|
Cartorhynchus
''Cartorhynchus'' (meaning "shortened snout") is an extinct genus of early ichthyosauriform marine reptile that lived during the Early Triassic epoch, about 248 million years ago. The genus contains a single species, ''Cartorhynchus lenticarpus'', named in 2014 by Ryosuke Motani and colleagues from a single nearly-complete skeleton found near Chaohu, Anhui Province, China. Along with its close relative '' Sclerocormus'', ''Cartorhynchus'' was part of a diversification of marine reptiles that occurred suddenly (over about one million years) during the Spathian substage, soon after the devastating Permian-Triassic extinction event, but they were subsequently driven to extinction by volcanism and sea level changes by the Middle Triassic. Measuring about long, ''Cartorhynchus'' was a small animal with a lizard-like body and a short torso; it probably swam in an eel-like manner at slow speeds. Its limbs bore extensive cartilage and could bend like flippers, which may have allo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartorhynchus Scale
''Cartorhynchus'' (meaning "shortened snout") is an extinct genus of early ichthyosauriform marine reptile that lived during the Early Triassic epoch, about 248 million years ago. The genus contains a single species, ''Cartorhynchus lenticarpus'', named in 2014 by Ryosuke Motani and colleagues from a single nearly-complete skeleton found near Chaohu, Anhui Province, China. Along with its close relative ''Sclerocormus'', ''Cartorhynchus'' was part of a diversification of marine reptiles that occurred suddenly (over about one million years) during the Spathian substage, soon after the devastating Permian-Triassic extinction event, but they were subsequently driven to extinction by volcanism and sea level changes by the Middle Triassic. Measuring about long, ''Cartorhynchus'' was a small animal with a lizard-like body and a short torso; it probably swam in an eel-like manner at slow speeds. Its limbs bore extensive cartilage and could bend like flippers, which may have allowed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
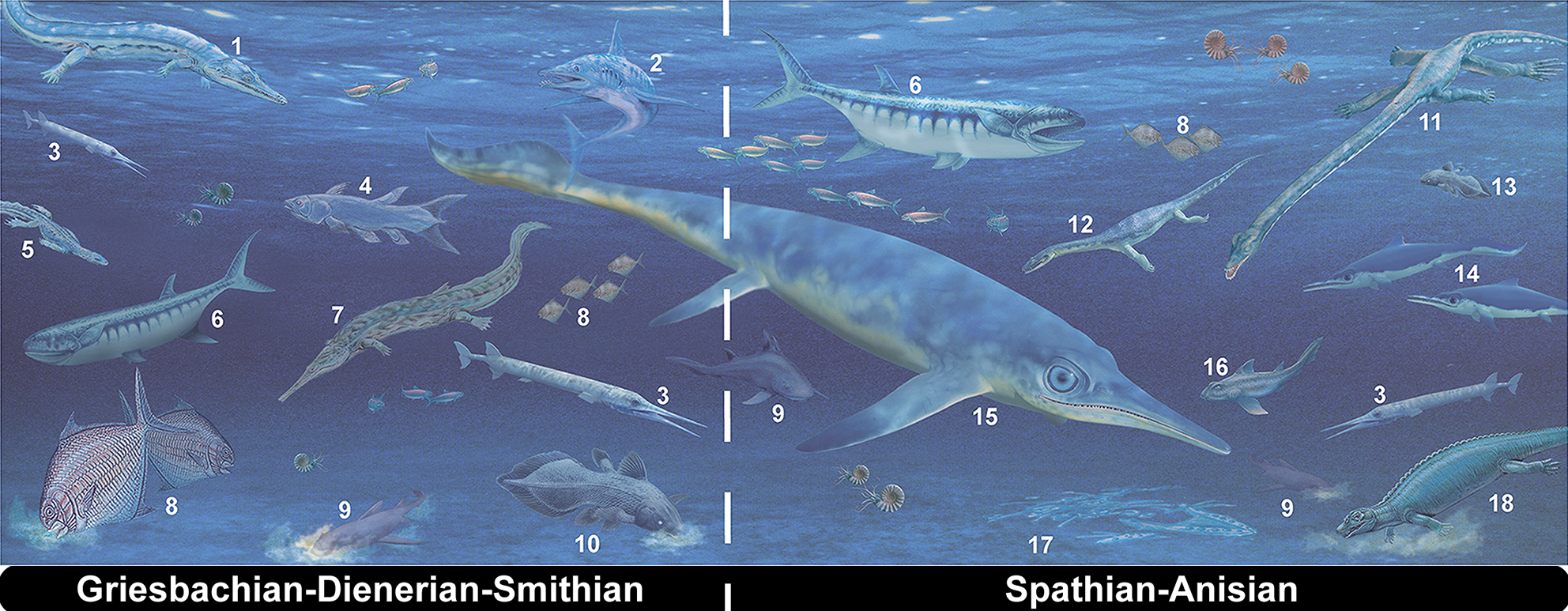
Sclerocormus
''Sclerocormus'' is an extinct genus of ichthyosauriform from the early Triassic period. The fossil was discovered in the central Anhui Province, China. It is currently only known from one specimen, however the fossil is mostly complete and as such further increases the understanding of the early evolution of ichthyosaurs. Description ''Sclerocormus'' is much larger than its closest relative ''Cartorhynchus'', with a total body length of and body mass of more than . Its proportions were unusual amongst basal ichthyosauriformes, with a short, heavily built trunk, a very long tail over 92 cm long (58% of the total body length), and a small skull with a short, narrow snout and toothless jaws. Like ''Cartorhynchus'', the skull of ''Sclerocormus'' is wide, with a short, edentulous snout much narrower than the skull roof. The skull is unusually short at only 6.25% of its body length, compared to 12% in ''Chaohusaurus'' and 15% in ''Hupehsuchus''. Unusually, the nasals of ''Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerocormus Stratigraphy
''Sclerocormus'' is an extinct genus of ichthyosauriform from the early Triassic period. The fossil was discovered in the central Anhui Province, China. It is currently only known from one specimen, however the fossil is mostly complete and as such further increases the understanding of the early evolution of ichthyosaurs. Description ''Sclerocormus'' is much larger than its closest relative ''Cartorhynchus'', with a total body length of and body mass of more than . Its proportions were unusual amongst basal ichthyosauriformes, with a short, heavily built trunk, a very long tail over 92 cm long (58% of the total body length), and a small skull with a short, narrow snout and toothless jaws. Like ''Cartorhynchus'', the skull of ''Sclerocormus'' is wide, with a short, edentulous snout much narrower than the skull roof. The skull is unusually short at only 6.25% of its body length, compared to 12% in ''Chaohusaurus'' and 15% in ''Hupehsuchus''. Unusually, the nasals of ''Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosauriformes
The Ichthyosauriformes are a group of marine reptiles, belonging to the Ichthyosauromorpha, that lived during the Mesozoic. The stem clade Ichthyosauriformes was in 2014 defined by Ryosuke Motani and colleagues as the group consisting of all ichthyosauromorphs that are more closely related to '' Ichthyosaurus communis'' than to '' Hupehsuchus nanchangensis''. Their synapomorphies include the possession of a long nasal bone, stretching to the front beyond the nostril; large scleral rings, filling the eye sockets; a narrow snout in top view; and converging digits with little space between them. The Ichthyosauriformes probably split off in the Early Triassic, about 250 million years ago; the last known forms lived in the middle Cretaceous. A basal ichthyosauriform is ''Cartorhynchus''; more derived species are part of the Ichthyopterygia which again include the Ichthyosauria Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosauriformes
The Ichthyosauriformes are a group of marine reptiles, belonging to the Ichthyosauromorpha, that lived during the Mesozoic. The stem clade Ichthyosauriformes was in 2014 defined by Ryosuke Motani and colleagues as the group consisting of all ichthyosauromorphs that are more closely related to '' Ichthyosaurus communis'' than to '' Hupehsuchus nanchangensis''. Their synapomorphies include the possession of a long nasal bone, stretching to the front beyond the nostril; large scleral rings, filling the eye sockets; a narrow snout in top view; and converging digits with little space between them. The Ichthyosauriformes probably split off in the Early Triassic, about 250 million years ago; the last known forms lived in the middle Cretaceous. A basal ichthyosauriform is ''Cartorhynchus''; more derived species are part of the Ichthyopterygia which again include the Ichthyosauria Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olenekian
In the geologic timescale, the Olenekian is an age in the Early Triassic epoch; in chronostratigraphy, it is a stage in the Lower Triassic series. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Olenekian is sometimes divided into the Smithian and the Spathian subages or substages. The Olenekian follows the Induan and is followed by the Anisian (Middle Triassic). The Olenekian saw the deposition of a large part of the Buntsandstein in Europe. The Olenekian is roughly coeval with the regional Yongningzhenian Stage used in China. Stratigraphic definitions The Olenekian Stage was introduced into scientific literature by Russian stratigraphers in 1956. The stage is named after Olenëk in Siberia. Before the subdivision in Olenekian and Induan became established, both stages formed the Scythian Stage, which has since disappeared from the official timescale. The base of the Olenekian is at the lowest occurrence of the ammonoids '' Hedenstroemia'' or '' Meekoceras graci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Triassic span the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose. Each has two surfaces and four borders. Structure The two nasal bones are joined at the midline internasal suture and make up the bridge of the nose. Surfaces The ''outer surface'' is concavo-convex from above downward, convex from side to side; it is covered by the procerus and nasalis muscles, and perforated about its center by a foramen, for the transmission of a small vein. The ''inner surface'' is concave from side to side, and is traversed from above downward, by a groove for the passage of a branch of the nasociliary nerve. Articulations The nasal articulates with four bones: two of the cranium, the frontal and ethmoid, and two of the face, the opposite nasal and the maxilla. Other animals In primitive bony fish and tetrapod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or ''os premaxillare'', intermaxillary bone or ''os intermaxillare'', and Goethe's bone. Human anatomy In human anatomy, the premaxilla is referred to as the incisive bone (') and is the part of the maxilla which bears the incisor teeth, and encompasses the anterior nasal spine and alar region. In the nasal cavity, the premaxillary element projects higher than the maxillary element behind. The palatal portion of the premaxilla is a bony plate with a generally transverse orientation. The incisive foramen is bound anteriorly and laterally by the premaxilla and posteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla. It is formed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Reports
''Scientific Reports'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific mega journal published by Nature Portfolio, covering all areas of the natural sciences. The journal was established in 2011. The journal states that their aim is to assess solely the scientific validity of a submitted paper, rather than its perceived importance, significance, or impact. In September 2016, the journal became the largest in the world by number of articles, overtaking '' PLOS ONE''. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Chemical Abstracts Service, the Science Citation Index Expanded, and selectively in Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor 4.996. Reviewing policy The ''Guide to Referees'' states that to be published, "a paper must be scientifically valid and technically sound in methodology and analysis", and reviewers have to ensure manuscripts "are not assessed based on their perceived impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowing through it. With a population of 24.89 million as of 2021, Shanghai is the most populous urban area in China with 39,300,000 inhabitants living in the Shanghai metropolitan area, the second most populous city proper in the world (after Chongqing) and the only city in East Asia with a GDP greater than its corresponding capital. Shanghai ranks second among the administrative divisions of Mainland China in human development index (after Beijing). As of 2018, the Greater Shanghai metropolitan area was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product (nominal) of nearly 9.1 trillion RMB ($1.33 trillion), exceeding that of Mexico with GDP of $1.22 trillion, the 15th largest in the world. Shanghai is one of the world's major centers for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word ''frons'' (meaning " forehead"). Structure of the frontal bone The frontal bone is made up of two main parts. These are the squamous part, and the orbital part. The squamous part marks the vertical, flat, and also the biggest part, and the main region of the forehead. The orbital part is the horizontal and second biggest region of the frontal bone. It enters into the formation of the roofs of the orbital and nasal cavities. Sometimes a third part is included as the nasal part of the frontal bone, and sometimes this is included with the squamous part. The nasal part is between the brow ridges, and ends in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)