|
Conowingo Dam
The Conowingo Dam (also Conowingo Hydroelectric Plant, Conowingo Hydroelectric Station) is a large hydroelectric dam in the lower Susquehanna River near the town of Conowingo, Maryland. The medium-height, masonry gravity dam is one of the largest non-federal hydroelectric dams in the U.S., and the largest dam in the state of Maryland. The dam sits about from the river mouth at the Chesapeake Bay, south of the Pennsylvania border and northeast of Baltimore, on the border between Cecil and Harford counties. The dam supports a 9,000-acre reservoir, which today covers the original town of Conowingo. During dam construction, the town was moved to its present location about northeast of the dam's eastern end. The rising water also would have covered Conowingo Bridge, the original U.S. Route 1 crossing, so it was demolished in 1927. U.S. Route 1 now crosses over the top of the dam. The Conowingo Reservoir, and the nearby Susquehanna State Park, provide many recreational oppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cecil County, Maryland
Cecil County () is a county located in the U.S. state of Maryland at the northeastern corner of the state, bordering both Pennsylvania and Delaware. As of the 2020 census, the population was 103,725. The county seat is Elkton. The county was named for Cecil Calvert, 2nd Baron Baltimore (1605–1675), the first Proprietary Governor of the Province (colony) of Maryland. With the eastern part of the county being closer to Philadelphia than to Baltimore, it is part of the Philadelphia-Camden-Wilmington, PA-NJ-DE-MD Metropolitan Statistical Area. The county is located in Wilmington's Radio Market and Baltimore's Designated Market Area. History The area now known as Cecil County was an important trading center long before the county's official organization in 1674 by proclamation of Lord Baltimore. It had previously been a northeastern part of a much larger Baltimore County, in the northeastern portion of the Province. This had included present-day Baltimore City and county ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone & Webster
Stone & Webster was an American engineering services company based in Stoughton, Massachusetts. It was founded as an electrical testing lab and consulting firm by electrical engineers Charles A. Stone and Edwin S. Webster in 1889. In the early 20th century, Stone & Webster was known for operating streetcar systems in many cities across the United States including Dallas, Houston and Seattle. Middleton, William D. (1967). ''The Time of the Trolley'', pp. 122–128. Milwaukee: Kalmbach Publishing. . The company grew to provide engineering, construction, environmental, and plant operation and maintenance services, and it has long been involved in power generation projects, starting with hydroelectric plants of the late 19th-century; and with most American nuclear power plants. Stone & Webster was acquired and integrated as a division of The Shaw Group in 2000, and in 2012, the French engineering conglomerate Technip acquired Stone & Webster's energy and chemical business, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Start
A black start is the process of restoring an electric power station or a part of an electric grid to operation without relying on the external electric power transmission network to recover from a total or partial shutdown.Knight, U.G. ''Power Systems in Emergencies - From Contingency Planning to Crisis Management '' John Wiley & Sons 2001 section 7.5 The 'Black Start' Situation Power to restart a generating station may come from an on-site standby generator. Alternatively, where a large amount of power is required, a tie-line to another generating plant may be used to start the facility. Once the main generating units are running, the electrical transmission network can be re-connected and electrical loads restored. Black-start power may be ensured by an agreement where a particular energy supplier is paid to make black start power available when required. Not all generating plants are suitable for providing black-start power to a network. Station service power Electrical g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) is the United States federal agency that regulates the transmission and wholesale sale of electricity and natural gas in interstate commerce and regulates the transportation of oil by pipeline in interstate commerce. FERC also reviews proposals to build interstate natural gas pipelines, natural gas storage projects, and liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals, in addition to licensing non-federal hydropower projects. FERC is composed of five commissioners who are nominated by the U.S. president and confirmed by the U.S. Senate. There may be no more than three commissioners of one political party serving on the commission at any given time. Primary duties The responsibilities of FERC include the following: * Regulating the transmission and sale of natural gas for resale in interstate commerce; * Regulating the transmission of oil by pipelines in interstate commerce; * Regulating the transmission and wholesale sales of electricit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power Transmission: Background and Policy Issues. The Capital.Net, Government Series. Pp. 1-42. * power stations: often located near energy and away from heavily populated areas * electrical substations to step voltage up or down * electric power transmission to carry power long distances * electric power distribution to individual customers, where voltage is stepped down again to the required service voltage(s). Grids are nearly always synchronous, meaning all distribution areas operate with three phase alternating current (AC) frequencies synchronized (so that voltage swings occur at almost the same time). This allows transmission of AC power throughout the area, connecting a large number of electricity generators and consumers and poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, largest city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the List of United States cities by population, sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Act of Consolidation, 1854, Since 1854, the city has been coextensive with Philadelphia County, Pennsylvania, Philadelphia County, the List of counties in Pennsylvania, most populous county in Pennsylvania and the urban core of the Delaware Valley, the Metropolitan statistical area, nation's seventh-largest and one of List of largest cities, world's largest metropolitan regions, with 6.245 million residents . The city's population at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census was 1,603,797, and over 56 million people live within of Philadelphia. Philadelphia was founded in 1682 by William Penn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk Southern
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad in the United States formed in 1982 with the merger of Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. With headquarters in Atlanta, the company operates 19,420 route miles (31,250 km) in 22 eastern states, the District of Columbia, and has rights in Canada over the Albany to Montréal route of the Canadian Pacific Railway. NS is responsible for maintaining , with the remainder being operated under trackage rights from other parties responsible for maintenance. Intermodal containers and trailers are the most common commodity type carried by NS, which have grown as coal business has declined throughout the 21st century; coal was formerly the largest source of traffic. The railway offers the largest intermodal rail network in eastern North America. NS was also the pioneer of Roadrailer service. Norfolk Southern and its chief competitor, CSX Transportation, have a duopoly on the transcontinental freight rail lines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia And Port Deposit Railroad
The Columbia and Port Deposit Railroad (C&PD) was a railroad that operated in Pennsylvania and Maryland in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It operated a main line between Columbia, Pennsylvania, and Port Deposit, Maryland, generally along the eastern shore of the Susquehanna River. It later acquired a branch line to Perryville, Maryland. The C&PD was subsequently purchased by the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) and, since the 1999 breakup of Conrail, is owned by Norfolk Southern Railway. History The C&PD, originally called the Washington and Maryland Line Railroad and then the Columbia and Maryland Line Railroad, was chartered in 1858. The C&PD began construction in 1866, as another rail line, a branch built by the Philadelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore Railroad (PW&B), approached Port Deposit from the southeast. The PRR, which controlled the PW&B, also purchased a controlling interest in the C&PD in 1866. The first completed section of the C&PD opened in 1868 and connected the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
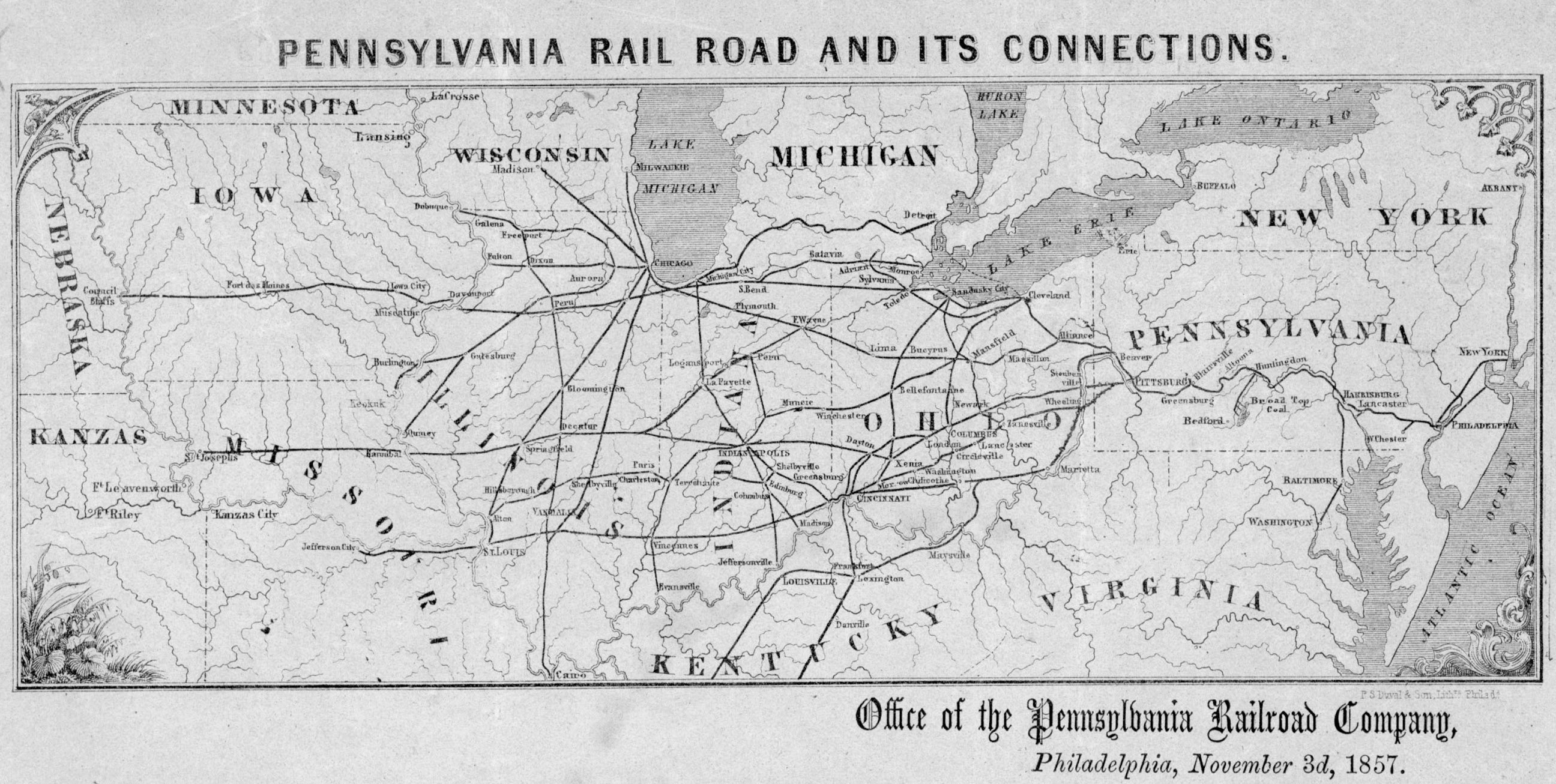
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named for the commonwealth in which it was established. By 1882, Pennsylvania Railroad had become the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Its budget was second only to the U.S. government. Over the years, it acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one hertz is the reciprocal of one second. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. Hertz are commonly expressed in multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. The units are sometimes also used as a representation of the energy of a photon, via the Planck relation ''E'' = ''hν'', where ''E'' is the photon's energy, ''ν'' is its f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Baltimore Sun
''The Baltimore Sun'' is the largest general-circulation daily newspaper based in the U.S. state of Maryland and provides coverage of local and regional news, events, issues, people, and industries. Founded in 1837, it is currently owned by Tribune Publishing. The ''Baltimore Sun's'' parent company, '' Tribune Publishing'', was acquired by Alden Global Capital, which operates its media properties through Digital First Media, in May 2021. History ''The Sun'' was founded on May 17, 1837, by printer/editor/publisher/owner Arunah Shepherdson Abell (often listed as "A. S. Abell") and two associates, William Moseley Swain, and Azariah H. Simmons, recently from Philadelphia, where they had started and published the '' Public Ledger'' the year before. Abell was born in Rhode Island, became a journalist with the ''Providence Patriot'' and later worked with newspapers in New York City and Boston.Van Doren, Charles and Robert McKendry, ed., ''Webster's American Biographies''. (Spring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryland Public Television
Maryland Public Television (MPT) is the Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) member state network for the U.S. state of Maryland. It operates under the auspices of the Maryland Public Broadcasting Commission, an agency of the Maryland state government that holds the licenses for all PBS member stations licensed in the state. Studios are located in the unincorporated community of Owings Mills in northwestern Baltimore County. MPT operates six full-power transmitters that cover nearly all of the state, plus Washington, D.C. and parts of Virginia, West Virginia, Delaware, and Pennsylvania. History WMPB (licensed to Baltimore) first signed on in 1969 as the first station of the Maryland Center for Public Broadcasting; it gained satellite stations in Salisbury, Hagerstown, and Annapolis between 1971 and 1975, resulting in a formation of a statewide public television network. The network adopted its current name in 1984. Maryland Instructional Television (Maryland ITV), a division ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)


.jpg)
.jpg)