|
Cypraeovula Iutsui
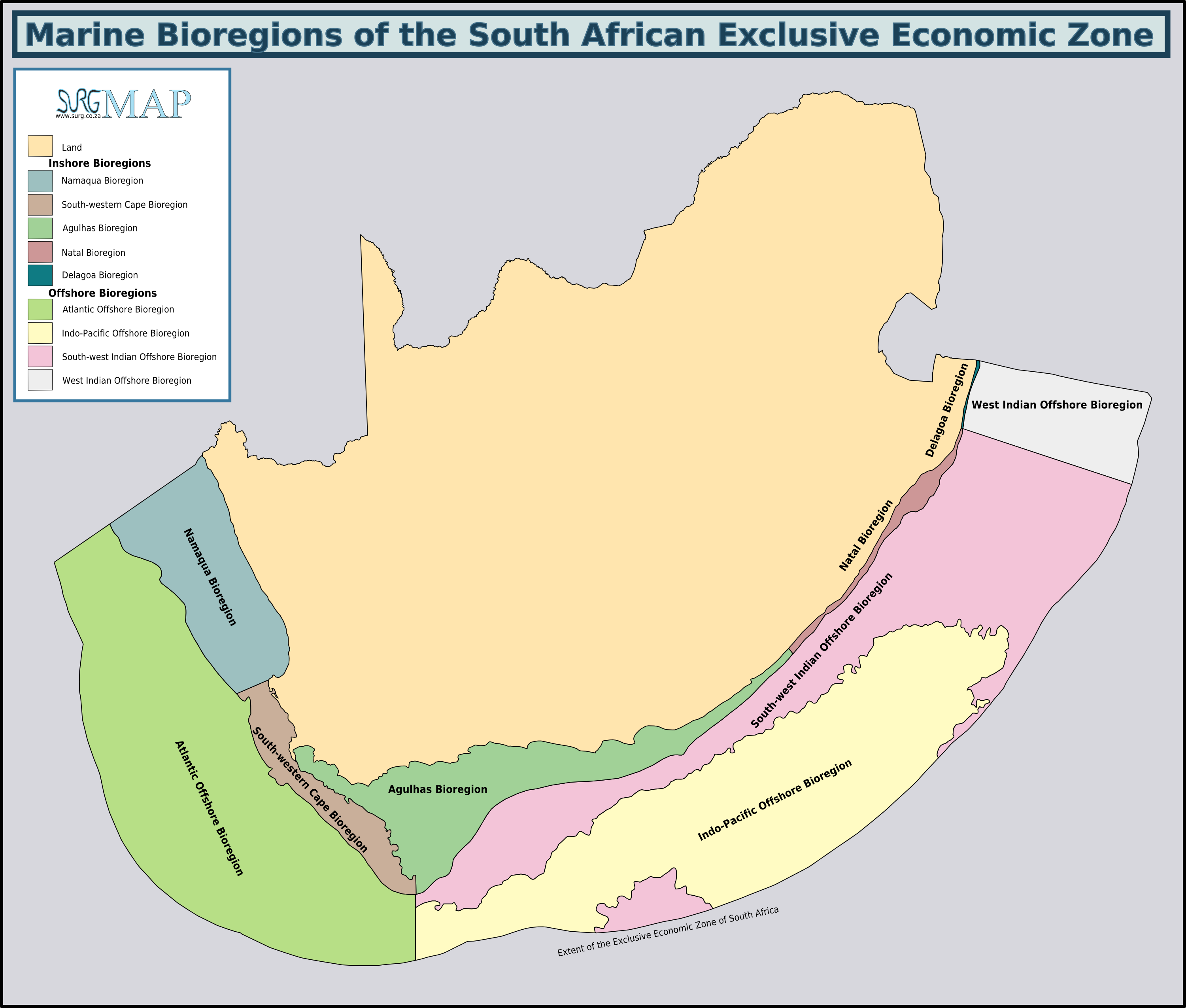
''Cypraeovula iutsui'' is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Cypraeidae, the cowries. Distribution This species occurs from the mouth of the Olifants River in the Western Cape, to Port Alfred, Eastern Cape, South Africa.Liltved, William Rune. ''Cowries and their relatives of southern Africa: A study of the southern African Cypraeacean and Velutinacean gastropod fauna'', Gordon Verhoef, Seacomber Publications, 2000. Description Thin transparent beige mantle has beige or black conical papillae. The siphon is the same colour as mantle. The cephalic tentacles are slender, elongate and off-white. The short translucent white foot is wide at the front and rounded at the rear. The shell is globular, often nearly spherical, up to 41mm in length. Atlantic specimens vary in colour from pale plum to opaque white, with little dorsal marking. Indian Ocean specimens are more colourful, and may have red to rut- brown dorsal markings. The labrum is broad with a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cypraeovula
''Cypraeovula'' is a genus of sea snails, marine (ocean), marine gastropod mollusks in the subfamily Pustulariinae of the family (biology), family Cypraeidae, the cowries. Species Species and subspecies within the genus ''Cypraeovula'' include according to the World Register of Marine Species: *'' Cypraeovula alfredensis'' (Schilder & Schilder 1929) ** ''Cypraeovula alfredensis transkeiana'' Lorenz, 2002 * ''Cypraeovula algoensis'' (John Edward Gray, Gray, 1825) * ''Cypraeovula amphithales'' (James Cosmo Melvill (naturalist), Melvill, 1888) * ''Cypraeovula capensis'' (John Edward Gray, Gray, 1828) * ''Cypraeovula castanea'' (Higgins, 1868) ** ''Cypraeovula castanea latebrosa'' Swarts & Liltved, 2000 **'' Cypraeovula castanea malani'' Lorenz & Bruno de Bruin, 2009 * ''Cypraeovula colligata'' Lorenz, 2002 * ''Cypraeovula connelli'' (Liltved, 1983) ** ''Cypraeovula connelli peelae'' Lorenz, 2002 *'' Cypraeovula coronata'' (Schilder, 1930) ** ''Cypraeovula coronata debruini'' Loren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agulhas Bank
The Agulhas Bank (, from Portuguese for Cape Agulhas, ''Cabo das Agulhas'', "Cape of Needles") is a broad, shallow part of the southern African continental shelf which extends up to south of Cape Agulhas before falling steeply to the abyssal plain. It is the ocean region where the warm Indian Ocean and the cold Atlantic Ocean meet. This convergence leads to treacherous sailing conditions, accounting for numerous wrecked ships in the area over the years. However, the meeting of the oceans here also fuels the nutrient cycle for marine life, making it one of the best fishing grounds in South Africa. Extent and characteristics South African marine ecoregions from the 2011 classification The Agulhas Bank stretches approximately along the African coast, from off Cape Peninsula (18°E) to Port Alfred (26°E), and up to from it. The bank slopes down relatively steeply from the coast to about deep and reaches before dropping steeply to on its southern edge. The shelf spans a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aperture (mollusc)
The aperture is an opening in certain kinds of mollusc shells: it is the main opening of the shell, where the head-foot part of the body of the animal emerges for locomotion, feeding, etc. The term ''aperture'' is used for the main opening in gastropod shells, scaphopod shells, and also for ''Nautilus'' and ammonite shells. The word is not used to describe bivalve shells, where a natural opening between the two shell valves in the closed position is usually called a ''gape''. Scaphopod shells are tubular, and thus they have two openings: a main anterior aperture and a smaller posterior aperture. As well as the aperture, some gastropod shells have additional openings in their shells for respiration; this is the case in some Fissurellidae (keyhole limpets) where the central smaller opening at the apex of the shell is called an orifice, and in the Haliotidae (abalones) where the row of respiratory openings in the shell are also called orifices. In gastropods In some prosobranch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columella (gastropod)
