|
Church Of The Holy Mother Of God, Donja Kamenica
The Church of the Holy Mother of God ( sr, Црква Свeте Богородице / ''Crkva Svete Bogorodice''; bg, Църква „Света Богородица“, ''Tsarkva „Sveta Bogoroditsa“'') is a medieval Eastern Orthodox church in the village of Donja Kamenica in Knjaževac Municipality, Zaječar District, eastern Serbia. The church is generally considered to have been built in the 14th century, when this area was part of the Second Bulgarian Empire's Vidin appanage, though alternative datings have been proposed. While small, the Church of the Holy Mother of God is notable for its unusual architectural style, in particular for its high narthex flanked by two sharp-pointed towers. These features, which hint at Hungarian or Transylvanian influences, are highly atypical for medieval Bulgarian church architecture. The church is richly decorated on the inside, with as many as eleven frescoes of historical figures. One of these portraits, captioned as a despot, is v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donja Kamenica
Donja Kamenica is a village in the municipality of Knjaževac, Serbia Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar .... According to the 2002 census, the village has a population of 360 people.Popis stanovništva, domaćinstava i Stanova 2002. Knjiga 1: Nacionalna ili etnička pripadnost po naseljima. Republika Srbija, Republički zavod za statistiku Beograd 2003. References Populated places in Zaječar District {{ZaječarRS-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
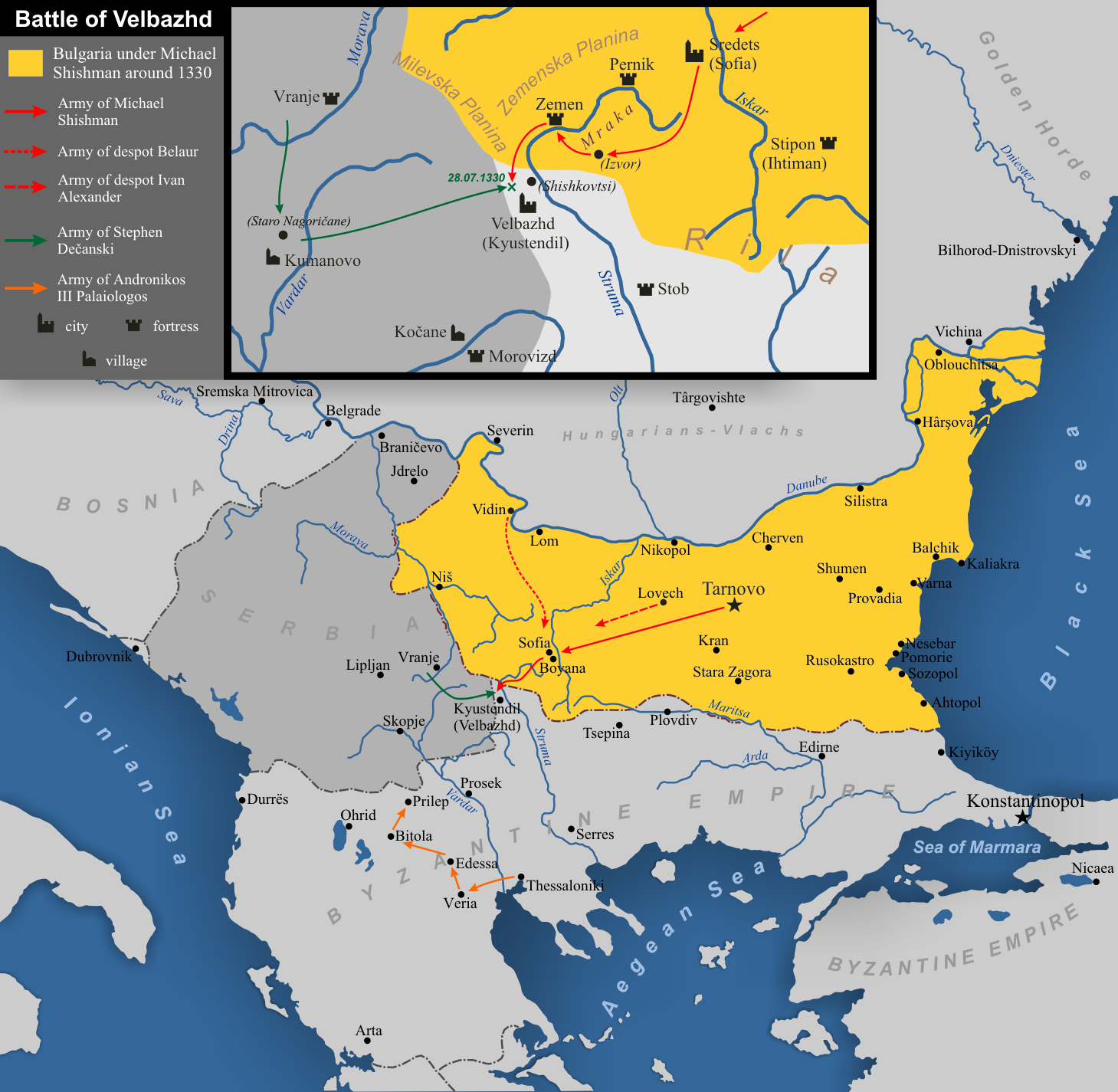
Michael Shishman Of Bulgaria
Michael Asen III ( bg, Михаил Асен III, ''Mihail Asen III'', commonly called Michael Shishman (Михаил Шишман, ''Mihail Šišman'')), ruled as tsar of Bulgaria from 1323 to 1330. The exact year of his birth is unknown but it was between 1280 and 1292. He was the founder of the last ruling dynasty of the Second Bulgarian Empire, the Shishman dynasty. After he was crowned, however, Michael used the name Asen to emphasize his connection with the Asen dynasty, the first one to rule over the Second Empire. An energetic and ambitious ruler, Michael Shishman led an aggressive but opportunistic and inconsistent foreign policy against the Byzantine Empire and the Kingdom of Serbia, which ended in the disastrous Battle of Velbazhd that claimed his own life. He was the last medieval Bulgarian ruler who aimed at military and political hegemony of the Bulgarian Empire over the Balkans and the last one who attempted to seize Constantinople. He was succeeded by his son Ivan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cella
A cella (from Latin for small chamber) or naos (from the Ancient Greek, Greek ναός, "temple") is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek temple, Greek or Roman temple in classical antiquity. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings, of a Monastery, hermit's or monk's cell, and since the 17th century, of a Cell (biology), biological cell in plants or animals. Greek and Roman temples In ancient Greek temple, Greek and Roman temples the cella was a room at the center of the building, usually containing a cult image or statue representing the particular deity venerated in the temple. In addition, the cella may contain a table to receive supplementary votive offerings such as votive statues of associated deities, precious and semi-precious stones, helmets, spear and arrow heads, swords, and war trophy, war trophies. No gatherings or sacrifices took place in the cella as the altar for sacrifices was always located outside the building along the axis and tempora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apse
In architecture, an apse (plural apses; from Latin 'arch, vault' from Ancient Greek 'arch'; sometimes written apsis, plural apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome, also known as an ''exedra''. In Byzantine, Romanesque, and Gothic Christian church (including cathedral and abbey) architecture, the term is applied to a semi-circular or polygonal termination of the main building at the liturgical east end (where the altar is), regardless of the shape of the roof, which may be flat, sloping, domed, or hemispherical. Smaller apses are found elsewhere, especially in shrines. Definition An apse is a semicircular recess, often covered with a hemispherical vault. Commonly, the apse of a church, cathedral or basilica is the semicircular or polygonal termination to the choir or sanctuary, or sometimes at the end of an aisle. Smaller apses are sometimes built in other parts of the church, especially for reliquaries or shrines of saints. Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a matter of controversy and there are a wide variety of forms and specialized terms to describe them. A dome can rest directly upon a Rotunda (architecture), rotunda wall, a Tholobate, drum, or a system of squinches or pendentives used to accommodate the transition in shape from a rectangular or square space to the round or polygonal base of the dome. The dome's apex may be closed or may be open in the form of an Oculus (architecture), oculus, which may itself be covered with a roof lantern and cupola. Domes have a long architectural lineage that extends back into prehistory. Domes were built in ancient Mesopotamia, and they have been found in Persian architecture, Persian, Ancient Greek architecture, Hellenistic, Ancient Roman architecture, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monuments Of Culture Of Great Importance (Serbia)
Immovable Cultural Heritage of Great Importance ( sr, Непокретна културна добра од великог значаја / ''Nepokretna kulturna dobra od velikog značaja'') are those objects of Immovable Cultural Heritage of Serbia, cultural heritage that enjoy the second-highest level of state protection in the Republic of Serbia, behind the Immovable Cultural Heritage of Exceptional Importance (Serbia), Immovable Cultural Heritage of Exceptional Importance. Immovable Cultural Heritage is classified as being of Great Importance upon decision by the National Assembly of Serbia. They are inscribed in the ''Central Register of Immovable cultural property'' maintained by the Institute for the Protection of Cultural Monuments of Serbia. Objects of Immovable cultural heritage have to fulfill one or more of those criteria defined in the ''Law on Cultural Heritage'' of 1994 in order to be categorized as being "of great importance": # importance for a certain area or time-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timok Valley
The Timok Valley ( sr, Тимочка Крајина, Timočka Krajina; bg, Тимошко, Timoshko; ro, Valea Timocului) is a geographical region in east-central Serbia around the Timok River. The Timok Valley corresponds to parts of two Serbian districts ( Bor and Zaječar), with a total 2002 census population of 284,112. Name The Serbian name is derived from the hydronym ''Timok'' and ''krajina'' ("frontier, march"), named such due to its location and history as a borderland. It was introduced in the Interwar period as denoting the Timok confluence with the Negotin Valley and Ključ, which are part of the Timok Valley. The term has no historical or geographical basis. In Romanian, the term "Timoc Valley" () is used for the area inhabited by the Romanian-speaking Vlachs. "Tribalia" is also used in Romanian. The region was sometimes known as Podunavia in Medieval times. Geography The Timok Valley roughly corresponds to the Bor and Zaječar districts of Serbia. It includes si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious leader; he is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians believe he is the incarnation of God the Son and the awaited Messiah (the Christ) prophesied in the Hebrew Bible. Virtually all modern scholars of antiquity agree that Jesus existed historically. Research into the historical Jesus has yielded some uncertainty on the historical reliability of the Gospels and on how closely the Jesus portrayed in the New Testament reflects the historical Jesus, as the only detailed records of Jesus' life are contained in the Gospels. Jesus was a Galilean Jew who was circumcised, was baptized by John the Baptist, began his own ministry and was often referred to as "rabbi". Jesus debated with fellow Jews on ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirot
Pirot ( sr-cyr, Пирот) is a city and the administrative center of the Pirot District in southeastern Serbia. According to 2011 census, the urban area of the city has a population of 38,785, while the population of the city administrative area has 57,928 inhabitants. The city has rich geographical features, including the mountains of Stara Planina, Vlaška Planina, Belava, Suva Planina; rivers which flow through the town, including Nišava, Jerma, Rasnička Reka, Temštica and the Visočica; and four lakes, the Zavoj Lake, Berovacko Lake, Krupac Lake and Sukovo Lake. It also has a rich culture, with notable Orthodox church buildings, including the Church of St. Petka, and the monastery of St. Georges and St. John the Theologian from the late 14th century, both of which display an example of medieval architecture. Pirot is known for its traditional woven carpet, the Pirot carpet (''Pirot ćilim''). Geography The municipality of Pirot covers an area of , with over seventy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trgoviški Timok
The Trgoviški Timok ( sr-cyr, Трговишки Тимок, "Timok of Trgovište") is a river in Serbia, also known as Korenatac (Cyrillic: Коренатац) or Strma river ( sr, Стрма река / ''Strma reka'', "Steep river"). It starts on the western slopes of the Balkan Mountains (Stara Planina mountains), right under the highest peak of the mountain in Serbia, Midžor, less than a kilometer from the Bulgarian border. The river runs to the east, receiving three smaller streams from the other peaks of Balkan mountain range with colorful names (''Babin Zub'' and ''Tri Uši'', Cyrillic: Бабин Зуб and Три Уши, "Oldwife's Tooth" and "Three Ears"). The river passes through the villages of Balta Berilovac, Vrtovac and Inovo. On this reach it receives the Debelička and Ćuštička rivers from the left and the Golaška and Inovska rivers from the right. At the village of Kalna, it is joined by the Stanjanska River, flowing down the northern slopes of the J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulgars, led by Asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)