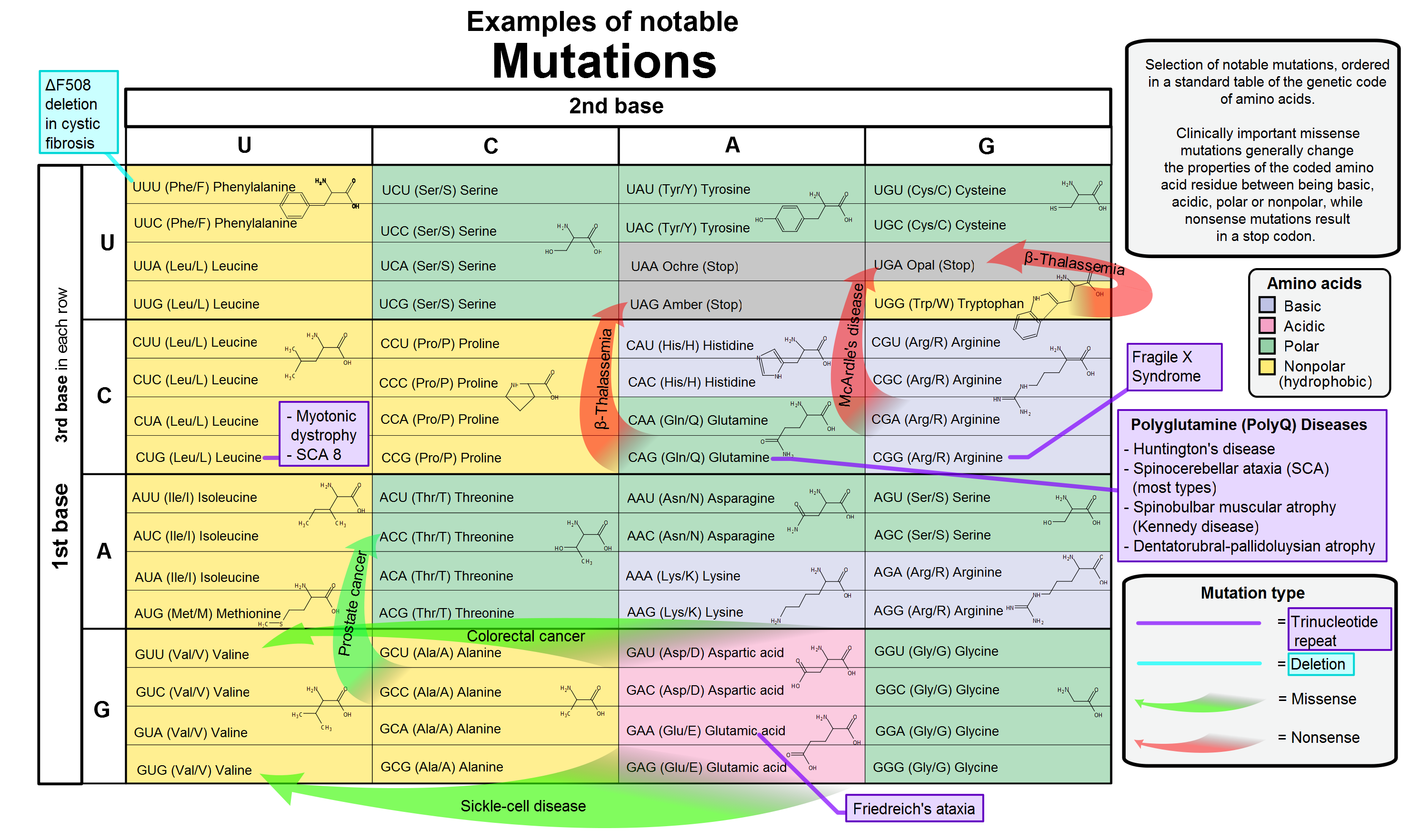
|
Conservative Mutation
A conservative replacement (also called a conservative mutation or a conservative substitution or a homologous replacement) is an amino acid replacement in a protein that changes a given amino acid to a different amino acid with similar biochemical properties (e.g. charge, hydrophobicity and size). Conversely, a radical replacement, or radical substitution, is an amino acid replacement that exchanges an initial amino acid by a final amino acid with different physicochemical properties. Description There are 20 naturally occurring amino acids, however some of these share similar characteristics. For example, leucine and isoleucine are both aliphatic, branched hydrophobes. Similarly, aspartic acid and glutamic acid are both small, negatively charged residues. Although there are many ways to classify amino acids, they are often sorted into six main classes on the basis of their structure and the general chemical characteristics of their side chains (R groups). Physicochem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid Replacement
Amino acid replacement is a change from one amino acid to a different amino acid in a protein due to point mutation in the corresponding DNA sequence. It is caused by nonsynonymous missense mutation which changes the codon sequence to code other amino acid instead of the original. Conservative and radical replacements Not all amino acid replacements have the same effect on function or structure of protein. The magnitude of this process may vary depending on how similar or dissimilar the replaced amino acids are, as well as on their position in the sequence or the structure. Similarity between amino acids can be calculated based on substitution matrices, physico-chemical distance, or simple properties such as amino acid size or charge (see also amino acid chemical properties). Usually amino acids are thus classified into two types: * Conservative replacement - an amino acid is exchanged into another that has similar properties. This type of replacement is expected to rarel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucine
Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-Carboxylic acid, carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain Isobutyl, isobutyl group, making it a Chemical polarity, non-polar Aliphatic compound, aliphatic amino acid. It is Essential amino acid, essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it; it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are foods that contain protein, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, and beans and other legumes. It is genetic code, encoded by the codons UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG. Leucine is named after the Greek language, Greek word for "white": ''λευκός'' (''leukós'', "white"), after its common appearance as a white powder, a property it shares with many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic beta carbon substituent. Tryptophan is also a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin, the hormone melatonin, and vitamin B3 (niacin). It is encoded by the codon UGG. Like other amino acids, tryptophan is a zwitterion at physiological pH where the amino group is protonated (–; pKa = 9.39) and the carboxylic acid is deprotonated ( –COO−; pKa = 2.38). Humans and many animals cannot synthesize tryptophan: they need to obtain it through their diet, making it an essential amino acid. Tryptophan is named after the digestive enzymes trypsin, which were used in its first isolation from casein proteins. It was assigned the one-letter symbol W based on the double ring being visually suggestive to the bulky letter. Function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. The one-letter symbol Y was assigned to tyrosine for being alphabetically nearest of those letters available. Note that T was assigned to the structurally simpler threonine, U was avoided for its similarity with V for valine, W was assigned to tryptophan, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids. The mnemonic t''Y''rosine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and chemical polarity, nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The chirality (chemistry)#Naming conventions, L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins coded for by DNA. Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), and the biological pigment melanin. It is Genetic code, encoded by the messenger RNA codons UUU and UUC. Phenylalanine is found naturally in the milk of mammals. It is used in the manufacture of food and drink products and sold as a nutritional supplement as it is a direct precursor to the neuromodulation, neuromodulator phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Amino Acids
An aromatic amino acid is an amino acid that includes an aromatic ring. Among the 20 standard amino acids, histidine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine, are classified as aromatic. Properties and function Optical properties Aromatic amino acids, excepting histidine, absorb ultraviolet light above and beyond 250 nm and will fluoresce under these conditions. This characteristic is used in quantitative analysis, notably in determining the concentrations of these amino acids in solution. Most proteins absorb at 280 nm due to the presence of tyrosine and tryptophan. Of the aromatic amino acids, tryptophan has the highest extinction coefficient; its absorption maximum occurs at 280 nm. The absorption maximum of tyrosine occurs at 274 nm. Role in protein structure and function Aromatic amino acids stabilize folded structures of many proteins. Aromatic residues are found predominantly sequestered within the cores of globular proteins, although often comprise key portions of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the protonated form (NH2+) under biological conditions, while the carboxyl group is in the deprotonated −COO− form. The "side chain" from the α carbon connects to the nitrogen forming a pyrrolidine loop, classifying it as a aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from the non-essential amino acid L-glutamate. It is encoded by all the codons starting with CC (CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG). Proline is the only proteinogenic amino acid which is a secondary amine, as the nitrogen atom is attached both to the α-carbon and to a chain of three carbons that together form a five-membered ring. History and etymology Proline was first isolated in 1900 by Richard Willstätter who obtained the amino a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical role in the metabolism and health of many species, including humans. Methionine is also involved in angiogenesis and various processes related to DNA transcription, epigenetic expression, and gene regulation. Methionine was first isolated in 1921 by John Howard Mueller. It is Genetic code, encoded by the codon AUG. It was named by Satoru Odake in 1925, as an abbreviation of its structural description 2-amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid. Biochemical details Methionine (abbreviated as Met or M; encoded by the codon AUG) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological pH conditions), an amino group (which is in the proton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form when dissolved in water), and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as ''E. coli''. It is encoded by all the codons starting AC (ACU, ACC, ACA, and ACG). Threonine sidechains are often hydrogen bonded; the most common small motifs formed are based on interactions with serine: ST turns, ST motifs (often at the beginning of alpha helices) and ST staples (usually at the middle of alpha helices). Modifications The threonine residue is susceptible to numerous posttranslational modifications. The hydroxyl side-chain can und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenocysteine
Selenocysteine (symbol Sec or U, in older publications also as Se-Cys) is the 21st proteinogenic amino acid. Selenoproteins contain selenocysteine residues. Selenocysteine is an analogue of the more common cysteine with selenium in place of the sulfur. Selenocysteine is present in several enzymes (for example glutathione peroxidases, tetraiodothyronine 5 deiodinase, tetraiodothyronine 5′ deiodinases, thioredoxin reductases, formate dehydrogenases, glycine reductases, selenophosphate synthetase 2, methionine-''R''-sulfoxide reductase B1 (SEPX1), and some hydrogenases). It occurs in all three Domain (biology), domains of life, including important enzymes (listed above) present in humans. Selenocysteine was discovered in 1974 by biochemist Thressa Stadtman at the National Institutes of Health. Chemistry Selenocysteine is the Se-analogue of cysteine. It is rarely encountered outside of living tissue (nor is it available commercially) because of its high susceptiblility to air-oxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. Cysteine is chiral, but both D and L-cysteine are found in nature. LCysteine is a protein monomer in all biota, and D-cysteine acts as a signaling molecule in mammalian nervous systems. Cysteine is named after its discovery in urine, which comes from the urinary bladder or cyst, from Ancient Greek, Greek κύστις ''kýstis'', "bladder". The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide bond, disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. When used as a food additive, cysteine has the E number E920. Cysteine is Genetic code, encoded by the codo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L- stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, '' sericum''. Serine's structure was established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |