|
Chaim Dov Keller
Chaim Dov Keller (1930August 17, 2020) was an American Haredi rabbi, Talmudic scholar, and rosh yeshiva (dean) of the Telshe Yeshiva in Chicago for six decades. He was also a member of the "''Nesius''" (Presidium) of the Moetzes Gedolei HaTorah of Agudath Israel of America. Biography Chaim Dov Keller was born in New York City in 1930.Hellman, Gershon. "Rav Chaim Dov Keller, zt'l". ''Ami'', August 19, 2020, pp. 46–7. He studied at Yeshiva University and subsequently attended the Telshe yeshiva in Cleveland, Ohio, under the leadership of Rabbis Chaim Mordechai Katz and Eliyahu Meir Bloch. Keller became a student and disciple of Bloch in particular. Telshe yeshiva in Chicago and Agudath Israel of America In 1960, Rabbi Avrohom Chaim Levin and Rabbi Chaim Schmelczer were hand-picked by Katz to open a new branch of the yeshiva in Chicago. Keller came to serve as rosh yeshiva of the Chicago branch the following year. The Chicago yeshiva became the main non-Hasidic Lithuanian yeshiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haredi Judaism
Haredi Judaism ( he, ', ; also spelled ''Charedi'' in English; plural ''Haredim'' or ''Charedim'') consists of groups within Orthodox Judaism that are characterized by their strict adherence to ''halakha'' (Jewish law) and traditions, in opposition to modern values and practices. Its members are usually referred to as ultra-Orthodox in English; however, the term "ultra-Orthodox" is considered pejorative by many of its adherents, who prefer terms like strictly Orthodox or Haredi. Haredi Jews regard themselves as the most religiously authentic group of Jews, although other movements of Judaism disagree. Some scholars have suggested that Haredi Judaism is a reaction to societal changes, including political emancipation, the ''Haskalah'' movement derived from the Enlightenment, acculturation, secularization, religious reform in all its forms from mild to extreme, the rise of the Jewish national movements, etc. In contrast to Modern Orthodox Judaism, followers of Haredi Judaism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Jews In Lithuania
The history of the Jews in Lithuania spans the period from the 14th century to the present day. There is still a small community in the country, as well as an extensive Lithuanian Jewish diaspora in Israel, the United States and other countries. Early history The origin of the Jews of Lithuania has been a subject of much speculation. The first reliable document attesting the presence of Jews in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania is the charter of 1388 granting privileges to the Jews in Trakai. The gathering together of the scattered Jewish settlers in sufficient numbers and with enough power to form communities and to obtain privileges from their Lithuanian rulers implies the lapse of considerable time from the first migrations. Therefore, various historians attempted to claim that Jews migrated to Lithuania earlier. For example, Abraham Harkavy (1835–1919) claimed that the first Jews migrated in the 10th century from the Khazar Khaganate (see also Khazar hypothesis of Ashkenazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boruch Sorotzkin
Rephoel Baruch Sorotzkin (February 5, 1917 - February 10, 1979) was the Rosh Yeshiva of the Telz Yeshiva in Cleveland and among American Jewry's foremost religious leaders. He was born on February 5, 1917 (13th of Shevat, 5677) in Zhetl, in the Grodno Governorate of the Russian Empire (present-day Belarus). His father, Rabbi Zalman Sorotzkin was the town's rabbi. As a young man, Sorotzkin studied under Rabbi Elchonon Wasserman in the Baranovich Yeshiva, and then under Rabbi Baruch Ber Lebovitz in Kamenitz. In 1940, Rabbi Boruch Sorotzkin married Rochel Bloch, daughter of the Telzer Rav and Rosh Yeshiva, Rabbi Avraham Yitzchak Bloch. Sorotzkin was involved in the "tension" over visas needed to flee: the two factions were "those from Lithuanian versus Polish Yeshivot;" control of the ''Kobe committee'' was by "students from the Polish yeshivot." The rabbi and his wife fled Europe at the start of World War II, via Shanghai, and made their way to the United States. There, they join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
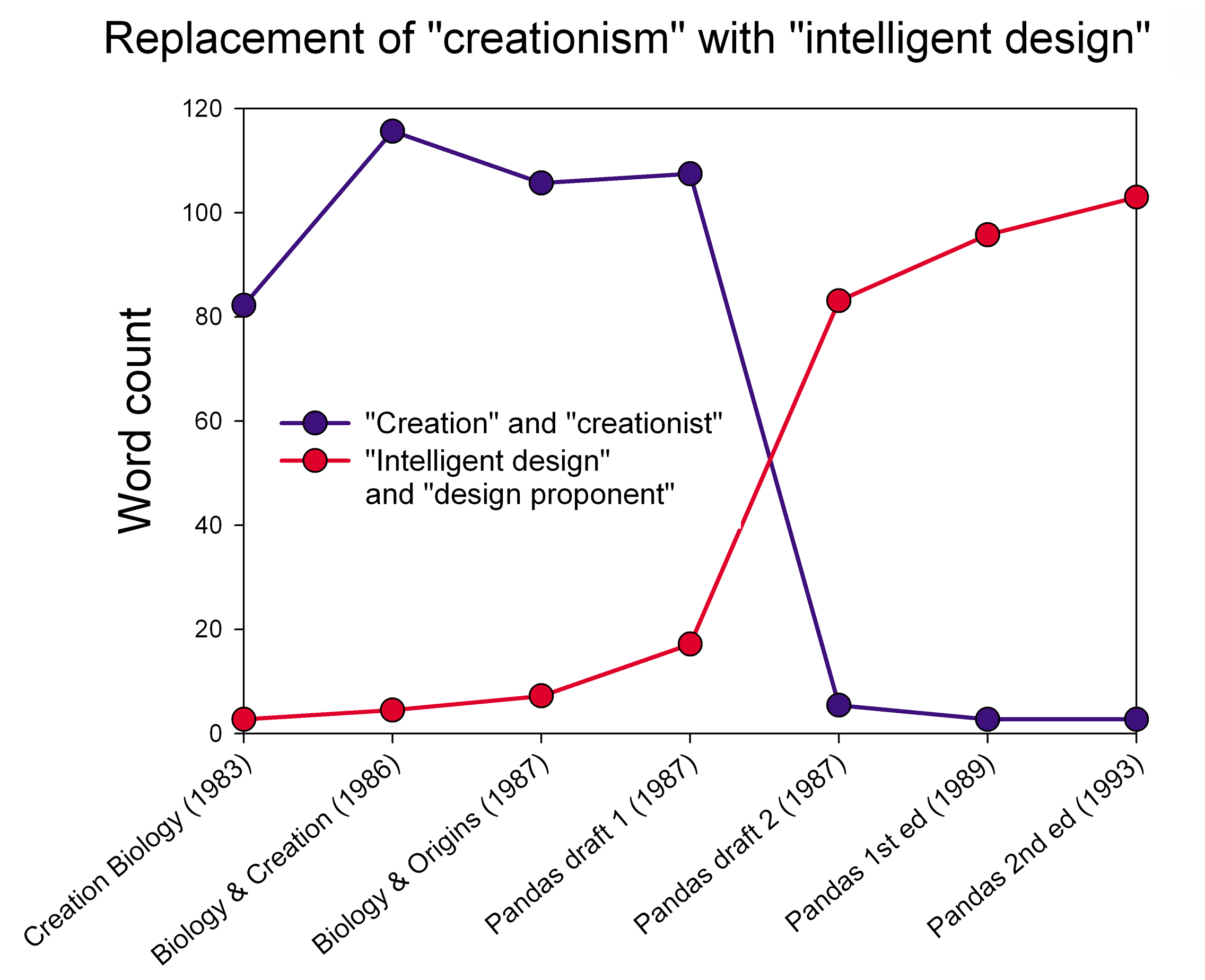
Intelligent Design
Intelligent design (ID) is a pseudoscientific argument for the existence of God, presented by its proponents as "an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins". Numbers 2006, p. 373; " Dcaptured headlines for its bold attempt to rewrite the basic rules of science and its claim to have found indisputable evidence of a God-like being. Proponents, however, insisted it was 'not a religious-based idea, but instead an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins – one that challenges strictly materialistic views of evolution.' Although the intellectual roots of the design argument go back centuries, its contemporary incarnation dates from the 1980s" Article available froUniversiteit Gent/ref> Proponents claim that "certain features of the universe and of living things are best explained by an intelligent cause, not an undirected process such as natural selection." * * ID is a form of creationism that lacks empirical support and offers no testable or tenable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitzmiller V , a town in the United States
{{disambig ...
Kitzmiller may refer to: People * John Kitzmiller (1913–1965), African-American actor * Johnny Kitzmiller (1904–1986), American football player and member of the College Football Hall of Fame * Karen B. Kitzmiller (1947-2002), American politician * Warren Kitzmiller (1943-2022), American politician See also * ''Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District'', 2005 United States court case * Kitzmiller, Maryland Kitzmiller is a town in Garrett County, Maryland, Garrett County, Maryland, United States. The population was 321 at the 2010 census. GeographyKit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeshiva College (Yeshiva University)
Yeshiva College is located in New York City’s Washington Heights neighborhood in Upper Manhattan. It is Yeshiva University’s undergraduate college of liberal arts and sciences for men. (Stern College for Women is Yeshiva College’s counterpart for women.) The architecture reflects a search for a distinctly Jewish style appropriate to American academia. Roughly 1,100 students from some two dozen countries, including students registered at Syms School of Business, attend Yeshiva College. On July 27, 2009, it was announced that Barry L. Eichler, Ph.D., would succeed David J. Srolovitz, Ph.D. as dean of Yeshiva College. Philosophy Students at Yeshiva College pursue a dual educational program that combines liberal arts and sciences and pre-professional studies with the study of Torah and Jewish heritage, reflecting Yeshiva’s educational philosophy of Torah Umadda, which translates loosely as “Torah and secular knowledge” (the interaction between Judaism and general cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chabad
Chabad, also known as Lubavitch, Habad and Chabad-Lubavitch (), is an Orthodox Jewish Hasidic dynasty. Chabad is one of the world's best-known Hasidic movements, particularly for its outreach activities. It is one of the largest Hasidic groups and Jewish religious organizations in the world. Unlike most Haredi groups, which are self-segregating, Chabad operates mainly in the wider world and caters to secularized Jews. Founded in 1775 by Rabbi Schneur Zalman of Liadi, the name "Chabad" () is an acronym formed from three Hebrew words— (the first three sephirot of the kabbalistic Tree of Life) (): "Wisdom, Understanding, and Knowledge"—which represent the intellectual and kabbalistic underpinnings of the movement. The name Lubavitch derives from the town in which the now-dominant line of leaders resided from 1813 to 1915. Other, non-Lubavitch scions of Chabad either disappeared or merged into the Lubavitch line. In the 1930s, the sixth Rebbe of Chabad, Rabbi Yosef Yitzcha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Jewish Observer
''The Jewish Observer'' was an American Orthodox Jewish magazine published by the Agudath Israel of America, from 1963 until 2009. It was put on "hiatus" in 2009, with plans to restart once the finances of the magazine, affected by the economic crisis, were figured out. As of 2019, it has not published any new issues since its 2009 hiatus. The magazine generally presented a ''haredi'' viewpoint. Published since 1963, it was printed nine months a year; the January and February issues were combined, and there were no issues in July or August. The magazine's website contains downloadable PDF copies of most issues while the website of the Lefkowitz Leadership Institute contains PDF files of every single issue since 1963. It was founded by Ernst L. Bodenheimer and Moshe Sherer, and the Editor for the first seven seasons was Nachman Bulman and from then until it ended publication was Nisson Wolpin. Contributors to the Jewish Observer included Avi Shafran, Zalman I. Posner, Mendel Wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Orthodox Judaism
Modern Orthodox Judaism (also Modern Orthodox or Modern Orthodoxy) is a movement within Orthodox Judaism that attempts to synthesize Jewish values and the observance of Jewish law with the secular, modern world. Modern Orthodoxy draws on several teachings and philosophies, and thus assumes various forms. In the United States, and generally in the Western world, ''Centrist Orthodoxy'' underpinned by the philosophy of ''Torah Umadda'' ("Torah and secular knowledge") is prevalent. In Israel, Modern Orthodoxy is dominated by Religious Zionism; however, although not identical, these movements share many of the same values and many of the same adherents.Charles S. Liebman''Modern orthodoxy in Israel''Judaism, Fall, 1998 Modern Orthodoxy Modern Orthodoxy comprises a fairly broad spectrum of movements; each movement draws upon several distinct, though related, philosophies, which (in some combination) provide the basis for all variations of the movement today. Characteristics In gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19 Pandemic In Illinois
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic began in the U.S. state of Illinois on January 24, 2020, when a woman in Chicago, who had just returned from the pandemic's place of origin in Wuhan, Hubei, China, tested positive for the virus. This was the second case of COVID-19 in the United States during the pandemic. The woman's husband was diagnosed with the disease a few days later, the first known case of human-to-human transmission in the United States. Community transmission was not suspected until March 8, when a case with no connection to other cases or recent travel was confirmed. In mid-March, as the number of known cases rose into the double digits, Governor J. B. Pritzker issued a disaster proclamation, the state's equivalent of a state of emergency, to respond to the crisis. The state took measures to halt the spread of the disease by closing all schools and colleges, ordering a stop to eviction enforcements, ordering all bars and restaurants closed to sit-in diners, and otherwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic. The symptoms of COVID‑19 are variable but often include fever, cough, headache, fatigue, breathing difficulties, Anosmia, loss of smell, and Ageusia, loss of taste. Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days incubation period, after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected Asymptomatic, do not develop noticeable symptoms. Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, Hypoxia (medical), hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shabbat
Shabbat (, , or ; he, שַׁבָּת, Šabbāṯ, , ) or the Sabbath (), also called Shabbos (, ) by Ashkenazim, is Judaism's day of rest on the seventh day of the week—i.e., Saturday. On this day, religious Jews remember the biblical stories describing the creation of the heaven and earth in six days and the redemption from slavery and The Exodus from Egypt, and look forward to a future Messianic Age. Since the Jewish religious calendar counts days from sunset to sunset, Shabbat begins in the evening of what on the civil calendar is Friday. Shabbat observance entails refraining from work activities, often with great rigor, and engaging in restful activities to honour the day. Judaism's traditional position is that the unbroken seventh-day Shabbat originated among the Jewish people, as their first and most sacred institution. Variations upon Shabbat are widespread in Judaism and, with adaptations, throughout the Abrahamic and many other religions. According to ''halakha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |