|
Chiasmal Syndrome
Chiasmal syndrome is the set of signs and symptoms that are associated with lesions of the optic chiasm, manifesting as various impairments of the affected's visual field according to the location of the lesion along the optic nerve. Pituitary adenomas are the most common cause; however, chiasmal syndrome may be caused by cancer, or associated with other medical conditions such as multiple sclerosis and neurofibromatosis. Cause Foroozen divides the causes of chiasmal syndromes into intrinsic and extrinsic causes. Intrinsic implies thickening of the chiasm itself and extrinsic implies compression by another structure. Other less common causes of chiasmal syndrome are metabolic, toxic, traumatic or infectious in nature. Intrinsic etiologies include gliomas and multiple sclerosis. Gliomas of the optic chiasm are usually derived from astrocytes. These tumors are slow growing and more often found children. However, they have a worse prognosis, especially if they have extended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andreas Vesalius
Andreas Vesalius (Latinized from Andries van Wezel) () was a 16th-century anatomist, physician, and author of one of the most influential books on human anatomy, ''De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (''On the fabric of the human body'' ''in seven books''). Vesalius is often referred to as the founder of modern human anatomy. He was born in Brussels, which was then part of the Habsburg Netherlands. He was a professor at the University of Padua (1537–1542) and later became Imperial physician at the court of Emperor Charles V. ''Andreas Vesalius'' is the Latinized form of the Dutch name Andries van Wesel. It was a common practice among European scholars in his time to Latinize their names. His name is also given as ''Andrea Vesalius'', ''André Vésale'', ''Andrea Vesalio'', ''Andreas Vesal'', ''Andrés Vesalio'' and ''Andre Vesale''. Early life and education Vesalius was born as Andries van Wesel to his father Anders van Wesel and mother Isabel Crabbe on 31 December 151 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
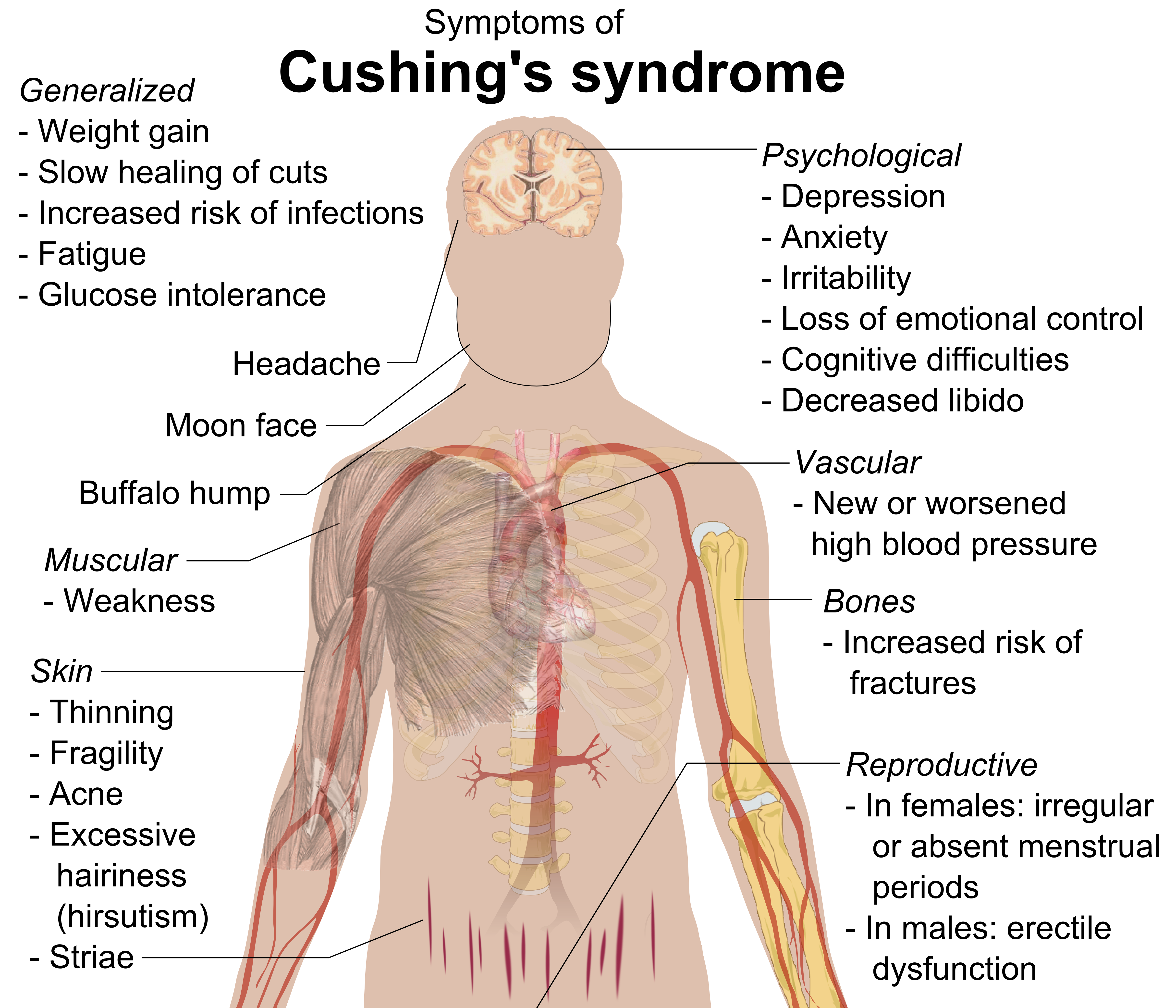
Cushing's Syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a round red face, a fat lump between the shoulders, weak muscles, weak bones, acne, and fragile skin that heals poorly. Women may have more hair and irregular menstruation. Occasionally there may be changes in mood, headaches, and a chronic feeling of tiredness. Cushing's syndrome is caused by either excessive cortisol-like medication, such as prednisone, or a tumor that either produces or results in the production of excessive cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cases due to a pituitary adenoma are known as Cushing's disease, which is the second most common cause of Cushing's syndrome after medication. A number of other tumors, often referred to as ectopic due to their placement outside the pituitary, may also cause Cushing's. Some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axons
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the Soma (biology), nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the peripheral nervous system, periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the Peripheral nervous system, peripheral and Central nervous system, central neurons. Nerve fibers are Axon#Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optic Tract
In neuroanatomy, the optic tract () is a part of the visual system in the brain. It is a continuation of the optic nerve that relays information from the optic chiasm to the ipsilateral lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus. It is composed of two individual tracts, the left optic tract and the right optic tract, each of which conveys visual information exclusive to its respective contralateral half of the visual field. Each of these tracts is derived from a combination of temporal and nasal retinal fibers from each eye that corresponds to one half of the visual field. In more specific terms, the optic tract contains fibers from the ipsilateral temporal hemiretina and contralateral nasal hemiretina. Visual system The optic tract carries retinal information relating to the whole visual field. Specifically, the left optic tract corresponds to the right visual field, while the right optic tract corresponds to the left visual field. To form the ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posteriorly
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragma Sellae
The diaphragma sellae or sellar diaphragm is a flat piece of dura mater with a circular hole allowing the vertical passage of the pituitary stalk. It retains the pituitary gland beneath it in the fossa hypophyseos as it almost completely roofs the fossa hypophyseos of the sella turcica, a part of the sphenoid bone. It has a posterior boundary at the dorsum sellae and an anterior boundary at the tuberculum sellae along with the two small eminences (one on either side) called the middle clinoid processes. The diaphragma sellae is innervated by the first division of the cranial trigeminal nerve. Surgical Significance Violation of the diaphragma sellae during an endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal pituitary tumor resection will result in a cerebrospinal fluid Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates. CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoid Planum
Sphenoid may refer to: * Sphenoid bone The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones ..., a bone in anatomy * Sphenoid (geometry), a tetrahedron with 2-fold mirror or rotation symmetry {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculum Sellae
The tuberculum sellae (or the tubercle of the sella turcica) is a part of the sphenoid bone that is an elevation behind the chiasmatic groove The superior surface of the body of the sphenoid bone is bounded behind by a ridge, which forms the anterior border of a narrow, transverse groove, the chiasmatic groove (optic groove, prechiasmatic sulcus), above and behind which lies the optic c .... A variable slight to prominent median elevation forming the posterior boundary of the chiasmatic groove and the anterior boundary of the hypophysial fossa. Additional Images File:Slide1iiii.JPG, Tuberculum sellae References External links * Diagram at uni-mainz.de Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnoid Layer
The arachnoid mater (or simply arachnoid) is one of the three meninges, the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. It is so named because of its resemblance to a spider web. The arachnoid mater is a derivative of the neural crest mesoectoderm in the embryo. Structure It is interposed between the two other meninges, the more superficial and much thicker dura mater and the deeper pia mater, from which it is separated by the subarachnoid space. The delicate arachnoid layer is not attached to the inside of the dura but against it and surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It does not line the brain down into its sulci (folds), as does the pia mater, with the exception of the longitudinal fissure, which divides the left and right cerebral hemispheres. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows under the arachnoid in the subarachnoid space, within a meshwork of trabeculae which span between the arachnoid and the pia. The arachnoid mater makes arachnoid villi, small pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased intracranial pressure, pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary incontinence, personality changes, or mental impairment. In babies, it may be seen as a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and Parinaud's syndrome, downward pointing of the eyes. Hydrocephalus can occur due to birth defects or be acquired later in life. Associated birth defects include neural tube defects and those that result in aqueductal stenosis. Other causes include meningitis, brain tumors, traumatic brain injury, intraventricular hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. The four types of hydrocephalus are communicating, noncommunicating, ''ex vacuo'', and normal pressure hydrocephalus, normal pressure. Diagnosis is typically made by physical examination and medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplastic
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rathke's Pouch
In embryogenesis, Rathke's pouch is an evagination at the roof of the developing mouth in front of the buccopharyngeal membrane. It gives rise to the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis), a part of the endocrine system. Development Rathke's pouch, and therefore the anterior pituitary, is derived from ectoderm. The pouch eventually loses its connection with the pharynx giving rise to the anterior pituitary. The anterior wall of Rathke's pouch proliferates, filling most of the pouch to form '' pars distalis'' and '' pars tuberalis''. The posterior wall forms '' pars intermedia''. In some organisms, the proliferating anterior wall does not fully occupy Rathke's pouch, leaving a remnant (Rathke's cleft) between the ''pars distalis'' and ''pars intermedia''. Clinical significance Rathke's pouch may develop benign cysts. Craniopharyngioma is a neoplasm which can arise from the epithelium within the cleft. Eponym It is named for Martin Rathke Martin Heinrich Rathke (25 August 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |