|
Common Normal (robotics)
In robotics the common normal of two non-intersecting joint axes is a line perpendicular to both axes. The common normal can be used to characterize robot arm links, by using the "common normal distance" and the angle between the link axes in a plane perpendicular to the common normal. When two consecutive joint axes are parallel, the common normal is not unique and an arbitrary common normal may be used, usually one that passes through the center of a coordinate system.''Foundations of Robotics: Analysis and Control'' by Tsuneo Yoshikawa 1990 page 33 The common normal is widely used in the representation of the frames of reference for robot joints and links, and the selection of minimal representations with the Denavit–Hartenberg parameters. See also * Denavit–Hartenberg parameters * Forward kinematics * Robotic arm A robotic arm is a type of mechanical arm, usually programmable, with similar functions to a human arm; the arm may be the sum total of the mechanism or may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
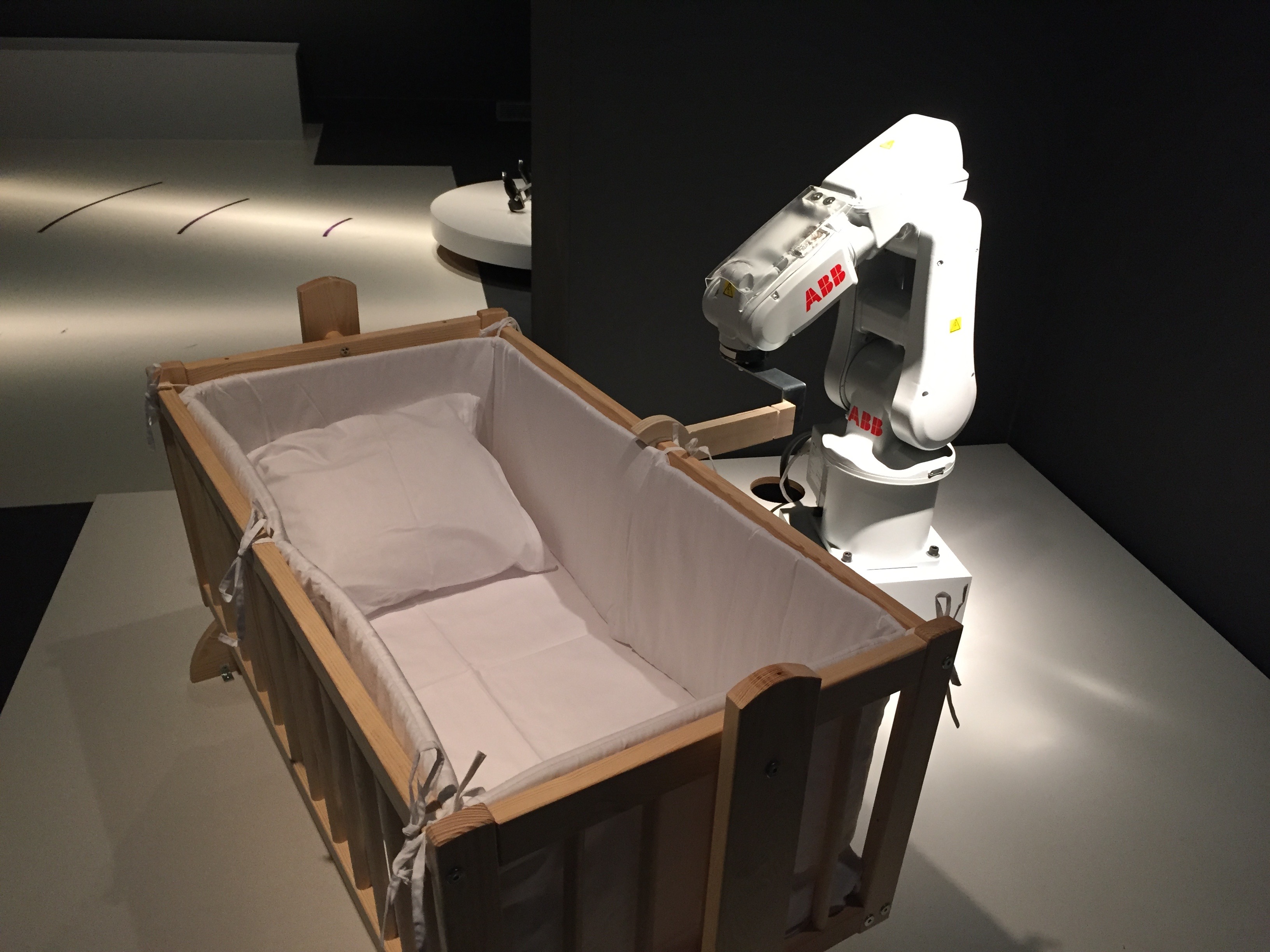
Robot Arm Model 1
A robot is a machine—especially one programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the control may be embedded within. Robots may be constructed to evoke human form, but most robots are task-performing machines, designed with an emphasis on stark functionality, rather than expressive aesthetics. Robots can be autonomous or semi-autonomous and range from humanoids such as Honda's ''Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility'' ( ASIMO) and TOSY's ''TOSY Ping Pong Playing Robot'' ( TOPIO) to industrial robots, medical operating robots, patient assist robots, dog therapy robots, collectively programmed ''swarm'' robots, UAV drones such as General Atomics MQ-1 Predator, and even microscopic nano robots. By mimicking a lifelike appearance or automating movements, a robot may convey a sense of intelligence or thought of its own. Autonomous things are expected to proliferate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotics
Robotics is an interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary branch of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Robotics integrates fields of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, Information engineering (field), information engineering, mechatronics, electronics, bioengineering, computer engineering, control engineering, software engineering, mathematics, etc. Robotics develops machines that can substitute for humans and replicate human actions. Robots can be used in many situations for many purposes, but today many are used in dangerous environments (including inspection of radioactive materials, bomb detection and bomb disposal, deactivation), manufacturing processes, or where humans cannot survive (e.g. in space, underwater, in high heat, and clean up and containment of hazardous materials and radiation). Robots can take any form, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frames Of Reference
