|
Chengdu Economic And Technological Development Zone
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the Sichuan Basin and the easternmost part of the Tibetan Plateau between the Jinsha River on the west, the Daba Mountains in the north and the Yungui Plateau to the south. Sichuan's capital city is Chengdu. The population of Sichuan stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai to the northwest, Gansu to the north, Shaanxi to the northeast, Chongqing to the east, Guizhou to the southeast, Yunnan to the south, and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the west. In antiquity, Sichuan was the home of the ancient states of Ba and Shu. Their conquest by Qin strengthened it and paved the way for Qin Shi Huang's unification of China under the Qin dynasty. During the Three Kingdoms era, Liu Bei's state of Shu was based in Sichuan. The area was dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; Simplified Chinese characters, simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu, is a Sub-provincial division, sub-provincial city which serves as the Capital city, capital of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a population of 20,937,757 inhabitants during the 2020 Chinese census, it is the fourth most populous city in China, and it is the only city apart from the four Direct-administered municipalities of China, direct-administered municipalities with a population of over 20 million (the other three are Chongqing, Shanghai and Beijing). It is traditionally the hub in Southwest China. Chengdu is located in central Sichuan. The surrounding Chengdu Plain is known as the "Country of Heaven" () and the "Land of Abundance". Its prehistoric settlers included the Sanxingdui culture. The site of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of China
The provincial level administrative divisions () are the highest-level administrative divisions of China. There are 34 such divisions claimed by the People's Republic of China, classified as 23 provinces (), five autonomous regions, four municipalities and two special administrative regions. The political status of Taiwan Province along with a small fraction of Fujian Province remain in dispute; those are under separate rule by the Republic of China, which is usually referred to as "Taiwan". Every province on Mainland China (including the island province of Hainan) has a Chinese Communist Party (CCP) provincial committee (), headed by a secretary (). The Committee Secretary is effectively in charge of the province, rather than the governor of the provincial government. The same arrangement exists for the autonomous regions and municipalities. Types of provincial level divisions Province The government of each standard province () is nominally led by a provincial committe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tian Xiangli
Tian Xiangli (; born March 1963) is a Chinese politician and the current current party branch secretary of the Sichuan Provincial Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, in office since December 2021. She has background in the Communist Youth League. Previously, she was the head of the United Front Department of Sichuan, and a member of its provincial party standing committee, and before that, Communist Party Secretary of Qinhuangdao, a city in Hebei, and the head of the propaganda department of Hebei province. Early life and education Tian was born in 1963 in Xingtai, Hebei. She graduated with a degree in Chinese at Hebei Teacher's College (later merged into Hebei North University), graduating in 1984. Career in Hebei She then joined the Communist Party of China. She took on local administrative positions in the provincial capital Shijiazhuang before becoming involved with the Communist Youth League organization in the province, serving successivel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khams Tibetan
Khams Tibetan () is the Tibetic languages, Tibetic language used by the majority of the people in Kham. Khams is one of the three branches of the traditional classification of Tibetic languages (the other two being Amdo Tibetan and Ü-Tsang). In terms of mutual intelligibility, Khams could communicate at a basic level with the Ü-Tsang branch (including Lhasa Tibetan). Both Khams Tibetan and Lhasa Tibetan evolve to not preserve the word-initial consonant clusters, which makes them very far from Classical Tibetan, especially when compared to the more Linguistic conservatism, conservative Amdo Tibetan. Also, Kham and Lhasa Tibetan evolved to be tonal language, tonal, which Classical Tibetan was not. Distribution Kham Tibetan is spoken in Kham, which is now divided between the eastern part of Tibet Autonomous Region, the southern part of Qinghai, the western part of Sichuan, and the northwestern part of Yunnan, China. Khampa Tibetan is also spoken by about 1,000 people in two encl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
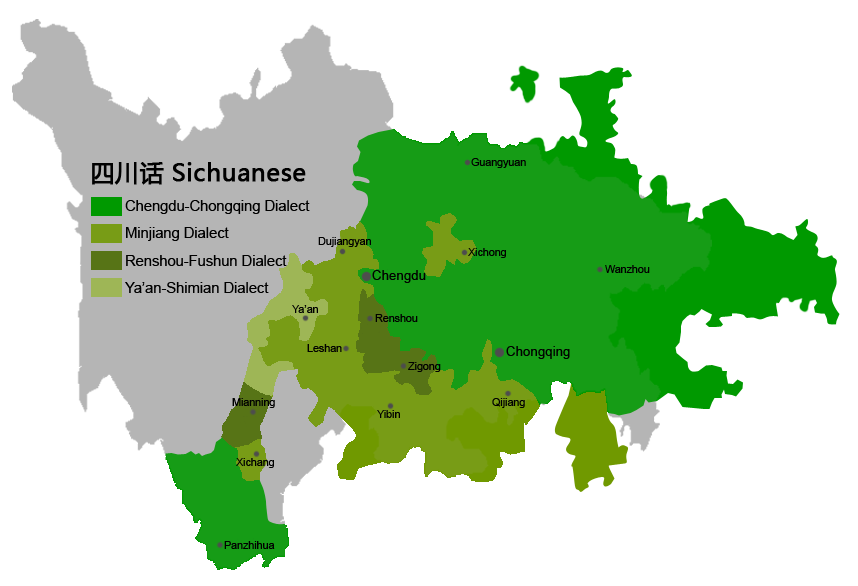
Sichuanese (language)
Sichuanese or Szechwanese ( zh, s=, t= ; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Si4cuan1hua4''; ), also called Sichuanese/Szechwanese Mandarin ( zh, s=四川官话, t=四川官話, p=Sìchuān Guānhuà, links=no) is a branch of Southwestern Mandarin spoken mainly in Sichuan and Chongqing, which was part of Sichuan Province until 1997, and the adjacent regions of their neighboring provinces, such as Hubei, Guizhou, Yunnan, Hunan and Shaanxi. Although "Sichuanese" is often synonymous with the Chengdu-Chongqing dialect, there is still a great amount of diversity among the Sichuanese dialects, some of which are mutually unintelligible with each other. In addition, because Sichuanese is the lingua franca in Sichuan, Chongqing and part of Tibet, it is also used by many Tibetan, Yi, Qiang and other ethnic minority groups as a second language. Sichuanese is more similar to Standard Chinese than southeastern Chinese varieties but is still quite divergent in phonology, vocabulary, and even grammar. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern Mandarin
Southwestern Mandarin (), also known as Upper Yangtze Mandarin (), is a Mandarin Chinese language spoken in much of Southwest China, including in Sichuan, Yunnan, Chongqing, Guizhou, most parts of Hubei, the northwestern part of Hunan, the northern part of Guangxi and some southern parts of Shaanxi and Gansu. Southwestern Mandarin is spoken by roughly 260 million people. If considered a language distinct from central Mandarin, it would be the eighth-most spoken language by native speakers in the world, behind Mandarin itself, Spanish, English, Hindi, Portuguese, Arabic and Bengali. Overview Modern Southwestern Mandarin was formed by the waves of immigrants brought to the regions during the Ming and Qing Dynasties. Because of the comparatively recent move, such dialects show more similarity to modern Standard Mandarin than to other varieties of Chinese like Cantonese or Hokkien. For example, like most Southern Chinese dialects, Southwestern Mandarin does not possess the retroflex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qiang People
The Qiang people ( Qiangic: ''Rrmea''; ) are an ethnic group in China. They form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognised by the People's Republic of China, with a population of approximately 310,000 in 2000. They live mainly in a mountainous region in the northwestern part of Sichuan (Szechwan) on the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Names The modern Qiang refer to themselves as Rma ( or , , ''erma'' in Chinese or ''RRmea'' in Qiang orthography) or a dialect variant of this word. However, they did not define themselves with the Chinese term "Qiang ethnicity" ( zh, 羌族) until 1950, when they were officially designated ''Qiāngzú''. History People called " Qiang" have been mentioned in ancient Chinese texts since 3,000 years ago when they first appeared in oracle bone inscriptions. However, this term was applied to a variety of groups that might not be the same as the modern Qiang. Many of the people formerly designated as "Qiang" were gradually removed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan People
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans live in the Chinese provinces of Gansu, Qinghai, Sichuan, and Yunnan, as well as in India, Nepal, and Bhutan. Tibetan languages belong to the Tibeto-Burman language group. The traditional or mythological explanation of the Tibetan people's origin is that they are the descendants of the human Pha Trelgen Changchup Sempa and rock ogress Ma Drag Sinmo. It is thought that most of the Tibeto-Burman speakers in Southwest China, including Tibetans, are direct descendants from the ancient Qiang people. Most Tibetans practice Tibetan Buddhism, although some observe the indigenous Bon religion and there is a small Muslim minority. Tibetan Buddhism influences Tibetan art, drama and architecture, while the harsh geography of Tibet has produced an adap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yi People
The Yi or Nuosu people,; zh, c=彝族, p=Yízú, l=Yi ethnicity historically known as the Lolo,; vi, Lô Lô; th, โล-โล, Lo-Lo are an ethnic group An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ... in China, Vietnam, and Thailand. Numbering nine million people, they are the seventh largest of the 55 Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. They live primarily in rural areas of Sichuan, Yunnan, Guizhou, and Guangxi, usually in mountainous regions. The Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture is home to the largest population of Yi people within mainland China, with two million Yi people in the region. For other countries, as of 1999, there were 3,300 Mantsi language, Mantsi-speaking Lô Lô people living in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive varieties of the Chinese language. The estimated 1.4 billion Han Chinese people, worldwide, are primarily concentrated in the People's Republic of China (including Mainland China, Hong Kong and Macau) where they make up about 92% of the total population. In the Republic of China (Taiwan), they make up about 97% of the population. People of Han Chinese descent also make up around 75% of the total population of Singapore. Originating from Northern China, the Han Chinese trace their cultural ancestry to the Huaxia, the confederation of agricultural tribes living along the Yellow River. This collective Neolithic confederation included agricultural tribes Hua and Xia, hence the name. They settled along the Central Plains around the middle and lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chinese Administrative Divisions By Population Density
The provincial level administrative divisions () are the highest-level administrative divisions of China. There are 34 such divisions claimed by the People's Republic of China, classified as 23 provinces (), five autonomous regions, four municipalities and two special administrative regions. The political status of Taiwan Province along with a small fraction of Fujian Province remain in dispute; those are under separate rule by the Republic of China, which is usually referred to as "Taiwan". Every province on Mainland China (including the island province of Hainan) has a Chinese Communist Party (CCP) provincial committee (), headed by a secretary (). The Committee Secretary is effectively in charge of the province, rather than the governor of the provincial government. The same arrangement exists for the autonomous regions and municipalities. Types of provincial level divisions Province The government of each standard province () is nominally led by a provincial committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chinese Administrative Divisions By Population
This is a list of Chinese administrative divisions in order of their total resident populations. It includes all provinces, autonomous regions, direct-controlled municipalities and special administrative regions controlled by the Republic of China (1912–1949) or the People's Republic of China (1949–present). For the Republic of China after 1949, see List of administrative divisions of Taiwan. Census data Current population References Footnotes Sources {{DEFAULTSORT:Chinese Administrative Divisions By Population Population Population Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ... Demographic lists China, population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |