|
Chen Tuan
Chen Tuan 陳摶 (allegedly October 10, 871 – July 22, 989) was a Chinese Taoist credited with creation of the kung fu system Liuhebafa ("Six Harmonies and Eight Methods"). Along with this internal art, he is also said to be associated with a method of qi (energy) cultivation known today as Taiji ruler and a 24-season Daoyin method (''ershisi shi daoyin fa'') using seated and standing exercises designed to prevent diseases that occur during seasonal changes throughout the year. Name and titles The character "Tuan" (摶) is sometimes confused with the very similar-looking character "Bo" (搏), thus the name is sometimes incorrectly romanized as Chen Bo or Chen Po. In Chinese, he is often respectfully referred to as "Aged Ancestor Chen Tuan" (陳摶老祖 Chén Tuán Lǎozǔ) and "Ancestral Teacher Xiyi" (希夷祖師 Xīyí Zǔshī). Chen Tuan, styled Tunan, titled himself Fuyao Zi (one soaring upward in the high sky, from Nan Hua Jing written by Zhuangzi). Known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasegawa Tōhaku
was a Japanese painter and founder of the Hasegawa school. He is considered one of the great painters of the Azuchi–Momoyama period (1573-1603), and he is best known for his folding screens, such as ''Pine Trees'' and ''Pine Tree and Flowering Plants'' (both registered National Treasures), or the paintings in walls and sliding doors at Chishaku-in, attributed to him and his son (also National Treasures). Biography Hasegawa Tōhaku, born in 1539 in Nanao,"Suiboku-ga." Encyclopædia Britannica Online. December 10, 2009 a town in (in the vicinity of present-day Ishikawa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The dynasty is divided into two periods: Northern Song and Southern Song. During the Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now Eastern China. The Southern Song (; 1127–1279) refers to the period after the Song lost control of its northern half to the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in the Jin–Song Wars. At that time, the Song court retreated south of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
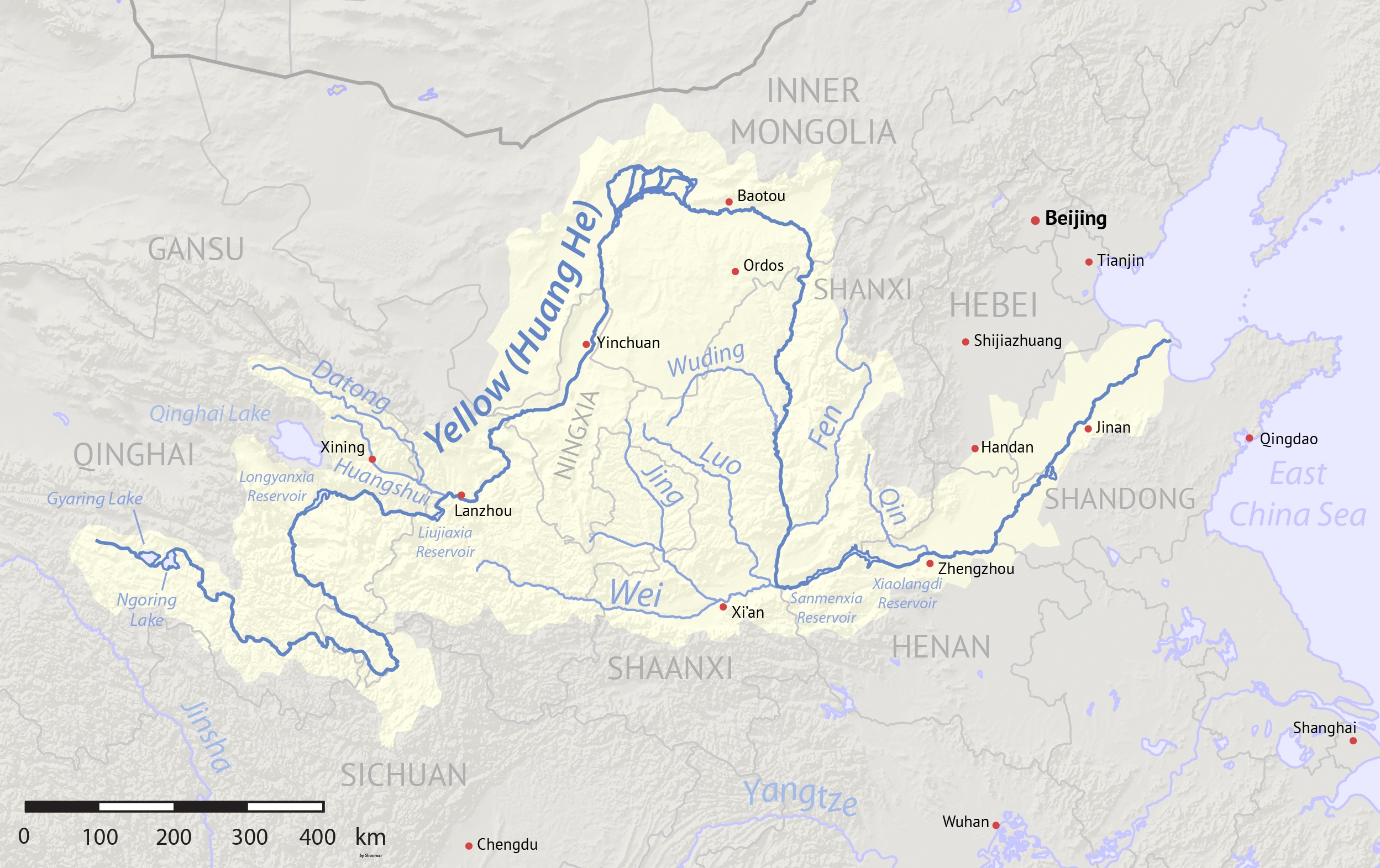
Yellow River Map
The Yellow River Map, Scheme, or Diagram, also known by its Chinese name as the Hetu, is an ancient Chinese diagram that appears in myths concerning the invention of writing by Cangjie and other culture heroes. It is usually paired with the Luoshu Squarenamed in reference to the Yellow River's Luo tributaryand used with the Luoshu in various contexts involving Chinese geomancy, numerology, philosophy, and early natural science. Geographical background The Yellow River (Chinese: ''Huang He'') flows from the Tibetan Plateau to the Bay of Bohai over a course of , making it the second-longest river in Asia and the sixth-longest in the world. Its ancient name was simply ''He'' before that character was broadened to be used in reference to most moderately sized rivers. The River Map has thus always been understood to be particularly in reference to the Yellow River and sometimes taken as a diagram of its course or the forces acting upon it. Astrological background T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yi Jing
The ''I Ching'' or ''Yi Jing'' (, ), usually translated ''Book of Changes'' or ''Classic of Changes'', is an ancient Chinese divination text that is among the oldest of the Chinese classics. Originally a divination manual in the Western Zhou period (1000750), the ''I Ching'' was transformed over the course of the Warring States and early imperial periods (500200) into a cosmological text with a series of philosophical commentaries known as the "Ten Wings". After becoming part of the Five Classics in the 2nd century BC, the ''I Ching'' was the subject of scholarly commentary and the basis for divination practice for centuries across the Far East, and eventually took on an influential role in Western understanding of East Asian philosophical thought. As a divination text, the ''I Ching'' is used for a traditional Chinese form of cleromancy known as ''I Ching'' divination, in which bundles of yarrow stalks are manipulated to produce sets of six apparently random numbers rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or a way of life, Confucianism developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius (551–479 BCE). Confucius considered himself a transmitter of cultural values inherited from the Xia (c. 2070–1600 BCE), Shang (c. 1600–1046 BCE) and Western Zhou dynasties (c. 1046–771 BCE). Confucianism was suppressed during the Legalist and autocratic Qin dynasty (221–206 BCE), but survived. During the Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE), Confucian approaches edged out the "proto-Taoist" Huang–Lao as the official ideology, while the emperors mixed both with the realist techniques of Legalism. A Confucian revival began during the Tang dynasty (618–907 CE). In the late Tang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
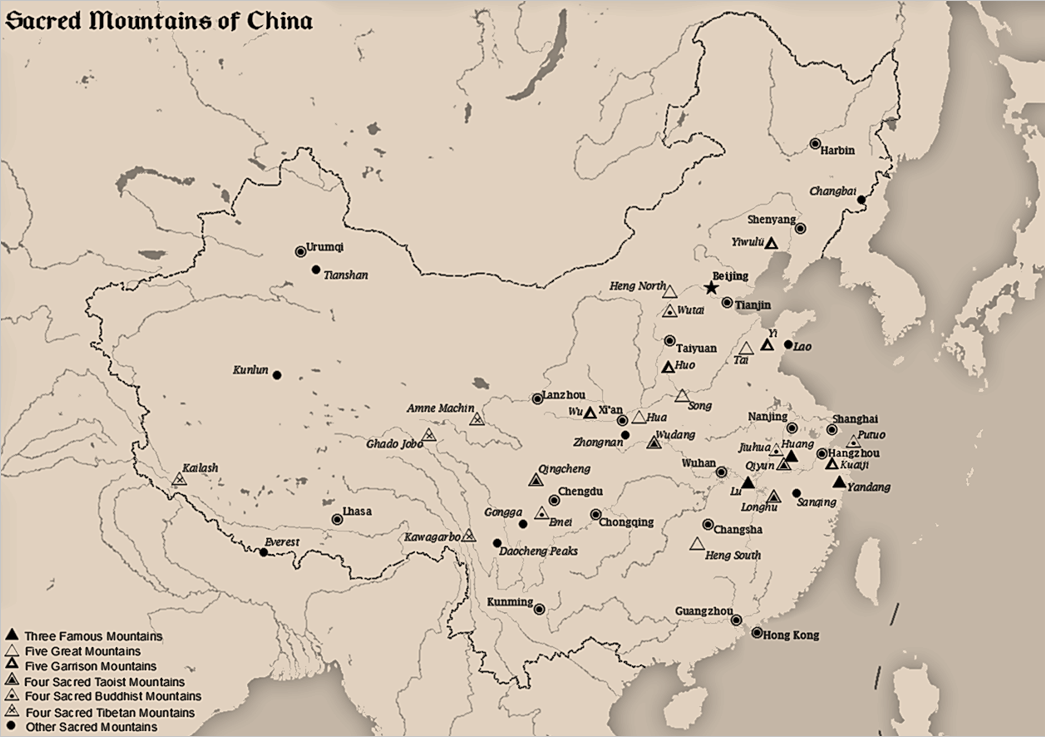
Sacred Mountains Of China
The Sacred Mountains of China are divided into several groups. The ''Five Great Mountains'' () refers to five of the most renowned mountains in Chinese history, and they were the subjects of imperial pilgrimage by emperors throughout ages. They are associated with the supreme God of Heaven and the five main cosmic deities of Chinese traditional religion. The group associated with Buddhism is referred to as the ''Four Sacred Mountains of Buddhism'' (), and the group associated with Taoism is referred to as the ''Four Sacred Mountains of Taoism'' (). The sacred mountains have all been important destinations for pilgrimage, the Chinese expression for pilgrimage () being a shortened version of an expression which means ''"paying respect to a holy mountain"'' (). The Five Great Mountains The ''Five Great Mountains'' or ''Wuyue'' are arranged according to the five cardinal directions of Chinese geomancy, which includes the center as a direction. The grouping of the five mountains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Hua
Mount Hua () is a mountain located near the city of Huayin in Shaanxi Province, about east of Xi'an. It is the "Western Mountain" of the Five Great Mountains of China and has a long history of religious significance. Originally classified as having three peaks, in modern times the mountain is classified as five main peaks, the highest of which is the South Peak at . Geography Mount Hua is situated in Huayin City, which is 120 kilometres (about 75 miles) from Xi'an. It is located near the southeast corner of the Ordos Loop section of the Yellow River basin, south of the Wei River valley, at the eastern end of the Qin Mountains, in Southern Shaanxi Province. It is part of the Qinling or Qin Mountains, which divide not only northern and southern Shaanxi, but also China. Summits Traditionally, only the giant plateau with its summits to the south of the peak Wuyun Feng (, Five Cloud Summit) was called Taihua Shan (, Great Flower Mountain). It could only be accessed through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Later Zhou Dynasty
Zhou, known as the Later Zhou (; ) in historiography, was a short-lived Chinese imperial dynasty and the last of the Five Dynasties that controlled most of northern China during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Founded by Guo Wei (Emperor Taizu), it was preceded by the Later Han dynasty and succeeded by the Northern Song dynasty. Founding of the dynasty Guo Wei, a Han Chinese, served as the Assistant Military Commissioner at the court of the Later Han, a regime ruled by Shatuo Turks. Liu Chengyou came to the throne of the Later Han in 948 after the death of the founding emperor, Gaozu. Guo Wei led a successful coup against the teenage emperor and then declared himself emperor of the new Later Zhou on New Year's Day in 951. Rule of Guo Wei Guo Wei, posthumously known as Emperor Taizu of Later Zhou, was the first Han Chinese ruler of northern China since 923. He is regarded as an able leader who attempted reforms designed to alleviate burdens faced by the peas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Wudang
The Wudang Mountains () consist of a mountain range in the northwestern part of Hubei, China, just south of Shiyan. They are home to a famous complex of Taoist temples and monasteries associated with the Lord of the North, Xuantian Shangdi. The Wudang Mountains are renowned for the practice of Tai chi and Taoism as the Taoist counterpart to the Shaolin Monastery, which is affiliated with Chinese Chán Buddhism. The Wudang Mountains are one of the " Four Sacred Mountains of Taoism" in China, an important destination for Taoist pilgrimages. The monasteries such as the Wudang Garden were made a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994 because of their religious significance and architectural achievement. Geography On Chinese maps, the name "Wudangshan" () is applied both to the entire mountain range (which runs east-west along the southern edge of the Han River, crossing several county-level divisions of Shiyan), and to the group of peaks located within Wudangshan subdistrict of Danjia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine Room Cave
9 is a number, numeral, and glyph. 9 or nine may also refer to: Dates * AD 9, the ninth year of the AD era * 9 BC, the ninth year before the AD era * 9, numerical symbol for the month of September Places * Nine, Portugal, a parish in the town of Vila Nova de Famalicão * Planet Nine, a planet proposed to exist in the outer Solar System * Zheleznogorsk, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, a closed town * The 9, a residential portion of Ameritrust Tower in Cleveland People * Louis Niñé (1922–1983), a New York politician whose surname is usually rendered "Nine" * Nine (rapper) (born 1969), a hip hop musician * Tech N9ne (born 1971), an American rapper Fictional characters * The Nine, epithet for the Nazgûl in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium * ⑨, a derogatory name for Cirno, an ice fairy from the dōjin game ''Touhou Project'' Literature * ''The Nine (book)'', a 2007 book by Jeffrey Toobin * ''NiNe. magazine'', a magazine for teenage girls * ''Nine'' (manga), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze River and the Huai River, bordering Jiangsu to the east, Zhejiang to the southeast, Jiangxi to the south, Hubei to the southwest, Henan to the northwest, and Shandong for a short section in the north. With a population of 63.65 million, Anhui is the 8th most populous province in China. It is the 22nd largest Chinese province based on area, and the 12th most densely-populated region of all 34 Chinese provincial regions. Anhui's population is mostly composed of Han Chinese. Languages spoken within the province include Jianghuai Mandarin, Wu, Hui, Gan and small portion of Zhongyuan Mandarin Chinese. The name "Anhui" derives from the names of two cities: Anqing and Huizhou (now Huangshan City). The abbreviation for Anhui is "" after the histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haozhou
Haozhou or Hao Prefecture () was a '' zhou'' (prefecture) in imperial China centering on modern Fengyang County, Anhui, China. It existed (intermittently) from 582 to 1367. Geography The administrative region of Haozhou in the Tang dynasty is in modern Anhui. It probably includes parts of modern: * Under the administration of Chuzhou: ** Fengyang County ** Mingguang ** Dingyuan County * Under the administration of Bengbu Bengbu () is a city in northern Anhui Province, China. Its population was 3,296,408 registered residents at the 2020 census. 1,968,027 lived in the built-up area made of four Bengbu urban districts and Fengyang County in Chuzhou Prefecture, larg ...: ** Bengbu References * Prefectures of the Sui dynasty Prefectures of the Tang dynasty Prefectures of the Song dynasty Prefectures of the Yuan dynasty Subprefectures of the Ming dynasty Prefectures of Yang Wu Prefectures of Southern Tang Prefectures of Later Zhou Former prefectures in Anhui { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |