|
Cheng's Jird
Cheng's jird (''Meriones chengi'') is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It was named in honour of the Chinese zoologist Professor Tso-hsin Cheng. It is found only in the Turpan Depression of eastern Xinjiang, China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and .... References Meriones (rodent) Rodents of China Mammals described in 1964 Endemic fauna of China Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Meriones-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/richochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Rabbits, hares, and pikas, whose i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muridae
The Muridae, or murids, are the largest family of rodents and of mammals, containing approximately 1,383 species, including many species of mice, rats, and gerbils found naturally throughout Eurasia, Africa, and Australia. The name Muridae comes from the Latin ' (genitive '), meaning "mouse", since all true mice belong to the family, with the more typical mice belonging to the genus '' Mus''. Distribution and habitat Murids are found nearly everywhere in the world, though many subfamilies have narrower ranges. Murids are not found in Antarctica or many oceanic islands. Although none of them are native to the Americas, a few species, notably the house mouse and black rat, have been introduced worldwide. Murids occupy a broad range of ecosystems from tropical forests to tundras. Fossorial, arboreal, and semiaquatic murid species occur, though most are terrestrial animals. The extensive list of niches filled by murids helps to explain their relative abundance. Diet and dentiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tso-hsin Cheng
Tso-hsin Cheng (郑作新 also transcribed as Zheng Zuoxin) (18 November 1906 – 27 June 1998) was a Chinese ornithologist known for his seminal work on the birds of China and mentoring a generation of researchers. Educated in the United States, he chose to stay in China after the Second World War while many of his academic colleagues moved to Taiwan. He was severely punished during the Cultural Revolution despite being a member of the Communist Party. Biography Early life Cheng was born in Fujian on November 18, 1906, and grew up with an interest in the local birds. His mother died of tuberculosis when he was very young and he was taken care of mostly by his grandmother. His father was one of the few Chinese with a higher education and knew English. His father taught him to speak English. As a young boy he was weak and his father encouraged the boy to take up sports. Cheng hiked in the mountains, played tennis and even became a champion 100 m sprinter. His early naturalist int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
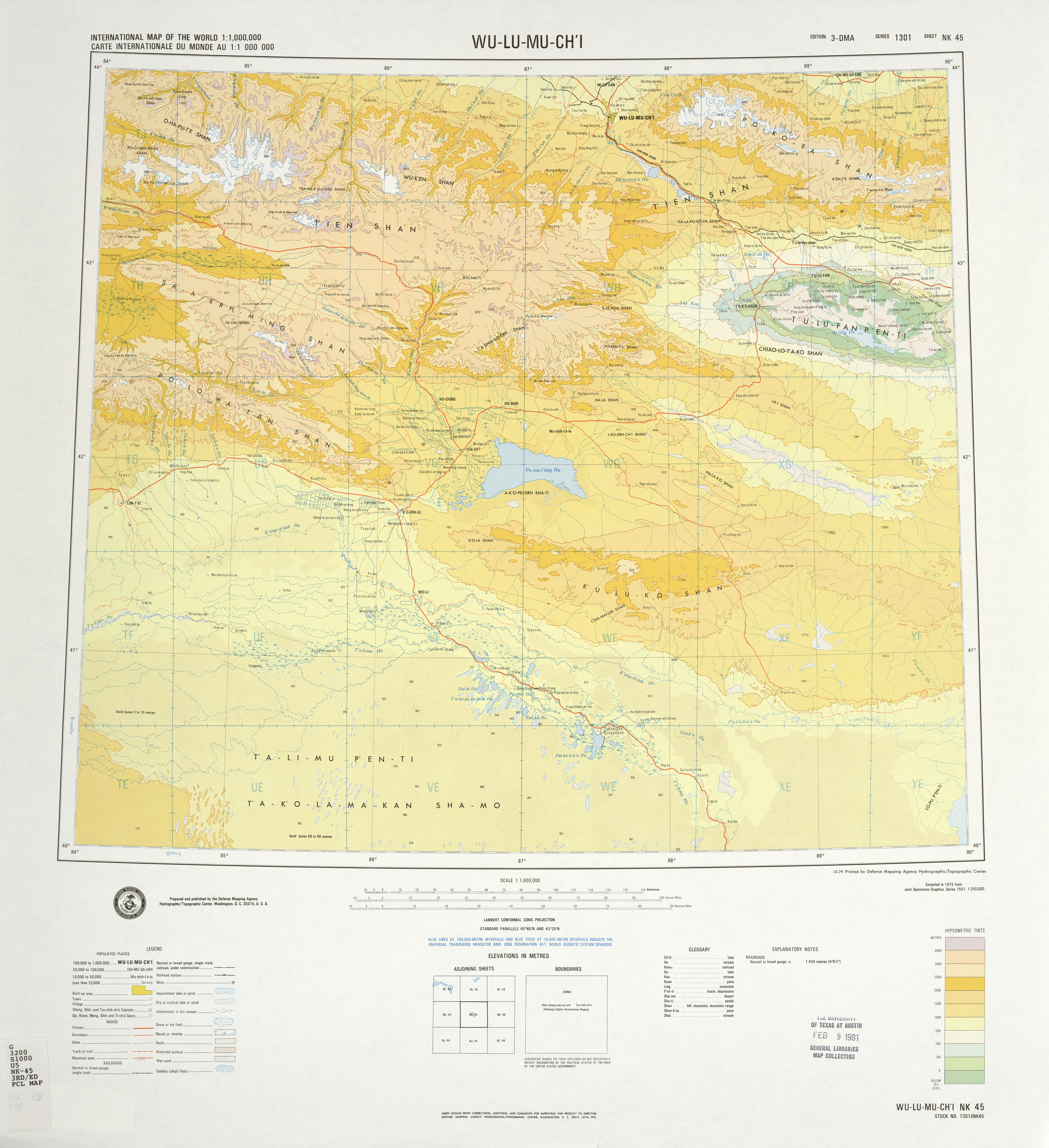
Turpan Depression
The Turpan Depression or Turfan Depression, is a fault (geology), fault-bounded trough located around and south of the city-oasis of Turpan, in the Xinjiang, Xinjiang Autonomous Region in far Western China, about southeast of the regional capital Ürümqi. It includes Lake Ayding, , the List of places on land with elevations below sea level, second or third lowest Depression (geology), depression on Earth. By some measures, it is also the hottest and driest area in China during the summer. Geology and relief The Turpan Basin is a fault-bounded trough located in the eastern part of the Tian Shan. It covers an area of . The surrounding mountain ranges are: the central Tian Shan in the west, the Bogda Shan in the north-west, the Haerlike Shan in the north-west, and the Jueluotage Shan in the south. Beyond the surrounding mountain ranges lie the Dzungaria, Junggar Basin in the north and the Tarim Basin in the south. Some geographers also use the term Turpan-Hami Basin, which is un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest of the country at the crossroads of Central Asia and East Asia. Being the largest province-level division of China by area and the 8th-largest country subdivision in the world, Xinjiang spans over and has about 25 million inhabitants. Xinjiang borders the countries of Mongolia, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India. The rugged Karakoram, Kunlun and Tian Shan mountain ranges occupy much of Xinjiang's borders, as well as its western and southern regions. The Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions, both administered by China, are claimed by India. Xinjiang also borders the Tibet Autonomous Region and the provinces of Gansu and Qinghai. The most well-known route of the historic Silk Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meriones (rodent)
''Meriones'' is a rodent genus that includes the gerbil most commonly kept as a pet, ''Meriones unguiculatus''. The genus contains most animals referred to as jirds, but members of the genera ''Sekeetamys'', ''Brachiones'', and sometimes ''Pachyuromys'' are also known as jirds. The distribution of ''Meriones'' ranges from northern Africa to Mongolia. ''Meriones'' jirds tend to inhabit arid regions including clay desert, sandy desert, and steppe, but are also in slightly wetter regions, and are an agriculture, agricultural pest (organism), pest. The genus was named by Johann Karl Wilhelm Illiger, Illiger in 1811, deriving from the Greek word ''μηρος'' (femur). However the name is shared with Greek warrior Meriones (mythology), Meriones in Homer's ''Iliad'' which has brought confusion to the meaning of the scientific names, specially for the popular pet Mongolian gerbil. Description Adult ''Meriones'' species range in size from 9 to 18 cm (head and body), with tails equal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodents Of China
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/richochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Rabbits, hares, and pikas, whose incisors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Described In 1964
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Fauna Of China
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)