The columella (meaning "little column") or (in older texts) pillar is a central anatomical feature of a coiled snail shell, a gastropod shell. The columella is often only clearly visible as a structure when the shell is broken, sliced in half vertically, or viewed as an X-ray image. The columella runs from the apex of the shell to the midpoint of the undersurface of the shell, or the tip of the siphonal canal in those shells which have a siphonal canal. If a snail shell is visualized as a cone of shelly material which is wrapped around a central axis, then the columella more or less coincides spatially with the central axis of the shell. In the case of shells that have an umbilicus, the columella is a hollow structure. The columella of some groups of gastropod shells can have a number of plications or folds (the columellar fold, plaits or plicae), which are usually visible when looking to the inner lip into the aperture of the shell. These folds can be wide or narrow, prominent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denticles (mollusc)
A denticle is any small tooth-like or bristle-like structure. "Denticle" may refer to: * Denticle (tooth feature), serrations on the teeth of dinosaurs, lizards, sharks, and mammals * Dermal denticle A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as we ...s or placoid scales, in cartilaginous fishes * Pulp stone or endolith, a calcified mass in the pulp of a tooth See also * Denticulation (architecture) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labrum (gastropod)
In the shell of gastropod mollusks (a snail shell), the lip is the free margin of the peristome (synonym: peritreme) or aperture (the opening) of the gastropod shell. In dextral (right-handed) shells (most snail shells are right-handed), the right side or outer side of the aperture is known as the outer lip (''labrum''). The left side of the aperture is known as the inner lip or columellar lip (''labium'') if there is a pronounced lip there. In those species where there is no pronounced lip, the part of the body whorl that adjoins the aperture is known as the parietal wall. The outer lip is usually thin and sharp in immature shells, and in some adults (e.g. the land snails '' Helicella'' and ''Bulimulus''). However, in some other land snails and in many marine species the outer lip is ''thickened'' (also called ''callused''), or ''reflected'' (turned outwards). In some other marine species it is curled inwards (''inflected''), as in the cowries such as '' Cypraea''. It can also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsum (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after Indian subcontinent, India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' (Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic) before the Pacific Ocean, Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Ming treasure voyages, Chinese explorers in the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foot (mollusc)
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gastropod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Snail
Sea snail is a common name for slow-moving marine gastropod molluscs, usually with visible external shells, such as whelk or abalone. They share the taxonomic class Gastropoda with slugs, which are distinguished from snails primarily by the absence of a visible shell. Definition Determining whether some gastropods should be called sea snails is not always easy. Some species that live in brackish water (such as certain neritids) can be listed as either freshwater snails or marine snails, and some species that live at or just above the high tide level (for example species in the genus '' Truncatella'') are sometimes considered to be sea snails and sometimes listed as land snails. Anatomy Sea snails are a very large group of animals and a very diverse one. Most snails that live in salt water respire using a gill or gills; a few species, though, have a lung, are intertidal, and are active only at low tide when they can move around in the air. These air-breathing species includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)