|
Contracted Out
Contraction may refer to: Linguistics * Contraction (grammar), a shortened word * Poetic contraction, omission of letters for poetic reasons * Elision, omission of sounds ** Syncope (phonology), omission of sounds in a word * Synalepha, merged syllables ** Synaeresis, combined vowels ** Crasis, merged vowels or diphthongs Mathematics and logic * Contraction (operator theory), in operator theory, state of a bounded operator between normed vector spaces after suitable scaling * Contraction hierarchies, in applied mathematics, a technique to speed up shortest-path routing * Contraction mapping, a type of function on a metric space * Edge contraction or vertex contraction, graph operations used in graph theory * Tensor contraction, an operation on one or more tensors that arises from the natural pairing of a finite-dimensional vector space and its dual * Left contraction and right contraction of multivectors in a geometric algebra, extensions of the inner product * One of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraction (grammar)
A contraction is a shortened version of the spoken and written forms of a word, syllable, or word group, created by omission of internal letters and sounds. In linguistic analysis, contractions should not be confused with crasis, abbreviations and initialisms (including acronyms), with which they share some semantic and phonetic functions, though all three are connoted by the term "abbreviation" in layman’s terms. Contraction is also distinguished from morphological clipping, where beginnings and endings are omitted. The definition overlaps with the term portmanteau (a linguistic '' blend''), but a distinction can be made between a portmanteau and a contraction by noting that contractions are formed from words that would otherwise appear together in sequence, such as ''do'' and ''not'', whereas a portmanteau word is formed by combining two or more existing words that all relate to a singular concept that the portmanteau describes. English English has a number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditional Independence
In probability theory, conditional independence describes situations wherein an observation is irrelevant or redundant when evaluating the certainty of a hypothesis. Conditional independence is usually formulated in terms of conditional probability, as a special case where the probability of the hypothesis given the uninformative observation is equal to the probability without. If A is the hypothesis, and B and C are observations, conditional independence can be stated as an equality: :P(A\mid B,C) = P(A \mid C) where P(A \mid B, C) is the probability of A given both B and C. Since the probability of A given C is the same as the probability of A given both B and C, this equality expresses that B contributes nothing to the certainty of A. In this case, A and B are said to be conditionally independent given C, written symbolically as: (A \perp\!\!\!\perp B \mid C). The concept of conditional independence is essential to graph-based theories of statistical inference, as it establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase II
Phase II, Phase 2 or Phase Two may refer to: Media * Marvel Cinematic Universe: Phase Two, six American superhero films from 2013–2015 * ''Star Trek: Phase II'', an unrealized television series based on the characters of Gene Roddenberry's ''Star Trek'' * ''Star Trek: Phase II'' (fan series), a fan-created science fiction series set in the ''Star Trek'' universe * ''Phase II'' (album), 2012 Prince Royce album * ''Phase 2'' (album), 2014 Fear, and Loathing in Las Vegas album * ''Phase II'', a Johnny Smith album * Phase II Pan Groove, a steel orchestra * '' Contracted: Phase II'', a 2015 horror film * '' Phase Two: Slowboat to Hades'', a Gorillaz compilation DVD Other * Phase II clinical trials, the second of the phases of clinical research * Phase II metabolism, conjugation reactions in drug metabolism * PHASE 2 (1955–2019), an American graffiti artist in New York City * Cosmos Phase II, a series of hang gliders * Phase 2 metro station * MediaWiki MediaWiki is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contracted (film)
''Contracted'' is a 2013 American zombie-body horror independent film written and directed by Eric England. It was first released on November 23, 2013, in the United States and stars Najarra Townsend as a young woman that finds herself suffering from a mysterious sexually transmitted disease after a rape. It has been compared to the 2012 film ''Thanatomorphose'', with which it shares similarities. ''Twitch Film'' has criticized the movie for its marketing, in which England describes the character Samantha's rape as a "one night stand". The original cast of the first film is featured in a sequel titled '' Contracted: Phase II'', written by Craig Walendziak and directed by Josh Forbes. The sequel was released in September 2015. Plot In a morgue, a man named BJ with an Abaddon tattoo has sex with a corpse that has a biohazard symbol on the toe tag; afterward, he handles an empty test tube while washing up. Samantha is trying to get over a recent break-up with her girlfriend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanide Contraction
The lanthanide contraction is the greater-than-expected decrease in atomic radii/ ionic radii of the elements in the lanthanide series from atomic number 57, lanthanum, to 71, lutetium, which results in smaller than otherwise expected atomic radii/ionic radii for the subsequent elements starting with 72, hafnium. Jolly, William L. ''Modern Inorganic Chemistry'', McGraw-Hill 1984, p. 22 The term was coined by the Norwegian geochemist Victor Goldschmidt in his series "Geochemische Verteilungsgesetze der Elemente" (Geochemical distribution laws of the elements). Goldschmidt, Victor M. "Geochemische Verteilungsgesetze der Elemente", Part V "Isomorphie und Polymorphie der Sesquioxyde. Die Lanthaniden-Kontraktion und ihre Konsequenzen", Oslo, 1925 Cause The effect results from poor shielding of nuclear charge (nuclear attractive force on electrons) by 4f electrons; the 6s electrons are drawn towards the nucleus, thus resulting in a smaller atomic radius. In single-electron atoms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraction (physics)
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions. Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic energy of a substance. When a substance is heated, molecules begin to vibrate and move more, usually creating more distance between themselves. Substances which contract with increasing temperature are unusual, and only occur within limited temperature ranges (see examples below). The relative expansion (also called strain (mechanics), strain) divided by the change in temperature is called the material's coefficient of linear thermal expansion and generally varies with temperature. As energy in particles increases, they start moving faster and faster weakening the intermolecular forces between them, therefore expanding the substance. Overview Predicting expansion If an equation of state is available, it can be used to predict the valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraction (economics)
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various events, such as a financial crisis, an external trade shock, an adverse supply shock, the bursting of an economic bubble, or a large-scale anthropogenic or natural disaster (e.g. a pandemic). In the United States, a recession is defined as "a significant decline in economic activity spread across the market, lasting more than a few months, normally visible in real GDP, real income, employment, industrial production, and wholesale-retail sales." The European Union has adopted a similar definition. In the United Kingdom, a recession is defined as negative economic growth for two consecutive quarters. Governments usually respond to recessions by adopting expansionary macroeconomic policies, such as increasing money supply and decr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wound Contraction
Wound healing refers to a living organism's replacement of destroyed or damaged tissue by newly produced tissue. In undamaged skin, the epidermis (surface, epithelial layer) and dermis (deeper, connective layer) form a protective barrier against the external environment. When the barrier is broken, a regulated sequence of biochemical events is set into motion to repair the damage. This process is divided into predictable phases: blood clotting ( hemostasis), inflammation, tissue growth (cell proliferation), and tissue remodeling (maturation and cell differentiation). Blood clotting may be considered to be part of the inflammation stage instead of a separate stage. The wound healing process is not only complex but fragile, and it is susceptible to interruption or failure leading to the formation of non-healing chronic wounds. Factors that contribute to non-healing chronic wounds are diabetes, venous or arterial disease, infection, and metabolic deficiencies of old age.Enoch, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contractility
Contractility refers to the ability for self-contraction, especially of the muscles or similar active biological tissue *Contractile ring in cytokinesis *Contractile vacuole *Muscle contraction **Myocardial contractility *See contractile cell for an overview of cell types in humans. See also *motility Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy. Definitions Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ... {{SIA Cell movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Contraction
Uterine contractions are muscle contractions of the uterine smooth muscle that occur during the menstrual cycle and labour. Uterine contractions occur throughout the menstrual cycle in the non-pregnant state and throughout gestation. Throughout menstrual cycle Uterine contractions that occur throughout the menstrual cycle, also termed ''endometrial waves'' or ''contractile waves'', appear to involve only the sub-endometrial layer of the myometrium. Follicular and luteal phase In the early follicular phase, uterine contractions in the non-pregnant woman occur 1—2 times per minute and last 10–15 seconds with a low intensity of usually 30 mmHg or less. This sub-endometrial layer is rich in estrogen and progesterone receptors. The frequency of contractions increases to 3–4 per minute towards ovulation. During the luteal phase, the frequency and intensity decrease, possibly to facilitate any implantation. Menstruation If implantation does not occur, the frequency of contract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
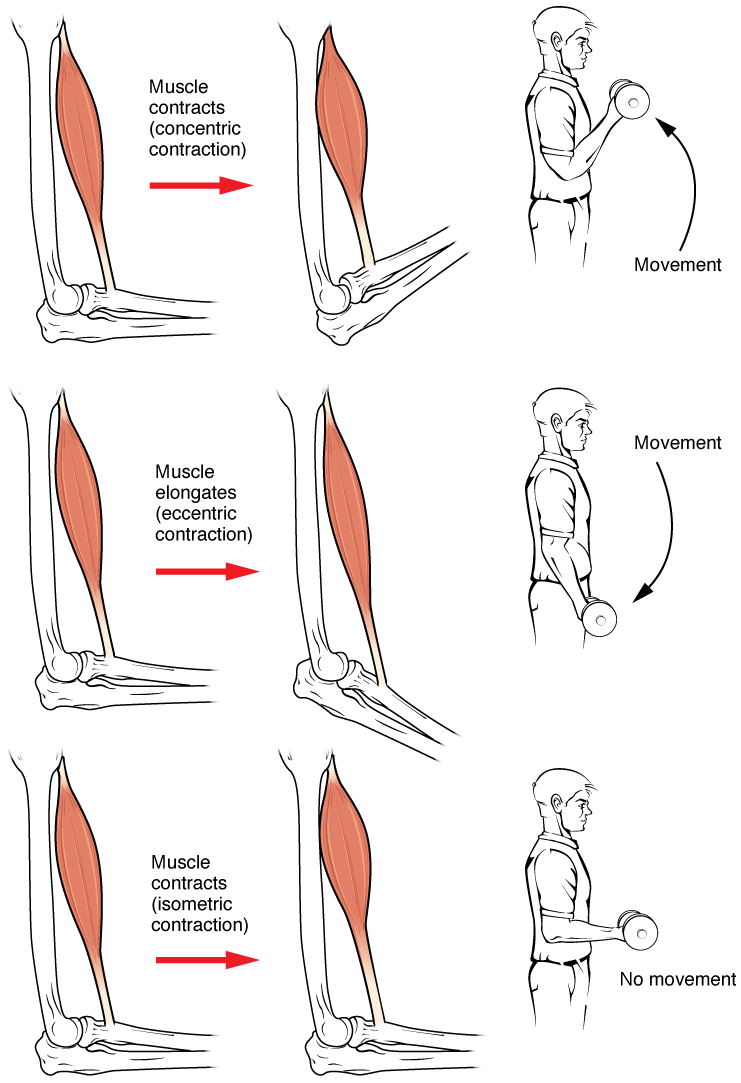
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the interaction of two types of filaments which are the thin and thick filaments. Thin filaments are two strands of actin coiled around each, and thick filaments consist of mostly elongated proteins called myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils which are important organelles in the skeletal muscle system. Muscle contraction can also be described based on two variables: length and tension. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraction (logic)
In proof theory, a structural rule is an inference rule that does not refer to any logical connective, but instead operates on the judgment or sequents directly. Structural rules often mimic intended meta-theoretic properties of the logic. Logics that deny one or more of the structural rules are classified as substructural logics. Common structural rules Three common structural rules are: * Weakening, where the hypotheses or conclusion of a sequent may be extended with additional members. In symbolic form weakening rules can be written as \frac on the left of the turnstile, and \frac on the right. * Contraction, where two equal (or unifiable) members on the same side of a sequent may be replaced by a single member (or common instance). Symbolically: \frac and \frac. Also known as factoring in automated theorem proving systems using resolution. Known as idempotency of entailment in classical logic. * Exchange, where two members on the same side of a sequent may be swapped. Symb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |