|
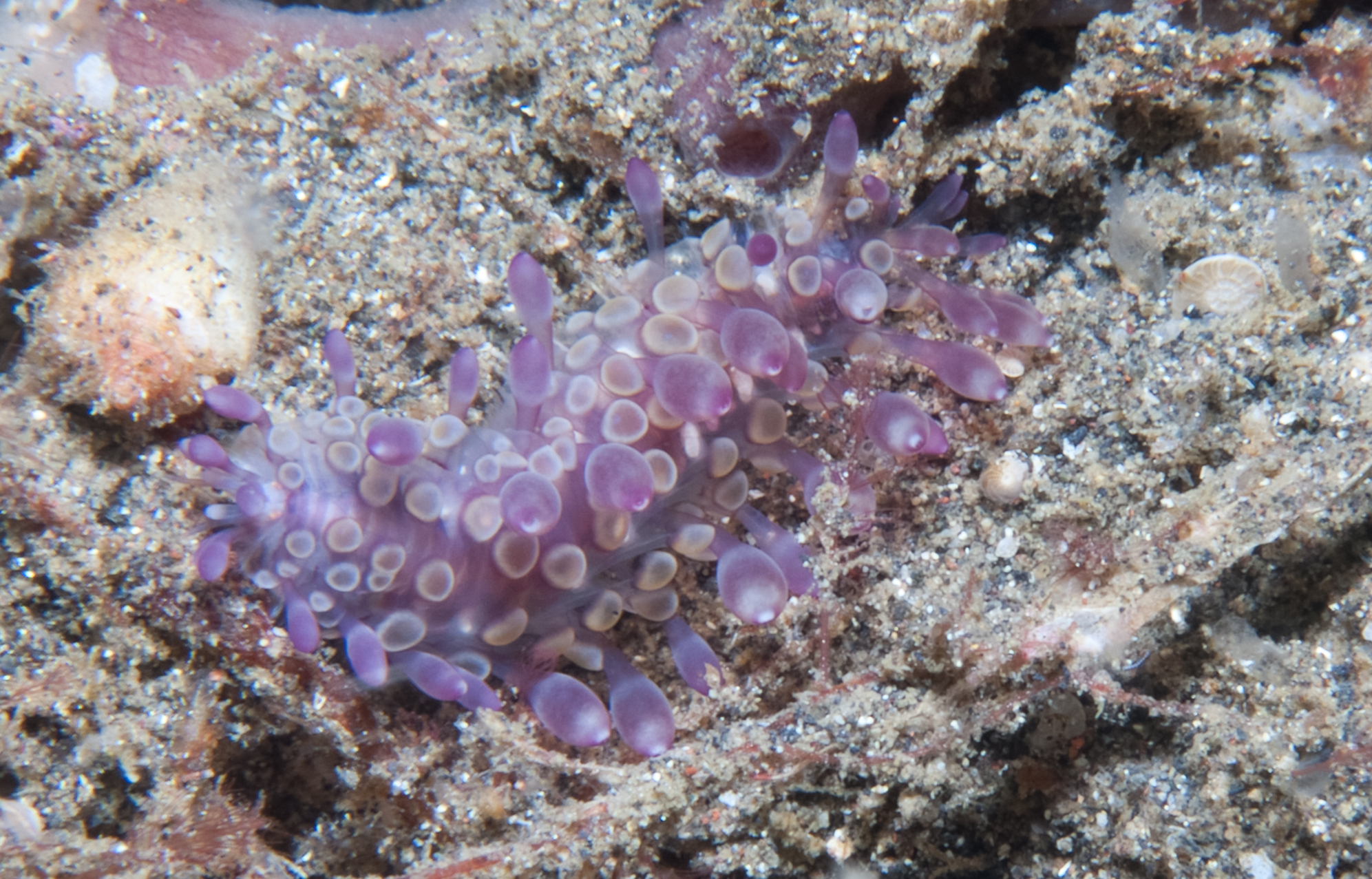
Cirroteuthis Muelleri
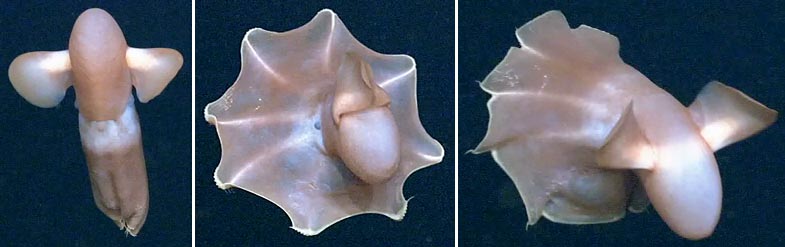
''Cirroteuthis muelleri'' was the first cirrate octopus species (and genus) to be scientifically described (in 1836). It is closely related to the genus ''Cirrothauma'' within the family Cirroteuthidae. At present the genus contains a single recognized species restricted to the Arctic Ocean and northern basins of the Atlantic and Pacific, but other species may be present in the southern hemisphere.Vecchione, M. & R.E. Young 2003''Cirroteuthis'' Eschricht, 1836 The Tree of Life Web Project. Description ''Cirroteuthis muelleri'' can reach a maximum length of 400 mm (mantle length 170 mm). Statements that ''C. muelleri'' reaches up to 1.5 m total length are erroneous (and involve unidentified '' Cirrothauma'', then regarded as ''Cirroteuthis'' sp., being mistakenly assumed to be ''C. muelleri''). It is off white or pale purple, with the inner side of the arms and the webs being brownish-purple. The head has well developed eyes with lenses. The upper and lower beaks are thin and rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Frederik Eschricht
Daniel Frederik Eschricht (18 March 1798 – 22 February 1863) was a Danish zoologist, physiologist, and anatomist known as an authority on whales. He was born in Copenhagen, and studied medicine at Frederiks Hospital, graduating in 1822. He was a student of François Magendie in Paris from 1824-1825, composing a thesis on cranial nerves, after which he studied with prominent European naturalists and anatomists, including Georges Cuvier. He joined the University of Copenhagen in 1829, becoming Professor of Anatomy and Physiology in 1836. The gray whale genus '' Eschrichtius'' was named for him a year after his death. In 1861, Eschricht dissected an orca and found thirteen common porpoises and fourteen seals inside. Jules Verne referred to the incident in the Sargasso chapter of Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea. He was elected as a member of the American Philosophical Society The American Philosophical Society (APS), founded in 1743 in Philadelphia, is a scholarly organiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrothauma
''Cirrothauma'' is a genus of deep water octopuses from the cirrate family Cirroteuthidae. The species ''Cirrothauma'' are fragile, gelatinous deep-sea octopods with a shell, a moderate saddle, and triangular wings. Their eyes either have lenses, as seen in the species ''Cirrothauma murrayi'' or they have reduced eyes without lenses, shown in the other extant species '' Cirrothauma magna''. Both species were placed in ''Cirrothauma'' due to the fact that they possess similar shells. These octopuses have been reported to live in all the world's oceans, except for the Southern Ocean. Species There are two currently recognised species within the genus ''Cirrothauma'' *'' Cirrothauma magna'' ( Hoyle, 1885) *''Cirrothauma murrayi ''Cirrothauma murrayi,'' commonly called the "Blind cirrate octopus," is a nearly blind octopus whose eyes can sense light, but not form images. It has been found worldwide, usually beneath the ocean's surface. Like other cirrates, it has an in ...'' Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirroteuthis Muelleri NOAA
''Cirroteuthis muelleri'' was the first cirrate octopus species (and genus) to be scientifically described (in 1836). It is closely related to the genus ''Cirrothauma'' within the family Cirroteuthidae. At present the genus contains a single recognized species restricted to the Arctic Ocean and northern basins of the Atlantic and Pacific, but other species may be present in the southern hemisphere.Vecchione, M. & R.E. Young 2003''Cirroteuthis'' Eschricht, 1836 The Tree of Life Web Project. Description ''Cirroteuthis muelleri'' can reach a maximum length of 400 mm (mantle length 170 mm). Statements that ''C. muelleri'' reaches up to 1.5 m total length are erroneous (and involve unidentified ''Cirrothauma'', then regarded as ''Cirroteuthis'' sp., being mistakenly assumed to be ''C. muelleri''). It is off white or pale purple, with the inner side of the arms and the webs being brownish-purple. The head has well developed eyes with lenses. The upper and lower beaks are thin and relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boreal Ecosystem
A boreal ecosystem is an ecosystem with a subarctic climate located in the Northern Hemisphere, approximately between 50° to 70°N latitude. These ecosystems are commonly known as taiga and are located in parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. The ecosystems that lie immediately to the south of boreal zones are often called hemiboreal. There are a variety of processes and species that occur in these areas as well. The Köppen symbols of boreal ecosystems are Dfc, Dwc, Dfd, and Dwd. Boreal Species The species within boreal ecosystems varies as it consists of both terrestrial and aquatic habitats. The species composition include many generalized and less specialized feeders. From the equator to the poles, species richness decreases, and there is a negative relationship with species richness changes as climate changes. However, despite not being as biodiverse as tropical systems, this area has a variety of species. Boreal ecosystems are filled with a multitude of flora specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Bed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'. The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of the ocean is very deep, where the seabed is known as the abyssal plain. Seafloor spreading creates mid-ocean ridges along the center line of major ocean basins, where the seabed is slightly shallower than the surrounding abyssal plain. From the abyssal plain, the seabed slopes upward toward the continents and becomes, in order from deep to shallow, the continental rise, slope, and shelf. The depth within the seabed itself, such as the depth down through a sediment core, is known as the “depth below seafloor.” The ecological environment of the seabed and the deepest waters are collectively known, as a habitat for creatures, as the “benthos.” Most of the seabed throughout the world's oceans is covered in layers of marine sediment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submersible
A submersible is a small watercraft designed to operate underwater. The term "submersible" is often used to differentiate from other underwater vessels known as submarines, in that a submarine is a fully self-sufficient craft, capable of independent cruising with its own power supply and air renewal system, whereas a submersible is usually supported by a nearby ship, surface vessel, very large floating structure, platform, shore team or sometimes a larger submarine. In common usage by the general public, however, the word "submarine" may be used to describe a craft that is by the technical definition actually a submersible. There are many types of submersibles, including both crewed and uncrewed craft, otherwise known as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) or unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs). Submersibles have many uses worldwide, such as oceanography, underwater archaeology, ocean exploration, adventure, equipment maintenance and recovery, and underwater videography. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is the world's largest island. It is one of three constituent countries that form the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark and the Faroe Islands; the citizens of these countries are all citizens of Denmark and the European Union. Greenland's capital is Nuuk. Though a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe (specifically Norway and Denmark, the colonial powers) for more than a millennium, beginning in 986.The Fate of Greenland's Vikings , by Dale Mackenzie Brown, ''Archaeological Institute of America'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calanoida
Calanoida is an order of copepods, a group of arthropods commonly found as zooplankton. The order includes around 46 families with about 1800 species of both marine and freshwater copepods between them. Description Calanoids can be distinguished from other planktonic copepods by having first antennae at least half the length of the body and biramous second antennae. However, their most distinctive anatomical trait is the presence of a joint between the fifth and sixth body segments. The largest specimens reach long, but most do not exceed long. Classification Calanoida contains the following families, as well as the genus '' Microdisseta'' (which is currently ''incertae sedis''); * Acartiidae * Aetideidae * Arctokonstantinidae * Arietellidae * Augaptilidae * Bathypontiidae * Calanidae * Calocalanidae * Candaciidae * Centropagidae * Clausocalanidae * Diaixidae * Diaptomidae * Discoidae * Epacteriscidae * Eucalanidae * Euchaetidae * Fosshageniidae * Heterorhabdidae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysidacea
The Mysidacea is a group of shrimp-like crustaceans in the superorder Peracarida, comprising the two extant orders Mysida and Lophogastrida and the prehistoric Pygocephalomorpha The order Pygocephalomorpha is an extinct group of peracarid crustaceans. Pygocephalomorpha were abundant from the Carboniferous until their extinction in the Permian. Families The order contains extinct five families, and seven genera ''incert .... Current data indicate that despite their external similarities, the three orders are not closely related, and the taxon Mysidacea is not used in modern taxonomy. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1208947 Malacostraca Obsolete arthropod taxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopoda
Isopoda is an order of crustaceans that includes woodlice and their relatives. Isopods live in the sea, in fresh water, or on land. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the abdomen that are used in respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax. Isopods have various feeding methods: some eat dead or decaying plant and animal matter, others are grazers, or filter feeders, a few are predators, and some are internal or external parasites, mostly of fish. Aquatic species mostly live on the seabed or bottom of freshwater bodies of water, but some taxa can swim for a short distance. Terrestrial forms move around by crawling and tend to be found in cool, moist places. Some species are able to roll themselves into a ball as a defense mechanism or to conserve moisture. There are over 10,000 identified species of isopod worldwide, with around 4,50 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynoidae
Polynoidae is a family of marine Polychaete worms known as "scale worms" due to the scale-like elytra on the dorsal surface. Almost 900 species are currently recognised belonging to 9 subfamilies and 167 genera. They are active hunters, but generally dwell in protected environments such as under stones. The group is widely distributed from shallow intertidal waters to hadal trenches. They are the most diverse group of polychaetes in terms of genus number and second most diverse in terms of species number which is almost 8% of all segmented worm species. Description Most Polynoidae species are short and flattened, but can reach as much as 20 cm in length and 10 cm width in ''Eulagisca gigantea'' and ''Eulagisca uschakovi''. Individuals are usually covered almost entirely by elytra, which can be shed and regenerated in many species. The elytra of some species are faintly bioluminescent, and leave glowing traces around the mouthparts of their predators, making those preda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopuses
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the center point of the eight limbs. The soft body can radically alter its shape, enabling octopuses to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their eight appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used both for respiration and for locomotion, by expelling a jet of water. Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse of all invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various regions of the ocean, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in the intertidal zone and others at abyssal depths. Most species grow quickly, mature early, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
