|
Castle Of Slavkov
Slavkov Castle (also known as Austerlitz Castle) is a Baroque palace in Slavkov u Brna in the Czech Republic. The town and the castle are chiefly known for the Battle of Austerlitz. History A first castle at the site was erected by the Teutonic Knights in the early 13th century, then the seat of a commandry within their Bohemian bailiwick. In the early 16th century it passed to the Moravian noble house of Kaunitz who had it rebuilt in a Renaissance style. The present-day palace with 115 rooms was erected from 1696 onwards according to plans designed by the Italian architect Domenico Martinelli. The conversion was finished under Prince Wenzel Anton of Kaunitz-Rietberg more than fifty years later. Wenzel Anton hired the painter Joseph Pichler to apply fresco Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wenzel Anton, Prince Of Kaunitz-Rietberg
Wenzel Anton, Prince of Kaunitz-Rietberg (german: Wenzel Anton Reichsfürst von Kaunitz-Rietberg, cz, Václav Antonín z Kounic a Rietbergu; 2 February 1711 – 27 June 1794) was an Austrian and Czech diplomat and statesman in the Habsburg monarchy. A proponent of enlightened absolutism, he held the office of State Chancellor for about four decades and was responsible for the foreign policies during the reigns of Maria Theresa, Joseph II, and Leopold II. In 1764, he was elevated to the noble rank of a Prince of the Holy Roman Empire ('' Reichfürst''). Family Kaunitz was born in Vienna, Austria, one of 19 children of Maximilian Ulrich, third Count of Kaunitz (1679–1746), and his consort Marie Ernestine, ''née'' Countess of East Frisia and Rietberg (1687–1758), an heiress of the Cirksena dynasty. The Kaunitz family (''Kounicové'') belonged to the old Czech nobility and, like the related Martinic dynasty, derived its lineage from the medieval Vršovci clan in the Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museums In The South Moravian Region
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make these items available for public viewing through exhibits that may be permanent or temporary. The largest museums are located in major cities throughout the world, while thousands of local museums exist in smaller cities, towns, and rural areas. Museums have varying aims, ranging from the conservation and documentation of their collection, serving researchers and specialists, to catering to the general public. The goal of serving researchers is not only scientific, but intended to serve the general public. There are many types of museums, including art museums, natural history museums, science museums, war museums, and children's museums. According to the International Council of Museums (ICOM), there are more than 55,000 museums in 202 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In The South Moravian Region
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vyškov District
Vyškov District ( cs, okres Vyškov) is one of seven districts (''okres'') within South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Its capital is the town of Vyškov. Complete list of municipalities Bohaté Málkovice - Bohdalice-Pavlovice - Bošovice - ''Brankovice'' - Bučovice - Chvalkovice (Vyškov District), Chvalkovice - Dětkovice (Vyškov District), Dětkovice - Dobročkovice - Dražovice (Vyškov District), Dražovice - Drnovice (Vyškov District), Drnovice - Drysice - Habrovany (Vyškov District), Habrovany - Heršpice - Hlubočany - Hodějice - Holubice (Vyškov District), Holubice - Hostěrádky-Rešov - Hoštice-Heroltice - Hrušky (Vyškov District), Hrušky - ''Hvězdlice'' - Ivanovice na Hané - Ježkovice - Kobeřice u Brna - Kojátky - Komořany (Vyškov District), Komořany - Kozlany (Vyškov District), Kozlany - Kožušice - Krásensko - Křenovice (Vyškov District), Křenovice - Křižanovice (Vyškov District), Křižanovice - Křižanovice u Vyškova - Kučer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 11 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815. Although France had already established a colonial empire overseas since the early 17th century, the French state had remained a kingdom under the Bourbons and a republic after the French Revolution. Historians refer to Napoleon's regime as the ''First Empire'' to distinguish it from the restorationist ''Second Empire'' (1852–1870) ruled by his nephew Napoleon III. The First French Empire is considered by some to be a " Republican empire." On 18 May 1804, Napoleon was granted the title Emperor of the French (', ) by the French and was crowned on 2 December 1804, signifying the end of the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, it was the third most populous monarchy in Europe after the Russian Empire and the United Kingdom. Along with Prussia, it was one of the two major powers of the German Confederation. Geographically, it was the third-largest empire in Europe after the Russian Empire and the First French Empire (). The empire was proclaimed by Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis II in 1804 in response to Napoleon's declaration of the First French Empire, unifying all Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg possessions under one central government. It remained part of the Holy Roman Empire until the latter's dissolution in 1806. It continued fighting against Napoleon throughout the Napoleonic Wars, except for a period between 1809 and 1813, when Austria was first all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
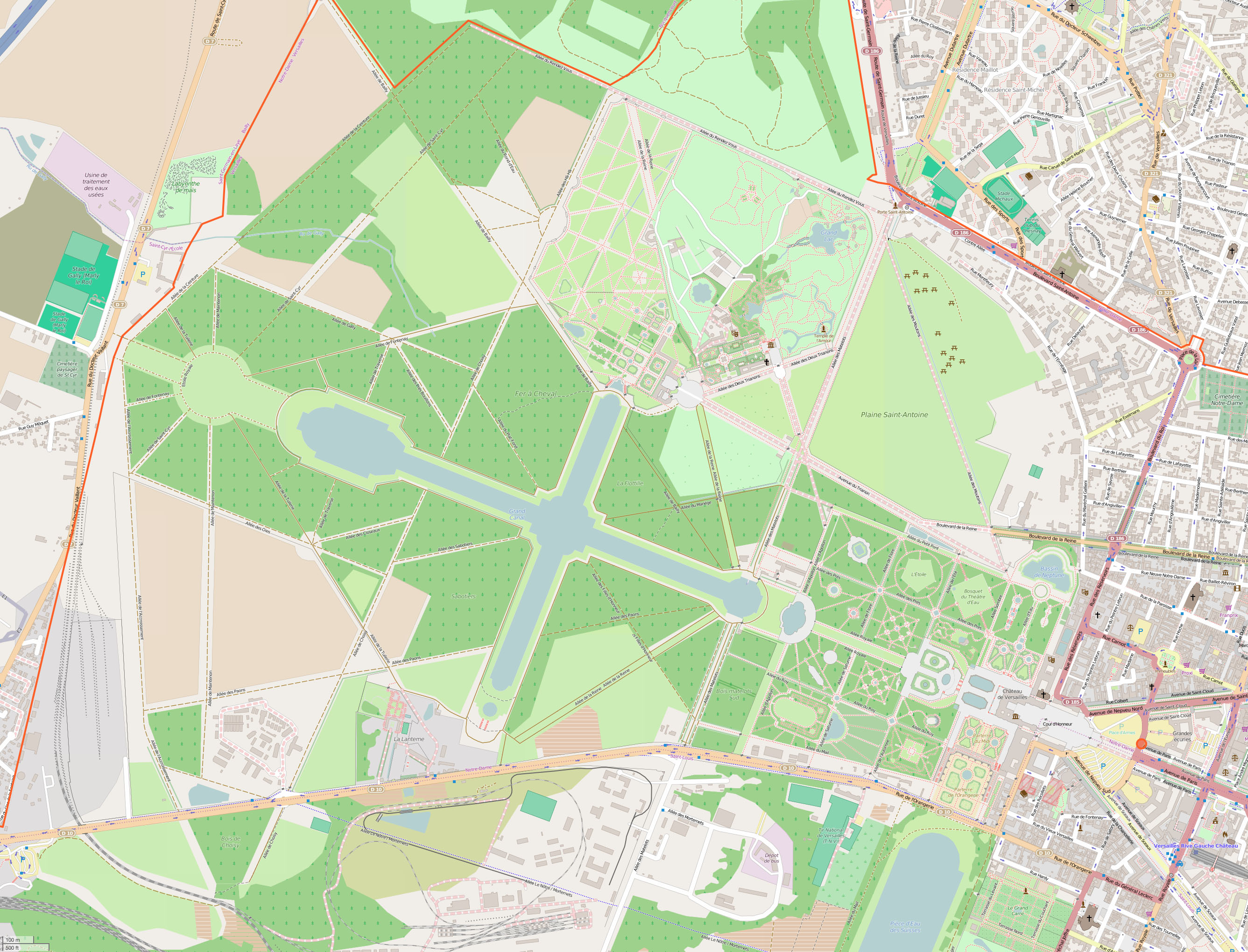
Gardens Of Versailles
The Gardens of Versailles (french: Jardins du château de Versailles ) occupy part of what was once the ''Domaine royal de Versailles'', the royal demesne of the château of Versailles. Situated to the west of the palace, the gardens cover some 800 hectares of land, much of which is landscaped in the classic French formal garden style perfected here by André Le Nôtre. Beyond the surrounding belt of woodland, the gardens are bordered by the urban areas of Versailles to the east and Le Chesnay to the north-east, by the National Arboretum de Chèvreloup to the north, the Versailles plain (a protected wildlife preserve) to the west, and by the Satory Forest to the south. Administered by the Public Establishment of the Palace, Museum and National Estate of Versailles, an autonomous public entity operating under the aegis of the French Ministry of Culture, the gardens are now one of the most visited public sites in France, receiving more than six million visitors a year. In addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresco
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting becomes an integral part of the wall. The word ''fresco'' ( it, affresco) is derived from the Italian adjective ''fresco'' meaning "fresh", and may thus be contrasted with fresco-secco or secco mural painting techniques, which are applied to dried plaster, to supplement painting in fresco. The fresco technique has been employed since antiquity and is closely associated with Italian Renaissance painting. The word ''fresco'' is commonly and inaccurately used in English to refer to any wall painting regardless of the plaster technology or binding medium. This, in part, contributes to a misconception that the most geographically and temporally common wall painting technology was the painting into wet lime plaster. Even in appar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Pichler (painter)
Joseph Pichler (May 9, 1730 – December 15, 1808) was an Austrian painter, best known for his frescoes. Pichler was born in the Carinthian village of Kötschach, which he left in 1752 to study at the Academy of Fine Arts in Vienna. Pichler remains primarily known for the frescoes commissioned by his long-time client Wenzel Anton, Prince of Kaunitz-Rietberg. Pichler applied frescoes in Kaunitz's Slavkov Castle (located in Slavkov u Brna), the castle's chapel, and the Palais Kaunitz-Wittgenstein, where he painted the frescoes in the stairwell and the banquet hall. Pichler also worked for the Habsburg-royal family, for whom he created the frescoes in the so-called Blauer Hof and probably also in adjunct buildings in their summer residence in Laxenburg __NOTOC__ Laxenburg (Central Bavarian: ''Laxnbuag'') is a market town in the district of Mödling, in the Austrian state of Lower Austria. Located about south of the Austrian capital Vienna, it is chiefly known for the Laxenburg ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domenico Martinelli
Domenico Martinelli (November 30, 1650 – September 11, 1718) was an Italian architect who worked for Carlo Fontana during 1678. He was an evident figure in the shaping of Baroque style in the North Alps. In 2010 a musical tribute called "Project Martinelli" was performed to him in Munich. Biography He was born in Lucca, Tuscany, and ordained a priest in his hometown. He studied at the Accademia di San Luca in Rome, where he taught architecture and prospective. In his time he traveled much of Europe, spanning from within Italy, to Austria, Bohemia, Moravia, Poland and the Netherlands. Not as well known as his contemporaries, he often worked with Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach and Johann Lukas von Hildebrandt. His influence on the Baroque style was notable in his work Stadtpalais Liechtenstein (Town Palace), in Vienna (1692–1705), which glorifies an elaborate staircase, derived from Bernini's Chigi-Odescalchi Palace, in Rome. He designed the Palais Harrach, Gartenpala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Architecture
Baroque architecture is a highly decorative and theatrical style which appeared in Italy in the early 17th century and gradually spread across Europe. It was originally introduced by the Catholic Church, particularly by the Jesuits, as a means to combat the Reformation and the Protestant church with a new architecture that inspired surprise and awe. It reached its peak in the High Baroque (1625–1675), when it was used in churches and palaces in Italy, Spain, Portugal, France, Bavaria and Austria. In the Late Baroque period (1675–1750), it reached as far as Russia and the Spanish and Portuguese colonies in Latin America. About 1730, an even more elaborately decorative variant called Rococo appeared and flourished in Central Europe. Baroque architects took the basic elements of Renaissance architecture, including domes and colonnades, and made them higher, grander, more decorated, and more dramatic. The interior effects were often achieved with the use of ''quadratura'', or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


