|
Ceratiomyxaceae
''Ceratiomyxa'' is a genus of plasmodial slime mould within the Eumycetozoa, first described by Pier Antonio Micheli. They are widely distributed and commonly found on decaying wood. The plasmodium often appears as white frost-like growth or thin watery layers on wood. Pillar or wall-like sporangia bud from the plasmodium and develop spores that undergo multiple divisions before they release flagellated zoospores. The zoospores will then pair off, undergo plasmogamy, and form zygotes that will later form new plasmodia. The genus currently contains 4 species. The most notable member is ''Ceratiomyxa fruticulosa,'' a slime mould found in most parts of the world. Other known species of ''Ceratiomyxa'' are mostly found in the tropics. Etymology ''Ceratiomyxa'' comes from the Latin word ''ceratus'' meaning "waxed" and the ancient Greek word ''myxa'' meaning "mucus". History of knowledge ''Ceratiomyxa'' was first described under the name ''Puccinia ramose'' (later revised to ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protostelia
Protosteliomycetes/Protosteliales (ICBN) or Protostelea/Protostelia/Protosteliida (ICZN) is a grouping of slime molds from the phylum Mycetozoa. The name can vary depending upon the taxon used. Other names include Protostelea, Protostelia, and Protostelida. When not implying a specific level of classification, the term protostelid or protosteloid amoeba is sometimes used. Protosteloid amoebae, also called protostelids, are amoebae that are capable of making simple fruiting bodies consisting of a cellular stalk topped by one or a few spores. All species are microscopic and are typically found on dead plant matter where they consume bacteria, yeasts, and fungal spores. Since protostelids are amoebae that make spores, they are considered to be slime molds. Classification It includes for example the following genera: * Cavosteliaceae (family) ** '' Cavostelium'' (genus) ** ''Planoprotostelium'' (genus) * Ceratiomyxaceae (family) ** ''Ceratiomyxa'' (genus) * Protosteliaceae (family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protosteliales
Protosteliomycetes/Protosteliales (ICBN) or Protostelea/Protostelia/Protosteliida (ICZN) is a grouping of slime molds from the phylum Mycetozoa. The name can vary depending upon the taxon used. Other names include Protostelea, Protostelia, and Protostelida. When not implying a specific level of classification, the term protostelid or protosteloid amoeba is sometimes used. Protosteloid amoebae, also called protostelids, are amoebae that are capable of making simple fruiting bodies consisting of a cellular stalk topped by one or a few spores. All species are microscopic and are typically found on dead plant matter where they consume bacteria, yeasts, and fungal spores. Since protostelids are amoebae that make spores, they are considered to be slime molds. Classification It includes for example the following genera: * Cavosteliaceae (family) ** '' Cavostelium'' (genus) ** ''Planoprotostelium'' (genus) * Ceratiomyxaceae (family) ** ''Ceratiomyxa'' (genus) * Protosteliaceae (family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
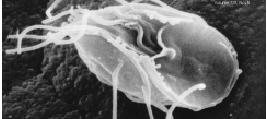
Ceratiomyxa Fruticulosa
''Ceratiomyxa'' is a genus of plasmodial slime mould within the Eumycetozoa, first described by Pier Antonio Micheli. They are widely distributed and commonly found on decaying wood. The plasmodium often appears as white frost-like growth or thin watery layers on wood. Pillar or wall-like sporangia bud from the plasmodium and develop spores that undergo multiple divisions before they release flagellated zoospores. The zoospores will then pair off, undergo plasmogamy, and form zygotes that will later form new plasmodia. The genus currently contains 4 species. The most notable member is ''Ceratiomyxa fruticulosa,'' a slime mould found in most parts of the world. Other known species of ''Ceratiomyxa'' are mostly found in the tropics. Etymology ''Ceratiomyxa'' comes from the Latin word ''ceratus'' meaning "waxed" and the ancient Greek word ''myxa'' meaning "mucus". History of knowledge ''Ceratiomyxa'' was first described under the name ''Puccinia ramose'' (later revised to ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional and currently no longer supported classification schemes, Amoebozoa is ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked " supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, variously named Unikonta, Amorphea or Opimoda. Amoebozoa includes many of the best-known amoeboid orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Schröter
Joseph Schröter (14 March 1837 – 12 December 1894) was a noted German mycologist, doctor and scientist. He wrote several books and texts, and discovered and described many species of flora and fungi. He also spent around fifteen years, from 1871 to 1886, as a military doctor, particularly in the Franco-Prussian War, in places such as Spandau, Rastatt and Breslau, and rising to the rank of colonel. Life In 1855 Schröter chose to study medicine in Breslau, Lower Silesia (Wrocław, Poland since 1945), but in 1856, he transferred to the Friedrich-Wilhelm Academy in Berlin, Prussia (Germany did not unite into a single nation state until 1871). In 1859 he earned his Doctor of Medicine degree. In the same year, he enlisted in the Prussian army, serving as a doctor in the Franco-Prussian war. He occupied this post to the end of the war, in 1871, before being stationed at Spandau, and later Rastatt. For his efforts as a doctor, as well as the various other contributions he made t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Hendrik Persoon
Christiaan Hendrik Persoon (1 February 1761 – 16 November 1836) was a German mycologist who made additions to Linnaeus' mushroom taxonomy. Early life Persoon was born in South Africa at the Cape of Good Hope, the third child of an immigrant Pomeranian father and Dutch mother. His mother died soon after he was born; at the age of thirteen his father (who died a year later) sent him to Europe for his education. Education Initially studying theology at Halle, at age 22 (in 1784) Persoon switched to medicine at Leiden and Göttingen. He received a doctorate from the "Kaiserlich-Leopoldinisch-Carolinische Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher" in 1799. Later years He moved to Paris in 1802, where he spent the rest of his life, renting an upper floor of a house in a poor part of town. He was apparently unemployed, unmarried, poverty-stricken and a recluse, although he corresponded with botanists throughout Europe. Because of his financial difficulties, Persoon agreed to do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratiomyxa Hemisphaerica
''Ceratiomyxa'' is a genus of plasmodial slime mould within the Eumycetozoa, first described by Pier Antonio Micheli. They are widely distributed and commonly found on decaying wood. The plasmodium often appears as white frost-like growth or thin watery layers on wood. Pillar or wall-like sporangia bud from the plasmodium and develop spores that undergo multiple divisions before they release flagellated zoospores. The zoospores will then pair off, undergo plasmogamy, and form zygotes that will later form new plasmodia. The genus currently contains 4 species. The most notable member is ''Ceratiomyxa fruticulosa,'' a slime mould found in most parts of the world. Other known species of ''Ceratiomyxa'' are mostly found in the tropics. Etymology ''Ceratiomyxa'' comes from the Latin word ''ceratus'' meaning "waxed" and the ancient Greek word ''myxa'' meaning "mucus". History of knowledge ''Ceratiomyxa'' was first described under the name ''Puccinia ramose'' (later revised to ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratiomyxa Morchella
''Ceratiomyxa'' is a genus of plasmodial slime mould within the Eumycetozoa, first described by Pier Antonio Micheli. They are widely distributed and commonly found on decaying wood. The plasmodium often appears as white frost-like growth or thin watery layers on wood. Pillar or wall-like sporangia bud from the plasmodium and develop spores that undergo multiple divisions before they release flagellated zoospores. The zoospores will then pair off, undergo plasmogamy, and form zygotes that will later form new plasmodia. The genus currently contains 4 species. The most notable member is ''Ceratiomyxa fruticulosa,'' a slime mould found in most parts of the world. Other known species of ''Ceratiomyxa'' are mostly found in the tropics. Etymology ''Ceratiomyxa'' comes from the Latin word ''ceratus'' meaning "waxed" and the ancient Greek word ''myxa'' meaning "mucus". History of knowledge ''Ceratiomyxa'' was first described under the name ''Puccinia ramose'' (later revised to ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratiomyxa Sphaerosperma
''Ceratiomyxa'' is a genus of plasmodial slime mould within the Eumycetozoa, first described by Pier Antonio Micheli. They are widely distributed and commonly found on decaying wood. The plasmodium often appears as white frost-like growth or thin watery layers on wood. Pillar or wall-like sporangia bud from the plasmodium and develop spores that undergo multiple divisions before they release flagellated zoospores. The zoospores will then pair off, undergo plasmogamy, and form zygotes that will later form new plasmodia. The genus currently contains 4 species. The most notable member is ''Ceratiomyxa fruticulosa,'' a slime mould found in most parts of the world. Other known species of ''Ceratiomyxa'' are mostly found in the tropics. Etymology ''Ceratiomyxa'' comes from the Latin word ''ceratus'' meaning "waxed" and the ancient Greek word ''myxa'' meaning "mucus". History of knowledge ''Ceratiomyxa'' was first described under the name ''Puccinia ramose'' (later revised to ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoospore
A zoospore is a motile asexual spore that uses a flagellum for locomotion. Also called a swarm spore, these spores are created by some protists, bacteria, and fungi to propagate themselves. Diversity Flagella types Zoospores may possess one or more distinct types of flagella - tinsel or "decorated", and whiplash, in various combinations. *Tinsellated (straminipilous) flagella have lateral filaments known as mastigonemes perpendicular to their main axis, which allow for more surface area, and disturbance of the medium, giving them the property of a rudder, that is, used for steering. *Whiplash flagella are straight, to power the zoospore through its medium. Also, the "default" zoospore only has the propelling, whiplash flagella. Both tinsel and whiplash flagella beat in a sinusoidal wave pattern, but when both are present, the tinsel beats in the opposite direction of the whiplash, to give two axes of control of motility. Morphological types In eukaryotes, the four main types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |