illegitimate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Legitimacy, in traditional Western
 Legitimacy also continues to be relevant to hereditary titles, with only legitimate children being admitted to the line of succession. Some monarchs, however, have succeeded to the throne despite the controversial status of their legitimacy. For example,
Legitimacy also continues to be relevant to hereditary titles, with only legitimate children being admitted to the line of succession. Some monarchs, however, have succeeded to the throne despite the controversial status of their legitimacy. For example,

 The proportion of children born outside marriage has been rising since the turn of the 21st century in most European Union countries, North America, and Australia. In Europe, besides the low levels of fertility rates and the delay of motherhood, another factor that now characterizes fertility is the growing percentage of births outside marriage. In the EU, this phenomenon has been on the rise in recent years in almost every country; and in eight EU countries, mostly in northern Europe, as well as in Iceland outside of the EU, it already accounts for the majority of births.
In 2009, 41% of children born in the
The proportion of children born outside marriage has been rising since the turn of the 21st century in most European Union countries, North America, and Australia. In Europe, besides the low levels of fertility rates and the delay of motherhood, another factor that now characterizes fertility is the growing percentage of births outside marriage. In the EU, this phenomenon has been on the rise in recent years in almost every country; and in eight EU countries, mostly in northern Europe, as well as in Iceland outside of the EU, it already accounts for the majority of births.
In 2009, 41% of children born in the

 Certainty of paternity has been considered important in a wide range of eras and cultures, especially when inheritance and citizenship were at stake, making the tracking of a man's estate and genealogy a central part of what defined a "legitimate" birth. The ancient
Certainty of paternity has been considered important in a wide range of eras and cultures, especially when inheritance and citizenship were at stake, making the tracking of a man's estate and genealogy a central part of what defined a "legitimate" birth. The ancient
 Nonmarital birth has affected not only the individuals themselves. The stress that such circumstances of birth once regularly visited upon families is illustrated in the case of
Nonmarital birth has affected not only the individuals themselves. The stress that such circumstances of birth once regularly visited upon families is illustrated in the case of  Some persons born outside of marriage have been driven to excel in their endeavors, for good or ill, by a desire to overcome the social stigma and disadvantage that attached to it. Nora Titone, in her book ''My Thoughts Be Bloody'', recounts how the shame and ambition of actor Junius Brutus Booth's two actor sons born outside of marriage, Edwin Booth and John Wilkes Booth, spurred them to strive, as rivals, for achievement and acclaim—John Wilkes, the assassin of
Some persons born outside of marriage have been driven to excel in their endeavors, for good or ill, by a desire to overcome the social stigma and disadvantage that attached to it. Nora Titone, in her book ''My Thoughts Be Bloody'', recounts how the shame and ambition of actor Junius Brutus Booth's two actor sons born outside of marriage, Edwin Booth and John Wilkes Booth, spurred them to strive, as rivals, for achievement and acclaim—John Wilkes, the assassin of
My Thoughts Be Bloody: The Bitter Rivalry Between Edwin and John Wilkes Booth That Led to an American Tragedy
'. New York: Simon and Schuster; 2010 ited September 24, 2011 . Historian John Ferling, in his book ''Jefferson and Hamilton: The Rivalry That Forged a Nation'', makes the same point: that Alexander Hamilton's nonmarital birth spurred him to seek accomplishment and distinction.
The Swedish artist Anders Zorn (1860–1920) was similarly motivated by his nonmarital birth to prove himself and excel in his métier.
Historian John Ferling, in his book ''Jefferson and Hamilton: The Rivalry That Forged a Nation'', makes the same point: that Alexander Hamilton's nonmarital birth spurred him to seek accomplishment and distinction.
The Swedish artist Anders Zorn (1860–1920) was similarly motivated by his nonmarital birth to prove himself and excel in his métier.
 Similarly, T. E. Lawrence's biographer Flora Armitage writes about being born outside of marriage: "The effect on . E.Lawrence of this discovery was profound; it added to the romantic urge for heroic conduct—the dream of the Sangreal—the seed of ambition, the desire for honor and distinction: the redemption of the blood from its taint." Another biographer, John E. Mack, writes in a similar vein: " s mother required of him that he ''redeem'' her fallen state by his own special achievements, by being a person of unusual value who accomplishes great deeds, preferably religious and ideally on an heroic scale. Lawrence did his best to fulfill heroic deeds. But he was plagued, especially after the events of the war activated his inner conflicts, by a deep sense of failure. Having been deceived as a child he was later to feel that he himself was a deceiver—that he had deceived the Arabs..." "Mrs. Lawrence's original hope that her sons would provide her personal redemption by becoming Christian missionaries was fulfilled only by awrence's brotherRobert." Mack elaborates further: "Part of his creativity and originality lies in his 'irregularity,' in his capacity to remain outside conventional ways of thinking, a tendency which... derives, at least in part, from his illegitimacy. Lawrence's capacity for invention and his ability to see unusual or humorous relationships in familiar situations come also... from his illegitimacy. He was not limited to established or 'legitimate' solutions or ways of doing things, and thus his mind was open to a wider range of possibilities and opportunities. t the same timeLawrence's illegitimacy had important social consequences and placed limitations upon him, which rankled him deeply... At times he felt socially isolated when erstwhile friends shunned him upon learning of his background. Lawrence's delight in making fun of regular officers and other segments of 'regular' society... derived... at least in part from his inner view of his own irregular situation. His fickleness about names for himself e changed his name twice to distance himself from his "Lawrence of Arabia" personais directly related... to his view of his parents and to his identification with them is father had changed his name after running off with T. E. Lawrence's future mother"
Similarly, T. E. Lawrence's biographer Flora Armitage writes about being born outside of marriage: "The effect on . E.Lawrence of this discovery was profound; it added to the romantic urge for heroic conduct—the dream of the Sangreal—the seed of ambition, the desire for honor and distinction: the redemption of the blood from its taint." Another biographer, John E. Mack, writes in a similar vein: " s mother required of him that he ''redeem'' her fallen state by his own special achievements, by being a person of unusual value who accomplishes great deeds, preferably religious and ideally on an heroic scale. Lawrence did his best to fulfill heroic deeds. But he was plagued, especially after the events of the war activated his inner conflicts, by a deep sense of failure. Having been deceived as a child he was later to feel that he himself was a deceiver—that he had deceived the Arabs..." "Mrs. Lawrence's original hope that her sons would provide her personal redemption by becoming Christian missionaries was fulfilled only by awrence's brotherRobert." Mack elaborates further: "Part of his creativity and originality lies in his 'irregularity,' in his capacity to remain outside conventional ways of thinking, a tendency which... derives, at least in part, from his illegitimacy. Lawrence's capacity for invention and his ability to see unusual or humorous relationships in familiar situations come also... from his illegitimacy. He was not limited to established or 'legitimate' solutions or ways of doing things, and thus his mind was open to a wider range of possibilities and opportunities. t the same timeLawrence's illegitimacy had important social consequences and placed limitations upon him, which rankled him deeply... At times he felt socially isolated when erstwhile friends shunned him upon learning of his background. Lawrence's delight in making fun of regular officers and other segments of 'regular' society... derived... at least in part from his inner view of his own irregular situation. His fickleness about names for himself e changed his name twice to distance himself from his "Lawrence of Arabia" personais directly related... to his view of his parents and to his identification with them is father had changed his name after running off with T. E. Lawrence's future mother"

Illegitimacy in Britain, 1700–1920
'.
A Prince of Our Disorder: The Life of T. E. Lawrence
">T. E. Lawrence">A Prince of Our Disorder: The Life of T. E. Lawrence
'. Harvard University Press; 1998 ited September 24, 2011 . *Charles Simic, "You Laugh Uncontrollably" (review of Bohumil Hrabal, ''Mr. Kafka and Other Tales from the Time of the Cult'', translated from the Czech by Paul Wilson, New Directions, 142 pp., $14.95 aper, ''
Illegitimacy: an examination of bastardy
'.
My Thoughts Be Bloody: The Bitter Rivalry between Edwin and John Wilkes Booth that Led to an American Tragedy
', New York, Simon and Schuster, 2010 ited September 24, 2011 .
Percentage of Births to Unmarried Mothers by State: 2014
(distribution of births outside marriage across the United States)
* Ari Shapiro, "Christopher Columbus' Son Had an Enormous Library. Its Catalog Was Just Found",
{{Authority control Legitimacy law, Civil law (common law) Family law Extramarital relationships de:Unehelichkeit
common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omniprese ...
, is the status of a child born to parents who are legally married to each other, and of a child conceived before the parents obtain a legal divorce. Conversely, ''illegitimacy'', also known as ''bastardy'', has been the status of a child born outside marriage, such a child being known as a bastard, a love child, a natural child, or illegitimate. In Scots law
Scots law () is the legal system of Scotland. It is a hybrid or mixed legal system containing civil law and common law elements, that traces its roots to a number of different historical sources. Together with English law and Northern Ireland l ...
, the terms natural son and natural daughter bear the same implications.
The importance of legitimacy has decreased substantially in Western countries since the sexual revolution
The sexual revolution, also known as the sexual liberation, was a social movement that challenged traditional codes of behavior related to sexuality and interpersonal relationships throughout the United States and the developed world from the 1 ...
of the 1960s and 1970s and the declining influence of conservative Christian churches in family and social life.
Births outside marriage now represent a large majority in many countries of Western Europe and the Americas, as well as in many former European colonies. In many Western-influenced cultures, stigma based on parents' marital status, and use of the word ''bastard'', are now widely considered offensive.
Law
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
's Statute of Merton (1235) stated, regarding illegitimacy: "He is a bastard that is born before the marriage of his parents." This definition also applied to situations when a child's parents could not marry, as when one or both were already married or when the relationship was incestuous.
The Poor Law of 1576 formed the basis of English bastardy law. Its purpose was to punish a bastard child's mother and putative father, and to relieve the parish from the cost of supporting mother and child. "By an act of 1576 (18 Elizabeth C. 3), it was ordered that bastards should be supported by their putative fathers, though bastardy orders in the quarter sessions date from before this date. If the genitor could be found, then he was put under very great pressure to accept responsibility and to maintain the child."
Under English law, a bastard could not inherit real property
In English common law, real property, real estate, immovable property or, solely in the US and Canada, realty, is land which is the property of some person and all structures (also called improvements or fixtures) integrated with or affixe ...
and could not be legitimized by the subsequent marriage of father to mother. There was one exception: when his father subsequently married his mother, and an older illegitimate son (a "bastard eignè") took possession of his father's lands after his death, he would pass the land on to his own heirs on his death, as if his possession of the land had been retroactively converted into true ownership. A younger non-bastard brother (a "mulier puisnè") would have no claim to the land.
There were many "natural children" of Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
's monarchy granted positions which founded prominent families. In the 14th century, Robert II of Scotland gifted one of his illegitimate sons estates in Bute Bute or BUTE may refer to:
People
* Marquess of Bute, a title in the Peerage of Great Britain; includes lists of baronets, earls and marquesses of Bute
* Lord of Bute, a title in medieval Scotland, including a list of lords
* Lucian Bute (born ...
, founding the Stewarts of Bute, and similarly a natural son of Robert III of Scotland was ancestral to the Shaw Stewarts of Greenock.
In Scots law
Scots law () is the legal system of Scotland. It is a hybrid or mixed legal system containing civil law and common law elements, that traces its roots to a number of different historical sources. Together with English law and Northern Ireland l ...
an illegitimate child, a "natural son" or "natural daughter", would be legitimated by the subsequent marriage of his parents, provided they were free to marry at the date of the conception. The Legitimation (Scotland) Act 1968 extended legitimation by the subsequent marriage of the parents to children conceived when their parents were not free to marry, but this was repealed in 2006 by the amendment of section 1 of the Law Reform (Parent and Child) (Scotland) Act 1986 (as amended in 2006) which abolished the status of illegitimacy stating that "(1) No person whose status is governed by Scots law shall be illegitimate ...".
The '' Legitimacy Act 1926'' of England and Wales legitimized the birth of a child if the parents subsequently married each other, provided that they had not been married to someone else in the meantime. The '' Legitimacy Act 1959'' extended the legitimization even if the parents had married others in the meantime and applied it to putative marriages which the parents incorrectly believed were valid. Neither the 1926 nor 1959 Acts changed the laws of succession to the British throne and succession to peerage and baronetcy titles. In Scotland children legitimated by the subsequent marriage of their parents have always been entitled to succeed to peerages and baronetcies and The Legitimation (Scotland) Act 1968 extended this right to children conceived when their parents were not free to marry. The ''Family Law Reform Act'' 1969 (c. 46) allowed a bastard to inherit on the intestacy of his parents. In canon and in civil law
Civil law may refer to:
* Civil law (common law), the part of law that concerns private citizens and legal persons
* Civil law (legal system), or continental law, a legal system originating in continental Europe and based on Roman law
** Private la ...
, the offspring of putative marriages have also been considered legitimate.
Since December 2003 in England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is ...
, April 2002 in Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. North ...
and May 2006 in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
, an unmarried father has parental responsibility if he is listed on the birth certificate.
In the United States, in the early 1970s a series of Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
decisions held that most common-law disabilities imposed upon illegitimacy were invalid as violations of the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. Still, children born out of wedlock may not be eligible for certain federal benefits (e.g., automatic naturalization
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-citizen of a country may acquire citizenship or nationality of that country. It may be done automatically by a statute, i.e., without any effort on the part of the i ...
when the father becomes a US citizen) unless the child has been legitimized in the appropriate jurisdiction.
Many other countries have legislatively abolished any legal disabilities of a child born out of wedlock.
In France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, legal reforms regarding illegitimacy began in the 1970s, but it was only in the 21st century that the principle of equality was fully upheld (through Act no. 2002-305 of 4 March 2002, removing mention of "illegitimacy" — ''filiation légitime'' and ''filiation naturelle''; and through law no. 2009-61 of 16 January 2009). In 2001, France was forced by the European Court of Human Rights
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR or ECtHR), also known as the Strasbourg Court, is an international court of the Council of Europe which interprets the European Convention on Human Rights. The court hears applications alleging that a ...
to change several laws that were deemed discriminatory, and in 2013 the Court ruled that these changes must also be applied to children born before 2001.
In some countries, the family law itself explicitly states that there must be equality between the children born outside and inside marriage: in Bulgaria, for example, the new 2009 Family Code lists "equality of the born during the matrimony, out of matrimony and of the adopted children" as one of the principles of family law.
The ''European Convention on the Legal Status of Children Born out of Wedlock'' came into force in 1978. Countries which ratify it must ensure that children born outside marriage are provided with legal rights as stipulated in the text of this convention. The convention was ratified by the UK in 1981 and by Ireland in 1988.
In later years, the inheritance rights of many illegitimate children have improved, and changes of laws have allowed them to inherit properties. More recently, the laws of England have been changed to allow illegitimate children to inherit entailed property, over their legitimate brothers and sisters.
Contemporary situation
Despite the decreasing legal relevance of illegitimacy, an important exception may be found in the nationality laws of many countries, which do not apply ''jus sanguinis
( , , ; 'right of blood') is a principle of nationality law by which citizenship is determined or acquired by the nationality or ethnicity of one or both parents. Children at birth may be citizens of a particular state if either or both of t ...
'' (nationality by citizenship of a parent) to children born out of wedlock, particularly in cases where the child's connection to the country lies only through the father. This is true, for example, of the United States, and its constitutionality was upheld in 2001 by the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
in ''Nguyen v. INS
''Nguyen v. INS'', 533 U.S. 53 (2001), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court upheld the validity of laws relating to U.S. citizenship at birth for children born outside the United States, out of wedlock, to an American parent. ...
''. In the UK, the policy was changed so that children born after 1 July 2006 could receive British citizenship from their father if their parents were unmarried at the time of the child's birth; illegitimate children born before this date cannot receive British citizenship through their father.
 Legitimacy also continues to be relevant to hereditary titles, with only legitimate children being admitted to the line of succession. Some monarchs, however, have succeeded to the throne despite the controversial status of their legitimacy. For example,
Legitimacy also continues to be relevant to hereditary titles, with only legitimate children being admitted to the line of succession. Some monarchs, however, have succeeded to the throne despite the controversial status of their legitimacy. For example, Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
Eli ...
succeeded to the throne though she was legally held illegitimate as a result of her parents' marriage having been annulled after her birth. Her older half-sister Mary I
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, and as "Bloody Mary" by her Protestant opponents, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain from January 1556 until her death in 1558. She ...
had acceded to the throne before her in a similar circumstance: her parents' marriage had been annulled in order to allow her father to marry Elizabeth's mother.
Annulment of marriage does not currently change the status of legitimacy of children born to the couple during their putative marriage, ''i.e.'', between their marriage ceremony and the legal annulment of their marriage. For example, canon 1137 of the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
's Code of Canon Law specifically affirms the legitimacy of a child born to a marriage that is declared null following the child's birth.
The Catholic Church is also changing its attitude toward unwed mothers and baptism of the children. In criticizing the priests who refused to baptize out-of-wedlock children, Pope Francis
Pope Francis ( la, Franciscus; it, Francesco; es, link=, Francisco; born Jorge Mario Bergoglio, 17 December 1936) is the head of the Catholic Church. He has been the bishop of Rome and sovereign of the Vatican City State since 13 March 2013. ...
argued that the mothers had done the right thing by giving life to the child and should not be shunned by the church:
Nonmarital births

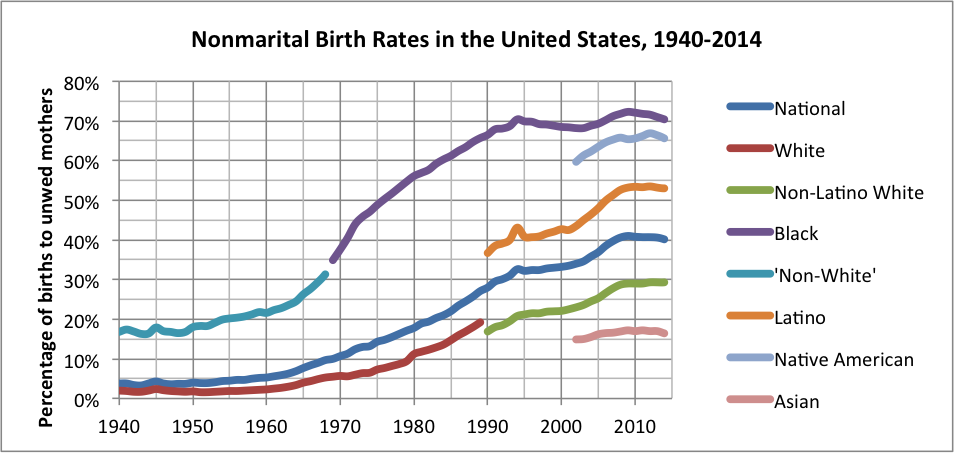
 The proportion of children born outside marriage has been rising since the turn of the 21st century in most European Union countries, North America, and Australia. In Europe, besides the low levels of fertility rates and the delay of motherhood, another factor that now characterizes fertility is the growing percentage of births outside marriage. In the EU, this phenomenon has been on the rise in recent years in almost every country; and in eight EU countries, mostly in northern Europe, as well as in Iceland outside of the EU, it already accounts for the majority of births.
In 2009, 41% of children born in the
The proportion of children born outside marriage has been rising since the turn of the 21st century in most European Union countries, North America, and Australia. In Europe, besides the low levels of fertility rates and the delay of motherhood, another factor that now characterizes fertility is the growing percentage of births outside marriage. In the EU, this phenomenon has been on the rise in recent years in almost every country; and in eight EU countries, mostly in northern Europe, as well as in Iceland outside of the EU, it already accounts for the majority of births.
In 2009, 41% of children born in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
were born to unmarried mothers, a significant increase from the 5% of half a century earlier. That includes 73% of non-Hispanic black children, 53% of Hispanic children (of all races), and 29% of non-Hispanic white children. In 2020, the proportion was almost similar, with 40.5% of children born in the US being born to unmarried mothers.
In April 2009, the National Center for Health Statistics announced that nearly 40 percent of American infants born in 2007 were born to an unwed mother; that of 4.3 million children, 1.7 million were born to unmarried parents, a 25 percent increase from 2002. Most births to teenagers in the USA (86% in 2007) are nonmarital; in 2007, 60% of births to women 20–24, and nearly one-third of births to women 25–29, were nonmarital. In 2007, teenagers accounted for just 23% of nonmarital births, down steeply from 50% in 1970.
In 2014, 42% of all births in the 28 EU countries were nonmarital. The percentage was also 42% in 2018. In 2018, births outside of marriage represented the majority of births in eight EU member states: France (60%), Bulgaria (59%), Slovenia (58%), Portugal (56%), Sweden (55%), Denmark and Estonia (both 54%), and the Netherlands (52%). The lowest percentage were in Greece, Cyprus, Croatia, Poland and Lithuania, with a percentage of under 30%.
To a certain degree, religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural ...
(the religiosity of the population - see Religion in Europe) correlates with the proportion of nonmarital births (e.g., Greece, Cyprus, Croatia have a low percentage of births outside marriage), but this is not always the case: Portugal (56% in 2018) is among the most religious countries in Europe.
The proportion of nonmarital births is also approaching half in the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. Th ...
(48.5%. in 2021), the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
(48.2% as of 2017) and Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
(46.7% as of 2016).
The prevalence of births to unmarried women varies not only between different countries, but also between different geographical areas of the same country: for example, in Germany, there are very strong differences between the regions of former West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
and East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
with a non-religious majority. Significantly more children are born out of wedlock in eastern Germany than in western Germany. In 2012, in eastern Germany 61.6% of births were to unmarried women, while in western Germany only 28.4% were. In the UK, in 2014, 59.4% of births were nonmarital in North East of England, 58.9% in Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
, 54.2% in North West England
North West England is one of nine official regions of England and consists of the ceremonial counties of England, administrative counties of Cheshire, Cumbria, Greater Manchester, Lancashire and Merseyside. The North West had a population of ...
, 52.4% in Yorkshire and the Humber, 52% in East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the ITL 1 statistical regions of England, first level of International Territorial Level, ITL for Statistics, statistical purposes. It comprises the eastern half of the area tradi ...
, 50.8% in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
, 50.4% in West Midlands, 48.5% in South West England, 45.5% in East of England
The East of England is one of the nine official regions of England. This region was created in 1994 and was adopted for statistics purposes from 1999. It includes the ceremonial counties of Bedfordshire, Cambridgeshire, Essex, Hertfordshire ...
, 43.2% in Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. North ...
, 42.9% in South East England
South East England is one of the nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It consists of the counties of Buckinghamshire, East Sussex, Hampshire, the Isle of Wight, Kent, Oxfordshire, Berkshi ...
, and 35.7% in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
.
In France, in 2012, 66.9% of births were nonmarital in Poitou-Charentes, while only 46.6% were in Ile-de-France (which contains Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
). One of the reasons for the lower prevalence of nonmarital births in the metropolis is the high number of immigrants from conservative world regions. In Canada, in Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
, the majority of births since 1995 onwards have been outside marriage. As of 2015, 63% of births were outside marriage in Quebec.
Traditionally conservative Catholic countries in the EU now also have substantial proportions of nonmarital births, as of 2016 (except where otherwise stated): Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal:
:* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian ...
(52.8% ), Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
(45.9%), Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
(41.7%), Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small land ...
(40.7%) Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
(40.2%), Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
(36.5%), Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
(31.8%)
The percentage of first-born children born out of wedlock is considerably higher (by roughly 10%, for the EU), as marriage often takes place after the first baby has arrived. For example, for the Czech Republic, whereas the total nonmarital births are less than half, 47.7%, (third quarter of 2015) the percentage of first-born outside marriage is more than half, 58.2%.
In Australia, in 1971, only 7% of births were outside of marriage, compared to 36% in 2020. The proportion of births outside of marriage was the highest in the Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory shares its borders with Western Au ...
(59%) and the lowest in the ACT (28%).
Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived ...
has the highest rates of non-marital childbearing in the world (55–74% of all children in this region are born to unmarried parents). In most countries in this traditionally Catholic region, children born outside marriage are now the norm. Recent figures from Latin America show non-marital births to be 74% in Colombia, 70% in Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to th ...
, 69% in Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal
, national_motto = "Fi ...
, 63% in the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
, 58% in Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, t ...
, 55% in Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
. In Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, non-marital births increased to 65.8% in 2009, up from 56.2% in 2000. In Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
, non-marital births increased to 70.7% in 2013, up from 48.3% in 2000.
Even in the early 1990s, the phenomenon was very common in Latin America. For example, in 1993, out-of-wedlock births in Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
were 41.5%, in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
43.6%, in Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
45.8%, in Costa Rica 48.2%, in Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, t ...
52.7%, in Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wa ...
58.1%, in El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by ...
73%, in Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
66% and in Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
80%.
Out-of-wedlock births are less common in Asia: in 1993 the rate in Japan was 1.4%; in Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, 3.1%; in China, 5.6%; in Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
, 6.4%; in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
, 21%; in Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
, 24%. However, in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, the out-of-wedlock birth rate was 37% in 2008–9, which skyrocketed to 52.1% by 2015.
Covert illegitimacy
Covert illegitimacy is a situation which arises when someone who is presumed to be a child's father (or mother) is in fact not the biological father (or mother). Frequencies as high as 30% are sometimes assumed in the media, but research by sociologist Michael Gilding traced these overestimates back to an informal remark at a 1972 conference.Philipp EE (1973) "Discussion: moral, social and ethical issues". In: Wolstenholme GEW, Fitzsimons DW, eds. ''Law and ethics of AID and embryo transfer''. Ciba Foundation symposium. Vol 17. London: Associated Scientific 63–66 The detection of unsuspected illegitimacy can occur in the context of medical genetic screening, in genetic family name research, and in immigration testing. Such studies show that covert illegitimacy is in fact less than 10% among the sampled African populations, less than 5% among the sampled Native American and Polynesian populations, less than 2% of the sampled Middle Eastern population, and generally 1%-2% among European samples.Causes for rise in nonmarital births
The rise in illegitimacy noted in Britain throughout the eighteenth century has been associated with the rise of new employment opportunities for women, making them less dependent upon a husband's earnings. However, the Marriage Act 1753 sought to curb this practice, by combining the spousals and nuptials; and by the start of the 19th century, social convention prescribed that brides be virgins at marriage, and illegitimacy became more socially discouraged, especially during theVictorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edward ...
. Later in the 20th century, the social changes of the 1960s and 1970s started to reverse this trend, with an increase in cohabitation and alternative family formation. Elsewhere in Europe and Latin America, the increase in nonmarital births from the late 20th century on has been linked to secularization, enhanced women's rights and standing in society, and the fall of authoritarian dictatorships.
Before the dissolution of Marxist-Leninist regimes in Europe, women's participation in the workforce was actively encouraged by most governments, but socially conservative regimes such as that of Nicolae Ceausescu practiced restrictive and natalist policies regarding family reproduction, such as total bans on contraception and abortion, and birth rates were tightly controlled by the state. After the dissolution of those regimes, the population was given more choices on how to organize their personal lives, and in regions such as former East Germany, the rate of births outside marriage increased dramatically: as of 2012, 61.6% of births there were outside marriage. Far-right regimes such as those of Francoist Spain
Francoist Spain ( es, España franquista), or the Francoist dictatorship (), was the period of Spanish history between 1939 and 1975, when Francisco Franco ruled Spain after the Spanish Civil War with the title . After his death in 1975, Sp ...
and Portugal's '' Estado Novo'' also fell, leading to the democratization and liberalization of society. In Spain and Portugal, important legal changes throughout the 1970s and 1980s included legalization of divorce, decriminalization of adultery
Adultery (from Latin ''adulterium'') is extramarital sex that is considered objectionable on social, religious, moral, or legal grounds. Although the sexual activities that constitute adultery vary, as well as the social, religious, and leg ...
, introduction of gender equality
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making; and the state of valuing d ...
in family law
Family law (also called matrimonial law or the law of domestic relations) is an area of the law that deals with family matters and domestic relations.
Overview
Subjects that commonly fall under a nation's body of family law include:
* Marri ...
, and removal of the ban on contraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth contr ...
.
In many countries there has been a dissociation between marriage and fertility, with the two no longer being closely associated—with births to unmarried couples, as well as childless
''Childless'' is a 2008 American drama film written and directed by Charlie Levi and starring Barbara Hershey, Joe Mantegna, James Naughton and Diane Venora.
The sudden passing of a teenage girl unsettles the four adults in her life. Jarred by ...
married couples, becoming more common and more socially acceptable. Contributions to these societal changes have been made by the weakening of social and legal norms that regulate peoples' personal lives and relations, especially in regard to marriage, secularization and decreased church control of reproduction, increased participation of women in the labor force, changes in the meaning of marriage, risk reduction, individualism, changing views on female sexuality, and availability of contraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth contr ...
. New concepts have emerged, such as that of reproductive rights
Reproductive rights are legal rights and freedoms relating to human reproduction, reproduction and reproductive health that vary amongst countries around the world. The World Health Organization defines reproductive rights as follows:
Reproduct ...
, though these concepts have not been accepted by all cultures. Under the notions of reproductive and sexual rights, individuals—not the state, church, community, etc.—shall decide whether and when individuals shall have children, their number and spacing, the circumstances under which individuals will or will not be sexually active, and their choice of intimate partners and type of relationship.
It is argued that in some places where the control of the church (especially the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
) was traditionally very strong, the social changes of the 1960s and 1970s have led to a negative reaction of the population against the lifestyles promoted by the church. One of the explanations of the current high rates of unmarried cohabitation in Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
is that the traditionally strong social control of the church and the Catholic doctrine over people's private relations and sexual morality has led the population to rebel against traditional and conservative social values; since 1995 the majority of births in this province are outside marriage, and as of 2015, in Quebec, 63% of children were born to unmarried women. The past few decades have seen decreased marriage rates in most Western countries, and this decrease has been accompanied by increased emergence of non-traditional family forms. Average marriage rates across OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
countries have fallen from 8.1 marriages per 1,000 people in 1970 to 5.0 in 2009.
Research on the situation in Bulgaria has concluded that
History

 Certainty of paternity has been considered important in a wide range of eras and cultures, especially when inheritance and citizenship were at stake, making the tracking of a man's estate and genealogy a central part of what defined a "legitimate" birth. The ancient
Certainty of paternity has been considered important in a wide range of eras and cultures, especially when inheritance and citizenship were at stake, making the tracking of a man's estate and genealogy a central part of what defined a "legitimate" birth. The ancient Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
dictum, "'' Mater semper certa est''" ("The dentity of themother is always certain", while the father is not), emphasized the dilemma.
In English common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omniprese ...
, Justice Edward Coke
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”.
History
The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-S ...
in 1626 promulgated the "Four Seas Rule" (''extra quatuor maria'') asserting that, absent impossibility of the father being fertile, there was a presumption of paternity that a married woman's child was her husband's child. That presumption could be questioned, though courts generally sided with the presumption, thus expanding the range of the presumption to a "Seven Seas Rule". But it was only with the Marriage Act 1753 that a formal and public marriage ceremony at civil law was required, whereas previously marriage had a safe haven
Safe haven may refer to:
* Sanctuary
Arts and entertainment
* ''Safe Haven'' (novel), a 2010 American novel by Nicholas Sparks
** ''Safe Haven'' (film), a 2013 American film adapted from the novel
* ''Safe Haven'' (short film), a 2009 American ...
if celebrated in an Anglican church. Still, many "clandestine" marriages occurred.
In many societies, people born out of wedlock did not have the same rights of inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Offici ...
as those within it, and in some societies, even the same civil right
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and political life o ...
s. In the United Kingdom and the United States, as late as the 1960s and in certain social strata even up to today, nonmarital birth has carried a social stigma.Flora Armitage, ''The Desert and the Stars: A Biography of Lawrence of Arabia'', p. 42. In previous centuries unwed mothers were forced by social pressure to give their children up for adoption. In other cases nonmarital children have been reared by grandparents or married relatives as the "sisters", "brothers" or "cousins" of the unwed mothers.
In most national jurisdiction
Jurisdiction (from Latin 'law' + 'declaration') is the legal term for the legal authority granted to a legal entity to enact justice. In federations like the United States, areas of jurisdiction apply to local, state, and federal levels.
Ju ...
s, the status of a child as a legitimate or illegitimate heir could be changed—in either direction—under the civil law
Civil law may refer to:
* Civil law (common law), the part of law that concerns private citizens and legal persons
* Civil law (legal system), or continental law, a legal system originating in continental Europe and based on Roman law
** Private la ...
: A legislative act could deprive a child of legitimacy; conversely, a marriage between the previously unmarried parents, usually within a specified time, such as a year, could retroactively legitimate a child's birth.
Fathers of illegitimate children often did not incur comparable censure
A censure is an expression of strong disapproval or harsh criticism. In parliamentary procedure, it is a Debate (parliamentary procedure), debatable main motion that could be adopted by a majority vote. Among the forms that it can take are a ster ...
or legal responsibility, due to social attitudes about sex, the nature of sexual reproduction, and the difficulty of determining paternity with certainty.
By the final third of the 20th century, in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, all the states had adopted uniform laws that codified the responsibility of both parents to provide support and care for a child, regardless of the parents' marital status, and gave nonmarital as well as adopted persons equal rights to inherit their parents' property. In the early 1970s, a series of Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
decisions abolished most, if not all, of the common-law disabilities of nonmarital birth, as being violations of the equal-protection clause of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. Generally speaking, in the United States, "illegitimate" has been supplanted by the phrase "born out of wedlock."
In contrast, other jurisdictions (particularly western continental European countries) tend to favour social parentage over the biological parentage. Here a man (not necessarily the biological father) may voluntarily recognise the child to be identified as the father, thus giving legitimacy to the child; the biological father does not have any special rights in this area. In France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
a mother may refuse to recognise her own child (see anonymous birth).
A contribution to the decline of the concept of illegitimacy had been made by increased ease of obtaining divorce. Before this, the mother and father of many children had been unable to marry each other because one or the other was already legally bound, by civil or canon law
Canon law (from grc, κανών, , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its members. It is th ...
, in a non-viable earlier marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between t ...
that did not permit divorce. Their only recourse, often, had been to wait for the death of the earlier spouse(s). Thus Polish political and military leader Józef Piłsudski
Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Naczelnik państwa, Chief of State (1918–1922) and Marshal of Poland, First Marshal of Second Polish Republic, Poland (from 1920). He was ...
(1867–1935) was unable to marry his second wife, Aleksandra, until his first wife, Maria, died in 1921; by this time, Piłsudski and Aleksandra had two out-of-wedlock daughters.
Social implications
 Nonmarital birth has affected not only the individuals themselves. The stress that such circumstances of birth once regularly visited upon families is illustrated in the case of
Nonmarital birth has affected not only the individuals themselves. The stress that such circumstances of birth once regularly visited upon families is illustrated in the case of Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theor ...
and his wife-to-be, Mileva Marić, who—when she became pregnant with the first of their three children, Lieserl—felt compelled to maintain separate domiciles in different cities.
 Some persons born outside of marriage have been driven to excel in their endeavors, for good or ill, by a desire to overcome the social stigma and disadvantage that attached to it. Nora Titone, in her book ''My Thoughts Be Bloody'', recounts how the shame and ambition of actor Junius Brutus Booth's two actor sons born outside of marriage, Edwin Booth and John Wilkes Booth, spurred them to strive, as rivals, for achievement and acclaim—John Wilkes, the assassin of
Some persons born outside of marriage have been driven to excel in their endeavors, for good or ill, by a desire to overcome the social stigma and disadvantage that attached to it. Nora Titone, in her book ''My Thoughts Be Bloody'', recounts how the shame and ambition of actor Junius Brutus Booth's two actor sons born outside of marriage, Edwin Booth and John Wilkes Booth, spurred them to strive, as rivals, for achievement and acclaim—John Wilkes, the assassin of Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
, and Edwin, a Unionist who a year earlier had saved the life of Lincoln's son, Robert Todd Lincoln, in a railroad accident.Nora Titone. My Thoughts Be Bloody: The Bitter Rivalry Between Edwin and John Wilkes Booth That Led to an American Tragedy
'. New York: Simon and Schuster; 2010 ited September 24, 2011 .
 Historian John Ferling, in his book ''Jefferson and Hamilton: The Rivalry That Forged a Nation'', makes the same point: that Alexander Hamilton's nonmarital birth spurred him to seek accomplishment and distinction.
The Swedish artist Anders Zorn (1860–1920) was similarly motivated by his nonmarital birth to prove himself and excel in his métier.
Historian John Ferling, in his book ''Jefferson and Hamilton: The Rivalry That Forged a Nation'', makes the same point: that Alexander Hamilton's nonmarital birth spurred him to seek accomplishment and distinction.
The Swedish artist Anders Zorn (1860–1920) was similarly motivated by his nonmarital birth to prove himself and excel in his métier.
 Similarly, T. E. Lawrence's biographer Flora Armitage writes about being born outside of marriage: "The effect on . E.Lawrence of this discovery was profound; it added to the romantic urge for heroic conduct—the dream of the Sangreal—the seed of ambition, the desire for honor and distinction: the redemption of the blood from its taint." Another biographer, John E. Mack, writes in a similar vein: " s mother required of him that he ''redeem'' her fallen state by his own special achievements, by being a person of unusual value who accomplishes great deeds, preferably religious and ideally on an heroic scale. Lawrence did his best to fulfill heroic deeds. But he was plagued, especially after the events of the war activated his inner conflicts, by a deep sense of failure. Having been deceived as a child he was later to feel that he himself was a deceiver—that he had deceived the Arabs..." "Mrs. Lawrence's original hope that her sons would provide her personal redemption by becoming Christian missionaries was fulfilled only by awrence's brotherRobert." Mack elaborates further: "Part of his creativity and originality lies in his 'irregularity,' in his capacity to remain outside conventional ways of thinking, a tendency which... derives, at least in part, from his illegitimacy. Lawrence's capacity for invention and his ability to see unusual or humorous relationships in familiar situations come also... from his illegitimacy. He was not limited to established or 'legitimate' solutions or ways of doing things, and thus his mind was open to a wider range of possibilities and opportunities. t the same timeLawrence's illegitimacy had important social consequences and placed limitations upon him, which rankled him deeply... At times he felt socially isolated when erstwhile friends shunned him upon learning of his background. Lawrence's delight in making fun of regular officers and other segments of 'regular' society... derived... at least in part from his inner view of his own irregular situation. His fickleness about names for himself e changed his name twice to distance himself from his "Lawrence of Arabia" personais directly related... to his view of his parents and to his identification with them is father had changed his name after running off with T. E. Lawrence's future mother"
Similarly, T. E. Lawrence's biographer Flora Armitage writes about being born outside of marriage: "The effect on . E.Lawrence of this discovery was profound; it added to the romantic urge for heroic conduct—the dream of the Sangreal—the seed of ambition, the desire for honor and distinction: the redemption of the blood from its taint." Another biographer, John E. Mack, writes in a similar vein: " s mother required of him that he ''redeem'' her fallen state by his own special achievements, by being a person of unusual value who accomplishes great deeds, preferably religious and ideally on an heroic scale. Lawrence did his best to fulfill heroic deeds. But he was plagued, especially after the events of the war activated his inner conflicts, by a deep sense of failure. Having been deceived as a child he was later to feel that he himself was a deceiver—that he had deceived the Arabs..." "Mrs. Lawrence's original hope that her sons would provide her personal redemption by becoming Christian missionaries was fulfilled only by awrence's brotherRobert." Mack elaborates further: "Part of his creativity and originality lies in his 'irregularity,' in his capacity to remain outside conventional ways of thinking, a tendency which... derives, at least in part, from his illegitimacy. Lawrence's capacity for invention and his ability to see unusual or humorous relationships in familiar situations come also... from his illegitimacy. He was not limited to established or 'legitimate' solutions or ways of doing things, and thus his mind was open to a wider range of possibilities and opportunities. t the same timeLawrence's illegitimacy had important social consequences and placed limitations upon him, which rankled him deeply... At times he felt socially isolated when erstwhile friends shunned him upon learning of his background. Lawrence's delight in making fun of regular officers and other segments of 'regular' society... derived... at least in part from his inner view of his own irregular situation. His fickleness about names for himself e changed his name twice to distance himself from his "Lawrence of Arabia" personais directly related... to his view of his parents and to his identification with them is father had changed his name after running off with T. E. Lawrence's future mother"

Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
' first son, Diego Columbus (born between 1474 and 1480; died 1526), by Columbus' wife, Filipa Moniz Perestrelo, followed in his father's footsteps to become the 2nd Admiral of the Indies, 2nd Viceroy of the Indies, and 4th Governor of the Indies.
Columbus' second son, Fernando Columbus (also known as Hernando; 1488–1539), was his out-of-wedlock son by Beatriz Enríquez de Arana and—while he grew up with a fair amount of power and privilege—due to the circumstances of his birth he never quite gained the prominence his father did. Hernando Columbus' biographer Edward Wilson-Lee says Hernando "always wanted to prove himself his father's son in spirit. he undertook th extraordinary project fbuilding a universal library
A library is a collection of materials, books or media that are accessible for use and not just for display purposes. A library provides physical (hard copies) or digital access (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location or a vi ...
that would oldevery book in the world... very much saw this as a counterpart to his father's desire to circumnavigate the world.... Hernando was going to build a universal library that would circumnavigate the world of knowledge." However, realizing that such a large collection of books would not be very useful without a way of organizing and distilling them, he employed an army of readers to read every book and distill it down to a short summary, or " epitome". The result was the ''Libro de los Epitomes'' (Book of Epitomes). Soon after Hernando's death in 1539 at age 50, this volume went missing for nearly 500 years—until in 2019 it was serendipitously discovered in a University of Copenhagen special collection. Many of the early printed publications that the ''Book of Epitomes'' summarizes are now lost; but thanks to the out-of-wedlock bibliophile
Bibliophilia or bibliophilism is the love of books. A bibliophile or bookworm is an individual who loves and frequently reads and/or collects books.
Profile
The classic bibliophile is one who loves to read, admire and collect books, often ama ...
Hernando Columbus, eager to emulate in his own way his father and "legitimate" half-brother, invaluable insights are becoming available into the knowledge and thought of the early Modern Period.
Violence and honor killings
While births outside marriage are considered acceptable in many world regions, in some parts of the world they remain highly stigmatized. Women who have given birth under such circumstances are often subjected to violence at the hands of their families; and may even become victims of so-called honor killings. These women may also be prosecuted under laws forbidding sexual relations outside marriage and may face consequent punishments, including stoning.In fiction
Illegitimacy has for centuries provided a motif and plot element to works of fiction by prominent authors, includingWilliam Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's natio ...
, Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a m ...
, Henry Fielding, Voltaire, Jane Austen, Alexandre Dumas, ''père'', Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Wilkie Collins, Anthony Trollope
Anthony Trollope (; 24 April 1815 – 6 December 1882) was an English novelist and civil servant of the Victorian era. Among his best-known works is a series of novels collectively known as the '' Chronicles of Barsetshire'', which revolves ...
, Alexandre Dumas, ''fils'', George Eliot, Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
, Leo Tolstoy
Count Lev Nikolayevich TolstoyTolstoy pronounced his first name as , which corresponds to the romanization ''Lyov''. () (; russian: link=no, Лев Николаевич Толстой,In Tolstoy's day, his name was written as in pre-refor ...
, Ivan Turgenev
Ivan Sergeyevich Turgenev (; rus, links=no, Ива́н Серге́евич Турге́невIn Turgenev's day, his name was written ., p=ɪˈvan sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ tʊrˈɡʲenʲɪf; 9 November 1818 – 3 September 1883 ( Old Style da ...
, Fyodor Dostoyevsky, Thomas Hardy
Thomas Hardy (2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, including the poetry of William Wo ...
, Alphonse Daudet, Bolesław Prus, Henry James, Joseph Conrad
Joseph Conrad (born Józef Teodor Konrad Korzeniowski, ; 3 December 1857 – 3 August 1924) was a Polish-British novelist and short story writer. He is regarded as one of the greatest writers in the English language; though he did not sp ...
, E. M. Forster, C. S. Forester, Marcel Pagnol, Grace Metalious
Grace Metalious (September 8, 1924 – February 25, 1964) was an American author known for her novel '' Peyton Place'', one of the best-selling works in publishing history.
Early life
Marie Grace DeRepentigny was born into poverty and a broken ...
, John Irving, and George R. R. Martin.
Notables
Some pre-20th-century individuals whose unconventional "illegitimate" origins did not prevent them from making (and in some cases helped inspire them to make) notable contributions to humanity's art or learning have includedLeone Battista Alberti
Leon Battista Alberti (; 14 February 1404 – 25 April 1472) was an Italian Renaissance humanist author, artist, architect, poet, priest, linguist, philosopher, and cryptographer; he epitomised the nature of those identified now as polymaths. ...
(1404–1472), Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially re ...
(1452–1519), Erasmus of Rotterdam (1466–1536), Jean le Rond d'Alembert
Jean-Baptiste le Rond d'Alembert (; ; 16 November 1717 – 29 October 1783) was a French mathematician, mechanician, physicist, philosopher, and music theorist. Until 1759 he was, together with Denis Diderot, a co-editor of the '' Encyclop� ...
(1717–1783), James Smithson (1764–1829), John James Audubon (1785–1851), Alexander Herzen
Alexander Ivanovich Herzen (russian: Алекса́ндр Ива́нович Ге́рцен, translit=Alexándr Ivánovich Gértsen; ) was a Russian writer and thinker known as the "father of Russian socialism" and one of the main fathers of agra ...
(1812—1870), Jenny Lind (1820–1887), and Alexandre Dumas, ''fils''"Dumas, Alexandre", '' The Encyclopedia Americana'', vol. 9, Danbury, CT, Grolier Incorporated, 1986, , pp. 466-467. (1824–1895).
See also
* Affiliation (family law) * Anne Orthwood's bastard trial * Bastard (Jewish law) * Bastard (law of England and Wales) * Childwite * Colonial American bastardy laws * Defect of birth * Filiation * Hague Adoption Convention * Illegitimacy in fiction * Legitimacy law in England and Wales * Legitime * Marks of distinction * Nonmarital birth rates by country * Non-paternity event * Orphan * Unintended pregnancyReferences
Bibliography
*Flora Armitage, ''The Desert and the Stars: a Biography of Lawrence of Arabia'', illustrated with photographs, New York,Henry Holt and Company
Henry Holt and Company is an American book-publishing company based in New York City. One of the oldest publishers in the United States, it was founded in 1866 by Henry Holt and Frederick Leypoldt. Currently, the company publishes in the fields ...
, 1955.
*Andrzej Garlicki
Andrzej is the Polish form of the given name Andrew.
Notable individuals with the given name Andrzej
* Andrzej Bartkowiak (born 1950), Polish film director and cinematographer
* Andrzej Bobola, S.J. (1591–1657), Polish saint, missionary and ma ...
, "Piłsudski, Józef Klemens," '' Polski słownik biograficzny'', vol. XXVI, Wrocław
Wrocław (; , . german: Breslau, , also known by other names) is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, roughly ...
, Polska Akademia Nauk, 1981, pp. 311–24.
*Shirley Foster Hartley, ''Illegitimacy'', University of California Press, 1975.
*Alysa Levene, Thomas Nutt & Samantha Williams, eds. Illegitimacy in Britain, 1700–1920
'.
Palgrave Macmillan
Palgrave Macmillan is a British academic and trade publishing company headquartered in the London Borough of Camden. Its programme includes textbooks, journals, monographs, professional and reference works in print and online. It maintains off ...
; 2005 ited 24 September 2011 .
* John E. Mack. A Prince of Our Disorder: The Life of T. E. Lawrence
">T. E. Lawrence">A Prince of Our Disorder: The Life of T. E. Lawrence
'. Harvard University Press; 1998 ited September 24, 2011 . *Charles Simic, "You Laugh Uncontrollably" (review of Bohumil Hrabal, ''Mr. Kafka and Other Tales from the Time of the Cult'', translated from the Czech by Paul Wilson, New Directions, 142 pp., $14.95 aper, ''
The New York Review of Books
''The New York Review of Books'' (or ''NYREV'' or ''NYRB'') is a semi-monthly magazine with articles on literature, culture, economics, science and current affairs. Published in New York City, it is inspired by the idea that the discussion of i ...
'', vol. LXIII, no. 8 (May 12, 2016), pp. 58–60.
* Jenny Teichman. Illegitimacy: an examination of bastardy
'.
Cornell University Press
The Cornell University Press is the university press of Cornell University; currently housed in Sage House, the former residence of Henry William Sage. It was first established in 1869, making it the first university publishing enterprise in ...
; 1982 ited September 24, 2011 .
*Nora Titone, My Thoughts Be Bloody: The Bitter Rivalry between Edwin and John Wilkes Booth that Led to an American Tragedy
', New York, Simon and Schuster, 2010 ited September 24, 2011 .
External links
Percentage of Births to Unmarried Mothers by State: 2014
(distribution of births outside marriage across the United States)
* Ari Shapiro, "Christopher Columbus' Son Had an Enormous Library. Its Catalog Was Just Found",
All Things Considered
''All Things Considered'' (''ATC'') is the flagship news program on the American network National Public Radio (NPR). It was the first news program on NPR, premiering on May 3, 1971. It is broadcast live on NPR affiliated stations in the United ...
, NPR newscast, 24 April 201{{Authority control Legitimacy law, Civil law (common law) Family law Extramarital relationships de:Unehelichkeit