as urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), is a serine protease present in humans and other animals. The human urokinase protein was discovered, but not named, by McFarlane and Pilling in 1947. Urokinase was originally i ...
. The use of preventative nasal mupirocin
Mupirocin, sold under the brand name Bactroban among others, is a topical antibiotic useful against superficial skin infections such as impetigo or folliculitis. It may also be used to get rid of methicillin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (MRSA) wh ...
is of unclear effect with respect to peritonitis. Of the three types of connection and fluid exchange systems (standard, twin-bag and y-set; the latter two involving two bags and only one connection to the catheter, the y-set uses a single y-shaped connection between the bags involving emptying, flushing out then filling the peritoneum through the same connection) the twin-bag and y-set systems were found superior to conventional systems at preventing peritonitis.
The fluid used for dialysis uses glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
as a primary osmotic agent, but this may lead to peritonitis
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part or ...
, the decline of kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
and peritoneal membrane function and other negative health outcomes. The acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
ity, high concentration and presence of lactate and products of the degradation of glucose in the solution (particularly the latter) may contribute to these health issues. Solutions that are neutral
Neutral or neutrality may refer to:
Mathematics and natural science Biology
* Neutral organisms, in ecology, those that obey the unified neutral theory of biodiversity
Chemistry and physics
* Neutralization (chemistry), a chemical reaction in ...
, use bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochemic ...
instead of lactate and have few glucose degradation products may offer more health benefits though this has not yet been studied.
Volume Shifts
The volume of dialysate removed as well as patient's weight are monitored. If more than 500ml of fluid are retained or a liter of fluid is lost across three consecutive treatments, the patient's physician is generally notified . Excessive loss of fluid can result inhypovolemic shock
Hypovolemic shock is a form of shock caused by severe hypovolemia (insufficient blood volume or extracellular fluid in the body). It could be the result of severe dehydration through a variety of mechanisms or blood loss. Hypovolemic shock is a ...
or hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dias ...
while excessive fluid retention can result in hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
and edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's Tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels t ...
. Also monitored is the color of the fluid removed: normally it is pink-tinged for the initial four cycles and clear or pale yellow afterward. The presence of pink or bloody effluent suggests bleeding inside the abdomen while feces indicates a perforated bowel and cloudy fluid suggests infection. The patient may also experience pain or discomfort if the dialysate is too acidic, too cold or introduced too quickly, while diffuse pain with cloudy discharge may indicate an infection. Severe pain in the rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the Gastrointestinal tract, gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the s ...
or perineum
The perineum in humans is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male, or between the anus and the vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone), includi ...
can be the result of an improperly placed catheter. The dwell can also increase pressure on the diaphragm causing impaired breathing, and constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel movement ...
can interfere with the ability of fluid to flow through the catheter.
Chronic Complications
Long term use of PD is associated with fibrosis of the peritoneum. A potentially fatal complication estimated to occur in roughly 2.5% of patients is encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis, in which the bowels become obstructed due to the growth of a thick layer offibrin
Fibrin (also called Factor Ia) is a fibrous, non-globular protein involved in the clotting of blood. It is formed by the action of the protease thrombin on fibrinogen, which causes it to polymerize. The polymerized fibrin, together with platele ...
within the peritoneum.
Other
Other complications includelow back pain
Low back pain (LBP) or lumbago is a common disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back, in between the lower edge of the ribs and the lower fold of the buttocks. Pain can vary from a dull constant ache to a sudden sharp feel ...
and hernia
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ (anatomy), organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the gr ...
or leaking fluid due to high pressure within the abdomen. Hypertriglyceridemia
Hypertriglyceridemia is the presence of high amounts of triglycerides in the blood. Triglycerides are the most abundant fatty molecule in most organisms. Hypertriglyceridemia occurs in various physiologic conditions and in various diseases, and h ...
and obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
are also concerns due to the large volume of glucose in the fluid, which can add 500-1200 calorie
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of on ...
s to the diet per day.
Method
Best practices for peritoneal dialysis state that before peritoneal dialysis should be implemented, the person's understanding of the process and support systems should be assessed, with education on how to care for the catheter and to address any gaps in understanding that may exist. The person should receive ongoing monitoring to ensure adequate dialysis, and be regularly assessed for complications. Finally, they should be educated on the importance of infection control and an appropriate medical regimen established with their cooperation. The abdomen is cleaned in preparation for surgery and a
The abdomen is cleaned in preparation for surgery and a catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Cath ...
is surgically inserted with one end in the abdomen and the other protruding from the skin. Before each infusion the catheter must be cleaned, and flow into and out of the abdomen tested. 2-3 liters of dialysis fluid is introduced into the abdomen over the next ten to fifteen minutes. The total volume is referred to as a ''dwell'' while the fluid itself is referred to as dialysate. The dwell can be as much as 3 liters, and medication can also be added to the fluid immediately before infusion. The dwell remains in the abdomen and waste products diffuse across the peritoneum from the underlying blood vessels. After a variable period of time depending on the treatment (usually 4–6 hours ), the fluid is removed and replaced with fresh fluid. This can occur automatically while the patient is sleeping (automated peritoneal dialysis, APD), or during the day by keeping two litres of fluid in the abdomen at all times, exchanging the fluids four to six times per day (continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis, CAPD).
The fluid used typically contains sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g ...
, lactate or bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochemic ...
and a high percentage of glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
to ensure hyperosmolarity. The amount of dialysis that occurs depends on the volume of the dwell, the regularity of the exchange and the concentration of the fluid. APD cycles between 3 and 10 dwells per night, while CAPD involves four dwells per day of 2-3 liters per dwell, with each remaining in the abdomen for 4–8 hours. The viscera accounts for roughly four-fifths of the total surface area of the membrane, but the parietal peritoneum is the most important of the two portions for PD. Two complementary models explain dialysis across the membrane - the three-pore model (in which molecules are exchanged across membranes which sieve molecules, either protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s, electrolytes or water, based on the size of the pores) and the distributed model (which emphasizes the role of capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
and the solution's ability to increase the number of active capillaries involved in PD). The high concentration of glucose drives the filtration of fluid by osmosis (osmotic UF) from the peritoneal capillaries to the peritoneal cavity. Glucose diffuses rather rapidly from the dialysate to the blood (capillaries). After 4-6 h of the dwell, the glucose osmotic gradient usually becomes too low to allow for further osmotic UF. Therefore, the dialysate will now be reabsorbed from the peritoneal cavity to the capillaries by means of the plasma colloid osmotic pressure, which exceeds the colloid osmotic pressure in the peritoneum by approximately 18-20 mmHg (cf. the Starling mechanism). Lymphatic absorption will also to some extent contribute to the reabsorption of fluid from the peritoneal cavity to the plasma. Patients with a high water permeability (UF-coefficient) of the peritoneal membrane can have an increased reabsorption rate of fluid from the peritoneum by the end of the dwell. The ability to exchange small solutes and fluid in-between the peritoneum and the plasma can be classified as high (fast), low (slow) or intermediate. High transporters tend to diffuse substances well (easily exchanging small molecules between blood and the dialysis fluid, with somewhat improved results with frequent, short-duration dwells such as with APD), while low transporters have a higher UF (due to the slower reabsorption of glucose from the peritoneal cavity, which results in somewhat better results with long-term, high-volume dwells), though in practice either type of transporter can generally be managed through the appropriate use of either APD or CAPD.
Though there are several different shapes and sizes of catheters that can be used, different insertion sites, number of cuffs in the catheter and immobilization, there is no evidence to show any advantages in terms of morbidity, mortality or number of infections, though the quality of information is not yet sufficient to allow for firm conclusions.
A peritoneal equilibration test may be done to assess a person for peritoneal dialysis by determining the characteristics of the peritoneal membrane mass transport characteristics.
Improvised Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis can be improvised in conditions such as combat surgery or disaster relief using surgical catheters and dialysate made from routinely available medical solutions to provide temporary renal replacement for people with no other options.Epidemiology
As of 2017, hemodialysis is the most widely available renal replacement modality found in 96% of countries whereas peritoneal dialysis (PD) is only available in 75% of countries. In 2016, the proportion of people receiving peritoneal dialysis (PD) was estimated at 11% with wide differences between different countries and regions. In Hong Kong andMexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
, PD is more common than the world average, with Mexico conducting most of its dialysis through PD, while Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
have rates lower than the world average. Peritoneal dialysis first models, patients requiring renal replacement therapy are placed on PD first, and financial incentives for using PD are associated with increase uptake of PD in multiple countries.
East and Southeast Asia
Hong Kong has the highest rate of PD use worldwide at 71.9% in 2014, while in Mainland China had 20% in 2014, 23% in Thailand during 2012, and 10-20% in Vietnam during 2011. Hong Kong had a PD-first model since 1985, Thailand began a PD-first model since 2008 which increased their levels of PD from <10%.Americas
Prevalence in of PD use was 9.7% in USA during 2013 and 16.3% in Canada during 2013. The lower PD rates in the USA are due to higher availability of large corporate owned hemodialysis centers. There have been recent increase in PD uptake in the USA due to changes to medicare reimbursement such asbundled payment Bundled payment is the reimbursement of health care providers (such as hospitals and physicians) "on the basis of expected costs for defined episodes of care." It has been described as "a middle ground" between fee-for-service reimbursement (in wh ...
for dialysis this incentivizes use of PD which is a less costly modality for dialysis.
Overall, prevalence of PD use is 24.6% in Latin America during 2011. Within Latin America, hemodialysis has a higher growth rate in use compared to PD between 1994 - 2010. In 2010, the most prevalent use of PD were in Mexico 55.9% and El Salvador 67.6%. Between 2000 - 2010, Columbia's PD rate dropped from 54% to 31.3%.
History
Peritoneal dialysis was first carried out in the 1920s; however, long term use did not come into medical practice until the 1960s. The timeline was * 1923 - Georg Ganter perform the first peritoneal dialysis. * 1968 - Henry Tenckhoff created the Tenckhoff catheter avoiding the need to replace the catheter in the abdomem for every therapy treatment.Comparison to Hemodialysis
Compared to hemodialysis, PD allows greater patient mobility, produces fewer swings in symptoms due to its continuous nature, andphosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
compounds are better removed, but large amounts of albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water-soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins ...
are removed which requires constant monitoring of nutritional status. The costs of PD are generally lower than those of HD in most parts of the world, this cost advantage is most apparent in developed economies. There is insufficient research to adequately compare the risks and benefits between CAPD and APD; a Cochrane Review
Cochrane (previously known as the Cochrane Collaboration) is a British international charitable organisation formed to organise medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professi ...
of three small clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietar ...
s found no difference in clinically important outcomes (i.e. morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
or mortality
Mortality is the state of being mortal, or susceptible to death; the opposite of immortality.
Mortality may also refer to:
* Fish mortality, a parameter used in fisheries population dynamics to account for the loss of fish in a fish stock throug ...
) for patients with end stage renal disease
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
, nor was there any advantage in preserving the functionality of the kidneys. The results suggested APD may have psychosocial advantages for younger patients and those who are employed or pursuing an education.
PD may also be used for patients with cardiac instability as it does not result in rapid and significant alterations to body fluids, and for patients with insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
-dependent diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
due to the inability to control blood sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
levels through the catheter.
Society and culture
Economics
The cost of dialysis treatment is related to how wealthy the country is. In the United States peritoneal dialysis costs the government about $53,400 per person per year.References
External links
Treatment Methods for Kidney Failure
-
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) is part of the United States National Institutes of Health, which in turn is part of the Department of Health and Human Services. NIDDK is approximately the fifth-largest ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Peritoneal Dialysis
Digestive system procedures
Medical treatments
Renal dialysis
World Health Organization essential medicines
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
de:Dialyse#Peritonealdialyse