|
Citrus Pulp
The juice vesicles, also known as citrus kernels (in aggregate, citrus pulp), of a citrus fruit are the membranous content of the fruit's endocarp. The vesicles contain the juice of the fruit and appear shiny and saclike. Vesicles come in two shapes: the superior and inferior, and these are distinct. Citrus fruits with more vesicles generally weigh more than those with fewer vesicles. Fruits with many segments, such as the grapefruit or pomelo, have more vesicles per segment than fruits with fewer segments, such as the kumquat and mandarin. Each vesicle in a segment in citrus fruits has approximately the same shape, size, and weight. About 5% of the weight of an average orange is made up of the membranes of the juice vesicles. Juice vesicles of the endocarp contain the components that provide the aroma typically associated with citrus fruit. These components are also found in the flavedo oil sacs. The vesicles and their inner juices contain many vitamins and minerals as well as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Single Juice Vesicle Of A Shiraz Lime
A, or a, is the first Letter (alphabet), letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''English alphabet#Letter names, a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, ''English articles, a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
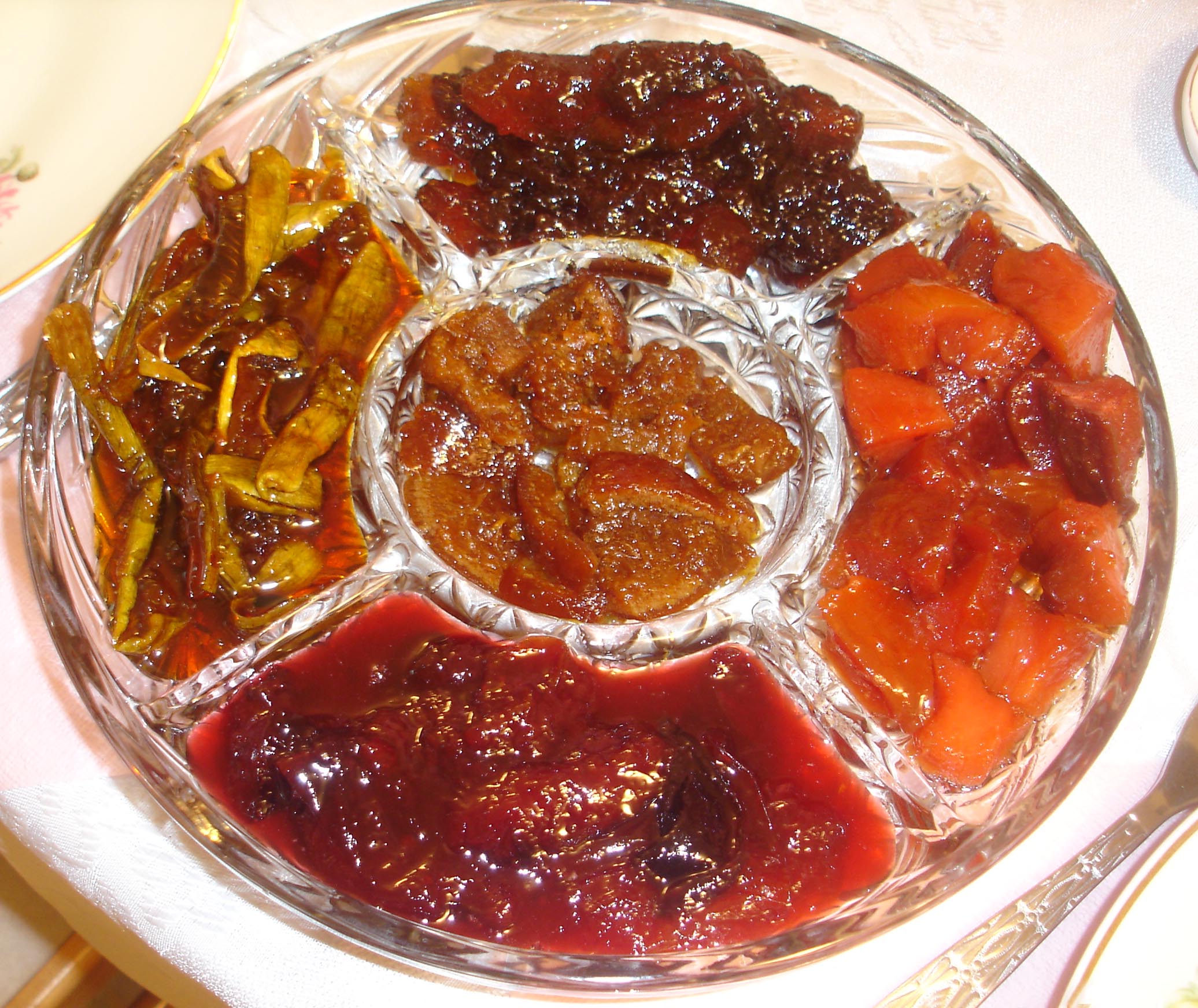
Fruit Preserves
Fruit preserves are preparations of fruits whose main preserving agent is sugar and sometimes acid, often stored in glass jars and used as a condiment or spread. There are many varieties of fruit preserves globally, distinguished by the method of preparation, type of fruit used, and its place in a meal. Sweet fruit preserves such as jams, jellies, and marmalades are often eaten at breakfast with bread or as an ingredient of a pastry or dessert, whereas more savory and acidic preserves made from " vegetable fruits" such as tomato, squash or zucchini, are eaten alongside savory foods such as cheese, cold meats, and curries. Techniques There are several techniques of making jam, with or without added water. One factor depends on the natural pectin content of the ingredients. When making jam with low-pectin fruits like strawberries, high-pectin fruit like orange can be added, or additional pectin in the form of pectin powder, citric acid or citrus peels. Often the fruit will b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
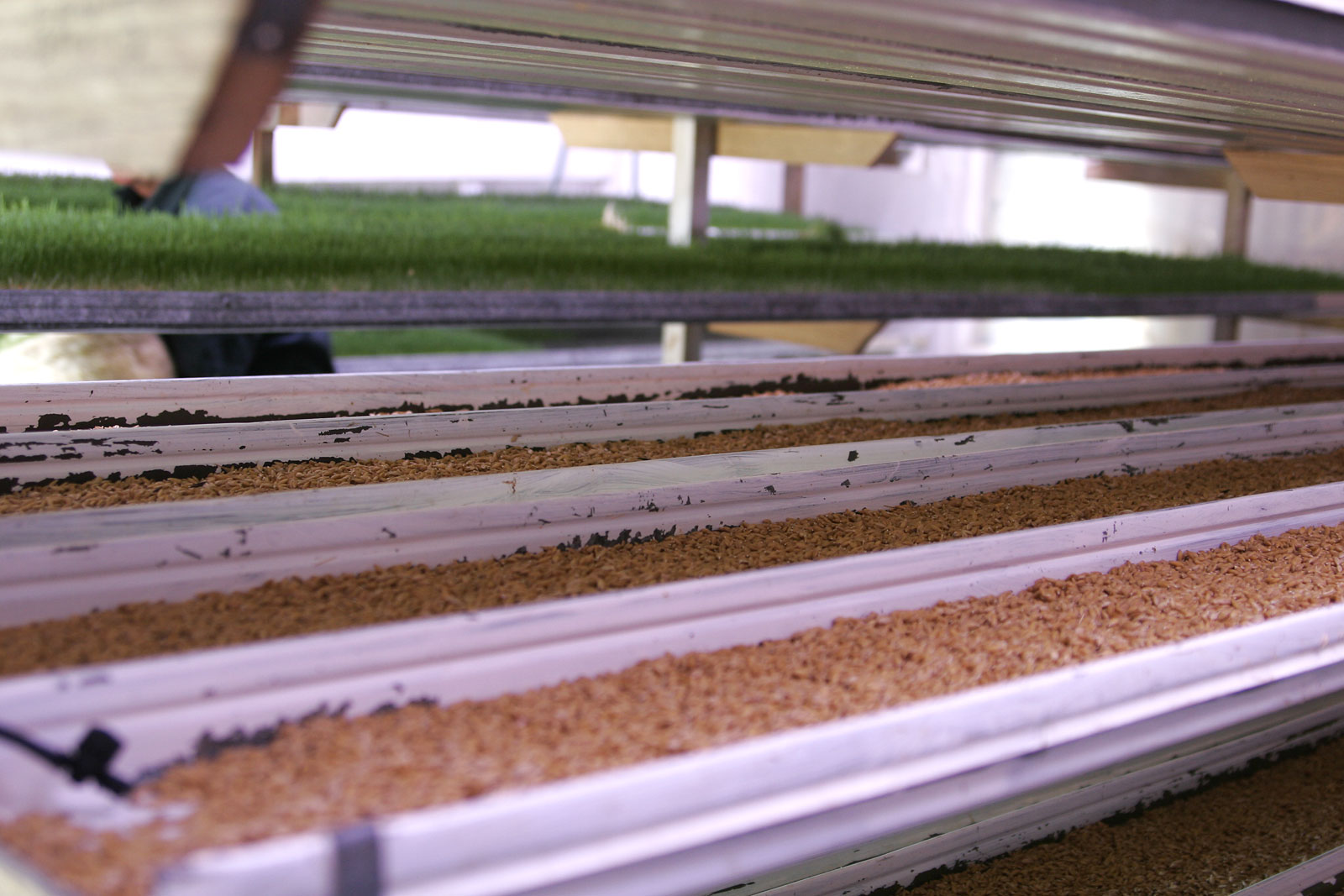
Fodder
Fodder (), also called provender (), is any agriculture, agricultural foodstuff used specifically to feed domesticated livestock, such as cattle, domestic rabbit, rabbits, sheep, horses, chickens and pigs. "Fodder" refers particularly to food given to the animals (including plants cut and carried to them), rather than that which they forage for themselves (called forage). Fodder includes hay, straw, silage, compressed and Compound feed, pelleted feeds, oils and mixed rations, and sprouting, sprouted grains and legumes (such as bean sprouts, fresh malt, or brewing#Brewer's spent grain, spent malt). Most animal feed is from plants, but some manufacturers add ingredients to processed feeds that are of animal origin. The worldwide animal feed trade produced 1.245 billion tons of compound feed in 2022 according to an estimate by the International Feed Industry Federation, with an annual growth rate of about 2%. The use of agricultural land to grow feed rather than human food can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Feed
Animal feed is food given to domestic animals, especially livestock, in the course of animal husbandry. There are two basic types: fodder and forage. Used alone, the word ''feed'' more often refers to fodder. Animal feed is an important input to animal agriculture, and is frequently the main cost of the raising or keeping of animals. Farms typically try to reduce cost for this food, by growing their own, grazing animals, or supplementing expensive feeds with substitutes, such as food waste like spent grain from beer brewing. Animal wellbeing is highly dependent on feed that reflects a well balanced nutrition. Some modern agricultural practices, such as fattening cows on grains or in feed lots, have detrimental effects on the environment and animals. For example, increased corn or other grain in feed for cows, makes their microbiomes more acidic weakening their immune systems and making cows a more likely vector for ''E. coli'', while other feeding practices can improve anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finger Lime - Juice Vesicles - 01
A finger is a prominent digit on the forelimbs of most tetrapod vertebrate animals, especially those with prehensile extremities (i.e. hands) such as humans and other primates. Most tetrapods have five digits (pentadactyly), Chambers 1998 p. 603 Oxford Illustrated pp. 311, 380 and short digits (i.e. significantly shorter than the metacarpal/metatarsals) are typically referred to as toes, while those that are notably elongated are called fingers. In humans, the fingers are flexibly articulated and opposable, serving as an important organ of tactile sensation and fine movements, which are crucial to the dexterity of the hands and the ability to grasp and manipulate objects. Land vertebrate fingers As terrestrial vertebrates were evolved from lobe-finned fish, their forelimbs are phylogenetically equivalent to the pectoral fins of fish. Within the taxa of the terrestrial vertebrates, the basic pentadactyl plan, and thus also the metacarpals and phalanges, undergo many vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Stabilization
