|
Crispus (other)
Flavius Julius Crispus (; 300 – 326) was the eldest son of the Roman emperor Constantine I, as well as his junior colleague ( ''caesar'') from March 317 until his execution by his father in 326. The grandson of the '' augustus'' Constantius I, Crispus was the elder half-brother of the future ''augustus'' Constantine II and became co-''caesar'' with him and with his cousin Licinius II at Serdica, part of the settlement ending the Cibalensean War between Constantine and his father's rival Licinius I. Crispus ruled from Augusta Treverorum ( Trier) in Roman Gaul between 318 and 323 and defeated the navy of Licinius I at the Battle of the Hellespont in 324, which with the land Battle of Chrysopolis won by Constantine forced the resignation of Licinius and his son, leaving Constantine the sole ''augustus'' and the Constantinian dynasty in control of the entire empire. It is unclear what the legal status of the relationship Crispus's mother Minervina had with Constantine w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar (title)
Caesar ( English Caesars; Latin ''Caesares''; in Greek: ''Kaîsar'') is a title of imperial character. It derives from the ''cognomen'' of Julius Caesar, a Roman dictator. The change from being a familial name to a title adopted by the Roman emperors can be traced to AD 68, following the fall of the Julio–Claudian dynasty. Origins The first known individual to bear the ''cognomen'' of "Caesar" was Sextus Julius Caesar, who is likewise believed to be the common ancestor of all subsequent Julii Caesares. Sextus' great-grandson was the dictator Gaius Julius Caesar. After he seized control of the Roman Republic following his war against the Senate, he adopted the title of ''dictator perpetuo'' ("dictator in perpetuity"), a title he only held for about a month before he was assassinated in 44 BC. Julius Caesar's death did not lead to the restoration of the Republic, and instead led to the rise of the Second Triumvirate, composed by three dictators including Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
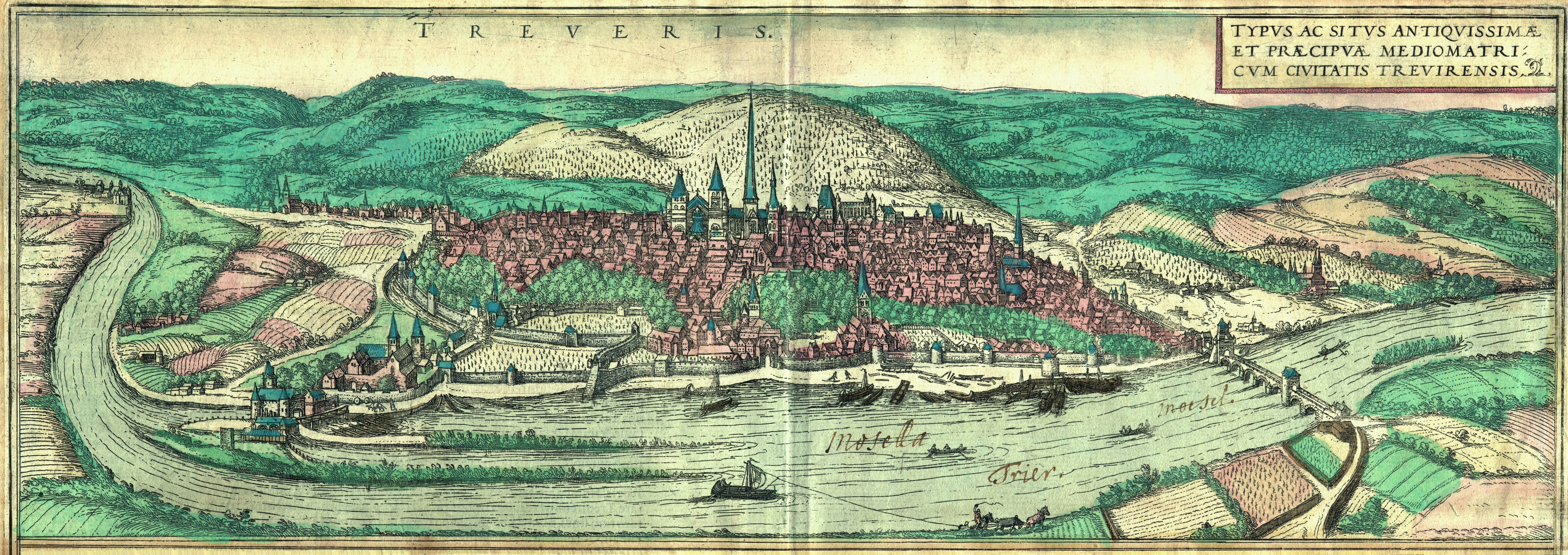
Augusta Treverorum
Trier in Rhineland-Palatinate, whose history dates to the Roman Empire, is often claimed to be the oldest city in Germany. Traditionally it was known in English by its French name of Treves. Prehistory The first traces of human settlement in the area of the city show evidence of linear pottery settlements dating from the early Neolithic period. Since the last pre-Christian centuries, members of the Celtic tribe of the Treveri settled in the area of today's Trier. Roman Empire The Romans under Julius Caesar first subdued the Treveri in 58 to 50 BC. No later than 16 BC, at the foot of the hill later christened the Petrisberg, upon which a military camp had been set up in 30 BC and abandoned again a few months later, the Romans founded the city of ("City of Augustus in the land of the Treveri"), which has a claim to being the oldest city in Germany. The honour of being named after the Emperor was only locally shared by Augsburg and Augst in northern Switzerland. Followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazarius (rhetorician)
Nazarius, (), was a Roman and a Latin rhetorician and panegyrist. He was, according to Ausonius, a professor of rhetoric at Burdigala (Bordeaux). The extant speech of which he is undoubtedly the author (in R.A.B. Mynors, ''XII Panegyrici Latini'', Oxford 1964, No. 4; English translation in C.E.V. Nixon / Barbara Rodgers, ''In Praise of Later Roman Emperors'', Berkeley 1994) was delivered in 321 CE to celebrate the fifteenth anniversary of the accession of Constantine the Great, and the fifth of his son Constantine's admission to the rank of Caesar. The preceding speech (No. 12), celebrating the victory of Constantine over Maxentius, delivered in 313 CE at Augusta Treverorum (Trier), has often been attributed to Nazarius, but the difference in style and vocabulary, and the more distinctly Christian Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Chri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princeps Iuventutis
''Princeps'' (plural: ''principes'') is a Latin word meaning "first in time or order; the first, foremost, chief, the most eminent, distinguished, or noble; the first man, first person". As a title, ''princeps'' originated in the Roman Republic wherein the leading member of the Senate was designated ''princeps senatus''. It is primarily associated with the Roman emperors as an unofficial title first adopted by Augustus () in 23 BC. Its use in this context continued until the regime of Diocletian (r. 284 – 305 AD) at the end of the third century. He preferred the title of ''dominus'', meaning "lord" or "master". As a result, the Roman Empire from Augustus to Diocletian is termed the "principate" (''principatus'') and from Diocletian onwards as the "dominate" (''dominatus''). Other historians define the reign of Augustus to Severus Alexander (r. 222 – 235) as the Principate, and the period afterwards as the "Autocracy". The medieval title "Prince" is a derivative of princeps. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactantius
Lucius Caecilius Firmianus Lactantius (c. 250 – c. 325) was an early Christian author who became an advisor to Roman emperor, Constantine I, guiding his Christian religious policy in its initial stages of emergence, and a tutor to his son Crispus. His most important work is the ''Institutiones Divinae'' ("The Divine Institutes"), an apologetic treatise intended to establish the reasonableness and truth of Christianity to pagan critics. He is best known for his apologetic works, widely read during the Renaissance by humanists, who called Lactantius the "Christian Cicero". Also often attributed to Lactantius is the poem '' The Phoenix'', which is based on the myth of the phoenix from Egypt and Arabia. Though the poem is not clearly Christian in its motifs, modern scholars have found some literary evidence in the text to suggest the author had a Christian interpretation of the eastern myth as a symbol of resurrection. Biography Lactantius was of Punic or Berber origin, born in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Christianity
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish diaspora. The first followers of Christianity were Jews or proselytes, commonly referred to as Jewish Christians and God-fearers. The Apostolic sees claim to have been founded by one or more of the apostles of Jesus, who are said to have dispersed from Jerusalem sometime after the crucifixion of Jesus, c. 26–36, perhaps following the Great Commission. Early Christians gathered in small private homes, known as house churches, but a city's whole Christian community would also be called a church – the Greek noun ἐκκλησία (''ekklesia'') literally means assembly, gathering, or congregation but is translated as church in most English translations of the New Testament. Many early Christians were merchants and others who had prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Latin
Late Latin ( la, Latinitas serior) is the scholarly name for the form of Literary Latin of late antiquity.Roberts (1996), p. 537. English dictionary definitions of Late Latin date this period from the , and continuing into the 7th century in the Iberian Peninsula. This somewhat ambiguously defined version of Latin was used between the eras of Classical Latin and Medieval Latin. Scholars do not agree exactly when Classical Latin should end or Medieval Latin should begin. Being a written language, Late Latin is not the same as Vulgar Latin. The latter served as ancestor of the Romance languages. Although Late Latin reflects an upsurge of the use of Vulgar Latin vocabulary and constructs, it remains largely classical in its overall features, depending on the author who uses it. Some Late Latin writings are more literary and classical, but others are more inclined to the vernacular. Also, Late Latin is not identical to Christian patristic Latin, used in the theological writings of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhetoric
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate particular audiences in specific situations. Aristotle defines rhetoric as "the faculty of observing in any given case the available means of persuasion" and since mastery of the art was necessary for victory in a case at law, for passage of proposals in the assembly, or for fame as a speaker in civic ceremonies, he calls it "a combination of the science of logic and of the ethical branch of politics". Rhetoric typically provides heuristics for understanding, discovering, and developing arguments for particular situations, such as Aristotle's three persuasive audience appeals: logos, pathos, and ethos. The five canons of rhetoric or phases of developing a persuasive speech were first codified in classical Rome: invention, arrangement, style ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tutor
TUTOR, also known as PLATO Author Language, is a programming language developed for use on the PLATO system at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign beginning in roughly 1965. TUTOR was initially designed by Paul Tenczar for use in computer assisted instruction (CAI) and computer managed instruction (CMI) (in computer programs called "lessons") and has many features for that purpose. For example, TUTOR has powerful answer-parsing and answer-judging commands, graphics, and features to simplify handling student records and statistics by instructors. TUTOR's flexibility, in combination with PLATO's computational power (running on what was considered a supercomputer in 1972), also made it suitable for the creation of games — including flight simulators, war games, dungeon style multiplayer role-playing games, card games, word games, and medical lesson games such as ''Bugs and Drugs'' (''BND''). TUTOR lives on today as the programming language for the Cyber1 PLATO Syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illegitimate
Legitimacy, in traditional Western common law, is the status of a child born to parents who are legally married to each other, and of a child conceived before the parents obtain a legal divorce. Conversely, ''illegitimacy'', also known as ''bastardy'', has been the status of a child born outside marriage, such a child being known as a bastard, a love child, a natural child, or illegitimate. In Scots law, the terms natural son and natural daughter bear the same implications. The importance of legitimacy has decreased substantially in Western countries since the sexual revolution of the 1960s and 1970s and the declining influence of conservative Christian churches in family and social life. Births outside marriage now represent a large majority in many countries of Western Europe and the Americas, as well as in many former European colonies. In many Western-influenced cultures, stigma based on parents' marital status, and use of the word ''bastard'', are now widely considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Licinius
Valerius Licinianus Licinius (c. 265 – 325) was Roman emperor from 308 to 324. For most of his reign he was the colleague and rival of Constantine I, with whom he co-authored the Edict of Milan, AD 313, that granted official toleration to Christians in the Roman Empire. He was finally defeated at the Battle of Chrysopolis (AD 324), and was later executed on the orders of Constantine I. Early reign Born to a Dacian peasant family in Moesia Superior, Licinius accompanied his close childhood friend, the future emperor Galerius, on the Persian expedition in 298. He was trusted enough by Galerius that in 307 he was sent as an envoy to Maxentius in Italy to attempt to reach some agreement about the latter's illegitimate political position. Galerius then trusted the eastern provinces to Licinius when he went to deal with Maxentius personally after the death of Severus II. Upon his return to the east Galerius elevated Licinius to the rank of ''Augustus'' in the West on 11 Novem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Chrysopolis
The Battle of Chrysopolis was fought on 18 September 324 at Chrysopolis (modern Üsküdar), near Chalcedon (modern Kadıköy), between the two Roman emperors Constantine I and Licinius. The battle was the final encounter between the two emperors. After his navy's defeat in the Battle of the Hellespont, Licinius withdrew his forces from the city of Byzantium across the Bosphorus to Chalcedon in Bithynia. Constantine followed, and won the subsequent battle. This left Constantine as the sole emperor, ending the period of the Tetrarchy. Background The navy of Licinius had suffered a catastrophic defeat at the Battle of the Hellespont. His admiral, Abantus, had been outfought by Constantine's son, the caesar Crispus, despite the latter's distinctly smaller fleet. Following this naval victory, Constantine crossed over to Asia Minor. An army, under the command of Licinius' newly appointed co-emperor Martinian, was guarding the coast at Lampsacus on the Hellespont. Constantine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


