|
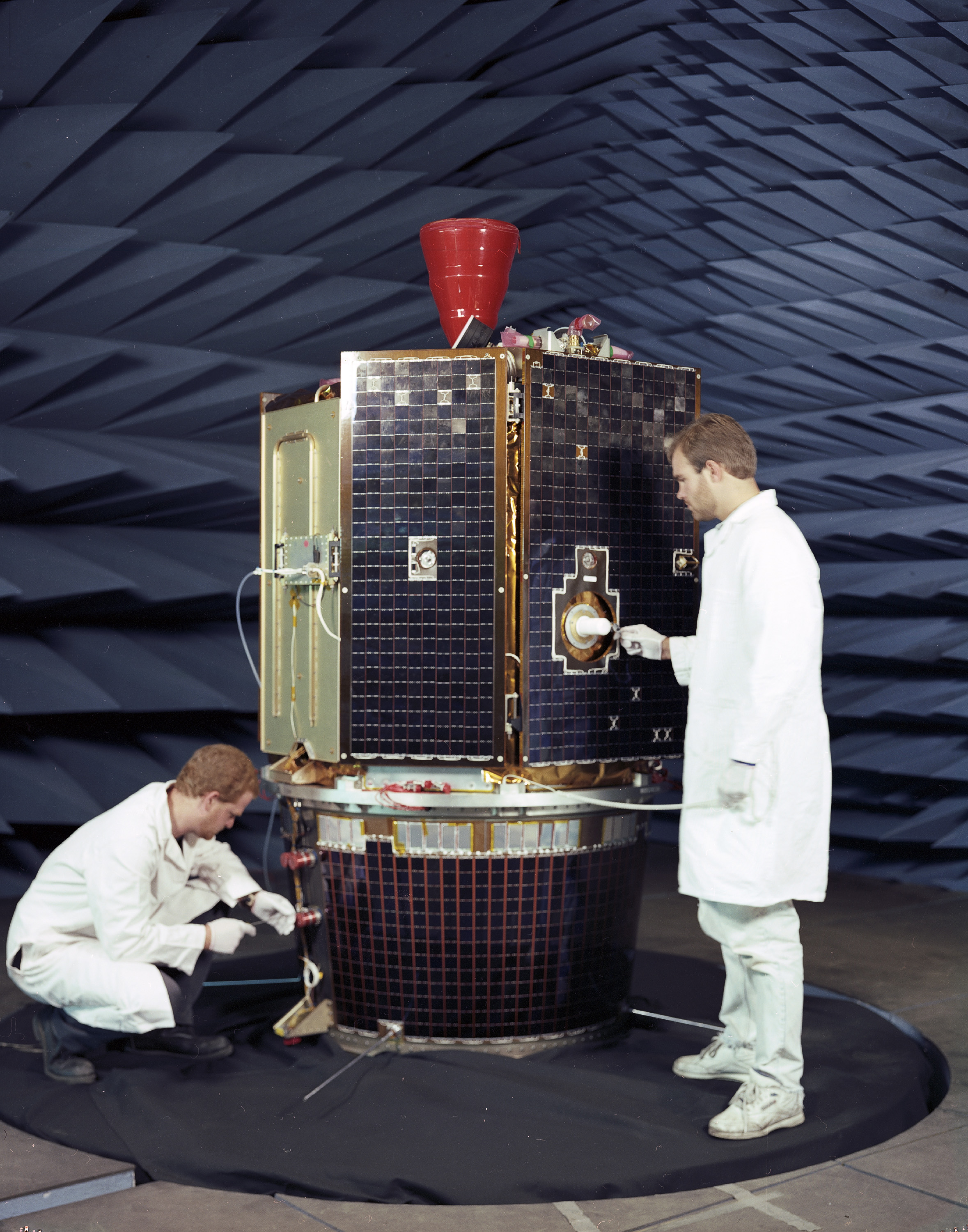
Cray J90
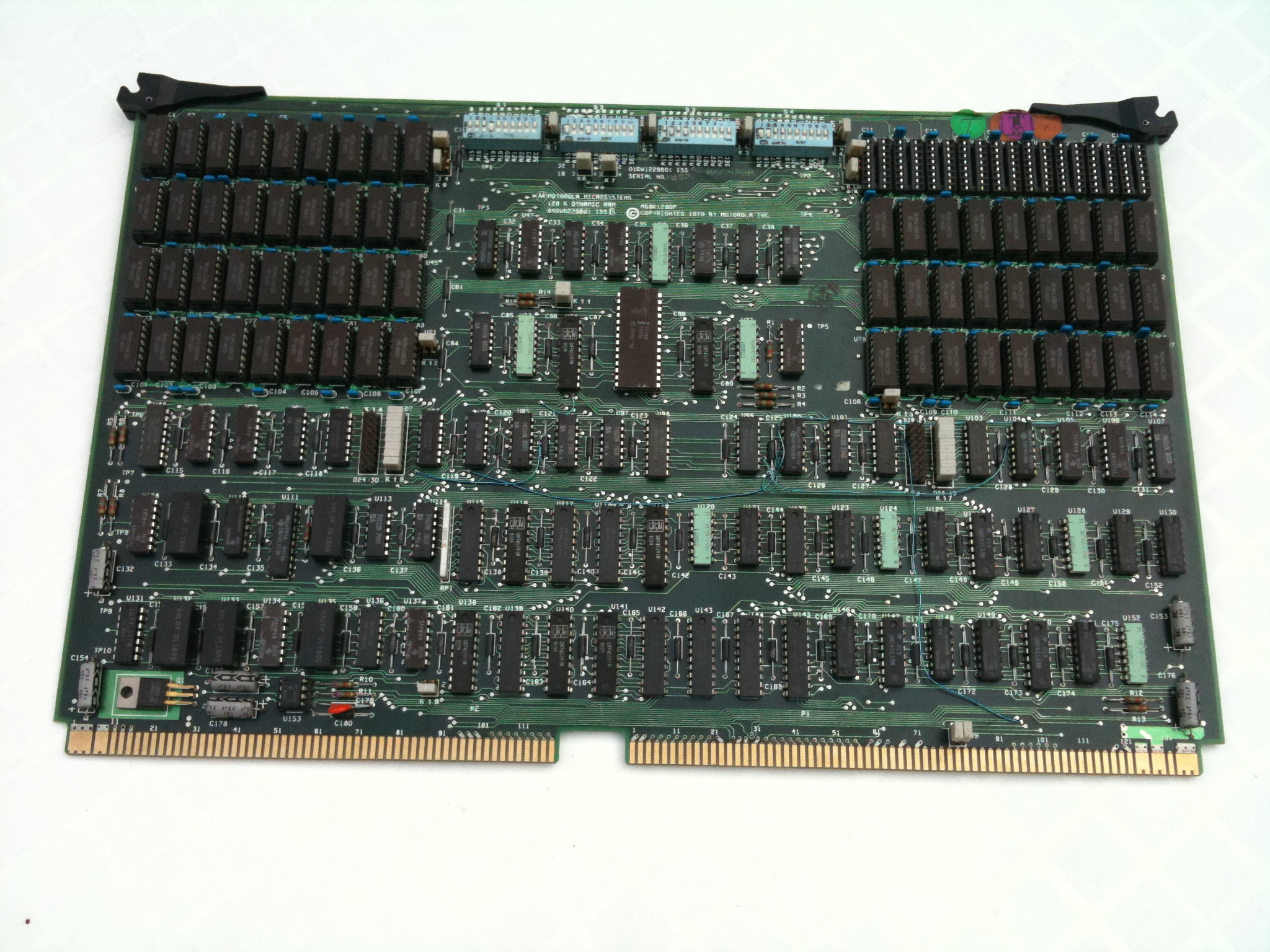
The Cray J90 series (code-named ''Jedi'' during development) was an air-cooled vector processor supercomputer first sold by Cray Research in 1994. The J90 evolved from the Cray Y-MP EL minisupercomputer, and is compatible with Y-MP software, running the same UNICOS operating system. The J90 supported up to 32 CMOS processors with a 10 ns (100 MHz) clock. It supported up to 4 GB of main memory and up to 48 GB/s of memory bandwidth, giving it considerably less performance than the contemporary Cray T90, but making it a strong competitor to other technical computers in its price range. All input/output in a J90 system was handled by an IOS (Input/Output Subsystem) called IOS Model V. The IOS-V was based on the VME64 bus and SPARC I/O processors (IOPs) running the VxWorks RTOS. The IOS was programmed to emulate the IOS Model E, used in the larger Cray Y-MP systems, in order to minimize changes in the UNICOS operating system. By using standard VME boards, a wide variety of commodity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray J916
Cray Inc., a subsidiary of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, is an American supercomputer manufacturer headquartered in Seattle, Washington. It also manufactures systems for data storage and analytics. Several Cray supercomputer systems are listed in the TOP500, which ranks the most powerful supercomputers in the world. Cray manufactures its products in part in Chippewa Falls, Wisconsin, where its founder, Seymour Cray, was born and raised. The company also has offices in Bloomington, Minnesota (which have been converted to Hewlett Packard Enterprise offices), and numerous other sales, service, engineering, and R&D locations around the world. The company's predecessor, Cray Research, Inc. (CRI), was founded in 1972 by computer designer Seymour Cray. Seymour Cray later formed Cray Computer Corporation (CCC) in 1989, which went bankrupt in 1995. Cray Research was acquired by Silicon Graphics (SGI) in 1996. Cray Inc. was formed in 2000 when Tera Computer Company purchased the Cray Rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VMEbus
VMEbus (Versa Module Europa or Versa Module Eurocard bus) is a computer bus standard, originally developed for the Motorola 68000 line of CPUs, but later widely used for many applications and standardized by the IEC as ANSI/IEEE 1014-1987. It is physically based on Eurocard sizes, mechanicals and connectors (DIN 41612), but uses its own signalling system, which Eurocard does not define. It was first developed in 1981 and continues to see widespread use today. History In 1979, during development of the Motorola 68000 CPU, one of their engineers, Jack Kister, decided to set about creating a standardized bus system for 68000-based systems. The Motorola team brainstormed for days to select the name VERSAbus. VERSAbus cards were large, , and used edge connectors. Only a few products adopted it, including the IBM System 9000 instrument controller and the Automatix robot and machine vision systems. Kister was later joined by John Black, who refined the specifications and creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray SV1
The Cray SV1 is a vector processor supercomputer from the Cray Research division of Silicon Graphics introduced in 1998. The SV1 has since been succeeded by the Cray X1 and X1E vector supercomputers. Like its predecessor, the Cray J90, the SV1 used CMOS processors, which lowered the cost of the system, and allowed the computer to be air-cooled. The SV1 was backwards compatible with J90 and Y-MP software, and ran the same UNIX-derived UNICOS operating system. The SV1 used Cray floating point representation, not the IEEE 754 floating point format used on the Cray T3E and some Cray T90 systems. Unlike earlier Cray designs, the SV1 included a vector cache. It also introduced a feature called multi-streaming, in which one processor from each of four processor boards work together to form a virtual processor with four times the performance. The SV1 processor was clocked at 300 MHz. Later variants of the SV1, the SV1e and SV1ex, ran at 500 MHz, the latter also having faster memory and sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray T3E
The Cray T3E was Cray Research's second-generation massively parallel supercomputer architecture, launched in late November 1995. The first T3E was installed at the Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center in 1996. Like the previous Cray T3D, it was a fully distributed memory machine using a 3D torus topology interconnection network. The T3E initially used the DEC Alpha 21164 (EV5) microprocessor and was designed to scale from 8 to 2,176 ''Processing Elements'' (PEs). Each PE had between 64 MB and 2 GB of DRAM and a 6-way interconnect router with a payload bandwidth of 480 MB/s in each direction. Unlike many other MPP systems, including the T3D, the T3E was fully self-hosted and ran the UNICOS/mk distributed operating system with a ''GigaRing'' I/O subsystem integrated into the torus for network, disk and tape I/O. The original T3E (retrospectively known as the T3E-600) had a 300 MHz processor clock. Later variants, using the faster 21164A (EV56) processor, comprised the T3E-900 (4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Cache
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost (time or energy) to access data from the main memory. A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations. Most CPUs have a hierarchy of multiple cache levels (L1, L2, often L3, and rarely even L4), with different instruction-specific and data-specific caches at level 1. The cache memory is typically implemented with static random-access memory (SRAM), in modern CPUs by far the largest part of them by chip area, but SRAM is not always used for all levels (of I- or D-cache), or even any level, sometimes some latter or all levels are implemented with eDRAM. Other types of caches exist (that are not counted towards the "cache size" of the most important caches mentioned above), such as the translation lookaside buffer (TLB) which is part of the memory management unit (MMU) whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray Y-MP
The Cray Y-MP was a supercomputer sold by Cray Research from 1988, and the successor to the company's X-MP. The Y-MP retained software compatibility with the X-MP, but extended the address registers from 24 to 32 bits. High-density VLSI ECL technology was used and a new liquid-cooling system was devised. The Y-MP ran the Cray UNICOS operating system. The Y-MP could be equipped with two, four or eight vector processors, with two functional units each and a clock cycle time of 6 ns (167 MHz). Peak performance was thus 333 megaflops per processor. Main memory comprised 128, 256 or 512 MB of SRAM. The original Y-MP (otherwise known as the Y-MP Model D) was housed in a chassis similar to the horseshoe-shaped X-MP, but with an extra rectangular cabinet added in the middle (containing the CPU boards), thus forming a "Y" shape in plan view. The system could be configured with one or two ''Model D'' IOSs (Input/Output Subsystems) and an optional Solid State Disk (SSD) of 256 MB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RTOS
A real-time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system (OS) for real-time applications that processes data and events that have critically defined time constraints. An RTOS is distinct from a time-sharing operating system, such as Unix, which manages the sharing of system resources with a scheduler, data buffers, or fixed task prioritization in a multitasking or multiprogramming environment. Processing time requirements need to be fully understood and bound rather than just kept as a minimum. All processing must occur within the defined constraints. Real-time operating systems are event-driven and preemptive, meaning the OS is capable of monitoring the relevant priority of competing tasks, and make changes to the task priority. Event-driven systems switch between tasks based on their priorities, while time-sharing systems switch the task based on clock interrupts. Characteristics A key characteristic of an RTOS is the level of its consistency concerning the amount of time it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VxWorks
VxWorks is a real-time operating system (or RTOS) developed as proprietary software by Wind River Systems, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Aptiv. First released in 1987, VxWorks is designed for use in embedded systems requiring real-time, deterministic performance and, in many cases, safety and security certification for industries such as aerospace and defense, medical devices, industrial equipment, robotics, energy, transportation, network infrastructure, automotive, and consumer electronics.VxWorks Goes 64-bit", Electronic Design, March 25, 2011 VxWorks supports AMD/Intel architecture, POWER architecture, ARM architectures and RISC-V. The RTOS can be used in multicore |
SPARC
SPARC (Scalable Processor Architecture) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture originally developed by Sun Microsystems. Its design was strongly influenced by the experimental Berkeley RISC system developed in the early 1980s. First developed in 1986 and released in 1987, SPARC was one of the most successful early commercial RISC systems, and its success led to the introduction of similar RISC designs from many vendors through the 1980s and 1990s. The first implementation of the original 32-bit architecture (SPARC V7) was used in Sun's Sun-4 computer workstation and server systems, replacing their earlier Sun-3 systems based on the Motorola 68000 series of processors. SPARC V8 added a number of improvements that were part of the SuperSPARC series of processors released in 1992. SPARC V9, released in 1993, introduced a 64-bit architecture and was first released in Sun's UltraSPARC processors in 1995. Later, SPARC processors were used in symm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray T90
The Cray T90 series (code-named ''Triton'' during development) was the last of a line of vector processing supercomputers manufactured by Cray Research, Inc, superseding the Cray C90 series. The first machines were shipped in 1995, and featured a 2.2 ns (450 MHz) clock cycle and two-wide vector pipes, for a peak speed of 1.8 gigaflops per processor; the high clock speed arises from the CPUs being built using ECL logic. As with the Cray J90, each CPU contained a scalar data cache, in addition to the instruction buffering/caching which has always been in Cray architectures. Configurations were available with between four and 32 processors, and with either IEEE 754 or traditional Cray floating-point arithmetic; the processors shared an SRAM main memory of up to eight gigabytes, with a bandwidth of three 64-bit words per cycle per CPU (giving a 32-CPU STREAM bandwidth of 360 gigabytes per second). The clock signal is distributed via a fiber-optic harness to the processors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jedi
Jedi (), Jedi Knights, or collectively the Jedi Order are the main heroic protagonists of many works of the '' Star Wars'' franchise. Working symbiotically alongside the Old Galactic Republic, and later supporting the Rebel Alliance, the Jedi Order is depicted as a monastic, academic, military, and meritocratic peacekeeping organization whose origin dates back thousands of years before the events of the first film released in the franchise. The fictional organization has inspired a real-world new religious movement and parody religion: Jediism. Within the fictional ''Star Wars'' galaxy, the Jedi are powerful guardians of order and justice, who, through intuition, rigorous training, and intensive self-discipline, are able to wield a supernatural power known as the Force, thus achieving for example the ability to move objects with the mind, perform incredible feats of strength, and connect to certain people's thoughts. As ''Star Wars'' creator George Lucas explains, the Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)