Heat stabilization is an additive-free preservation technology for tissue samples which stops degradation and changes immediately and permanently. Heat stabilization uses rapid conductive heating, under controlled pressure, to generate a fast, homogeneous and irreversible thermal denaturation of proteins, resulting in a complete and permanent elimination of all enzymatic activity that would otherwise cause further biological changes to the tissue sample ''ex vivo''. Due to the permanent inactivation of enzymes, heat stabilization overcomes the drawbacks of conventional tissue sample preservation techniques, such as snap-freezing followed by inhibitors. Understanding the role of proteins, peptides and small molecules in normal and diseased tissue is crucial to defining their potential use as drugs, drug targets or disease biomarkers. Yet biological changes begin the moment tissue is removed from its native environment. Dramatic alterations at the molecular level occur within seconds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drum Drying
Drum drying is a method used for drying out liquids from raw materials with a drying drum. In the drum-drying process, pureed raw ingredients are dried at relatively low temperatures over rotating, high-capacity drums that produce sheets of drum-dried product. This product is milled to a finished flake or powder form. Modern drum drying techniques results in dried ingredients which reconstitute immediately and retain much of their original flavor, color and nutritional value. Some advantages of drum drying include the ability to dry viscous foods which cannot be easily dried with other methods. Drum dryers are easy to operate and maintain. Other products where drum drying can be used are, for example, starches, breakfast cereals, baby food Baby food is any soft, easily consumed Human food, food other than breastmilk or infant formula that is made specifically for human babies between six months and two years old. The food comes in many varieties and flavors that are purchased re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasteurization
In food processing, pasteurization (American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), also pasteurisation) is a process of food preservation in which packaged foods (e.g., milk and fruit juices) are treated with mild heat, usually to less than , to eliminate pathogens and extend shelf life. Pasteurization either destroys or deactivates microorganisms and enzymes that contribute to food spoilage or the risk of disease, including vegetative bacteria, but most Endospore, bacterial spores survive the process. Pasteurization is named after the French microbiologist Louis Pasteur, whose research in the 1860s demonstrated that thermal processing would deactivate unwanted microorganisms in wine. Spoilage enzymes are also inactivated during pasteurization. Today, pasteurization is used widely in the dairy industry and other food processing industries for food preservation and food safety. By the year 1999, most liquid products were heat treated in a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectic Enzyme
Pectinases are a group of enzymes that breaks down pectin, a polysaccharide found in plant cell walls, through hydrolysis, transelimination and deesterification reactions. Commonly referred to as pectic enzymes, they include pectolyase, pectozyme, and polygalacturonase, one of the most studied and widely used commercial pectinases. It is useful because pectin is the jelly-like matrix which helps cement plant cells together and in which other cell wall components, such as cellulose fibrils, are embedded. Therefore, pectinase enzymes are commonly used in processes involving the degradation of plant materials, such as speeding up the extraction of fruit juice from fruit, including apples and sapota. Pectinases have also been used in wine production since the 1960s. The function of pectinase in brewing is twofold, first it helps break down the plant (typically fruit) material and so helps the extraction of flavors from the mash. Secondly the presence of pectin in finished wine causes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variety (botany)
In botanical nomenclature, variety (abbreviated var.; in ) is a taxonomic rank below that of species and subspecies, but above that of form. As such, it gets a three-part infraspecific name. It is sometimes recommended that the subspecies rank should be used to recognize geographic distinctiveness, whereas the variety rank is appropriate if the taxon is seen throughout the geographic range of the species. Example The pincushion cactus, ''Escobaria vivipara'', is a wide-ranging variable species occurring from Canada to Mexico, and found throughout New Mexico below about . Nine varieties have been described. Where the varieties of the pincushion cactus meet, they intergrade. The variety ''Escobaria vivipara'' var. ''arizonica'' is from Arizona, while ''Escobaria vivipara'' var. ''neo-mexicana'' is from New Mexico. Definitions The term is defined in different ways by different authors. However, the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants, while recognizing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |