|
Casino (Cuban Salsa)
In Cuba, a popular dance known as Casino was marketed abroad as Cuban-style salsa or Salsa Cubana to distinguish it from other salsa styles when the name was popularized in the 1970s. Dancing Casino is an expression of popular social culture in Cuba and many Cubans consider casino a part of their social and cultural activities centering on their popular music. The origins of the name ''Casino'' are ''casinos deportivos'', the dance halls where a lot of social dancing was done among the better off, white Cubans during the mid-1950s and onward. Historically, Casino traces its origin as a partner dance from Son Cubano, fused with partner figures and turns adopted from the Cuban Mambo, Cuban Cha Cha Cha, Rumba Guaguancó and North American Jive. As with Son, Danzón and Cha Cha Cha, it is traditionally, though less often today, danced ''a contratiempo''. This means that, distinct from subsequent forms of salsa, no step is taken on the first and fifth beats in each clave patte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CUBA Havana - Salsa Anthony And Steph
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and Atlantic Ocean meet. Cuba is located east of the Yucatán Peninsula (Mexico), south of both the American state of Florida and the Bahamas, west of Hispaniola ( Haiti/Dominican Republic), and north of both Jamaica and the Cayman Islands. Havana is the largest city and capital; other major cities include Santiago de Cuba and Camagüey. The official area of the Republic of Cuba is (without the territorial waters) but a total of 350,730 km² (135,418 sq mi) including the exclusive economic zone. Cuba is the second-most populous country in the Caribbean after Haiti, with over 11 million inhabitants. The territory that is now Cuba was inhabited by the Ciboney people from the 4th millennium BC with the Guanaha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuban Rumba
Rumba is a secular genre of Cuban music involving dance, percussion, and song. It originated in the northern regions of Cuba, mainly in urban Havana and Matanzas, during the late 19th century. It is based on African music and dance traditions, namely Abakuá and yuka, as well as the Spanish-based ''coros de clave''. According to Argeliers León, rumba is one of the major "genre complexes" of Cuban music, and the term rumba complex is now commonly used by musicologists. This complex encompasses the three traditional forms of rumba (yambú, guaguancó and columbia), as well as their contemporary derivatives and other minor styles. Traditionally performed by poor workers of African descent in streets and ''solares'' (courtyards), rumba remains one of Cuba's most characteristic forms of music and dance. Vocal improvisation, elaborate dancing and polyrhythmic drumming are the key components of all rumba styles. '' Cajones'' (wooden boxes) were used as drums until the early 20th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Dance
Group dances are danced by groups of people simultaneously, as opposed to individuals dancing alone or individually, and as opposed to couples dancing together but independently of others dancing at the same time, if any. The dances are generally, but not always, coordinated or standardized in such a way that all the individuals in the group are dancing the same steps at the same time. Alternatively, various groups within the larger group may be dancing different, but complementary, parts of the larger dance. An exception to this generalization must be pointed out where groups of individuals are dancing independently of each other, but with the purpose of creating a "group" feeling or experience, such as might accompany various forms of ritual dancing. Group dances include the following dance forms or styles: * Folk dance ** Circle dance ** Contra dance ** English Country Dance ** Maypole dance ** Square dance *** Traditional square dance *** Modern western square dance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solo Dance
A solo dance is a dance done by an individual dancing alone, as opposed to couples dancing together but independently of others dancing at the same time, if any, and as opposed to groups of people dancing simultaneously in a coordinated manner. Solo dancers are usually the best dancers in a group or dance school. Most solo dancers start after about 6–7 years of dance or sooner. Most soloists are company kids of their dance school. They are usually in more than one dance. In Comparsas, there are various soloists who strut in front. They usually dance at the edges of the street so that the viewing public can appreciate their moves. Most male soloists carry a large lantern-like artifact on a large pole, resting on an oily pouch, which they make spin at will. Dance is a way to express emotions. See also *Sean-nós dance * Sean-nós dance in America *Irish dance *Step dance *Stepping (African-American) Stepping or step-dancing (a type of step dance) is a form of percussi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
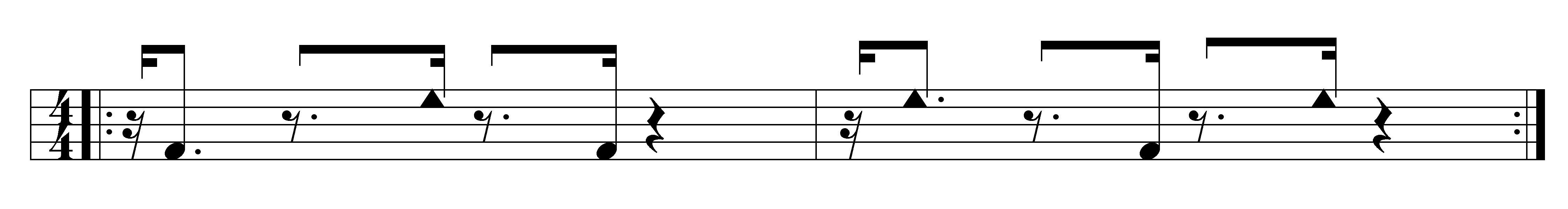
Guaguancó
Guaguancó () is a subgenre of Cuban rumba, combining percussion, voices, and dance. There are two main styles: Havana and Matanzas. Percussion * battery of three conga drummers: the ''tumba'' (lowest), ''tres dos'' (middle, playing a counter-clave), and ''quinto'' (highest, and lead drum). These parts may also be played on cajones, wooden boxes. * claves usually played by a singer * guagua (aka Catà) (hollowed piece of bamboo) * maraca and/or a chekeré playing the main beats Other instruments may be used on occasion, for example spoons, palitos (wooden sticks striking the side of the drum), and tables and walls played like drums. Clave Rumba clave is the key pattern (guide pattern) used in guaguancó. There is some debate as to how the 4/4 rumba clave should be notated for guaguancó. In actual practice, the third and fourth stroke often fall in rhythmic positions that do not fit neatly into music notation. Triple-pulse strokes can be substituted for duple-pulse strokes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macho
Machismo (; ; ; ) is the sense of being " manly" and self-reliant, a concept associated with "a strong sense of masculine pride: an exaggerated masculinity". Machismo is a term originating in the early 1930s and 1940s best defined as having pride in one’s masculinity. It is associated with "a man's responsibility to provide for, protect, and defend his family". Machismo is strongly and consistently associated with dominance, aggression, exhibition, and nurturance. The correlation to machismo is found to be deeply rooted in family dynamics and culture. The word has a long history both in Spain and Portugal, including the Spanish and Portuguese languages. in Portuguese and Spanish is a strictly masculine term, derived from from the Latin ''mascŭlus'', which means "male". It was originally associated with the ideal societal role men were expected to play in their communities, most particularly Iberian language-speaking societies and countries. In addition, due to Mexico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead (dance)
In some types of partner dance, lead and follow are designations for the two dancers' roles in a dance pairing. The leader is responsible for guiding the couple and initiating transitions to different dance steps and, in improvised dances, for choosing the dance steps to perform. The leader communicates choices to the follower, and directs the follower by means of subtle physical and visual signals, thereby allowing the pair to be smoothly coordinated. The amount of direction given by the leader depends on several factors, including dance style, social context of the dance, and experience and personalities of the dancers. Gender roles Traditionally, the male dance partner is the leader and the female dance partner is the follower, though this is not always the case, such as in Schottische danced in the Madrid style where women lead and men follow (although this is not totally true: during the dance there is an exchange of roles, the leader becomes the follower and vice versa.). M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area of , about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8.7% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. In general terms, Asia is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents of Earth#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. The Venezuelan government maintains a claim against Guyana to Guayana Esequiba. Venezuela is a federal presidential republic consisting of 23 states, the Capital District and federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with Haiti, making Hispaniola one of only two Caribbean islands, along with Saint Martin, that is shared by two sovereign states. The Dominican Republic is the second-largest nation in the Antilles by area (after Cuba) at , and third-largest by population, with approximately 10.7 million people (2022 est.), down from 10.8 million in 2020, of whom approximately 3.3 million live in the metropolitan area of Santo Domingo, the capital city. The official language of the country is Spanish. The native Taíno people had inhabited Hispaniola before the arrival of Europeans, dividing it into five chiefdoms. They had constructed an advanced farming and hunting society, and were in the process of becoming an organized civilization. The Taínos also in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyrhythm
Polyrhythm is the simultaneous use of two or more rhythms that are not readily perceived as deriving from one another, or as simple manifestations of the same meter. The rhythmic layers may be the basis of an entire piece of music (cross-rhythm), or a momentary section. Polyrhythms can be distinguished from irrational rhythms, which can occur within the context of a single part; polyrhythms require at least two rhythms to be played concurrently, one of which is typically an irrational rhythm. Concurrently in this context means within the same rhythmic cycle. The underlying pulse, whether explicit or implicit can be considered one of the concurrent rhythms. For example, the son clave is poly-rhythmic because its 3 section suggests a different meter from the pulse of the entire pattern. In western art music In some European art music, polyrhythm periodically contradicts the prevailing meter. For example, in Mozart's opera ''Don Giovanni'', two orchestras are heard playing toget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |