|
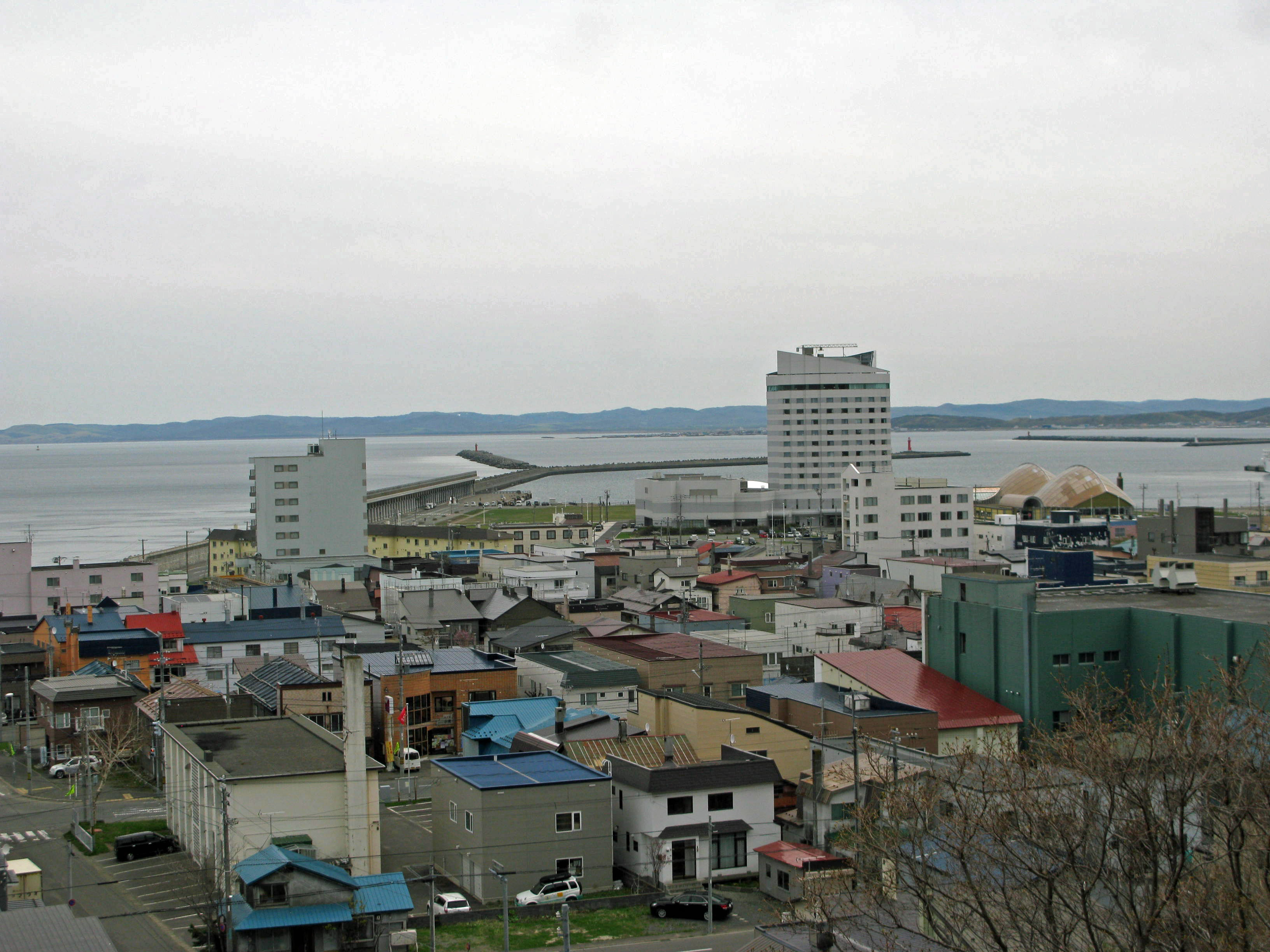
Wakkanai
' meaning "cold water river" is a city located in Sōya Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital of Sōya Subprefecture. It contains Japan's northernmost point, Cape Sōya, from which the Russian island of Sakhalin can be seen. As of 1 June 1975, the city has an estimated population of 55,465 and a population density of 72.8 persons per km2 (189 persons per mi2). The total area is . Wakkanai is also home to Japan's first nursing home built inside the central train station of its city, a novel approach to caring for Japan's growing elderly population that has since been imitated in several other cities. History Wakkanai was originally home to an Ainu population. The first Japanese settlement was established in 1685. *1879: The village of Wakkanai was founded. *1897: Sōya Subprefecture established. *1901: Wakkanai village became Wakkanai town. *1949: Wakkanai town became Wakkanai city. *1955: Soya village was merged into Wakkanai city. *1959: Wakkanai Airport opened. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakkanai Airport
is an airport located east southeast of Wakkanai, Hokkaidō, Japan. Wakkanai is the northernmost airport in Japan that is capable of handling jet aircraft; due to its small size, it is susceptible to closures during the coldest winter months, in which case incoming aircraft are often diverted to Asahikawa Airport. It has one jet bridge, one apron gate for mid-sized jet aircraft, and two apron gates for commuter aircraft. History Wakkanai Airport opened to passenger traffic in 1960, initially on an irregular basis. Air Nippon began scheduled service to Okadama Airport and Rishiri Airport in 1974, followed by Rebun Airport in 1978 and New Chitose Airport in 1980. Air Nippon discontinued the short Rebun and Rishiri commuter flights in 2003 due to poor load factors. In 1987, the 1,200 m main runway was extended to 1,800 m, allowing All Nippon Airways to begin jet service to Tokyo. The flight was initially seasonal and did not become a year-round service until 1997. The city of Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
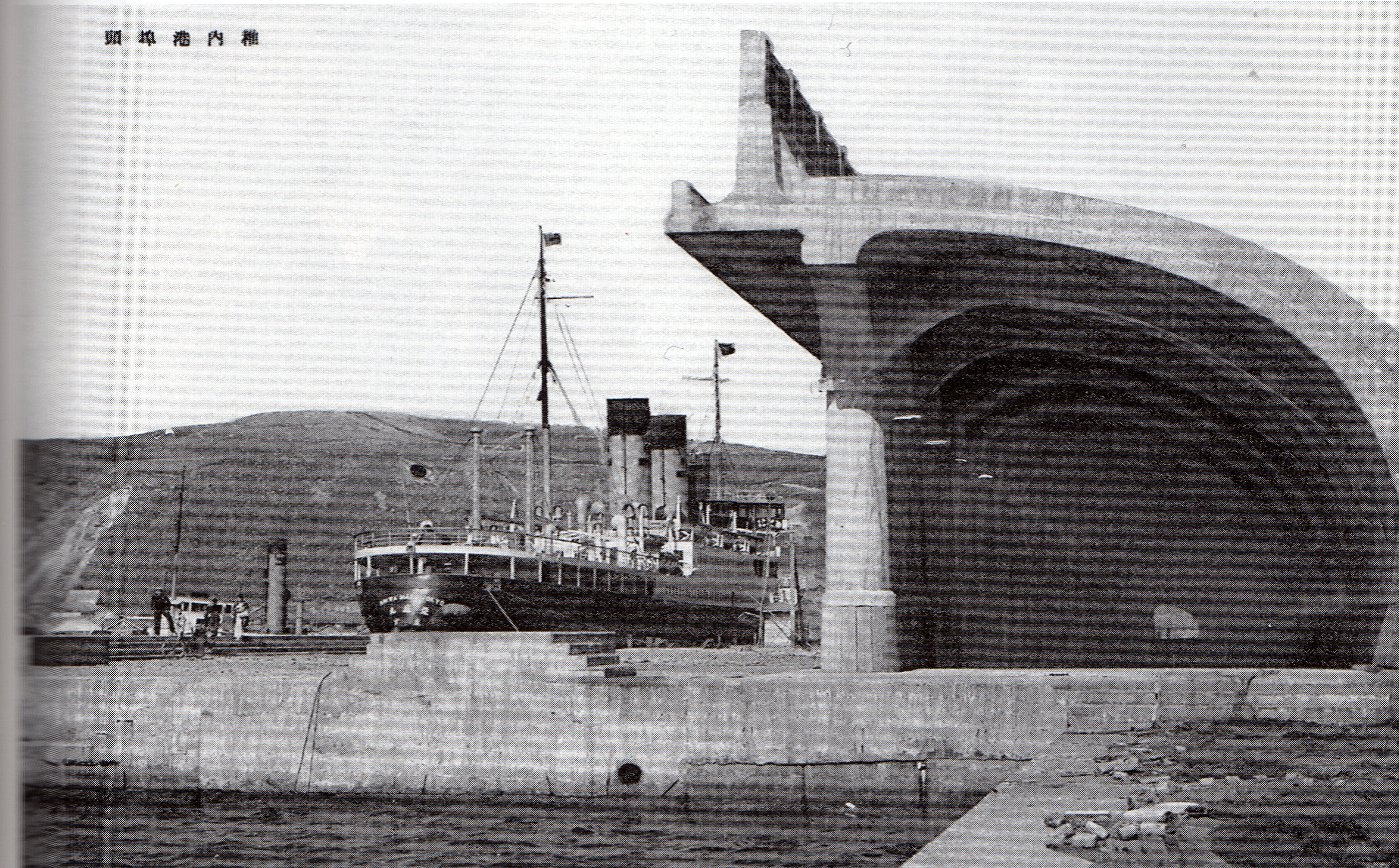
North Breakwater Dome
The is a long arched " semi-domical" structure in the port area of Wakkanai, Hokkaidō, Japan. Rising to a height of above the sea and extending some , with seventy columns, an intercolumniation of , and a width from column to wall of , the form, inspired by a Roman arcade, is said to be without parallel. History In accordance with the 1905 Treaty of Portsmouth, South Sakhalin was incorporated into the Empire of Japan and governed as Karafuto Prefecture. To improve maritime connections between Wakkanai and Sakhalin, between 1910 and 1919 plans were laid for the redevelopment of the old fishing port of Wakkanai, with civil engineer in charge. Measures included a north breakwater to protect the port from windstorms and high waves, paired with a sand groin to the south to enclose the port, together with land reclamation and the construction of moorings. Initial plans for the north breakwater were for its parapet to rise to a height of , but this was considered insufficient to wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hokkaido
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel. The largest city on Hokkaidō is its capital, Sapporo, which is also its only ordinance-designated city. Sakhalin lies about 43 kilometers (26 mi) to the north of Hokkaidō, and to the east and northeast are the Kuril Islands, which are administered by Russia, though the four most southerly are claimed by Japan. Hokkaidō was formerly known as ''Ezo'', ''Yezo'', ''Yeso'', or ''Yesso''. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Hokkaidō" in Although there were Japanese settlers who ruled the southern tip of the island since the 16th century, Hokkaido was considered foreign territory that was inhabited by the indigenous people of the island, known as the Ainu people. While geographers such as Mogami Tokunai and Mamiya Rinzō explored the isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hokkaido Prefecture
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel. The largest city on Hokkaidō is its capital, Sapporo, which is also its only ordinance-designated city. Sakhalin lies about 43 kilometers (26 mi) to the north of Hokkaidō, and to the east and northeast are the Kuril Islands, which are administered by Russia, though the four most southerly are claimed by Japan. Hokkaidō was formerly known as ''Ezo'', ''Yezo'', ''Yeso'', or ''Yesso''. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Hokkaidō" in Although there were Japanese settlers who ruled the southern tip of the island since the 16th century, Hokkaido was considered foreign territory that was inhabited by the indigenous people of the island, known as the Ainu people. While geographers such as Mogami Tokunai and Mamiya Rinzō explored the isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sōya Subprefecture
is a subprefecture of Hokkaido Prefecture, Japan. Its population is estimated to be 77,500 as of July 31, 2004 and its area is . It is the northernmost subprefecture of Japan. Wakkanai Airport is located in Wakkanai. Rishiri Airport is located in Rishirifuji, Rishiri District. Geography Municipalities Mergers History *1897: Sōya Subprefecture established; Sōya, Esashi, Rishiri, Rebun Districts placed under its jurisdiction *1948: Toyotomi village (now town), Teshio District transferred from Rumoi Subprefecture is a subprefecture of Hokkaido Prefecture, Japan. As of 2011, it had a population of 52,627 and an area of . The population density of the subprefecture, 13 people per km2, is very low compared to the rest of Japan. The population of Rumoi Subpr ... *2010: Horonobe town, Teshio District transferred from Rumoi Subprefecture External links Official website Subprefectures in Hokkaido {{Hokkaido-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Sōya
is the northernmost point of the island of Hokkaidō, Japan. It is situated in Wakkanai, Sōya Subprefecture. The is at the cape, although the true northernmost point under Japanese control is a small deserted island called Bentenjima, northwest. Since the cape is just away across La Perouse Strait from Cape Crillon, Sakhalin Island, Russia, it is possible to catch a glimpse of the island of Sakhalin on a clear day. There are more than ten monuments at Cape Sōya, including the Monument of the northernmost Point of Japan, the Tower of Prayer (a memorial to Korean Air Lines Flight 007, shot down in 1983), a statue of Mamiya Rinzō, the Monument of Peace (a memorial to the sunken submarine , and others). Sōya Misaki settlement, east of the cape, has many facilities known to be "the northernmost in Japan", such as the northernmost lighthouse ( Cape Sōya Lighthouse), the northernmost filling station (Idemitsu Cape Sōya SS), the northernmost elementary school (Ōmisaki Element ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
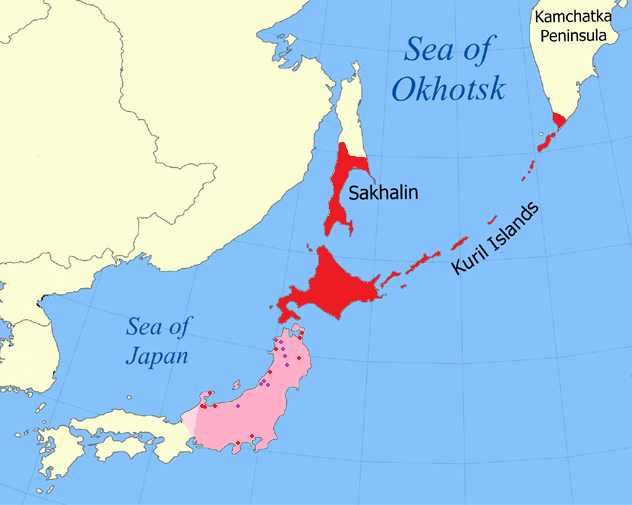
Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: Yh-mif) is the largest island of Russia. It is north of the Japanese archipelago, and is administered as part of the Sakhalin Oblast. Sakhalin is situated in the Pacific Ocean, sandwiched between the Sea of Okhotsk to the east and the Sea of Japan to the west. It is located just off Khabarovsk Krai, and is north of Hokkaido in Japan. The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of which are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The Island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ). Sakhalin was once part of China during the Qing dynasty, although Chinese control was relaxed at times. Sakhalin was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hills
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit. Terminology The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as tall, or as steep as a mountain. Geographers historically regarded mountains as hills greater than above sea level, which formed the basis of the plot of the 1995 film ''The Englishman who Went up a Hill but Came down a Mountain''. In contrast, hillwalkers have tended to regard mountains as peaks above sea level. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' also suggests a limit of and Whittow states "Some authorities regard eminences above as mountains, those below being referred to as hills." Today, a mountain is usually defined in the UK and Ireland as any summit at least high, while the official UK government's definition of a mountain is a summit of or higher. Some definitions include a topographical prominence requirement, typically or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakwater Structure
A breakwater is a permanent structure constructed at a coastal area to protect against tides, currents, waves, and storm surges. Part of a coastal management system, breakwaters are installed to minimize erosion, and to protect anchorages, helping isolate vessels within them from marine hazards such as prop washes and wind-driven waves. A breakwater, also known in some contexts as a jetty, may be connected to land or freestanding, and may contain a walkway or road for vehicle access. On beaches where longshore drift threatens the erosion of beach material, smaller structures on the beach, usually perpendicular to the water's edge, may be installed. Their action on waves and current is intended to slow the longshore drift and discourage mobilisation of beach material. In this usage they are more usually referred to as groynes. Purposes Breakwaters reduce the intensity of wave action in inshore waters and thereby provide safe harbourage. Breakwaters may also be small structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ainu People
The Ainu are the indigenous people of the lands surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, including Hokkaido Island, Northeast Honshu Island, Sakhalin Island, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula and Khabarovsk Krai, before the arrival of the Yamato Japanese and Russians. These regions are referred to as in historical Japanese texts. Official estimates place the total Ainu population of Japan at 25,000. Unofficial estimates place the total population at 200,000 or higher, as the near-total assimilation of the Ainu into Japanese society has resulted in many individuals of Ainu descent having no knowledge of their ancestry. As of 2000, the number of "pure" Ainu was estimated at about 300 people. In 1966, there were about 300 native Ainu speakers; in 2008, however, there were about 100. Names This people's most widely known ethnonym, "Ainu" ( ain, ; ja, アイヌ; russian: Айны) means "human" in the Ainu language, particularly as opposed to , divine beings. Ainu also i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Base
A submarine base is a military base that shelters submarines and their personnel. Examples of present-day submarine bases include HMNB Clyde, Île Longue (the base for France's Force océanique stratégique), Naval Submarine Base Kings Bay, Naval Submarine Base New London, and Rybachiy Nuclear Submarine Base (near Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky). INS Vajrabahu and INS Satavahana are the submarine bases of the Indian Navy. A new underground submarine base, INS Varsha is under construction near Vishakhapatnam for the new expanding fleet of Indian nuclear submarines. The Israeli navy bases its growing submarine force in Haifa. Former submarine bases include DORA 1, , Naval Submarine Base Bangor (now part of Naval Base Kitsap), Mare Island Naval Shipyard (a nuclear-capable base), Ordnance Island in Bermuda during World War II, and the formerly-classified Soviet base at Balaklava in the now Autonomous Republic of Crimea. The Holland Torpedo Boat Station at hamlet of New Suffolk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manchester and Duluth; these access the sea via rivers or canals. Because of their roles as ports of entry for immigrants as well as soldiers in wartime, many port cities have experienced dramatic multi-ethnic and multicultural changes throughout their histories. Ports are extremely important to the global economy; 70% of global merchandise trade by value passes through a port. For this reason, ports are also often densely populated settlements that provide the labor for processing and handling goods and related services for the ports. Today by far the greatest growth in port development is in Asia, the continent with some of the world's largest and busiest ports, such as Singapore and the Chinese ports of Shanghai and Ningbo-Zhou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |