|
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (cardiac MRI), also known as cardiovascular MRI, is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology used for non-invasive assessment of the function and structure of the cardiovascular system. Conditions in which it is performed include congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathies and valvular heart disease, diseases of the aorta such as dissection, aneurysm and coarctation, coronary heart disease and it can be used to look at pulmonary veins. It is contraindicated if there is a permanent pacemaker or defibrillator, intracerebral clips or claustrophobia. Conventional MRI sequences are adapted for cardiac imaging by using ECG gating and high temporal resolution protocols. The development of cardiac MRI is an active field of research and continues to see a rapid expansion of new and emerging techniques. Uses Cardiovascular MRI is complementary to other imaging techniques, such as echocardiography, cardiac CT, and nuclear medicine. The technique has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
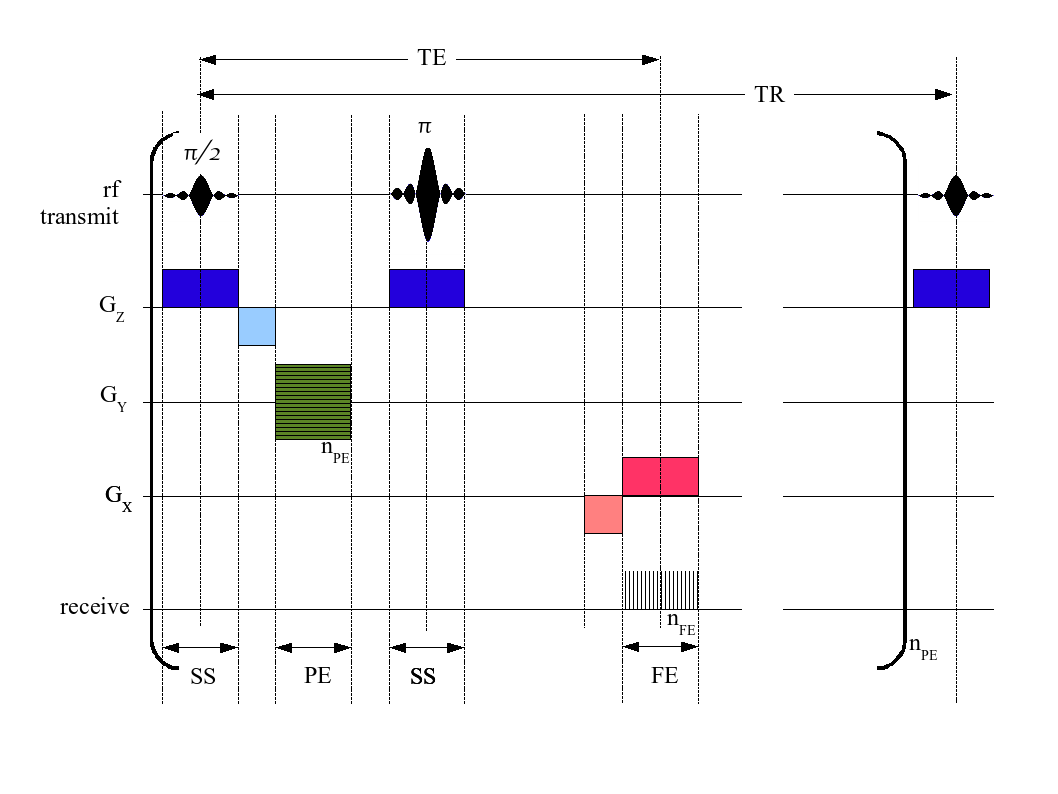
MRI Sequence
An MRI sequence in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a particular setting of pulse sequences and pulsed field gradients, resulting in a particular image appearance. A multiparametric MRI is a combination of two or more sequences, and/or including other specialized MRI configurations such as spectroscopy. Spin echo T1 and T2 Each tissue returns to its equilibrium state after excitation by the independent relaxation processes of T1 ( spin-lattice; that is, magnetization in the same direction as the static magnetic field) and T2 ( spin-spin; transverse to the static magnetic field). To create a T1-weighted image, magnetization is allowed to recover before measuring the MR signal by changing the repetition time (TR). This image weighting is useful for assessing the cerebral cortex, identifying fatty tissue, characterizing focal liver lesions, and in general, obtaining morphological information, as well as for post-contrast imaging. To create a T2-weighted image, magnetizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances (such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia), inadequate coronary artery blood flow (such as myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction), and electrolyte disturbances (such as hypokalemia and hyperkalemia). Traditionally, "ECG" usually means a 12-lead ECG taken while lying down as discussed below. However, other devices can record the electrical activity of the heart such as a Holter monitor but also s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
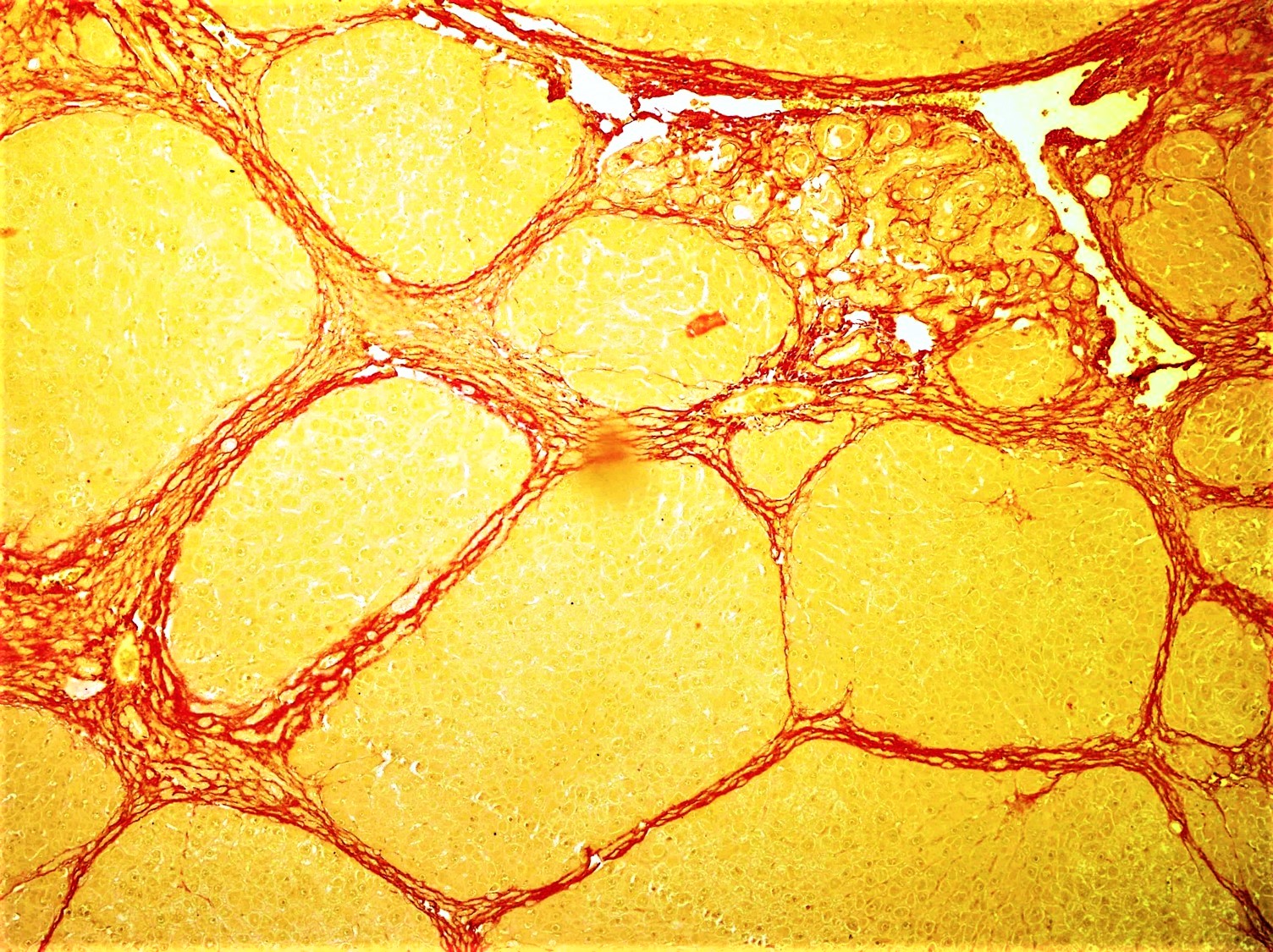
Fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of permanent scar tissue. Repeated injuries, chronic inflammation and repair are susceptible to fibrosis where an accidental excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, such as the collagen is produced by fibroblasts, leading to the formation of a permanent fibrotic scar. In response to injury, this is called scarring, and if fibrosis arises from a single cell line, this is called a fibroma. Physiologically, fibrosis acts to deposit connective tissue, which can interfere with or totally inhibit the normal architecture and function of the underlying organ or tissue. Fibrosis can be used to describe the pathological state of excess deposition of fibrous tissue, as well as the process of connective tissue deposition in healing. Define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck or jaw. Often it occurs in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
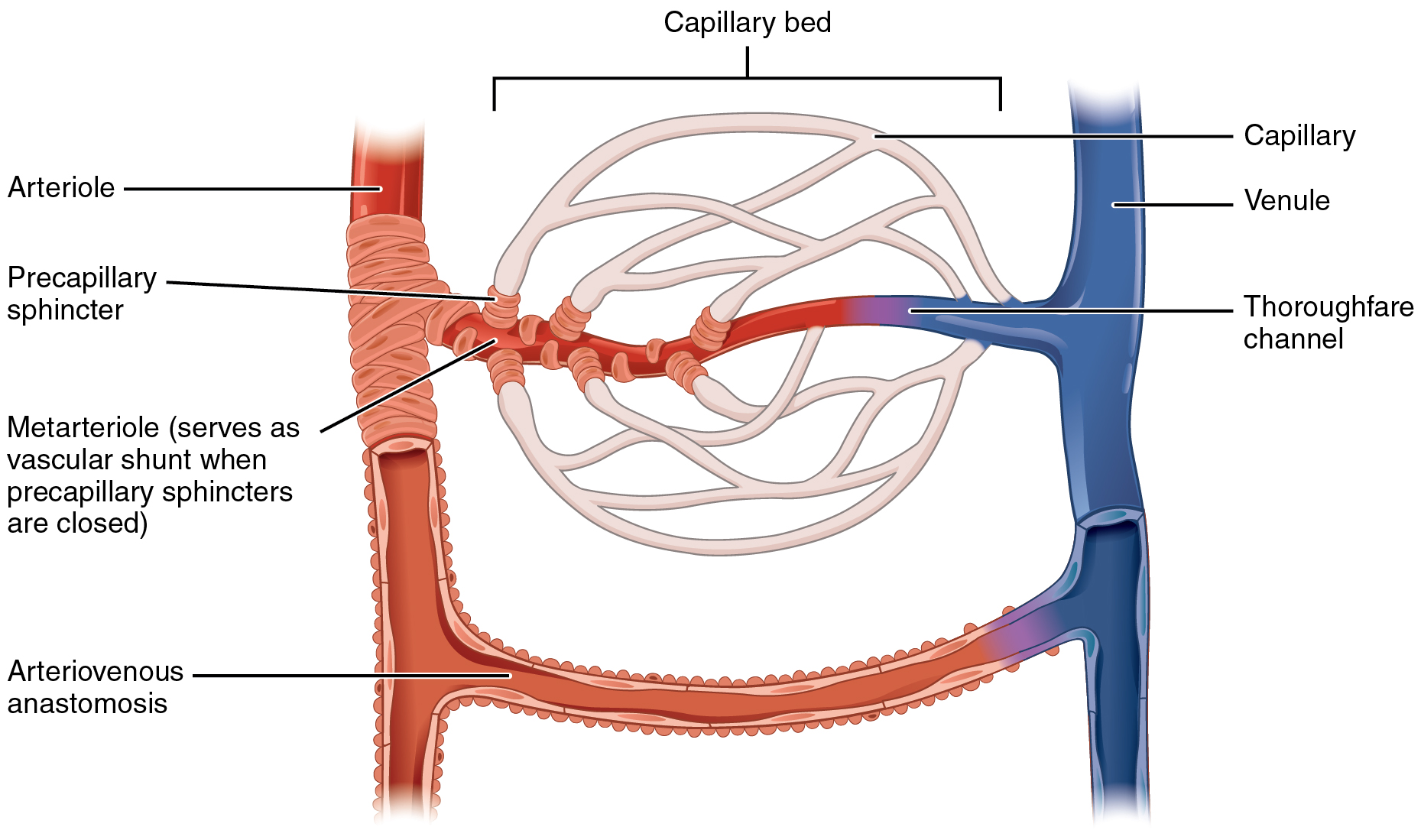
Microvasculature
The microcirculation is the circulation of the blood in the smallest blood vessels, the microvessels of the microvasculature present within organ tissues. The microvessels include terminal arterioles, metarterioles, capillaries, and venules. Arterioles carry oxygenated blood to the capillaries, and blood flows out of the capillaries through venules into veins. In addition to these blood vessels, the microcirculation also includes lymphatic capillaries and collecting ducts. The main functions of the microcirculation are the delivery of oxygen and nutrients and the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2). It also serves to regulate blood flow and tissue perfusion thereby affecting blood pressure and responses to inflammation which can include edema (swelling). Most vessels of the microcirculation are lined by flattened cells of the endothelium and many of them are surrounded by contractile cells called pericytes. The endothelium provides a smooth surface for the flow of blood and regul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicardial Coronary Arteries
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle (myocardium). Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Cardiac veins then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenated. Because the rest of the body, and most especially the brain, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightest interruptions, the heart is required to function continuously. Therefore its circulation is of major importance not only to its own tissues but to the entire body and even the level of consciousness of the brain from moment to moment. Interruptions of coronary circulation quickly cause heart attacks (myocardial infarctions), in which the heart muscle is damaged by oxygen starvation. Such interruptions are usually caused by coronary ischemia linked to coronary artery disease, and sometimes to embolism from other causes like obstruction in blood flow through vessels. Structure Coronary arteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasodilation
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasoconstriction, which is the narrowing of blood vessels. When blood vessels dilate, the flow of blood is increased due to a decrease in vascular resistance and increase in cardiac output. Therefore, dilation of arterial blood vessels (mainly the arterioles) decreases blood pressure. The response may be intrinsic (due to local processes in the surrounding tissue) or extrinsic (due to hormones or the nervous system). In addition, the response may be localized to a specific organ (depending on the metabolic needs of a particular tissue, as during strenuous exercise), or it may be systemic (seen throughout the entire systemic circulation). Endogenous substances and drugs that cause vasodilation are termed vasodilators. Such vasoactivity is necessary for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Heart Defect
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure. The cause of a congenital heart defect is often unknown. Risk factors include certain infections during pregnancy such as rubella, use of certain medications or drugs such as alcohol or tobacco, parents being closely related, or poor nutritional status or obesity in the mother. Having a parent with a congenital heart defect is also a risk factor. A number of genetic conditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Overload
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromatosis (HH or HHC), a genetic disorder, and transfusional iron overload, which can result from repeated blood transfusions. Signs and symptoms Organs most commonly affected by hemochromatosis include the liver, heart, and endocrine glands. Hemochromatosis may present with the following clinical syndromes: * liver: chronic liver disease and cirrhosis of the liver. * heart: heart failure, cardiac arrhythmia. * hormones: diabetes (see below) and hypogonadism (insufficiency of the sex hormone producing glands) which leads to low sex drive and/or loss of fertility in men and loss of menstrual cycle in women. * metabolism: diabetes in people with iron overload occurs as a result of selective iron deposition in islet beta cells in the pancreas lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocarditis
Myocarditis, also known as inflammatory cardiomyopathy, is an acquired cardiomyopathy due to inflammation of the heart muscle. Symptoms can include shortness of breath, chest pain, decreased ability to exercise, and an irregular heartbeat. The duration of problems can vary from hours to months. Complications may include heart failure due to dilated cardiomyopathy or cardiac arrest. Myocarditis is most often due to a viral infection. Other causes include bacterial infections, certain medications, toxins and autoimmune disorders. A diagnosis may be supported by an electrocardiogram (ECG), increased troponin, heart MRI, and occasionally a heart biopsy. An ultrasound of the heart is important to rule out other potential causes such as heart valve problems. Treatment depends on both the severity and the cause. Medications such as ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and diuretics are often used. A period of no exercise is typically recommended during recovery. Corticosteroids or int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. An irregular heart beat and fainting may occur. Those affected are at an increased risk of sudden cardiac death. Types of cardiomyopathy include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (broken heart syndrome). In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy the heart muscle enlarges and thickens. In dilated cardiomyopathy the ventricles enlarge and weaken. In restrictive cardiomyopathy the ventricle stiffens. In many cases, the cause cannot be determined. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is usually inherited, whereas dilated cardiomyopathy is inherited in about one third of cases. Dilated cardiomyopathy may also result from alcohol, heavy m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
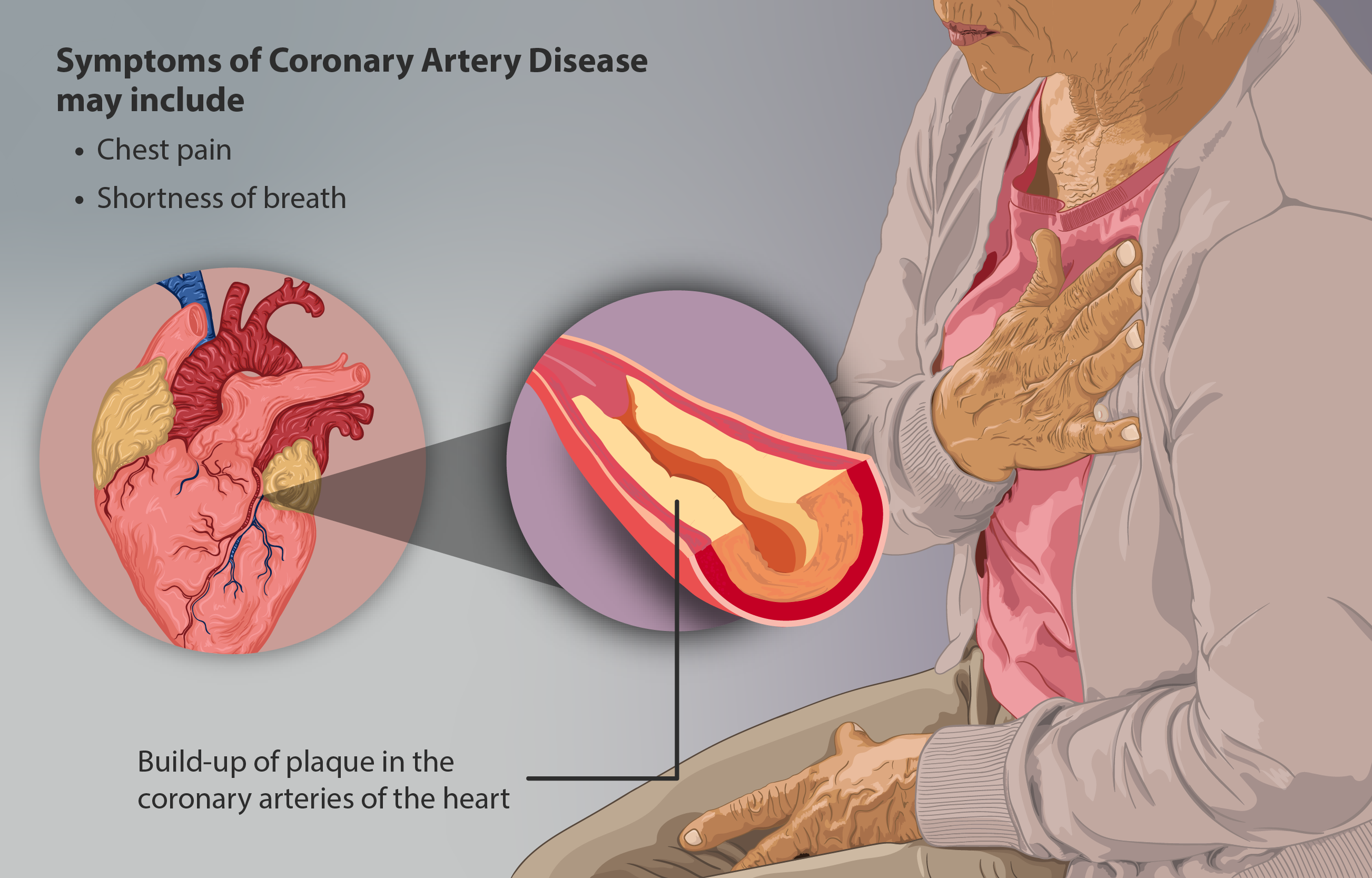
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque An atheroma, or atheromatous plaque, is an abnormal and reversible accumulation of material in the inner layer of an arterial wall. The material consists of mostly macrophage cells, or debris, containing lipids, calcium and a variable amount ... in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional Stress (psychological), stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |