|
Common Lisp The Language
''Common Lisp the Language'' is a reference book by Guy L. Steele about a set of technical standards and programming languages named Common Lisp. History Before standardizing The first edition (Digital Press, 1984; ; 465 pages) was written by Guy L. Steele Jr., Scott E. Fahlman, Richard P. Gabriel, David A. Moon, and Daniel L. Weinreb. It served as the basis for the Common Lisp technical standard by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), and is thus termed ANSI Common Lisp. During standardizing The second edition (Digital Press, 1990; ; 1029 pages) was written by Guy L. Steele Jr. It reflected the then-current status of the standardizing process and documented important new features such as Common Lisp Object System (CLOS), the loop macro, and conditions. It also has a chapter on series and generators. After standardizing The ANSI Common Lisp standard was published in 1994 and differs from the language dialects described in ''Common Lisp the Language'' (1984) and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Book
A reference work is a work, such as a paper, book or periodical (or their electronic equivalents), to which one can refer for information. The information is intended to be found quickly when needed. Such works are usually ''referred'' to for particular pieces of information, rather than read beginning to end. The writing style used in these works is informative; the authors avoid use of the first person, and emphasize facts. Indices are a common navigation feature in many types of reference works. Many reference works are compiled by a team of contributors whose work is coordinated by one or more editors, rather than by an individual author. Updated editions are usually published as needed, in some cases annually (''Whitaker's Almanack'', '' Who's Who''). Reference works include almanacs, atlases, bibliographies, biographical sources, catalogs such as library catalogs and art catalogs, concordances, dictionaries, directories such as business directories and teleph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialect (computing)
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Most programming languages are text-based formal languages, but they may also be graphical. They are a kind of computer language. The description of a programming language is usually split into the two components of syntax (form) and semantics (meaning), which are usually defined by a formal language. Some languages are defined by a specification document (for example, the C programming language is specified by an ISO Standard) while other languages (such as Perl) have a dominant implementation that is treated as a reference. Some languages have both, with the basic language defined by a standard and extensions taken from the dominant implementation being common. Programming language theory is the subfield of computer science that studies the design, implementation, analysis, characterization, and classification of programming languages. Definitions There are many considerations when defining wha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1984 Non-fiction Books
Events January * January 1 – The Bornean Sultanate of Brunei gains full independence from the United Kingdom, having become a British protectorate in 1888. * January 7 – Brunei becomes the sixth member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). * January 10 ** The United States and the Vatican (Holy See) restore full diplomatic relations. ** The Victoria Agreement is signed, institutionalising the Indian Ocean Commission. *January 24 – Steve Jobs launches the Macintosh personal computer in the United States. February * February 3 ** Dr. John Buster and the research team at Harbor–UCLA Medical Center announce history's first embryo transfer from one woman to another, resulting in a live birth. ** STS-41-B: Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' is launched on the 10th Space Shuttle mission. * February 7 – Astronauts Bruce McCandless II and Robert L. Stewart make the first untethered space walk. * February 8– 19 – The 1984 Winter Olympics are held in Sarajevo, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Lisp Publications
Common may refer to: Places * Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts * Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts * Clapham Common, originally common land, now a park in London, UK * Common Moss, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Lexington Common, a common land area in Lexington, Massachusetts * Salem Common Historic District, a common land area in Salem, Massachusetts People * Common (rapper) (born 1972), American hip hop artist, actor, and poet * Andrew Ainslie Common (born 1841), English amateur astronomer * Andrew Common (born 1889), British shipping director * John Common, American songwriter, musician and singer * Thomas Common (born 1850), Scottish translator and literary critic Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Common'' (film), a 2014 BBC One film, written by Jimmy McGovern, on the UK's Joint Enterprise Law * Dol Common, a character in ''The Alchemist'' by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirror Website
Mirror sites or mirrors are replicas of other websites or any network node. The concept of mirroring applies to network services accessible through any protocol, such as HTTP or FTP. Such sites have different URLs than the original site, but host identical or near-identical content. Mirror sites are often located in a different geographic region than the original, or upstream site. The purpose of mirrors is to reduce network traffic, improve access speed, ensure availability of the original site for technical or political reasons, or provide a real-time backup of the original site. Mirror sites are particularly important in developing countries, where internet access may be slower or less reliable. The maintainers of some mirrors choose not to replicate the entire contents of the upstream server they are mirroring because of technical constraints, or selecting only a subset relevant to their purpose, such as software written in a particular programming language, runnable on a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LaTeX
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latexes are found in nature, but synthetic latexes are common as well. In nature, latex is found as a milky fluid found in 10% of all flowering plants (angiosperms). It is a complex emulsion that coagulates on exposure to air, consisting of proteins, alkaloids, starches, sugars, oils, tannins, resins, and gums. It is usually exuded after tissue injury. In most plants, latex is white, but some have yellow, orange, or scarlet latex. Since the 17th century, latex has been used as a term for the fluid substance in plants, deriving from the Latin word for "liquid". It serves mainly as defense against herbivorous insects. Latex is not to be confused with plant sap; it is a distinct substance, separately produced, and with different functions. The word latex is also used to refer to natural latex rubber, particularly non- vulcanized rubber. Such is the case in products like latex gloves, latex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTML
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript. Web browsers receive HTML documents from a web server or from local storage and render the documents into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page semantically and originally included cues for the appearance of the document. HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages. With HTML constructs, images and other objects such as interactive forms may be embedded into the rendered page. HTML provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, links, quotes, and other items. HTML elements are delineated by ''tags'', written using angle brackets. Tags such as and directly introduce content into the page. Other tags such as sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Lisp HyperSpec
The Common Lisp HyperSpec is a technical standard document written in the hypertext format ''Hypertext Markup Language'' (HTML). It is not the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Common Lisp standard, but is based on it, with permission from ANSI and the International Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS, X3). Originally developed by Kent Pitman at Harlequin, it is now copyrighted by LispWorks Ltd. It is approximately 15 megabytes (MB) of data in 2,300 files which contain approximately 105,000 hyperlinks. The HyperSpec is used by many Common Lisp development environments (examples: LispWorks, the Superior Lisp Interaction Mode for Emacs (SLIME) for looking up reference information on the constructs of ANSI Common Lisp. The HyperSpec is also available for download. Before the ANSI Common Lisp standard, the book '' Common Lisp the Language'' had been used as a Common Lisp standard reference. Allegro Common Lisp Allegro Common Lisp is a programming lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserved Word
In a computer language, a reserved word (also known as a reserved identifier) is a word that cannot be used as an identifier, such as the name of a variable, function, or label – it is "reserved from use". This is a syntactic definition, and a reserved word may have no user-defined meaning. A closely related and often conflated notion is a keyword, which is a word with special meaning in a particular context. This is a semantic definition. By contrast, names in a standard library but not built into the language are not considered reserved words or keywords. The terms "reserved word" and "keyword" are often used interchangeably – one may say that a reserved word is "reserved for use as a keyword" – and formal use varies from language to language; for this article we distinguish as above. In general reserved words and keywords need not coincide, but in most modern languages keywords are a subset of reserved words, as this makes parsing easier, since keywords cannot be confus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
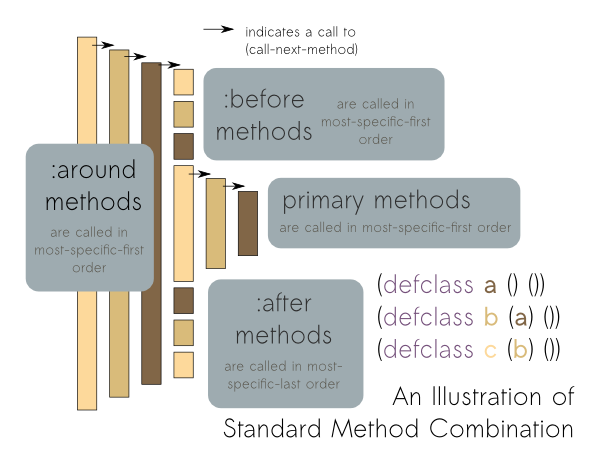
Common Lisp Object System
The Common Lisp Object System (CLOS) is the facility for object-oriented programming which is part of ANSI Common Lisp. CLOS is a powerful dynamic object system which differs radically from the OOP facilities found in more static languages such as C++ or Java. CLOS was inspired by earlier Lisp object systems such as MIT Flavors and CommonLoops, although it is more general than either. Originally proposed as an add-on, CLOS was adopted as part of the ANSI standard for Common Lisp and has been adapted into other Lisp dialects such as EuLisp or Emacs Lisp. Features The basic building blocks of CLOS are methods, classes, instances of those classes, and generic functions. CLOS provides macros to define those: defclass, defmethod, and defgeneric. Instances are created with the method make-instance. Classes can have multiple superclasses, a list of slots (member variables in C++/Java parlance) and a special metaclass. Slots can be allocated by class (all instances of a class sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical Standard
A technical standard is an established norm or requirement for a repeatable technical task which is applied to a common and repeated use of rules, conditions, guidelines or characteristics for products or related processes and production methods, and related management systems practices. A technical standard includes definition of terms; classification of components; delineation of procedures; specification of dimensions, materials, performance, designs, or operations; measurement of quality and quantity in describing materials, processes, products, systems, services, or practices; test methods and sampling procedures; or descriptions of fit and measurements of size or strength. It is usually a formal document that establishes uniform engineering or technical criteria, methods, processes, and practices. In contrast, a custom, convention, company product, corporate standard, and so forth that becomes generally accepted and dominant is often called a ''de facto'' standard. A techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international standards so that American products can be used worldwide. ANSI accredits standards that are developed by representatives of other standards organizations, government agencies, consumer groups, companies, and others. These standards ensure that the characteristics and performance of products are consistent, that people use the same definitions and terms, and that products are tested the same way. ANSI also accredits organizations that carry out product or personnel certification in accordance with requirements defined in international standards. The organization's headquarters are in Washington, D.C. ANSI's operations office is located in New York City. The ANSI annual operatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |