|
Cauca Valley Montane Forests
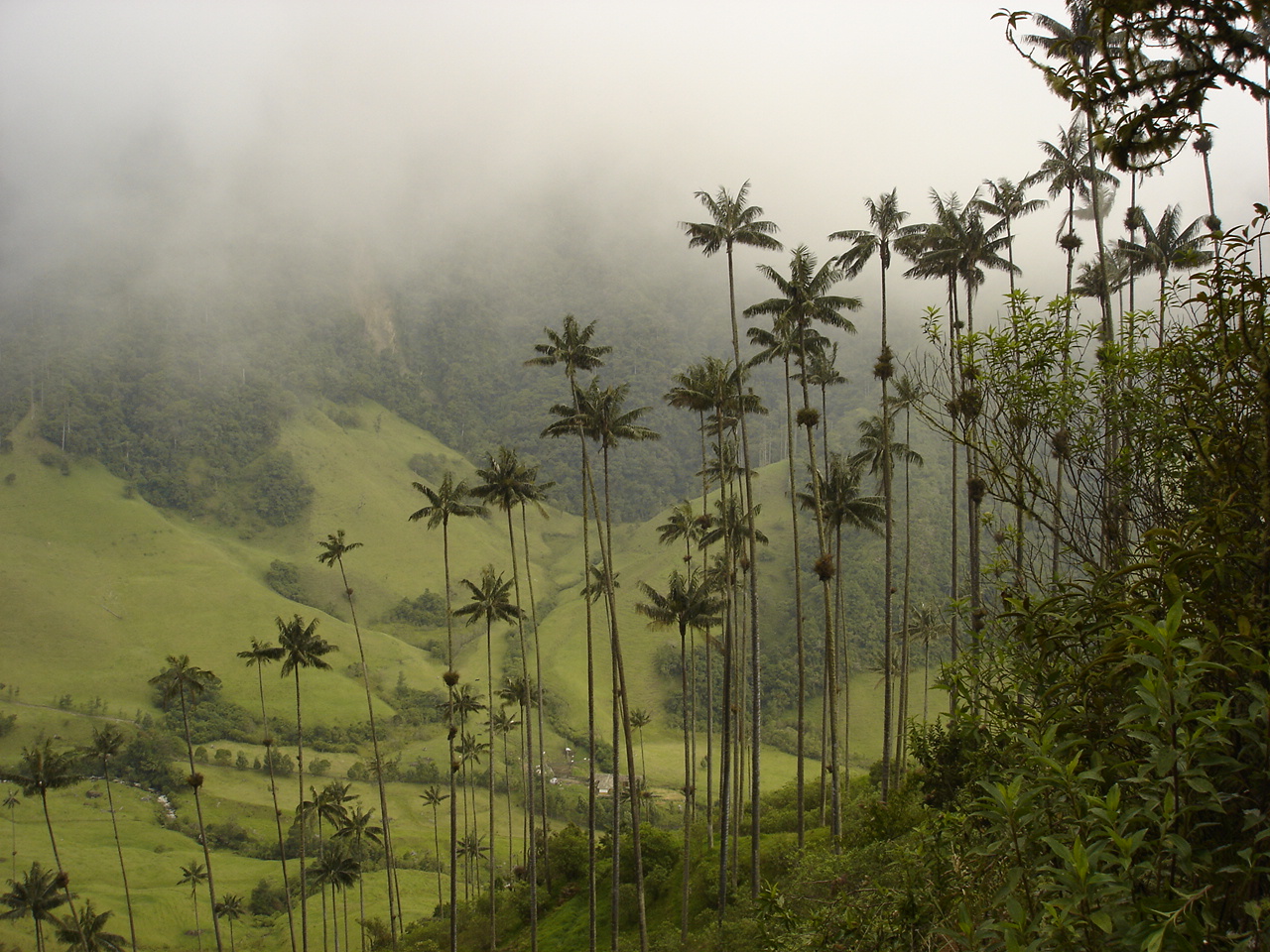
The Cauca Valley montane forests (NT0109) is an ecoregion in western Colombia. It covers the sides of the Cauca Valley, which runs from south to north between the Central and Western Ranges (''cordilleras'') of the Colombian Andes. The ecoregion is home to very diverse fauna and flora, due in part to its varied elevations and climates, in part to its position near the isthmus of Panama, the route along which North American species invaded South America and then diversified as they moved to the upper parts of the Andes. Little of the original habitat remains at lower levels, but higher up there are sizeable blocks of forest, some of which are protected. Geography Location The Cauca Valley runs from south to north between the Cordillera Central and Cordillera Occidental of the Colombian Andes. It has an area of . The ecoregion covers both sides of the Cauca River valley, above the narrow strip of Cauca Valley dry forests that runs along the river. On the highest land of the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manizales
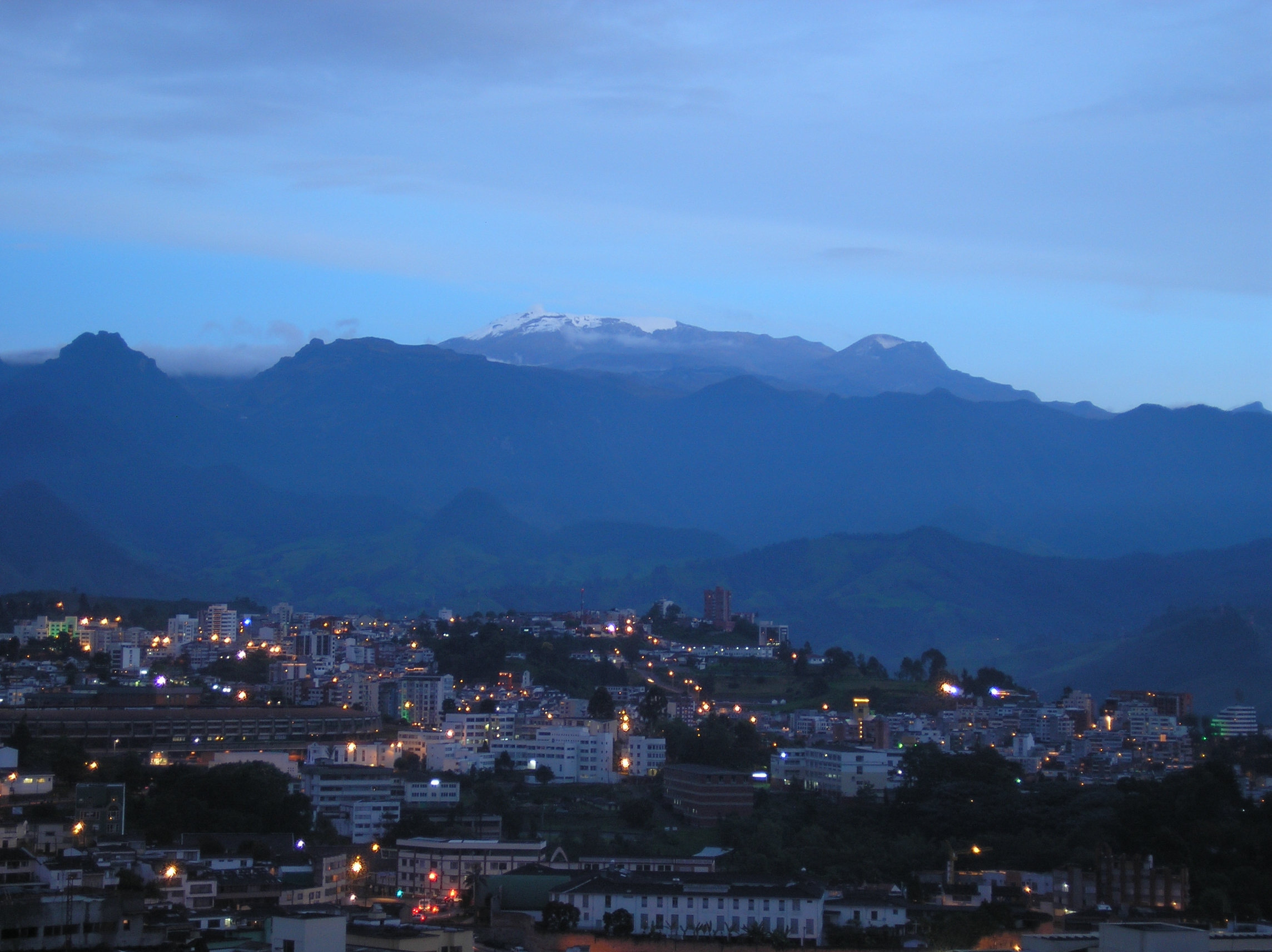
Manizales () is a city in central Colombia. It is the capital of the Caldas Department, Department of Caldas, and lies near the Nevado del Ruiz volcano. Currently, the city is the main center for the production of Colombian coffee and an important hub for higher educational institutions. History Manizales was founded on October 12, 1849. The city was founded by a group of twenty Antioquia Department, Antioquians (''The Expedition of the 20''), who came from Neira, Caldas, Neira and Salamina, Caldas, Salamina. Geography Manizales is the capital city of one of the smallest Colombian departments. The city is described as having an "abrupt topography", and lies on the Colombian Central Mountain Range (part of the longest continental mountain range, the Andes), with a great deal of ridgelines and steep slopes, which, combined with the seismic instability of the area, has required architectural adaptations and public works to make the city safer. Even though Manizales has this very di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838 by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (), "life", meaning "ancient life" ). It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from , and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): # Cambrian # Ordovician # Silurian # Devonian # Carboniferous # Permian The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic was a time of dramatic geological, climatic, and evolutionary change. The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared. Arthropods, molluscs, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and synapsids all evolved during the Paleozoic. Life began in the ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Marta Montane Forests
The Santa Marta montane forests (NT0159) is an ecoregion in the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta, a massif on the Caribbean coast of northern Colombia. The ecoregion covers altitudes from near sea level up to around , where it gives way to Santa Marta páramo. The isolation of the massif and the range of elevations and climates has resulted in a wide variety of species including many endemics. The lower levels contained tropical rainforest, which has largely been cleared. Higher up, this gives way to cloud forest. Much of this has also been cleared for coffee plantations, pasture for sheep and cattle, and farming. Geography Location The ecoregion covers the slopes of the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta in the north of Colombia, with an area of . The range rises to snow-covered peaks only from the Caribbean sea. The ecoregion is almost entirely surrounded by the Sinú Valley dry forests ecoregion. To the northeast and northwest it transitions directly into Guajira–Barranquilla xer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordillera Oriental Montane Forests
The Cordillera Oriental montane forests (NT0118) is an ecoregion in Venezuela and Colombia along the east slopes of the eastern cordillera of the Andes. The extensive region of submontane and montane forests includes distinctive flora and fauna in the north, center and southern sections. The ecoregion is home to numerous endemic species of fauna. Despite extensive changes due to logging, farming and ranching, large areas of the original habitat remain intact, and the ecoregion has rich biodiversity. Geography Location The Cordillera Oriental montane forests ecoregion extends along eastern slopes of the Cordillera Oriental of the Colombian Andes, mostly in Colombia but in the northwest of Venezuela to the west of Lake Maracaibo. It has an area of . At the northern end of the cordillera the ecoregion gives way to Guajira–Barranquilla xeric scrub. To the east, from north it south it adjoins the Maracaibo dry forests, Catatumbo moist forests, Venezuelan Andes montane forests, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
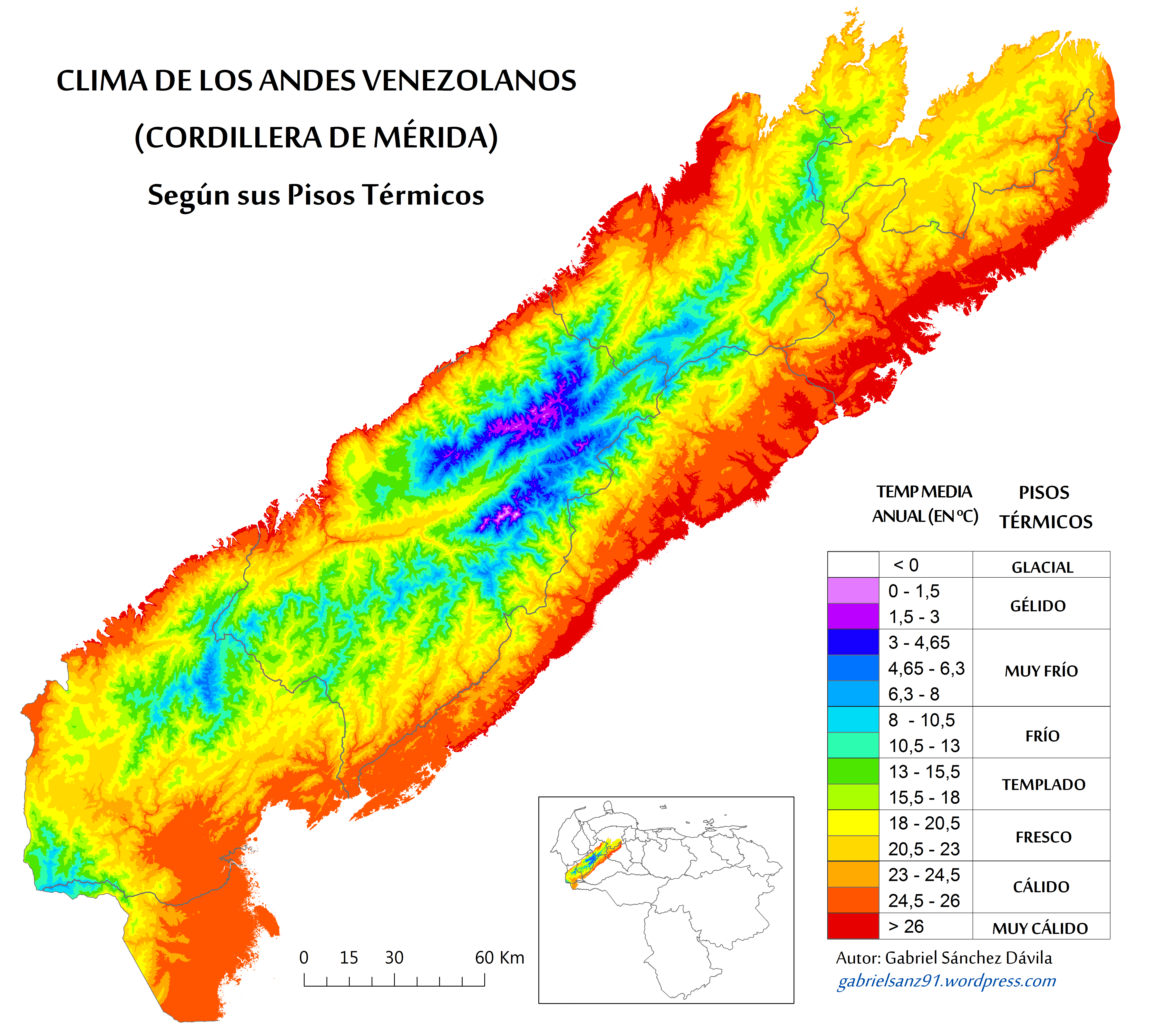
Venezuelan Andes Montane Forests
The Venezuelan Andes montane forests (NT0175) is an ecoregion in the northern arm of the Andes in Venezuela. It contains montane and cloud forests, reaching up to the high-level Cordillera de Merida páramo high moor ecoregion. The forests are home to many endemic species of flora and fauna. Their lower levels are threatened by migrant farmers, who clear patches of forest to grow crops, then move on. Geography Location The Venezuelan Andes montane forests ecoregion covers most of the Venezuelan states of Mérida and Trujillo, much the state of Táchira and the highlands of the states of Lara and Barinas. It includes a small area in Colombia. It covers the lower part of the Venezuelan extension of the Cordillera Occidental of the northern Andes. It has an area of . To the southeast it adjoins the Llanos and the Apure–Villavicencio dry forests, and to the southwest adjoins the Cordillera Oriental montane forests. To the northwest it adjoins the Catatumbo moist forests and the Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Of Endemism
A Centre of Endemism is an area in which the ranges of restricted-range species overlap, or a localised area which has a high occurrence of endemics. Centres of endemism may overlap with biodiversity hotspots which are biogeographic regions characterized both by high levels of plant endemism ''and by serious levels of habitat loss''. The exact delineation of centres of endemism is difficult and some overlap with one another. Centres of endemism are high conservation priority areas. Examples of Centres of Endemism Tanzania A local centre of endemism is focussed on an area of lowland forests around the plateaux inland of Lindi in SE Tanzania, with between 40 and 91 species of vascular plants which are not found elseware. Southern Africa There are at least 19 centres of plant endemism,Van Wyk and Smith, (2001) ''Regions of Floristic Endemism'' including the following: * Albany Centre of Plant Endemism * Barberton Centre of Plant Endemism * Cape Floristic Region * Drakensberg A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical And Subtropical Moist Broadleaf Forests
Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests (TSMF), also known as tropical moist forest, is a subtropical and tropical forest habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Description TSMF is generally found in large, discontinuous patches centered on the equatorial belt and between the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn, TSMF are characterized by low variability in annual temperature and high levels of rainfall of more than annually. Forest composition is dominated by evergreen and semi-deciduous tree species. These trees number in the thousands and contribute to the highest levels of species diversity in any terrestrial major habitat type. In general, biodiversity is highest in the forest canopy. The canopy can be divided into five layers: overstory canopy with emergent crowns, a medium layer of canopy, lower canopy, shrub level, and finally understory. These forests are home to more species than any other terrestrial ecosystem: Half of the world's sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laterite
Laterite is both a soil and a rock type rich in iron and aluminium and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by intensive and prolonged weathering of the underlying parent rock, usually when there are conditions of high temperatures and heavy rainfall with alternate wet and dry periods. Tropical weathering (''laterization'') is a prolonged process of chemical weathering which produces a wide variety in the thickness, grade, chemistry and ore mineralogy of the resulting soils. The majority of the land area containing laterites is between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. Laterite has commonly been referred to as a soil type as well as being a rock type. This and further variation in the modes of conceptualizing about laterite (e.g. also as a complete weathering profile or theory about weathering) has led to calls for the term to be abandoned alto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |