|
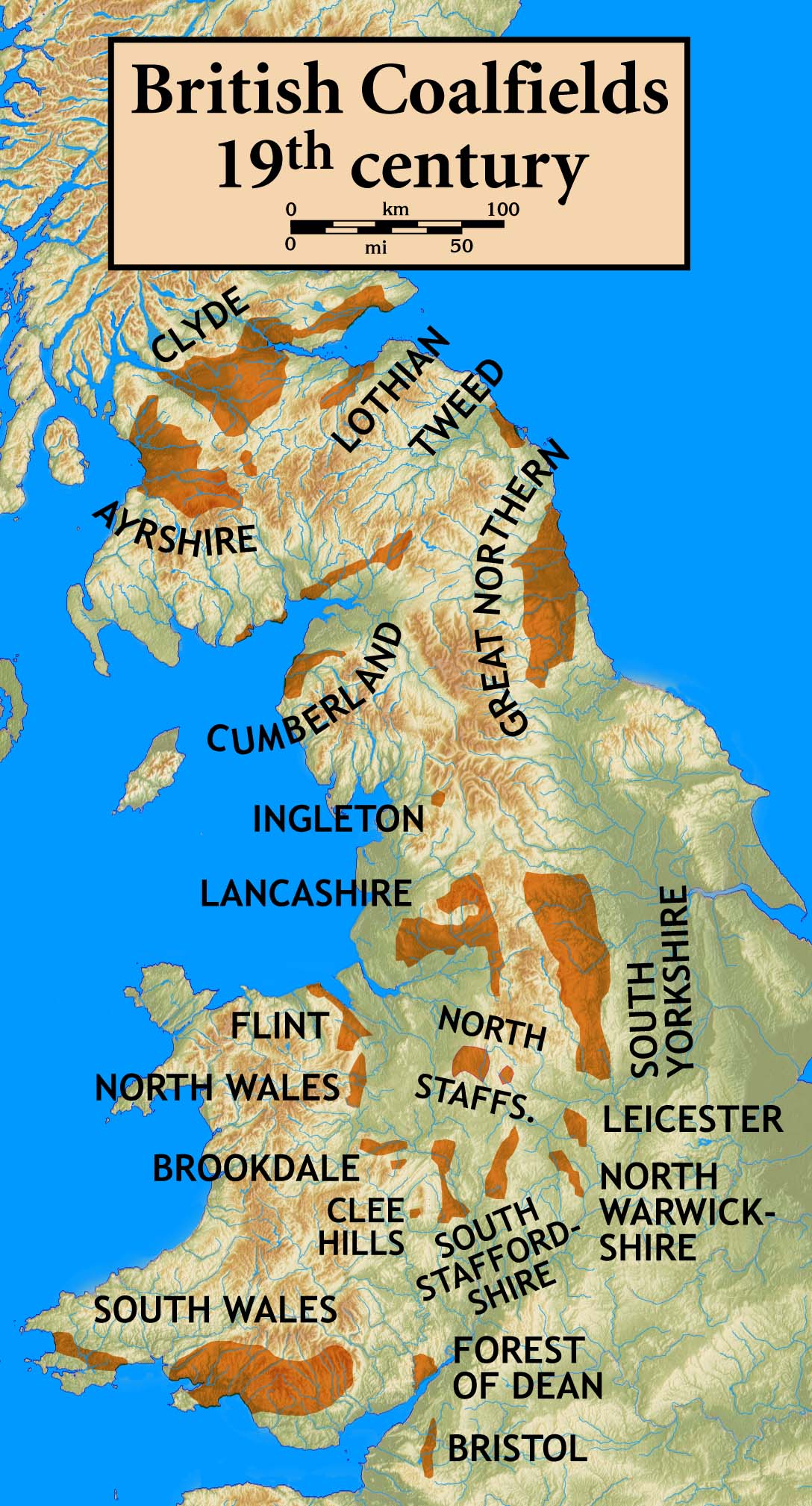
Coal Measures Group
The Coal Measures Group is a lithostratigraphical term coined to refer to the coal-bearing succession of rock strata which occur in the United Kingdom within the Westphalian Stage of the Carboniferous Period. Other than in Northern Ireland the term is now obsolete in formal use and is replaced by the Pennine Coal Measures Group, Scottish Coal Measures Group and the South Wales Coal Measures Group for the three distinct depositional provinces of the British mainland. Pennine Coal Measures Group Within the Pennine Basin the Pennine Coal Measures Group is preceded (underlain) by the Millstone Grit Group which is of Namurian age. It is succeeded (overlain) by the Warwickshire Group which comprises a largely non-productive sequence of red beds. It comprises the: :* Pennine Upper Coal Measures Formation :* Pennine Middle Coal Measures Formation :* Pennine Lower Coal Measures Formation The 'Pennine Basin' includes all of the coalfields of northern England and the English Midlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithostratigraphy
Lithostratigraphy is a sub-discipline of stratigraphy, the geological science associated with the study of strata or rock layers. Major focuses include geochronology, comparative geology, and petrology. In general, strata are primarily igneous or sedimentary relating to how the rock was formed. Sedimentary layers are laid down by deposition of sediment associated with weathering processes, decaying organic matter (biogenic) or through chemical precipitation. These layers are often distinguishable as having many fossils and are important for the study of biostratigraphy. Igneous layers occur as stacks of lava flows, layers of lava fragments (called tephra) both erupted onto the Earth's surface by volcanoes, and in layered intrusions formed deep underground. Igneous layers are generally devoid of fossils and represent magmatic or volcanic activity that occurred during the geologic history of an area. There are a number of principles that are used to explain the appearance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warwickshire Group
The Warwickshire Group is a lithostratigraphic unit of rock strata defined within the British Carboniferous system. Within the Pennine Basin it overlies (i.e. postdates) the Coal Measures Group and is deemed to be of late Westphalian and Stephanian age. In the South Wales Coalfield it consists of the Pennant Sandstone Formation and overlying Grovesend Formation. It contains the youngest Carboniferous rocks in Britain. The name Warwickshire Group is a relatively recent one, replacing a variety of earlier names for the succession of coal-barren red-beds such as Barren Coal Measures and Red Measures which overlie the productive coal measures. It is derived from the Warwickshire Coalfield The Warwickshire Coalfield extends between Warwick and Tamworth in the English Midlands. It is about from north to south and its width is around half that distance. Its western margin is defined by the 'Western Boundary Fault'. In the northeast ... where they achieve their thickest develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Of Dean Coalfield
The Forest of Dean Coalfield, underlying the Forest of Dean, in west Gloucestershire, is one of the smaller coalfields in the British Isles, although intensive mining during the 19th and 20th centuries has had enormous influence on the landscape, history, culture, and economy of the area. For hundreds of years, mining in the Forest of Dean Coalfield has been regulated through a system of freemining, in which individuals who qualify are granted leases to mine specified areas, known as ''gales''. The Coal Industry Nationalisation Act 1946 exempted the Forest of Dean because of its unique form of ownership and history, allowing the unique privilege to continue intact. The last of the big gales closed in 1965 and today only a few small collieries are still operating. Geology and hydrology The Forest of Dean Coalfield formed during Upper Carboniferous times, when the area was a nearshore-intertidal environment of semi-marine estuaries and swamps. The area today is a raised basin pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Coalfield
The Bristol Coalfield is a geologically complex coalfield in the west of England. Comprising the coal-bearing rocks arranged around the Coalpit Heath Syncline and Kingsdown Anticline, it extends beneath the eastern parts of the city of Bristol and northwards through southern Gloucestershire. The coalfield is sometimes referred to together with the Somerset Coalfield, which lies to its south, as the Bristol and Somerset Coalfield. There are also two outlying coal-mining areas, the Severn Coalfield and the Nailsea Basin which are described below. Several coal seams are named in the sequence in the Bristol Coalfield. The seams are listed stratigraphically with the uppermost (youngest) at the head of the list and the lowermost (oldest) at the foot. Not all seams are named, nor are all seams present at any one location. :Upper Coal Measures :* Pensford No 1 :* Pensford No 2 :* Pensford No 3 :* Bromley No 4 :* Bromley No 5 :* Rock Vein of Brislington :* Salridge :* Mangotsfield (?Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Wales Coalfield
The South Wales Coalfield ( cy, Maes glo De Cymru) extends across Pembrokeshire, Carmarthenshire, Swansea, Neath Port Talbot, Bridgend, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Merthyr Tydfil, Caerphilly, Blaenau Gwent and Torfaen. It is rich in coal deposits, especially in the South Wales Valleys. Description It comprises a fully exposed synclinorium with a varying thickness of coal measures (Upper Carboniferous/Pennsylvanian) with thick, workable seams in the lower parts and generally thinner and sparser seams in the upper parts, together with a development of sandstones (Pennant Sandstone). These sandstones have been much used in building construction (including the characteristic terraces of former miners' houses) and give rise to bleak uplands rising 300–600 metres above sea level between the steep-sided valleys in which most deep mines were developed. The coal generally increases in grade or "rank" from east to west, with bituminous coals in the east, and anthracite in the west, mostly to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London-Brabant Massif
The London-Brabant Massif or London-Brabant Platform is, in the tectonic structure of Europe, a structural high or massif that stretches from the Rhineland in western Germany across northern Belgium (in the province of Brabant) and the North Sea to the sites of East Anglia and the middle Thames in southern England. The massif also occurs in the Belgian subsurface, where it is bounded to the northeast by the Roer Valley Graben that runs diagonally through Dutch Limburg. The Midlands Microcraton (southeastern Wales and part of western England) is often considered part of the massif and to reflect this the names Wales–Brabant Massif, Wales–London–Brabant Massif and Wales–Brabant High are sometimes used. The London–Brabant Massif is part of the former microcontinent Avalonia. To the south it borders the Rhenohercynian Zone of the Hercynian orogeny. To the northeast it is flanked by the Anglo-Dutch Basin in the subsurface of the North Sea. At times in geologic history the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglesey Coalfield
The Anglesey Coalfield is a minor British coalfield. Although it is situated in north-west Wales, this isolated coalfield on Anglesey Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island ... is not usually considered to form a part of the North Wales Coalfield which lies in Flintshire and Denbighshire in north-east Wales although both measures were formed during the Carboniferous period. Stretching from Nant and Hirdrefaig in the Pentre Berw area along Cors Ddyga ("Tygai's marsh") and under the sea at Malltraeth village which was called 'yr Iard' or 'Iard Malltraeth'. On the western side of the Afon Cefni lies Cors Malltraeth. It was named after Cwmwd Malltraeth (Commote) which was the old Welsh way of dividing the Isle of Mona by the Welsh Princes and the Church. Both coalfields measure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Wales Coalfield
The North Wales Coalfield comprises the Flintshire Coalfield in the north and the Denbighshire Coalfield in the south. It extends from Point of Ayr in the north, through the Wrexham area to Oswestry in Shropshire in the south. A much smaller area on Anglesey where coal was formerly mined is not usually considered to form a part of the coalfield, although it is geographically in the North Wales region. History In north Wales, the Flintshire manors of Ewloe, Hopedale, and Mostyn and the Denbighshire manor of Brymbo were recorded as making profits from trading coal during the 14th and 15th centuries. By 1593, coal was exported from ports on the Dee estuary. Trade developed swiftly and by 1616, the principal collieries were at Bagillt, Englefield, Leaderbrook, Mostyn, Uphfytton and Wepre. Most were horizontal adits or shallow bell pits, although a few were sufficiently large to have accumulations of water and ventilation problems. In the Denbighshire Coalfield, the areas of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
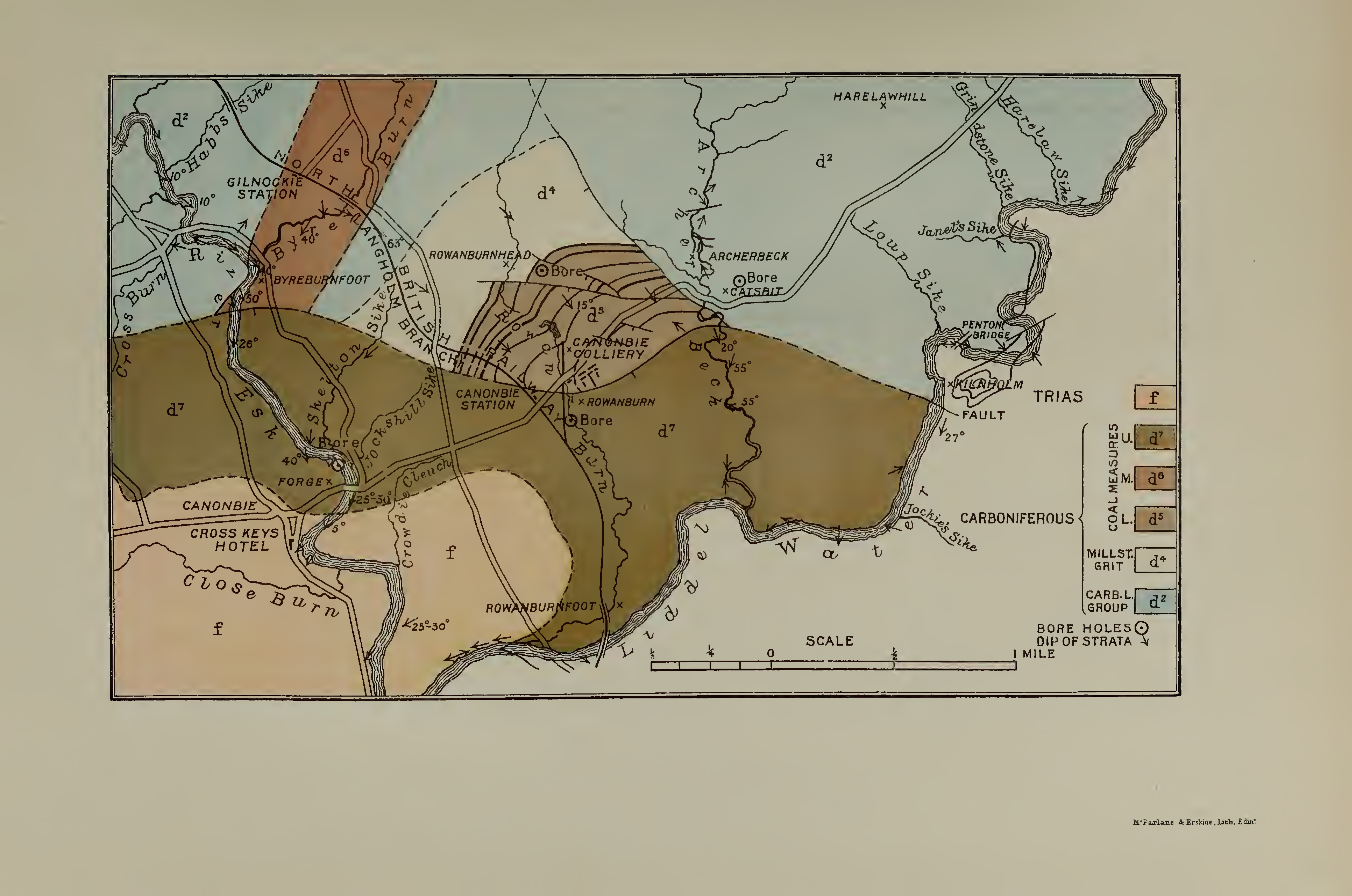
Canonbie Coalfield
The Canonbie Coalfield is a small and largely concealed coalfield at Canonbie in the south of Scotland. A comprehensive survey by Peach and Horne was published in 1903. Canonbie colliery was worked until 1920, and another mine at Archerbeck continued until 1942. Recent work has indicated potentially economically workable reserves beneath a cover of New Red Sandstone rocks. The following coal seams occur within the Pennine Middle Coal Measures Formation in this coalfield: * Knottyholm * Archerbeck * Six Foot * Nine Foot * Five Foot * Eight Foot * Seven Foot Further less important seams lie within the underlying Pennine Lower Coal Measures Formation and within the overlying strata of the Pennine Upper Coal Measures Formation and the Warwickshire Group including the 'High Coal' at the base of the latter. New Proposal In 2014, New Age Exploration Limited proposed a new coal mine in the Canonbie area. They estimated that the new mine could operate for 26 years and yield 1.4 mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Midlands
The Midlands (also referred to as Central England) are a part of England that broadly correspond to the Kingdom of Mercia of the Early Middle Ages, bordered by Wales, Northern England and Southern England. The Midlands were important in the Industrial Revolution of the 18th and 19th centuries. They are split into the West Midlands and East Midlands. The region's biggest city, Birmingham often considered the social, cultural, financial and commercial centre of the Midlands, is the second-largest city and metropolitan area in the United Kingdom. Symbolism A saltire (diagonal cross) may have been used as a symbol of Mercia as early as the reign of Offa. By the 13th century, the saltire had become the attributed arms of the Kingdom of Mercia. The arms are blazoned ''Azure, a saltire Or'', meaning a gold (or yellow) saltire on a blue field. The saltire is used as both a flag and a coat of arms. As a flag, it is flown from Tamworth Castle, the ancient seat of the Mercian Kings, to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |