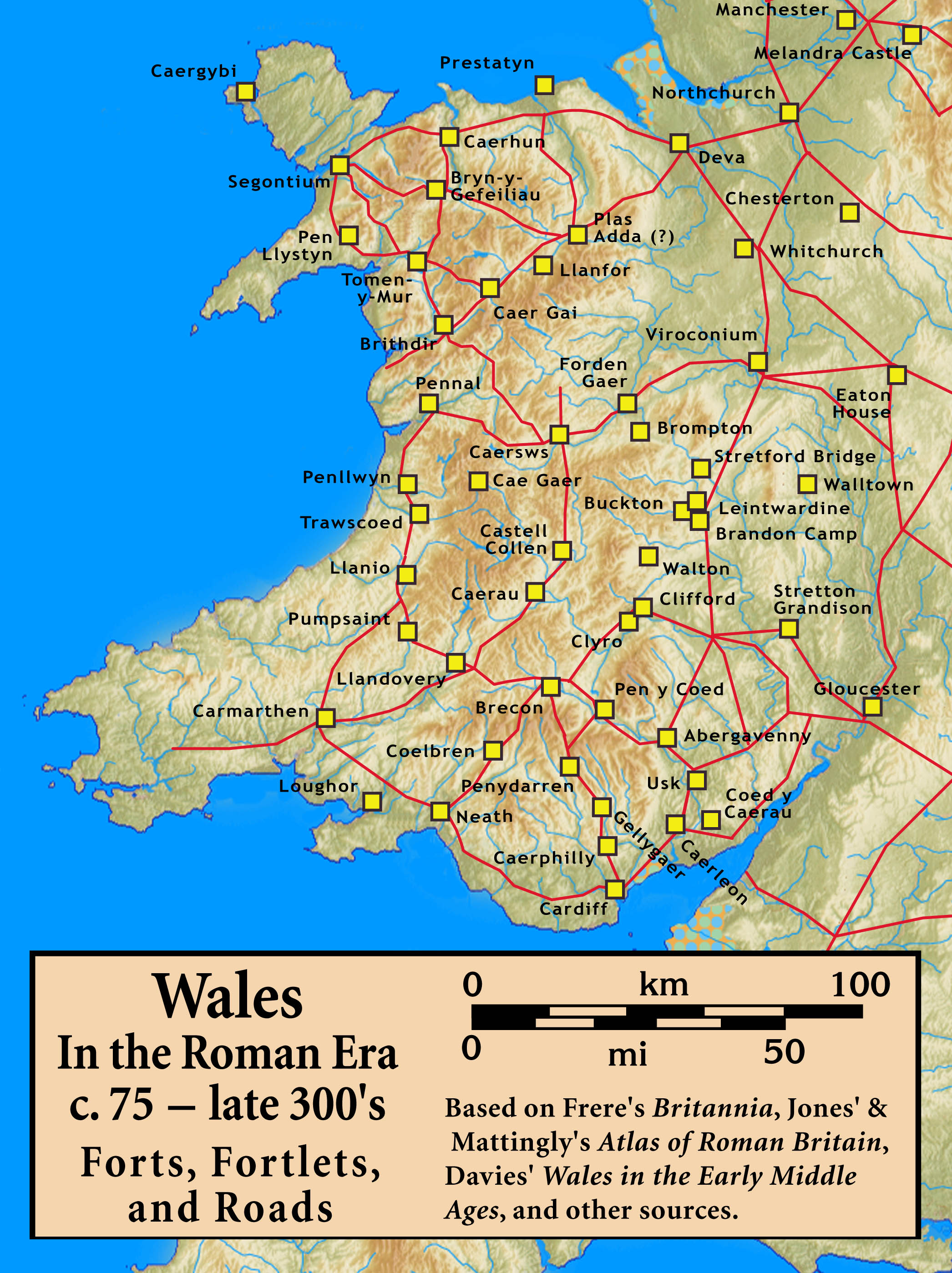
|
Castra Of Basarabi-Murfatlar
The castra of Basarabi was a fort in the Roman province of Moesia. Its remains are located in Murfatlar (Romania). See also *List of castra Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition of the castra refl ... Notes External linksRoman castra from Romania - Google MapsEarth Roman auxiliary forts in Romania History of Dobruja Historic monuments in Constanța County {{Dacia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballia'. It included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Albania, northern parts of North Macedonia (Moesia Superior), Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobruja and small parts of Southern Ukraine (Moesia Inferior). Geography In ancient geographical sources, Moesia was bounded to the south by the Haemus (Balkan Mountains) and Scardus (Šar) mountains, to the west by the Drinus (Drina) river, on the north by the Donaris (Danube) and on the east by the Euxine (Black Sea). History The region of Moesia was inhabited chiefly by Thracian, Illyrian, and Thraco-Illyrian peoples. The name of the region comes from Moesi, the Latin name of a Thracian tribe who lived there before the Roman conquest. Parts of Moes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacidava (castra)
Sacidava was a stonebuilt castra, fort in the Ancient Rome, Roman province of Moesia near the Getic settlement and later Roman city of Sacidava, Moesia that developed around the fort. It is located at Musait between the villages of Rasova and Dunareni, on a high hill on the right bank of the Danube. It is included in the Tabula Peutingeriana as ''Sagadava'' and the Notitia Dignitatum as ''Sacidava''. History The fort was built in the 2nd century CE as part of the Roman frontier system, the Moesian Limes, in the eastern section later known as the ''limes Scythiae Minoriae'', or Scythian limes. It was an important military outpost serving mainly the city of Civitas Tropaensium and controlling the supply and transport on the Danube limes. It was built near a former Dacian fort of the Saci tribe which seems to have been their capital from the 4th century BCE until the beginning of the 1st century CE. Toles, their leader, was an ally of Octavian. The fort had several developm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capidava (castra)
Capidava (''Kapidaua'', ''Cappidava'', ''Capidapa'', ''Calidava'',''Calidaua'') was originally an important Geto-Dacian centre on the right bank of the Danube. After the Roman conquest, it became a civil and military centre in the province of Moesia Inferior (later Scythia Minor) and part of the defensive frontier system of the Moesian Limes along the Danube. It is located in the village with the same name in Constanța County, Romania. Ancient sources Tabula Peutingeriana Capidava is depicted in the form ''Calidava''/''Calidaua'' in Segmentum VIII of Tabula Peutingeriana (1st–4th century) on a Roman road between Axiopolis and Carsium. The map provides distances between Axiopolis, Capidava and Carsium which coincide with the distances between the sites. This is also verified by the discovery of a milestone at Seimenii Mici that indicates the distance of 18,000 feet (27 km) from Axiopolis to Capidava. Notitia Dignitatum Capidava appears on an illu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulmetum (castra)
Ulmetum was a castra, fort in the Roman province of Moesia near the present village of Pantelimonul de Sus. The first mixed civil and military settlement dates from the 2nd c. AD. The walls were greatly strengthened at the end of the 4th century (during the reign of Emperor Theodosius I (379-395). It had an important strategic role to protect the road for the transport of goods between the Roman cities of Noviodunum (castra), Noviodunum and Durostorum. After a period of abandonment due to the Hunnic attacks between the last quarter of the 5th century and the middle of the 6th century, it was partially rebuilt.Cetatea Ulmetum https://www.minac.ro/cetatea-ulmetum.html Gallery File:Ulmetum - Bazilica.jpg File:Ulmetum 3.jpg Ulmetum 5.jpg Situl arheologic „Cetatea Ulmetum” de la Pantelimon-CT-I-s-A-02726 (5).JPG See also *List of castra#Moesia, List of castra References External linksRoman castra from Romania - Google MapsEarth Roman auxiliary forts in Romania His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constanța
Constanța (, , ) is a city in the Dobruja Historical regions of Romania, historical region of Romania. A port city, it is the capital of Constanța County and the country's Cities in Romania, fourth largest city and principal port on the Black Sea coast. It is also the oldest continuously inhabited city in the region, founded around 600 BC, and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest in Europe. As of the 2021 Romanian census, 2021 census, Constanța has a population of 263,688. The Constanța metropolitan area includes 14 localities within of the city. It is one of the largest metropolitan areas in Romania. Ethnic Romanians became a majority in the city in the early 20th century. The city still has small Tatars, Tatar and Greek people, Greek communities, which were substantial in previous centuries, as well as Turkish people, Turkish and Romani people, Romani residents, among others. Constanța has a rich multicultural heritage, as, throughout history, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basarabi
Murfatlar () is a town in Constanța County, Northern Dobruja, Romania. It officially became a town in 1989, as a result of the Romanian rural systematization program. Etymology The name of the town originates from the Turkish word of Arabic origin ''murvet'' (meaning "generous man"). Between 1921 and 1965, and from 1975 to 2007, the locality was known as ''Basarabi''. On June 26, 2007 the lower house of Romania's Parliament, the Chamber of Deputies, approved a proposal to have the name changed back to Murfatlar, which was also ratified by the Senate and promulgated by the president of Romania on December 20, 2007. Administration Murfatlar is a port on the Danube–Black Sea Canal and has a population of 9, 173 as of 2021. A complex of caves was found carved in the hills nearby, see the Basarabi Cave Complex. The village of Siminoc (historical name: ''Turc-Murfat'') is administered by the town of Murfatlar. The name of the village comes from the flower Helichrysum arenarium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castra
''Castra'' () is a Latin language, Latin term used during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire for a military 'camp', and ''castrum'' () for a 'Fortification, fort'. Either could refer to a building or plot of land, used as a fortified military base.. Included is a discussion about the typologies of Roman fortifications. In English language, English usage, ''castrum'' commonly translates to "Roman fort", "Roman camp" and "Roman fortress". Scholastic convention tends to translate ''castrum'' as "fort", "camp", "marching camp" or "fortress". Romans used the term ''castrum'' for different sizes of camps – including large Roman legion, legionary fortresses, smaller forts for Cohort (military unit), cohorts or for auxiliary forces, military camp, temporary encampments, and "marching" forts. The diminutive form ''castellum'' was used for fortlets, typically occupied by a detachment of a cohort or a ''centuria''. Etymology ''Castrum'' appears in Oscan language, Oscan and Umbrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman governor, governor. For centuries, it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the Roman diocese, imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the Praetorian prefecture, imperial prefectures). History A province was the basic and, until the Tetrarchy (from AD 293), the largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy. During the republic and early empire, provinces were generally governed by politicians of Roman senate, senatorial rank, usually former Roman consul, consuls or former praetors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murfatlar
Murfatlar () is a town in Constanța County, Northern Dobruja, Romania. It officially became a town in 1989, as a result of the Romanian rural systematization program. Etymology The name of the town originates from the Turkish word of Arabic origin ''murvet'' (meaning "generous man"). Between 1921 and 1965, and from 1975 to 2007, the locality was known as ''Basarabi''. On June 26, 2007 the lower house of Romania's Parliament, the Chamber of Deputies, approved a proposal to have the name changed back to Murfatlar, which was also ratified by the Senate and promulgated by the president of Romania on December 20, 2007. Administration Murfatlar is a port on the Danube–Black Sea Canal and has a population of 9, 173 as of 2021. A complex of caves was found carved in the hills nearby, see the Basarabi Cave Complex. The village of Siminoc (historical name: ''Turc-Murfat'') is administered by the town of Murfatlar. The name of the village comes from the flower Helichrysum arenarium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a mainly continental climate, and an area of with a population of 19 million people. Romania is the List of European countries by area, twelfth-largest country in Europe and the List of European Union member states by population, sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Europe's second-longest river, the Danube, empties into the Danube Delta in the southeast of the country. The Carpathian Mountains cross Romania from the north to the southwest and include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of . Bucharest is the country's Bucharest metropolitan area, largest urban area and Economy of Romania, financial centre. Other major urban centers, urban areas include Cluj-Napoca, Timiș ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Castra
Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition of the castra reflects the most important zones of the empire from a military point of view. Many castra were disposed along frontiers particularly in Northern and Central Europe. Another focal point was the Eastern border, where the Roman Empire confronted one of its long-term enemies, the Persian Empire. Other castra were located in strategically important zones, as in Egypt, from which most of the wealth of the empire came. Finally, other castra were located in zones in which the Romans experienced local unrest, such as Northern Spain and Judea. Provinces where the Roman power was unchallenged, such as Italy, Gaul, Africa and Greece, were provided with few or no castra. In the long history of the Roman Empire, the character of the military policy of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |