|
Castoridae
Castoridae is a family of rodents that contains the two living species of beavers and their fossil relatives. A formerly diverse group, only a single genus is extant today, ''beaver, Castor.'' Two other genera of "giant beavers", ''Castoroides'' and ''Trogontherium,'' became extinct in the Late Pleistocene. Characteristics Castorids are medium-sized mammals, although large compared with most other rodents. They are semiaquatic, with sleek bodies and webbed hind feet, and are more agile in the water than on land. Their tails are flattened and scaly, adaptations that help them manoeuvre in the water. Castorids live in small family groups that each occupy a specific territory, based around a lodge and dam constructed from sticks and mud. They are herbivores, feeding on leaves and grasses in the summer, and woody plants such as willow in the winter. They have powerful incisors and the typical rodent dentition, dental formula: Evolution The earliest castorids belong to the ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Beaver
The North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') is one of two Extant taxon, extant beaver species, along with the Eurasian beaver (''Castor fiber''). It is native to North America and has been introduced in South America (Patagonia) and Europe (primarily Finland and Karelia). The North American beaver is one of the national symbols of Canada and the official state mammal of Oregon and New York (state), New York. North American (Canadian) beavers are widespread across the continental United States, Canada, southern Alaska, and some parts of northern Mexico. In Canada and the United States, the North American beaver is often referred to simply as "beaver", although this can cause some confusion because another distantly related rodent, ''Aplodontia rufa'', is often called the "mountain beaver". Other vernacular names, including American beaver and Canadian beaver, distinguish this species from the other Extant taxon, extant beaver species, ''Eurasian beaver, Castor fiber'', which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaver
Beavers (genus ''Castor'') are large, semiaquatic rodents of the Northern Hemisphere. There are two existing species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers are the second-largest living rodents, after capybaras, weighing up to . They have stout bodies with large heads, long chisel-like incisors, brown or gray fur, hand-like front feet, webbed back feet, and tails that are flat and scaly. The two species differ in skull and tail shape and fur color. Beavers can be found in a number of freshwater habitats, such as rivers, streams, lakes and ponds. They are herbivorous, consuming tree bark, aquatic plants, grasses and sedges. Beavers build dams and lodges using tree branches, vegetation, rocks and mud; they chew down trees for building material. Dams restrict water flow, forming ponds, and lodges (usually built in ponds) serve as shelters. Their infrastructure creates wetlands used by many other species, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodents
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/ricochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Once included with rodents, rabbits, hares, and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnotocastor
''Agnotocastor'' is an extinct member of the beaver family Castoridae. Unlike its modern relative, this species took the place of muskrats in the rivers of North America during the Oligocene The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that defin ... epoch. The earliest species is ''A. galushai'', which is also the first reliable member of the Castoridae. It is known chiefly from North America, with a single record from Central Asia. References Prehistoric beavers Eocene rodents Oligocene rodents Prehistoric rodent genera Eocene mammals of Asia Oligocene mammals of Asia Eocene mammals of North America Oligocene mammals of North America Fossil taxa described in 1935 {{paleo-rodent-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trogontherium
''Trogontherium'' is an extinct genus of Eurasian giant beavers that lived from the Late Pliocene to the Late Pleistocene. Fossils of ''Trogontherium'' have been found across northern Eurasia, from Western Europe to China and Siberia. Taxonomy ''Trogontherium'' was originally described in 1809 from a skull given to Gotthelf Fischer von Waldheim from the collection of Russian aristocrat Alexander Sergeyevich Stroganov found near Taganrog on the coast of the Sea of Azov in southern Russia, suggested to be Early Pleistocene in age. Originally, no species name was given. In 1824, Georges Cuvier cited the type species name as being ''T. cuvieri,'' attributing the species name to von Waldheim, which has been followed by later authors.'''' Although the origin of the name was previously obscure, a 2024 study confirmed that the species name ''T. cuvieri'' was first used in a previously overlooked 1814 publication by von Waldheim. ''T. cuvieri'' is known from the Late Pliocene to Pleisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeocastor
''Palaeocastor'' ('ancient beaver') is an extinct genus of beavers that lived in the North American Badlands during the late Oligocene period to early Miocene, 29.5~18.5 million years ago. ''Palaeocastor'' was much smaller than modern beavers. There are several species including ''Palaeocastor fossor, Palaeocastor magnus,'' ''Palaeocastor wahlerti'', and ''Palaeocastor peninsulatus.'' The animals first became known on grounds of their fossilized burrows, the "Devil's corkscrews." Biology Some members of this genus made corkscrew-shaped burrows and tunnels. Like many early castorids, ''Palaeocastor'' was predominantly a burrowing animal instead of an aquatic animal. Fossil evidence suggests they may have lived in family groups like modern beavers and employed a K reproductive strategy instead of the normal r-strategy of most rodents. Based on size and habitat, ''Palaeocastor fossor'' has been compared to a black-tailed prairie dog ('' Cynomys ludovicianus''). "Devil's corksc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steneofiber
''Steneofiber'' is an extinct genus of beavers from the Miocene. They contain several species of beavers. Amongst them are ''S.barbouri'', ''S.complexus'', ''S.depereti'', ''S.fossor'', ''S.gradatus'', and ''S.hesperus''. Their various species are found all the way from the eastern end of the Iberian peninsula to southern Japan. ''S.depereti'' has been found in northwest Germany. These small, 30-cm-long (1-ft-long) creatures probably lived in large freshwater lakes, like present day beavers. A semiaquatic lifestyle is indicated by the presence of combing-claws, which living beavers use to waterproof their fur. Most likely, it was incapable of bringing down trees like its modern relatives. ''Steneofibers'' were more terrestrial than modern beavers, living in burrows, but fossils are still found near ancient water sources. The finding of a possible family group of ''Steneofiber'' skeletons in France has been used to infer that the genus employed a K-selected reproductive strategy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
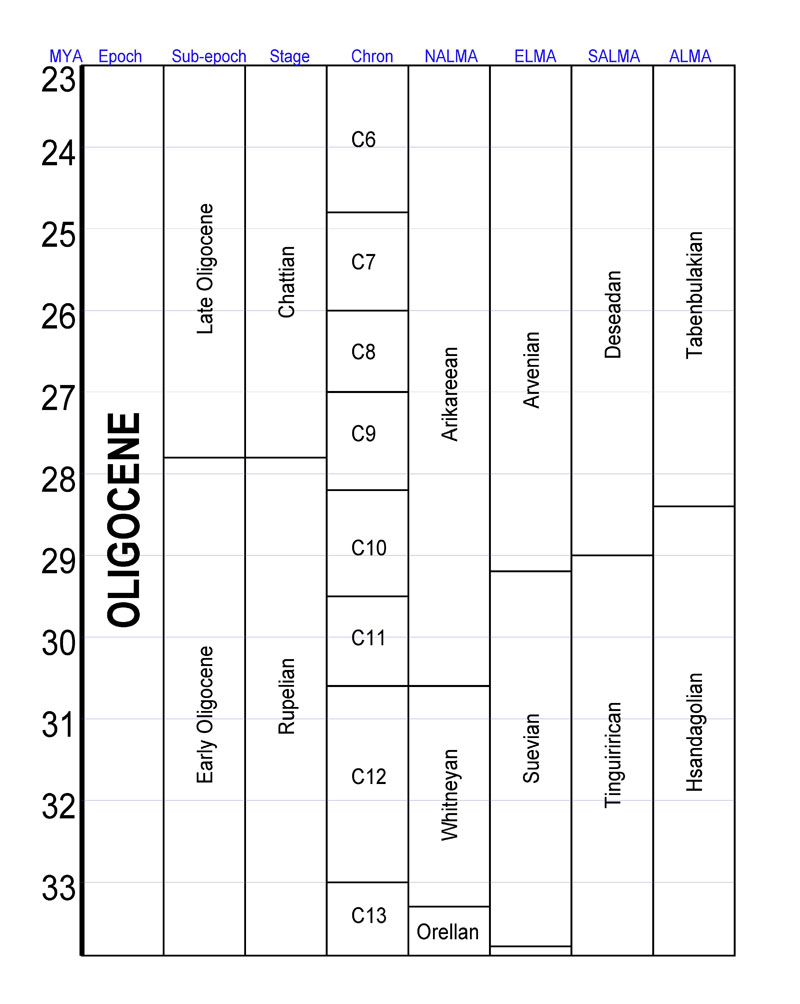
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes Middle America (Americas), Middle America (comprising the Caribbean, Central America, and Mexico) and Northern America. North America covers an area of about , representing approximately 16.5% of Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in list of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilisations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a social constructionism, historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish straits, the Ural Mountains an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebraska
Nebraska ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwest; and Wyoming to the west. Nebraska is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 16th-largest state by land area, with just over . With a population of over 2 million as of 2024, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 38th-most populous state and the List of states and territories of the United States by population density, eighth-least densely populated. Its List of capitals in the United States, capital is Lincoln, Nebraska, Lincoln, and its List of municipalities in Nebraska, most populous city is Omaha, Nebraska, Omaha, which is on the Missouri River. Nebraska was admitted into the United States in 1867, two years after the end of the American Civil War. The Nebras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |