|
Cooker Lo Presti
Cooker may refer to several types of cooking appliances and devices used for cooking foods. Cookers * AGA cooker – a heat storage stove and cooker, which works on the principle that a heavy frame made from cast iron components can absorb heat from a relatively low-intensity but continuously-burning source, and the accumulated heat can then be used when needed for cooking. Originally heated by slow-burning coal, the Aga cooker was invented in 1922 by the Nobel Prize-winning Swedish physicist Gustaf Dalén (1869–1937), who was employed first as the chief engineer of the Swedish AGA company. * Cook stove – heated by burning wood, charcoal, animal dung or crop residue. Cook stoves are commonly used for cooking and heating food in households that lack access to clean, modern facilities for cooking. * Electric cooker – an electric powered cooking device for heating and cooking of food * Gas stove (British English) – uses natural gas, propane, butane, liquefied petroleum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooker
Cooker may refer to several types of cooking appliances and devices used for cooking foods. Cookers * AGA cooker – a heat storage stove and cooker, which works on the principle that a heavy frame made from cast iron components can absorb heat from a relatively low-intensity but continuously-burning source, and the accumulated heat can then be used when needed for cooking. Originally heated by slow-burning coal, the Aga cooker was invented in 1922 by the Nobel Prize-winning Swedish physicist Gustaf Dalén (1869–1937), who was employed first as the chief engineer of the Swedish AGA company. * Cook stove – heated by burning wood, charcoal, animal dung or crop residue. Cook stoves are commonly used for cooking and heating food in households that lack access to clean, modern facilities for cooking. * Electric cooker – an electric powered cooking device for heating and cooking of food * Gas stove (British English) – uses natural gas, propane, butane, liquefied petroleum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Cooker
An electric cooker is an electric powered cooking device for heating and cooking of food. An electric cooker often has four stoves and one or two ovens. There will be knobs to determine the temperature of the ovens and stoves. Unlike gas stoves that are powered by gas, it is powered by electricity. Usually they have four rings on top of the hob, similar to most gas cookers. Besides stoves or ranges, common types include hot plates, slow cookers (or crock pots), electric toasters, rice cookers, electric teakettles, and the now obsolete Dub Cookers. See also *Cooker *Electric stove An electric stove or electric range is a stove with an integrated electrical heating device to cook and bake. Electric stoves became popular as replacements for solid-fuel (wood or coal) stoves which required more labor to operate and maintain. ... References Cooking appliances {{Cooking-tool-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferromagnetic
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) which results in a large observed magnetic permeability, and in many cases a large magnetic coercivity allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials are the familiar metals noticeably attracted to a magnet, a consequence of their large magnetic permeability. Magnetic permeability describes the induced magnetization of a material due to the presence of an ''external'' magnetic field, and it is this temporarily induced magnetization inside a steel plate, for instance, which accounts for its attraction to the permanent magnet. Whether or not that steel plate acquires a permanent magnetization itself, depends not only on the strength of the applied field, but on the so-called coercivity of that material, which varies greatly among ferromagnetic materials. In physics, several different types of material magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (along with the similar effect ferrimagneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, Convection (heat transfer), thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes. Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species (mass transfer in the form of advection), either cold or hot, to achieve heat transfer. While these mechanisms have distinct characteristics, they often occur simultaneously in the same system. Heat conduction, also called diffusion, is the direct microscopic exchanges of kinetic energy of particles (such as molecules) or quasiparticles (such as lattice waves) through the boundary between two systems. When an object is at a different temperature from another body or its surroundings, heat flows so that the body and the surroundings reach the same temperature, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induction Heating
Induction heating is the process of heating electrically conductive materials, namely metals or semi-conductors, by electromagnetic induction, through heat transfer passing through an induction coil that creates an electromagnetic field within the coil to heat up and possibly melt steel, copper, brass, graphite, gold, silver, aluminum, or carbide. An induction heater consists of an electromagnet and an electronic oscillator that passes a high-frequency alternating current (AC) through the electromagnet. The rapidly alternating magnetic field penetrates the object, generating electric currents inside the conductor called eddy currents. The eddy currents flow through the resistance of the material, and heat it by Joule heating. In ferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic materials, such as iron, heat also is generated by magnetic hysteresis losses. The frequency of the electric current used for induction heating depends on the object size, material type, coupling (between the work coil and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
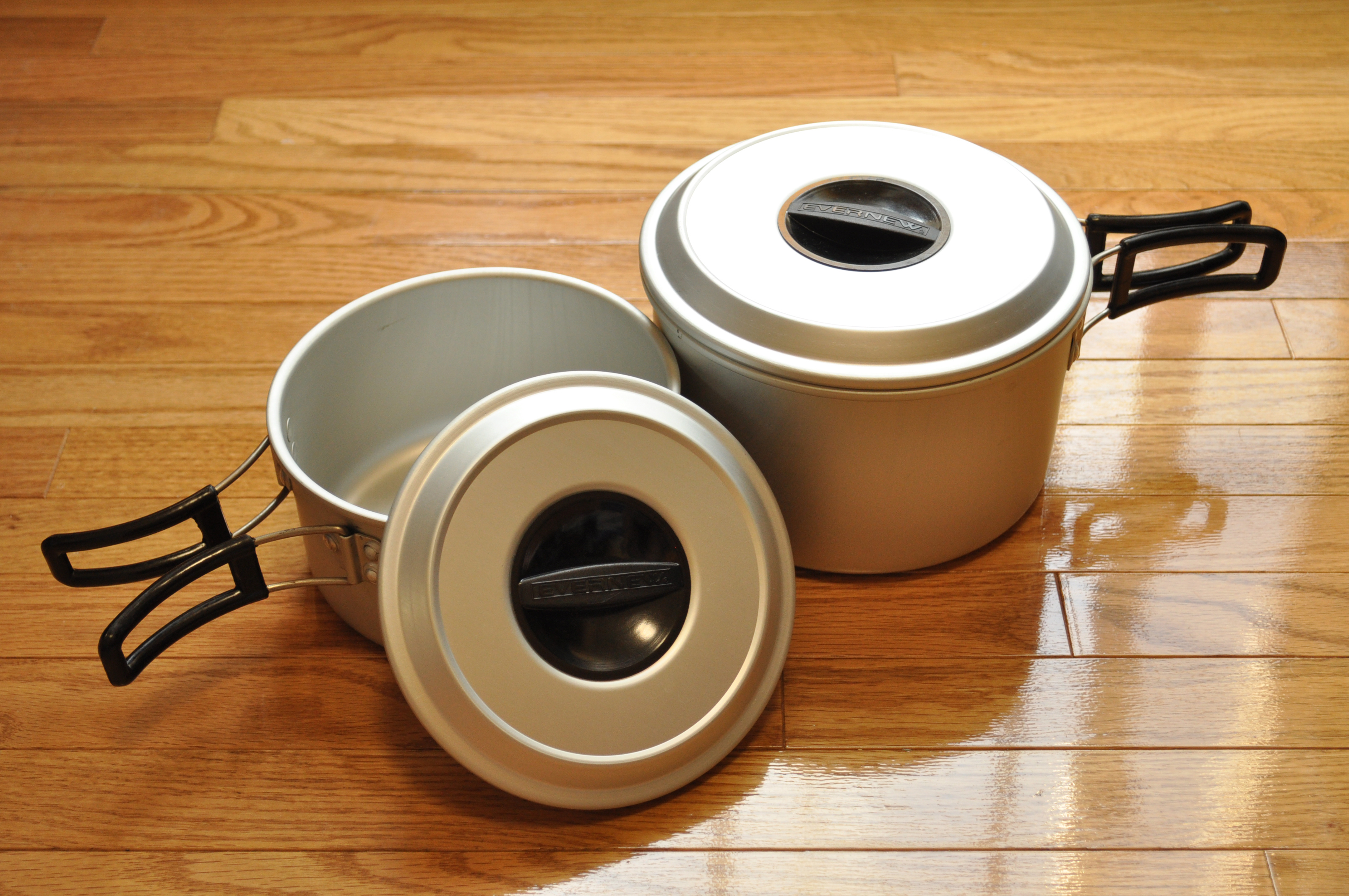
Cooking Vessel
Cookware and bakeware is food preparation equipment, such as cooking pots, pans, baking sheets etc. used in kitchens. Cookware is used on a stove or range cooktop, while bakeware is used in an oven. Some utensils are considered both cookware and bakeware. There is a great variety of cookware and bakeware in shape, material, and inside surface. Some materials conduct heat well; some retain heat well. Some surfaces are non-stick; some require seasoning. Some pots and their lids have handles or knobs made of low thermal conductance materials such as bakelite, plastic or wood, which make them easy to pick up without oven gloves. A good cooking pot design has an "overcook edge" which is what the lid lies on. The lid has a dripping edge that prevents condensation fluid from dripping off when handling the lid (taking it off and holding it 45°) or putting it down. History The history of cooking vessels before the development of pottery is minimal due to the limited archaeolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
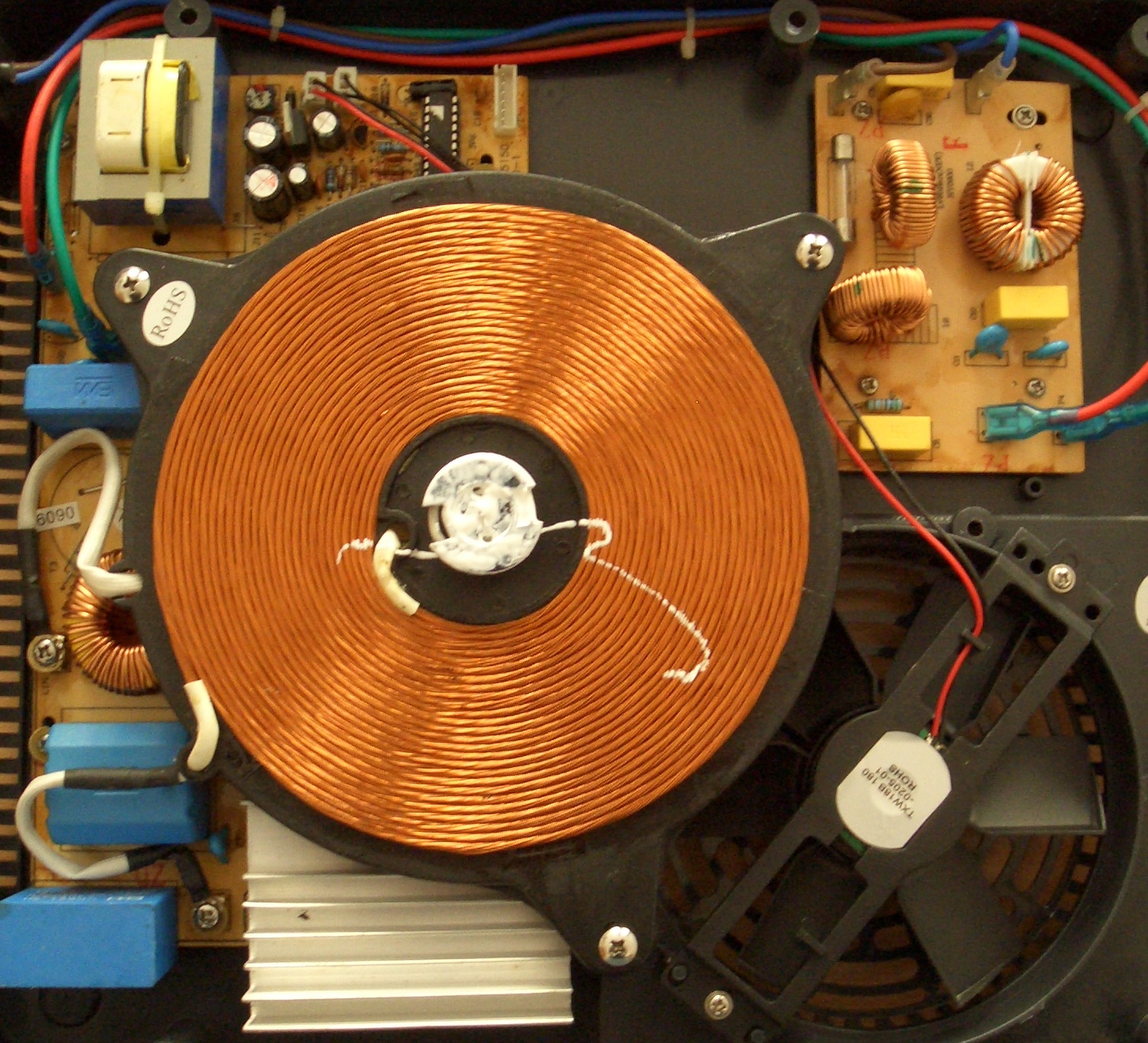
Induction Cooking
Induction cooking is performed using direct induction heating of cooking vessels, rather than relying on indirect radiation, convection, or thermal conduction. Induction cooking allows high power and very rapid increases in temperature to be achieved, and changes in heat settings are instantaneous. In an induction stove (also "induction hob" or "induction cooktop"), a cooking vessel with a ferromagnetic base is placed on a heat-proof glass-ceramic surface above a coil of copper wire with an alternating electric current passing through it. The resulting oscillating magnetic field wirelessly induces an electrical current in the vessel. This large eddy current flowing through the resistance of a thin layer of metal in the base of the vessel results in resistive heating. For nearly all models of induction cooktops, a cooking vessel must be made of, or contain, a ferrous metal such as cast iron or some stainless steels. The iron in the pot concentrates the current to produce he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extractor Hood
A kitchen hood, exhaust hood, extractor hood, or range hood is a device containing a mechanical fan that hangs above the stove or cooktop in the kitchen. It removes airborne grease, combustion products, fumes, smoke, heat, and steam from the air by evacuation of the air and filtration. In commercial kitchens exhaust hoods are often used in combination with fire suppression devices so that fumes from a grease fire are properly vented and the fire is put out quickly. Commercial vent hoods may also be combined with a fresh air fan that draws in exterior air, circulating it with the cooking fumes, which is then drawn out by the hood. In most exhaust hoods, a filtration system removes grease (the grease trap) and other particles. Although many vent hoods exhaust air to the outside, some recirculate the air to the kitchen. In a recirculating system, filters may be used to remove odors in addition to the grease. The device is known as an extractor hood in the United Kingdom, as a rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy but has since also been applied to other sources of heat energy, such as nuclear energy (via nuclear fission and nuclear fusion). The heat energy released by reactions of fuels can be converted into mechanical energy via a heat engine. Other times, the heat itself is valued for warmth, cooking, or industrial processes, as well as the illumination that accompanies combustion. Fuels are also used in the cells of organisms in a process known as cellular respiration, where organic molecules are oxidized to release usable energy. Hydrocarbons and related organic molecules are by far the most common source of fuel used by humans, but other substances, including radioactive metals, are also utilized. Fuels are contrasted with other substances or de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flammable
A combustible material is something that can burn (i.e., ''combust'') in air. A combustible material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable material catches fire immediately on exposure to flame. The degree of flammability or combustibility in air depends largely upon the volatility of the material - this is related to its composition-specific vapour pressure, which is temperature dependent. The quantity of vapour produced can be enhanced by increasing the surface area of the material forming a mist or dust. Take wood as an example. Finely divided wood dust can undergo explosive combustion and produce a blast wave. A piece of paper (made from wood) catches on fire quite easily. A heavy oak desk is much harder to ignite, even though the wood fibre is the same in all three materials. Common sense (and indeed scientific consensus until the mid-1700s) would seem to suggest that ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquefied Petroleum Gas
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG or LP gas) is a fuel gas which contains a flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases, specifically propane, propylene, butylene, isobutane and n-butane. LPG is used as a fuel gas in heating appliances, cooking equipment, and vehicles. It is increasingly used as an aerosol propellant and a refrigerant, replacing chlorofluorocarbons in an effort to reduce damage to the ozone layer. When specifically used as a vehicle fuel, it is often referred to as autogas or even just as gas. Varieties of LPG that are bought and sold include mixes that are mostly propane (), mostly butane (), and, most commonly, mixes including both propane and butane. In the northern hemisphere winter, the mixes contain more propane, while in summer, they contain more butane. In the United States, mainly two grades of LPG are sold: commercial propane and HD-5. These specifications are published by the Gas Processors Association (GPA) and the American Society of Testing and Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butane
Butane () or ''n''-butane is an alkane with the formula C4H10. Butane is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. Butane is a highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gas that quickly vaporizes at room temperature. The name butane comes from the root but- (from butyric acid, named after the Greek word for butter) and the suffix -ane. It was discovered by the chemist Dr. Walter Snelling in 1912. It was found dissolved in crude petroleum in 1864 by Edmund Ronalds, who was the first to describe its properties. Butane is one of a group of liquefied petroleum gases (LP gases). The others include propane, propylene, butadiene, butylene, isobutylene, and mixtures thereof. Butane burns more cleanly than gasoline and coal. Density The density of butane is highly dependent on temperature and pressure in the reservoir. For example, the density of liquid phase is 571.8±1 kg/m3 (for pressures up to 2MPa and temperature 27±0.2 °C), while the density of liq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)