In physics and astronomy, a frame of reference (or reference frame) is an abstract coordinate system whose origin, orientation, and scale are specified by a set of reference points― geometric points whose position is identified both mathematically (with numerical coordinate values) and physically (signaled by conventional markers). For ''n'' dimensions, reference points are sufficient to fully define a reference frame. Using rectangular Cartesian coordinates, a reference frame may be defined with a reference point at the origin and a reference point at one unit distance along each of the ''n'' coordinate axes. In Einsteinian relativity, reference frames are used to specify the relationship between a moving observer and the phenomenon under observation. In this context, the term often becomes observational frame of reference (or observational reference frame), which implies that the observer is at rest in the frame, although not necessarily located at its origin. A rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denavit–Hartenberg Parameters
In mechanical engineering, the Denavit–Hartenberg parameters (also called DH parameters) are the four parameters associated with a particular convention for attaching reference frames to the links of a spatial kinematic chain, or robot manipulator. Jacques Denavit and Richard Hartenberg introduced this convention in 1955 in order to standardize the coordinate frames for spatial linkages. Richard Paul demonstrated its value for the kinematic analysis of robotic systems in 1981. While many conventions for attaching reference frames have been developed, the Denavit–Hartenberg convention remains a popular approach. Denavit–Hartenberg convention A commonly used convention for selecting frames of reference in robotics applications is the Denavit and Hartenberg (D–H) convention which was introduced by Jacques Denavit and Richard S. Hartenberg. In this convention, coordinate frames are attached to the joints between two links such that one transformation is associated wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forward Kinematics
In robot kinematics, forward kinematics refers to the use of the kinematic equations of a robot to compute the position of the end-effector from specified values for the joint parameters. The kinematics equations of the robot are used in robotics Robotics is an interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary branch of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist human ..., computer games, and animation. The reverse process, that computes the joint parameters that achieve a specified position of the end-effector, is known as inverse kinematics. Kinematics equations The kinematics equations for the series chain of a robot are obtained using a rigid transformation to characterize the relative movement allowed at each joint and separate rigid transformation to define the dimensions of each link. The result is a sequence of rigid transformation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotic Arm
A robotic arm is a type of mechanical arm, usually programmable, with similar functions to a human arm; the arm may be the sum total of the mechanism or may be part of a more complex robot. The links of such a manipulator are connected by joints allowing either rotational motion (such as in an articulated robot) or translational (linear) displacement. The links of the manipulator can be considered to form a kinematic chain. The terminus of the kinematic chain of the manipulator is called the end effector and it is analogous to the human hand. However, the term "robotic hand" as a synonym of the robotic arm is often proscribed. Types * Cartesian robot / Gantry robot: Used for pick and place work, application of sealant, assembly operations, handling machine tools and arc welding. It is a robot whose arm has three prismatic joints, whose axes are coincident with a Cartesian coordinator. * collaborative robot / Cobot: Cobot applications contrast with traditional industri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |