Electrocardiography on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an

 The overall goal of performing an ECG is to obtain information about the electrical functioning of the heart. Medical uses for this information are varied and often need to be combined with knowledge of the structure of the heart and physical examination signs to be interpreted. Some indications for performing an ECG include the following:
* Chest pain or suspected
The overall goal of performing an ECG is to obtain information about the electrical functioning of the heart. Medical uses for this information are varied and often need to be combined with knowledge of the structure of the heart and physical examination signs to be interpreted. Some indications for performing an ECG include the following:
* Chest pain or suspected
 For adults, evidence does not support the use of ECGs among those without symptoms or at low risk of
For adults, evidence does not support the use of ECGs among those without symptoms or at low risk of
 Electrocardiograms are recorded by machines that consist of a set of electrodes connected to a central unit. Early ECG machines were constructed with analog electronics, where the signal drove a motor to print out the signal onto paper. Today, electrocardiographs use analog-to-digital converters to convert the electrical activity of the heart to a
Electrocardiograms are recorded by machines that consist of a set of electrodes connected to a central unit. Early ECG machines were constructed with analog electronics, where the signal drove a motor to print out the signal onto paper. Today, electrocardiographs use analog-to-digital converters to convert the electrical activity of the heart to a
 Electrodes are the actual conductive pads attached to the body surface. Any pair of electrodes can measure the electrical potential difference between the two corresponding locations of attachment. Such a pair forms ''a lead''. However, "leads" can also be formed between a physical electrode and a ''virtual electrode,'' known as Wilson's central terminal (WCT), whose potential is defined as the average potential measured by three limb electrodes that are attached to the right arm, the left arm, and the left foot, respectively.
Commonly, 10 electrodes attached to the body are used to form 12 ECG leads, with each lead measuring a specific electrical potential difference (as listed in the table below).
Leads are broken down into three types: limb; augmented limb; and precordial or chest. The 12-lead ECG has a total of three ''limb leads'' and three ''augmented limb leads'' arranged like spokes of a wheel in the
Electrodes are the actual conductive pads attached to the body surface. Any pair of electrodes can measure the electrical potential difference between the two corresponding locations of attachment. Such a pair forms ''a lead''. However, "leads" can also be formed between a physical electrode and a ''virtual electrode,'' known as Wilson's central terminal (WCT), whose potential is defined as the average potential measured by three limb electrodes that are attached to the right arm, the left arm, and the left foot, respectively.
Commonly, 10 electrodes attached to the body are used to form 12 ECG leads, with each lead measuring a specific electrical potential difference (as listed in the table below).
Leads are broken down into three types: limb; augmented limb; and precordial or chest. The 12-lead ECG has a total of three ''limb leads'' and three ''augmented limb leads'' arranged like spokes of a wheel in the
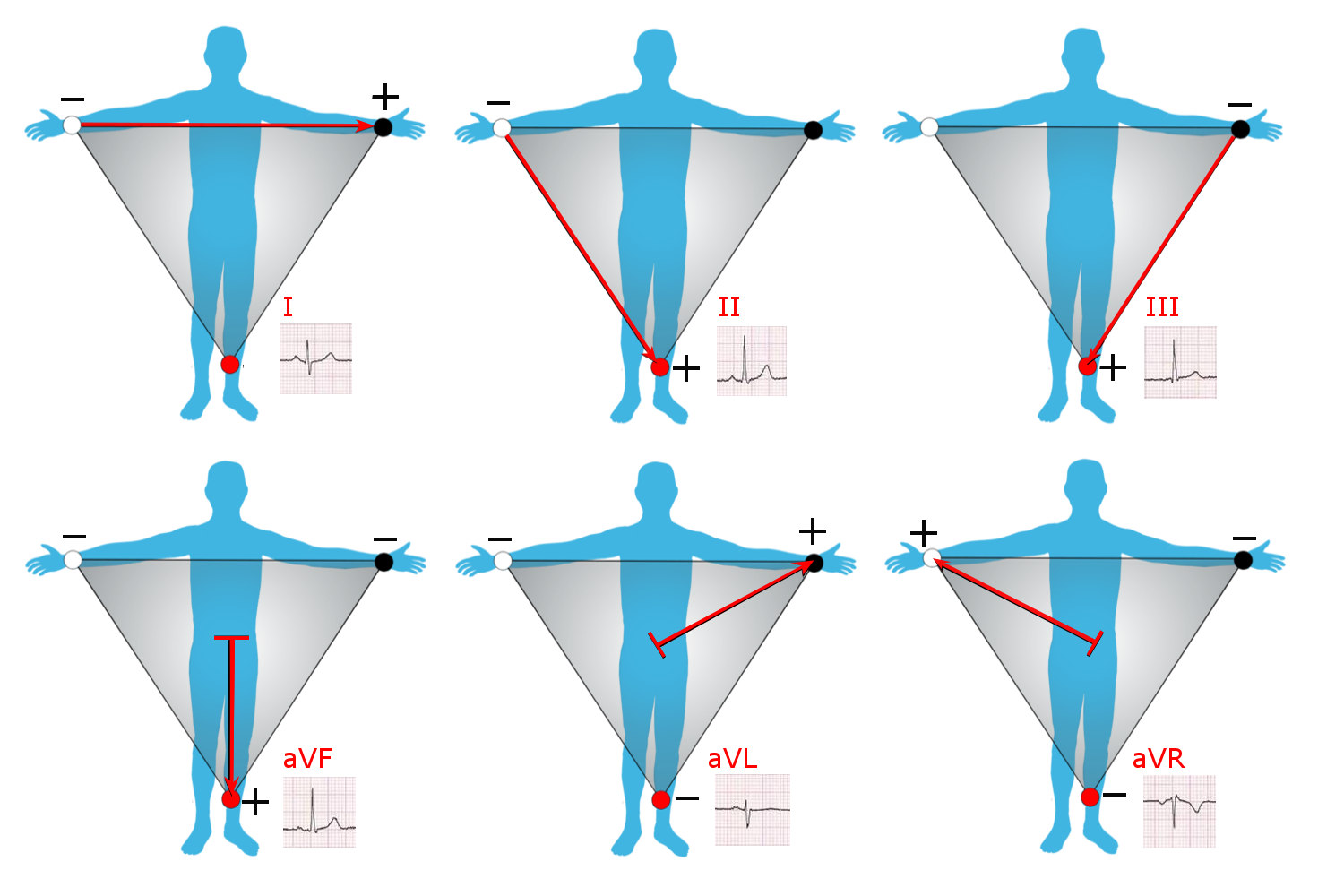
 Leads I, II and III are called the ''limb leads''. The electrodes that form these signals are located on the limbs – one on each arm and one on the left leg. The limb leads form the points of what is known as
Leads I, II and III are called the ''limb leads''. The electrodes that form these signals are located on the limbs – one on each arm and one on the left leg. The limb leads form the points of what is known as
 Each of the 12 ECG leads records the electrical activity of the heart from a different angle, and therefore align with different anatomical areas of the heart. Two leads that look at neighboring anatomical areas are said to be ''contiguous''.
In addition, any two precordial leads next to one another are considered to be contiguous. For example, though V4 is an anterior lead and V5 is a lateral lead, they are contiguous because they are next to one another.
Each of the 12 ECG leads records the electrical activity of the heart from a different angle, and therefore align with different anatomical areas of the heart. Two leads that look at neighboring anatomical areas are said to be ''contiguous''.
In addition, any two precordial leads next to one another are considered to be contiguous. For example, though V4 is an anterior lead and V5 is a lateral lead, they are contiguous because they are next to one another.

 Interpretation of the ECG is ultimately that of pattern recognition.
In order to understand the patterns found, it is helpful to understand the theory of what ECGs represent.
The theory is rooted in electromagnetics and boils down to the four following points:
* depolarization of the heart ''toward'' the positive electrode produces a positive deflection
* depolarization of the heart ''away'' from the positive electrode produces a negative deflection
* repolarization of the heart ''toward'' the positive electrode produces a negative deflection
* repolarization of the heart ''away'' from the positive electrode produces a positive deflection
Thus, the overall direction of depolarization and repolarization produces positive or negative deflection on each lead's trace.
For example, depolarizing from right to left would produce a positive deflection in lead I because the two vectors point in the same direction.
In contrast, that same depolarization would produce minimal deflection in V1 and V2 because the vectors are perpendicular, and this phenomenon is called isoelectric.
Normal rhythm produces four entities – a P wave, a QRS complex, a T wave, and a U wave – that each have a fairly unique pattern.
* The P wave represents atrial depolarization.
* The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization.
* The T wave represents ventricular repolarization.
* The U wave represents papillary muscle repolarization.
Changes in the structure of the heart and its surroundings (including blood composition) change the patterns of these four entities.
The U wave is not typically seen and its absence is generally ignored. Atrial repolarisation is typically hidden in the much more prominent QRS complex and normally cannot be seen without additional, specialised electrodes.
Interpretation of the ECG is ultimately that of pattern recognition.
In order to understand the patterns found, it is helpful to understand the theory of what ECGs represent.
The theory is rooted in electromagnetics and boils down to the four following points:
* depolarization of the heart ''toward'' the positive electrode produces a positive deflection
* depolarization of the heart ''away'' from the positive electrode produces a negative deflection
* repolarization of the heart ''toward'' the positive electrode produces a negative deflection
* repolarization of the heart ''away'' from the positive electrode produces a positive deflection
Thus, the overall direction of depolarization and repolarization produces positive or negative deflection on each lead's trace.
For example, depolarizing from right to left would produce a positive deflection in lead I because the two vectors point in the same direction.
In contrast, that same depolarization would produce minimal deflection in V1 and V2 because the vectors are perpendicular, and this phenomenon is called isoelectric.
Normal rhythm produces four entities – a P wave, a QRS complex, a T wave, and a U wave – that each have a fairly unique pattern.
* The P wave represents atrial depolarization.
* The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization.
* The T wave represents ventricular repolarization.
* The U wave represents papillary muscle repolarization.
Changes in the structure of the heart and its surroundings (including blood composition) change the patterns of these four entities.
The U wave is not typically seen and its absence is generally ignored. Atrial repolarisation is typically hidden in the much more prominent QRS complex and normally cannot be seen without additional, specialised electrodes.
 The standard printing speed in the United States is 25 mm per sec (5 big boxes per second), but in other countries it can be 50 mm per sec.
Faster speeds such as 100 and 200 mm per sec are used during electrophysiology studies.
Not all aspects of an ECG rely on precise recordings or having a known scaling of amplitude or time.
For example, determining if the tracing is a sinus rhythm only requires feature recognition and matching, and not measurement of amplitudes or times (i.e., the scale of the grids are irrelevant).
An example to the contrary, the voltage requirements of left ventricular hypertrophy require knowing the grid scale.
The standard printing speed in the United States is 25 mm per sec (5 big boxes per second), but in other countries it can be 50 mm per sec.
Faster speeds such as 100 and 200 mm per sec are used during electrophysiology studies.
Not all aspects of an ECG rely on precise recordings or having a known scaling of amplitude or time.
For example, determining if the tracing is a sinus rhythm only requires feature recognition and matching, and not measurement of amplitudes or times (i.e., the scale of the grids are irrelevant).
An example to the contrary, the voltage requirements of left ventricular hypertrophy require knowing the grid scale.
 The heart has several axes, but the most common by far is the axis of the QRS complex (references to "the axis" imply the QRS axis).
Each axis can be computationally determined to result in a number representing degrees of deviation from zero, or it can be categorized into a few types.
The QRS axis is the general direction of the ventricular depolarization wavefront (or mean electrical vector) in the frontal plane.
It is often sufficient to classify the axis as one of three types: normal, left deviated, or right deviated.
Population data shows that a normal QRS axis is from −30° to 105°, with 0° being along lead I and positive being inferior and negative being superior (best understood graphically as the hexaxial reference system).
Beyond +105° is
The heart has several axes, but the most common by far is the axis of the QRS complex (references to "the axis" imply the QRS axis).
Each axis can be computationally determined to result in a number representing degrees of deviation from zero, or it can be categorized into a few types.
The QRS axis is the general direction of the ventricular depolarization wavefront (or mean electrical vector) in the frontal plane.
It is often sufficient to classify the axis as one of three types: normal, left deviated, or right deviated.
Population data shows that a normal QRS axis is from −30° to 105°, with 0° being along lead I and positive being inferior and negative being superior (best understood graphically as the hexaxial reference system).
Beyond +105° is
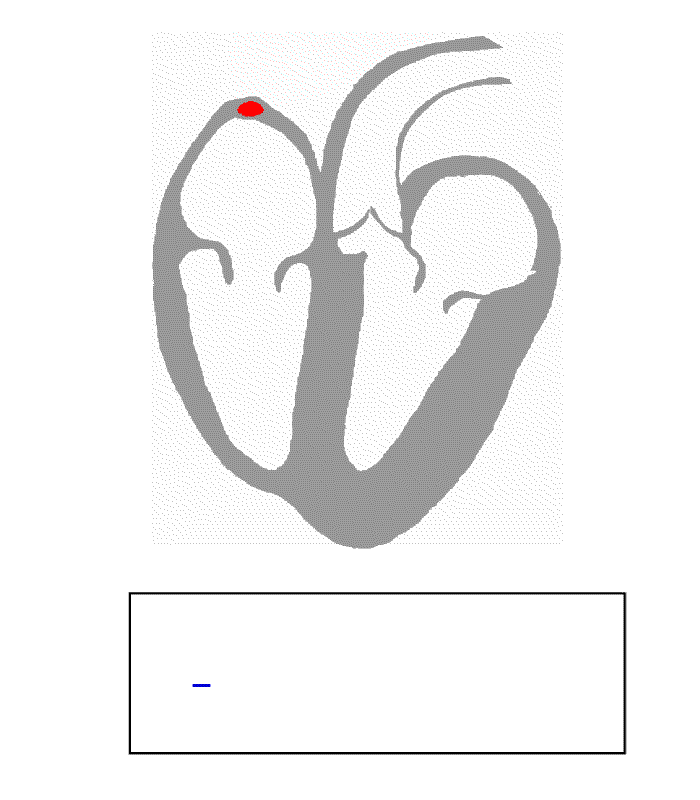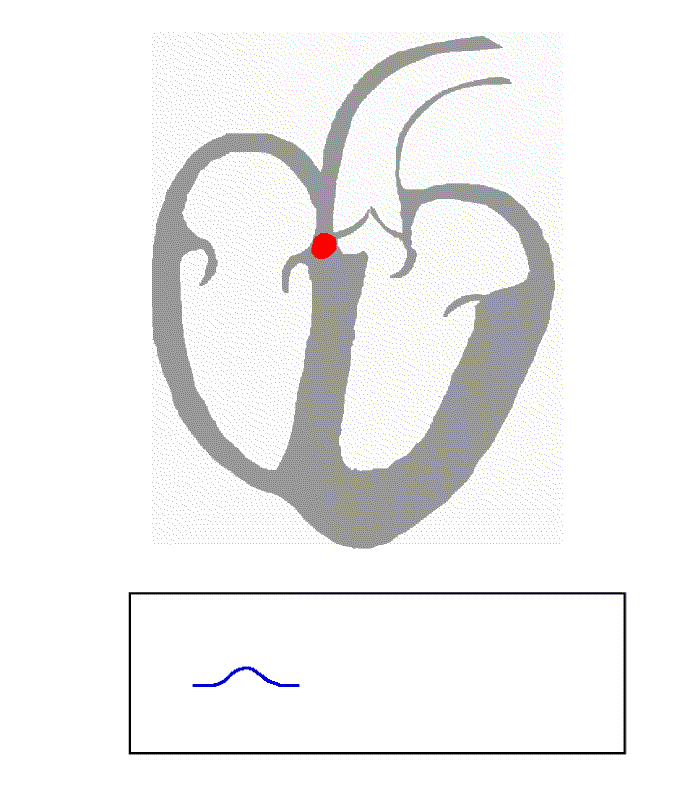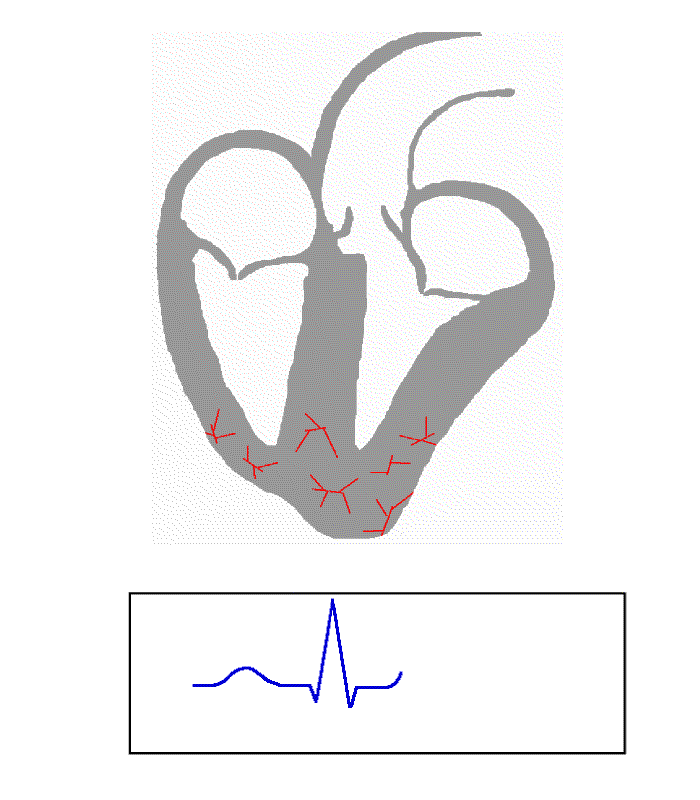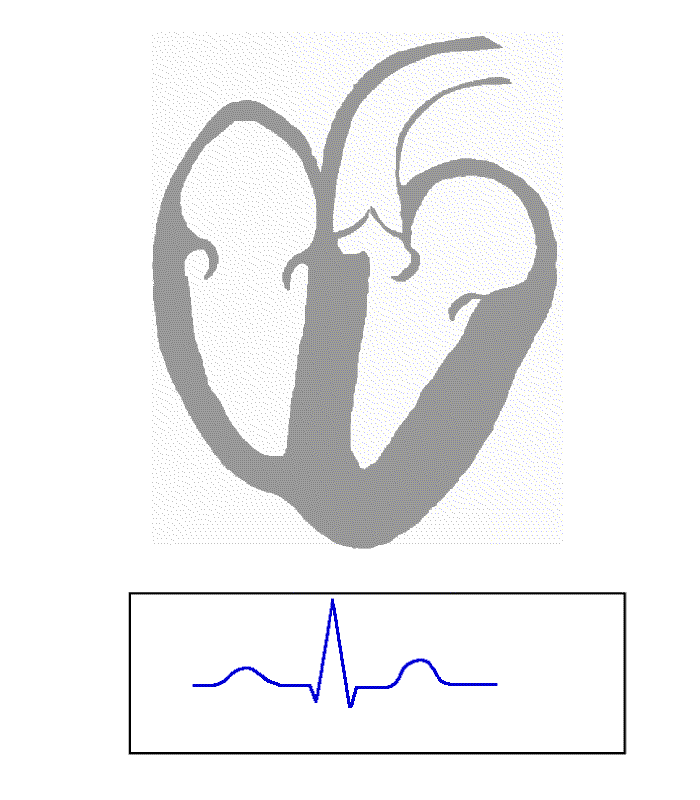 All of the waves on an ECG tracing and the intervals between them have a predictable time duration, a range of acceptable amplitudes (voltages), and a typical morphology. Any deviation from the normal tracing is potentially pathological and therefore of clinical significance.
For ease of measuring the amplitudes and intervals, an ECG is printed on graph paper at a standard scale: each 1 mm (one small box on the standard 25mm/s ECG paper) represents 40 milliseconds of time on the x-axis, and 0.1 millivolts on the y-axis.
All of the waves on an ECG tracing and the intervals between them have a predictable time duration, a range of acceptable amplitudes (voltages), and a typical morphology. Any deviation from the normal tracing is potentially pathological and therefore of clinical significance.
For ease of measuring the amplitudes and intervals, an ECG is printed on graph paper at a standard scale: each 1 mm (one small box on the standard 25mm/s ECG paper) represents 40 milliseconds of time on the x-axis, and 0.1 millivolts on the y-axis.
 The animation shown to the right illustrates how the path of electrical conduction gives rise to the ECG waves in the limb leads. Recall that a positive current (as created by depolarization of cardiac cells) traveling towards the positive electrode and away from the negative electrode creates a positive deflection on the ECG. Likewise, a positive current traveling away from the positive electrode and towards the negative electrode creates a negative deflection on the ECG. The red arrow represents the overall direction of travel of the depolarization. The magnitude of the red arrow is proportional to the amount of tissue being depolarized at that instance. The red arrow is simultaneously shown on the axis of each of the 3 limb leads. Both the direction and the magnitude of the red arrow's projection onto the axis of each limb lead is shown with blue arrows. Then, the direction and magnitude of the blue arrows are what theoretically determine the deflections on the ECG. For example, as a blue arrow on the axis for Lead I moves from the negative electrode, to the right, towards the positive electrode, the ECG line rises, creating an upward wave. As the blue arrow on the axis for Lead I moves to the left, a downward wave is created. The greater the magnitude of the blue arrow, the greater the deflection on the ECG for that particular limb lead.
Frames 1–3 depict the depolarization being generated in and spreading through the Sinoatrial node. The SA node is too small for its depolarization to be detected on most ECGs. Frames 4–10 depict the depolarization traveling through the atria, towards the Atrioventricular node. During frame 7, the depolarization is traveling through the largest amount of tissue in the atria, which creates the highest point in the P wave. Frames 11–12 depict the depolarization traveling through the AV node. Like the SA node, the AV node is too small for the depolarization of its tissue to be detected on most ECGs. This creates the flat PR segment.
Frame 13 depicts an interesting phenomenon in an over-simplified fashion. It depicts the depolarization as it starts to travel down the interventricular septum, through the Bundle of His and
The animation shown to the right illustrates how the path of electrical conduction gives rise to the ECG waves in the limb leads. Recall that a positive current (as created by depolarization of cardiac cells) traveling towards the positive electrode and away from the negative electrode creates a positive deflection on the ECG. Likewise, a positive current traveling away from the positive electrode and towards the negative electrode creates a negative deflection on the ECG. The red arrow represents the overall direction of travel of the depolarization. The magnitude of the red arrow is proportional to the amount of tissue being depolarized at that instance. The red arrow is simultaneously shown on the axis of each of the 3 limb leads. Both the direction and the magnitude of the red arrow's projection onto the axis of each limb lead is shown with blue arrows. Then, the direction and magnitude of the blue arrows are what theoretically determine the deflections on the ECG. For example, as a blue arrow on the axis for Lead I moves from the negative electrode, to the right, towards the positive electrode, the ECG line rises, creating an upward wave. As the blue arrow on the axis for Lead I moves to the left, a downward wave is created. The greater the magnitude of the blue arrow, the greater the deflection on the ECG for that particular limb lead.
Frames 1–3 depict the depolarization being generated in and spreading through the Sinoatrial node. The SA node is too small for its depolarization to be detected on most ECGs. Frames 4–10 depict the depolarization traveling through the atria, towards the Atrioventricular node. During frame 7, the depolarization is traveling through the largest amount of tissue in the atria, which creates the highest point in the P wave. Frames 11–12 depict the depolarization traveling through the AV node. Like the SA node, the AV node is too small for the depolarization of its tissue to be detected on most ECGs. This creates the flat PR segment.
Frame 13 depicts an interesting phenomenon in an over-simplified fashion. It depicts the depolarization as it starts to travel down the interventricular septum, through the Bundle of His and

 * In 1872,
* In 1872,
The whole ECG course on 1 A4 paper
fro
ECGpedia
a wiki encyclopedia fo
a course on interpretation of ECG
Wave Maven – a large database of practice ECG questions
provided by
PysioBank – a free scientific database with physiologic signals (here ecg)
EKG Academy – free EKG lectures, drills and quizzes
ECG Learning Center
created by Eccles Health Sciences Library at
 Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an electrogram
An electrogram (EGM) is a recording of electrical activity of organs such as the brain and heart, measured by monitoring changes in electric potential.
Brain Electroencephalography (EEG)
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is an electrical recording ...
of the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
which is a graph of voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to ...
versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials ...
s placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle ...
depolarization followed by repolarization
In neuroscience, repolarization refers to the change in membrane potential that returns it to a negative value just after the depolarization phase of an action potential which has changed the membrane potential to a positive value. The repolariza ...
during each cardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, followin ...
(heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances (such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a fast heart rate arising from the lower chambers of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period ...
), inadequate coronary artery blood flow (such as myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
), and electrolyte disturbances (such as hypokalemia and hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occa ...
).
Traditionally, "ECG" usually means a 12-lead ECG taken while lying down as discussed below.
However, other devices can record the electrical activity of the heart such as a Holter monitor but also some models of smartwatch
A smartwatch is a wearable computer in the form of a watch; modern smartwatches provide a local touchscreen interface for daily use, while an associated smartphone app provides management and telemetry, such as long-term biomonitoring. Whil ...
are capable of recording an ECG.
ECG signals can be recorded in other contexts with other devices.
In a conventional 12-lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles ("leads") and is recorded over a period of time (usually ten seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, followin ...
.
There are three main components to an ECG: the P wave, which represents depolarization of the atria; the QRS complex, which represents depolarization of the ventricles; and the T wave
In electrocardiography, the T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles. The interval from the beginning of the QRS complex to the apex of the T wave is referred to as the ''absolute refractory period''. The last half of the T wave ...
, which represents repolarization of the ventricles.
During each heartbeat, a healthy heart has an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells
350px, Image showing the cardiac pacemaker or SA node, the primary pacemaker within the electrical_conduction_system_of_the_heart">SA_node,_the_primary_pacemaker_within_the_electrical_conduction_system_of_the_heart.
The_muscle_contraction.htm ...
in the sinoatrial node, spreads throughout the atrium, and passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers, spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of heart drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.
Medical uses

 The overall goal of performing an ECG is to obtain information about the electrical functioning of the heart. Medical uses for this information are varied and often need to be combined with knowledge of the structure of the heart and physical examination signs to be interpreted. Some indications for performing an ECG include the following:
* Chest pain or suspected
The overall goal of performing an ECG is to obtain information about the electrical functioning of the heart. Medical uses for this information are varied and often need to be combined with knowledge of the structure of the heart and physical examination signs to be interpreted. Some indications for performing an ECG include the following:
* Chest pain or suspected myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
(heart attack), such as ST elevated myocardial infarction (STEMI) or non-ST elevated myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)
* Symptoms such as shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing di ...
, murmurs, fainting, seizure
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with lo ...
s, funny turns, or arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adult ...
s including new onset palpitations or monitoring of known cardiac arrhythmias
* Medication monitoring (e.g., drug-induced QT prolongation, Digoxin toxicity
Digoxin toxicity, also known as digoxin poisoning, is a type of poisoning that occurs in people who take too much of the medication digoxin or eat plants such as foxglove that contain a similar substance. Symptoms are typically vague. They may in ...
) and management of overdose (e.g., tricyclic overdose)
* Electrolyte abnormalities
Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function, ...
, such as hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occa ...
* Perioperative monitoring in which any form of anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), ...
is involved (e.g., monitored anesthesia care, general anesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a medically induced loss of consciousness that renders the patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general ...
). This includes preoperative assessment and intraoperative and postoperative monitoring.
* Cardiac stress test
A cardiac stress test (also referred to as a cardiac diagnostic test, cardiopulmonary exercise test, or abbreviated CPX test) is a cardiological test that measures the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical enviro ...
ing
* Computed tomography angiography
Computed tomography angiography (also called CT angiography or CTA) is a computed tomography technique used for angiography—the visualization of arteries and veins—throughout the human body. Using contrast injected into the blood vessels, im ...
(CTA) and magnetic resonance angiography
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a group of techniques based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to image blood vessels. Magnetic resonance angiography is used to generate images of arteries (and less commonly veins) in order to evaluate ...
(MRA) of the heart (ECG is used to "gate" the scanning so that the anatomical position of the heart is steady)
* Clinical cardiac electrophysiology, in which a catheter is inserted through the femoral vein and can have several electrodes along its length to record the direction of electrical activity from within the heart.
ECGs can be recorded as short intermittent tracings or ''continuous'' ECG monitoring. Continuous monitoring is used for critically ill patients, patients undergoing general anesthesia, and patients who have an infrequently occurring cardiac arrhythmia that would unlikely be seen on a conventional ten-second ECG. Continuous monitoring can be conducted by using Holter monitors, internal and external defibrillator
Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach). A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current (often called a ''coun ...
s and pacemakers, and/or biotelemetry.
Screening
 For adults, evidence does not support the use of ECGs among those without symptoms or at low risk of
For adults, evidence does not support the use of ECGs among those without symptoms or at low risk of cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, hea ...
as an effort for prevention. This is because an ECG may falsely indicate the existence of a problem, leading to misdiagnosis, the recommendation of invasive procedures, and overtreatment
Unnecessary health care (overutilization, overuse, or overtreatment) is health care provided with a higher volume or cost than is appropriate.
In the United States, where health care costs are the highest as a percentage of GDP, overuse was the ...
. However, persons employed in certain critical occupations, such as aircraft pilots, may be required to have an ECG as part of their routine health evaluations. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM, or HOCM when obstructive) is a condition in which the heart becomes thickened without an obvious cause. The parts of the heart most commonly affected are the interventricular septum and the ventricles. This r ...
screening may also be considered in adolescents as part of a sports physical out of concern for sudden cardiac death.
Electrocardiograph machines
 Electrocardiograms are recorded by machines that consist of a set of electrodes connected to a central unit. Early ECG machines were constructed with analog electronics, where the signal drove a motor to print out the signal onto paper. Today, electrocardiographs use analog-to-digital converters to convert the electrical activity of the heart to a
Electrocardiograms are recorded by machines that consist of a set of electrodes connected to a central unit. Early ECG machines were constructed with analog electronics, where the signal drove a motor to print out the signal onto paper. Today, electrocardiographs use analog-to-digital converters to convert the electrical activity of the heart to a digital signal
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; a ...
. Many ECG machines are now portable and commonly include a screen, keyboard, and printer on a small wheeled cart. Recent advancements in electrocardiography include developing even smaller devices for inclusion in fitness trackers and smart watches. These smaller devices often rely on only two electrodes to deliver a single lead I. Portable twelve-lead devices powered by batteries are also available.
Recording an ECG is a safe and painless procedure. The machines are powered by mains power but they are designed with several safety features including an earthed (ground) lead.
Other features include:
* Defibrillation
Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach). A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current (often called a ''coun ...
protection: any ECG used in healthcare may be attached to a person who requires defibrillation and the ECG needs to protect itself from this source of energy.
* Electrostatic discharge
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a sudden and momentary flow of electric current between two electrically charged objects caused by contact, an electrical short or dielectric breakdown. A buildup of static electricity can be caused by tribochar ...
is similar to defibrillation discharge and requires voltage protection up to 18,000 volts.
* Additionally, circuitry called the right leg driver can be used to reduce common-mode interference (typically the 50 or 60 Hz mains power).
* ECG voltages measured across the body are very small. This low voltage necessitates a low noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference aris ...
circuit, instrumentation amplifiers, and electromagnetic shielding.
* Simultaneous lead recordings: earlier designs recorded each lead sequentially, but current models record multiple leads simultaneously.
Most modern ECG machines include automated interpretation algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
s. This analysis calculates features such as the PR interval
In electrocardiography, the PR interval is the period, measured in milliseconds, that extends from the beginning of the P wave (the onset of atrial depolarization) until the beginning of the QRS complex (the onset of ventricular depolarization); ...
, QT interval
The QT interval is a measurement made on an electrocardiogram used to assess some of the electrical properties of the heart. It is calculated as the time from the start of the Q wave to the end of the T wave, and approximates to the time taken ...
, corrected QT (QTc) interval, PR axis, QRS axis, rhythm and more. The results from these automated algorithms are considered "preliminary" until verified and/or modified by expert interpretation. Despite recent advances, computer misinterpretation remains a significant problem and can result in clinical mismanagement.
Cardiac monitors
Besides the standard electrocardiograph machine, there are other devices capable of recording ECG signals. Portable devices have existed since the Holter monitor was produced in 1962. Traditionally, these monitors have used electrodes with patches on the skin to record the ECG, but new devices can stick to the chest as a single patch without need for wires, developed by Zio (Zio XT), TZ Medical (Trident),Philips
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), commonly shortened to Philips, is a Dutch multinational conglomerate corporation that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, it has been mostly headquartered in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarters is ...
(BioTel) and BardyDx (CAM) among many others.
Implantable devices such as the artificial cardiac pacemaker
An artificial cardiac pacemaker (or artificial pacemaker, so as not to be confused with the natural cardiac pacemaker) or pacemaker is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to the chambers of the heart eit ...
and implantable cardioverter-defibrillator are capable of measuring a "far field" signal between the leads in the heart and the implanted battery/generator that resembles an ECG signal (technically, the signal recorded in the heart is called an electrogram
An electrogram (EGM) is a recording of electrical activity of organs such as the brain and heart, measured by monitoring changes in electric potential.
Brain Electroencephalography (EEG)
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is an electrical recording ...
, which is interpreted differently).
Advancement of the Holter monitor became the implantable loop recorder that performs the same function but in an implantable device with batteries that last on the order of years.
Additionally, there are available various Arduino kits with ECG sensor modules and smartwatch
A smartwatch is a wearable computer in the form of a watch; modern smartwatches provide a local touchscreen interface for daily use, while an associated smartphone app provides management and telemetry, such as long-term biomonitoring. Whil ...
devices that are capable of recording an ECG signal as well, such as with the 4th generation Apple Watch, Samsung Galaxy Watch 4 and newer devices.
Electrodes and leads
coronal plane
The coronal plane (also known as the frontal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into dorsal and ventral sections. It is perpendicular to the sagittal and transverse planes.
Details
The coronal plane is an example of a longitud ...
(vertical), and six ''precordial leads'' or ''chest leads'' that lie on the perpendicular transverse plane
The transverse plane (also known as the horizontal plane, axial plane and transaxial plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into superior and inferior sections. It is perpendicular to the coronal and sagittal planes.
List of cli ...
(horizontal).
In medical settings, the term ''leads'' is also sometimes used to refer to the electrodes themselves, although this is technically incorrect.
The 10 electrodes in a 12-lead ECG are listed below.
Two types of electrodes in common use are a flat paper-thin sticker and a self-adhesive circular pad.
The former are typically used in a single ECG recording while the latter are for continuous recordings as they stick longer.
Each electrode consists of an electrically conductive electrolyte gel and a silver/silver chloride conductor.
The gel typically contains potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a salt ...
– sometimes silver chloride
Silver chloride is a chemical compound with the chemical formula Ag Cl. This white crystalline solid is well known for its low solubility in water (this behavior being reminiscent of the chlorides of Tl+ and Pb2+). Upon illumination or heat ...
as well – to permit electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
conduction from the skin to the wire and to the electrocardiogram.
The common virtual electrode, known as Wilson's central terminal (VW), is produced by averaging the measurements from the electrodes RA, LA, and LL to give an average potential of the body:
:
In a 12-lead ECG, all leads except the limb leads are assumed to be unipolar (aVR, aVL, aVF, V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6).
The measurement of a voltage requires two contacts and so, electrically, the unipolar leads are measured from the common lead (negative) and the unipolar lead (positive).
This averaging for the common lead and the abstract unipolar lead concept makes for a more challenging understanding and is complicated by sloppy usage of "lead" and "electrode".
In fact, instead of being a constant reference, VW has a value that fluctuates throughout the heart cycle. It also does not truly represent the center-of-heart potential due to the body parts the signals travel through.
Limb leads

 Leads I, II and III are called the ''limb leads''. The electrodes that form these signals are located on the limbs – one on each arm and one on the left leg. The limb leads form the points of what is known as
Leads I, II and III are called the ''limb leads''. The electrodes that form these signals are located on the limbs – one on each arm and one on the left leg. The limb leads form the points of what is known as Einthoven's triangle
Einthoven's triangle is an imaginary formation of three limb leads in a triangle used in electrocardiography, formed by the two shoulders and the pubis. The shape forms an inverted equilateral triangle with the heart at the center. It is named aft ...
.
* Lead I is the voltage between the (positive) left arm (LA) electrode and right arm (RA) electrode:
:
* Lead II is the voltage between the (positive) left leg (LL) electrode and the right arm (RA) electrode:
:
* Lead III is the voltage between the (positive) left leg (LL) electrode and the left arm (LA) electrode:
:
Augmented limb leads
Leads aVR, aVL, and aVF are the ''augmented limb leads''. They are derived from the same three electrodes as leads I, II, and III, but they use Goldberger's central terminal as their negative pole. Goldberger's central terminal is a combination of inputs from two limb electrodes, with a different combination for each augmented lead. It is referred to immediately below as "the negative pole". * Lead ''augmented vector right'' (aVR) has the positive electrode on the right arm. The negative pole is a combination of the left arm electrode and the left leg electrode: : * Lead ''augmented vector left'' (aVL) has the positive electrode on the left arm. The negative pole is a combination of the right arm electrode and the left leg electrode: : * Lead ''augmented vector foot'' (aVF) has the positive electrode on the left leg. The negative pole is a combination of the right arm electrode and the left arm electrode: : Together with leads I, II, and III, augmented limb leads aVR, aVL, and aVF form the basis of the hexaxial reference system, which is used to calculate the heart's electrical axis in the frontal plane. Older versions of the nodes (VR, VL, VF) use Wilson's central terminal as the negative pole, but the amplitude is too small for the thick lines of old ECG machines. The Goldberger terminals scale up (augments) the Wilson results by 50%, at the cost of sacrificing physical correctness by not having the same negative pole for all three.Precordial leads
The ''precordial leads'' lie in the transverse (horizontal) plane, perpendicular to the other six leads. The six precordial electrodes act as the positive poles for the six corresponding precordial leads: (V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6). Wilson's central terminal is used as the negative pole. Recently, unipolar precordial leads have been used to create bipolar precordial leads that explore the right to left axis in the horizontal plane.Specialized leads
Additional electrodes may rarely be placed to generate other leads for specific diagnostic purposes. ''Right-sided'' precordial leads may be used to better study pathology of the right ventricle or for dextrocardia (and are denoted with an R (e.g., V5R). ''Posterior leads'' (V7 to V9) may be used to demonstrate the presence of a posterior myocardial infarction. TheLewis lead
A Lewis Lead (also called the S5 lead) is a modified ECG lead used to detect atrial flutter waves when atrial flutter is suspected clinically, based on signs and symptoms, but is not definitely demonstrated on the standard 12 lead ECG. In order to ...
or S5-lead (requiring an electrode at the right sternal border in the second intercostal space) can be used to better detect atrial activity in relation to that of the ventricles.
An ''esophogeal lead'' can be inserted to a part of the esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to t ...
where the distance to the posterior wall of the left atrium is only approximately 5–6 mm (remaining constant in people of different age and weight). An esophageal lead avails for a more accurate differentiation between certain cardiac arrhythmias, particularly atrial flutter, AV nodal reentrant tachycardia and orthodromic atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia
Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), or atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia, is a type of abnormal fast heart rhythm and is classified as a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). AVRT is most commonly associated with Wolff ...
. It can also evaluate the risk in people with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, as well as terminate supraventricular tachycardia caused by re-entry.
An intracardiac electrogram (ICEG) is essentially an ECG with some added ''intracardiac leads'' (that is, inside the heart). The standard ECG leads (external leads) are I, II, III, aVL, V1, and V6. Two to four intracardiac leads are added via cardiac catheterization. The word "electrogram" (EGM) without further specification usually means an intracardiac electrogram.
Lead locations on an ECG report
A standard 12-lead ECG report (an electrocardiograph) shows a 2.5 second tracing of each of the twelve leads. The tracings are most commonly arranged in a grid of four columns and three rows. The first column is the limb leads (I, II, and III), the second column is the augmented limb leads (aVR, aVL, and aVF), and the last two columns are the precordial leads (V1 to V6). Additionally, a rhythm strip may be included as a fourth or fifth row. The timing across the page is continuous and not tracings of the 12 leads for the same time period. In other words, if the output were traced by needles on paper, each row would switch which leads as the paper is pulled under the needle. For example, the top row would first trace lead I, then switch to lead aVR, then switch to V1, and then switch to V4, and so none of these four tracings of the leads are from the same time period as they are traced in sequence through time.Contiguity of leads
Electrophysiology
The study of the conduction system of the heart is calledcardiac electrophysiology
Cardiac electrophysiology is a branch of cardiology and basic science focusing on the electrical activities of the heart. The term is usually used in clinical context, to describe studies of such phenomena by invasive (intracardiac) catheter reco ...
(EP). An EP study is performed via a right-sided cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization (heart cath) is the insertion of a catheter into a chamber or vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.
A common example of cardiac catheterization is coronary catheterization th ...
: a wire with an electrode at its tip is inserted into the right heart chambers from a peripheral vein, and placed in various positions in close proximity to the conduction system so that the electrical activity of that system can be recorded.
Standard catheter positions for an EP study include "high right atrium" or hRA near the sinus node, a "His" across the septal wall of the tricuspid valve to measure bundle of His, a "coronary sinus" into the coronary sinus, and a "right ventricle" in the apex of the right ventricle.
Interpretation
Interpretation of the ECG is fundamentally about understanding the electrical conduction system of the heart. Normal conduction starts and propagates in a predictable pattern, and deviation from this pattern can be a normal variation or be pathological. An ECG does not equate with mechanical pumping activity of the heart, for example, pulseless electrical activity produces an ECG that should pump blood but no pulses are felt (and constitutes amedical emergency
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long-term health, sometimes referred to as a situation risking "life or limb". These emergencies may require assistance from another, qualified ...
and CPR
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure consisting of chest compressions often combined with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spont ...
should be performed).
Ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and n ...
produces an ECG but is too dysfunctional to produce a life-sustaining cardiac output. Certain rhythms are known to have good cardiac output and some are known to have bad cardiac output.
Ultimately, an echocardiogram or other anatomical imaging modality is useful in assessing the mechanical function of the heart.
Like all medical tests, what constitutes "normal" is based on population studies. The heartrate range of between 60 and 100 beats per minute (bpm) is considered normal since data shows this to be the usual resting heart rate.
Theory
Background grid
ECGs are normally printed on a grid. The horizontal axis represents time and the vertical axis represents voltage. The standard values on this grid are shown in the adjacent image at 25mm/sec: * A small box is 1 mm × 1 mm and represents 0.1 mV × 0.04 seconds. * A large box is 5 mm × 5 mm and represents 0.5 mV × 0.20 seconds. The "large" box is represented by a heavier line weight than the small boxes.Rate and rhythm
In a normal heart, the heart rate is the rate at which the sinoatrial node depolarizes since it is the source of depolarization of the heart. Heart rate, like othervital signs
Vital signs (also known as vitals) are a group of the four to six most crucial medical signs that indicate the status of the body's vital (life-sustaining) functions. These measurements are taken to help assess the general physical health of a ...
such as blood pressure and respiratory rate, change with age.
In adults, a normal heart rate is between 60 and 100 bpm (normocardic), whereas it is higher in children.
A heart rate below normal is called "bradycardia
Bradycardia (also sinus bradycardia) is a slow resting heart rate, commonly under 60 beats per minute (BPM) as determined by an electrocardiogram. It is considered to be a normal heart rate during sleep, in young and healthy or elderly adults, ...
" (<60 in adults) and above normal is called "tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ( ...
" (>100 in adults).
A complication of this is when the atria and ventricles are not in synchrony and the "heart rate" must be specified as atrial or ventricular (e.g., the ventricular rate in ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and n ...
is 300–600 bpm, whereas the atrial rate can be normal 0–100or faster 00–150.
In normal resting hearts, the physiologic rhythm of the heart is normal sinus rhythm
A sinus rhythm is any cardiac rhythm in which depolarisation of the cardiac muscle begins at the sinus node. It is characterised by the presence of correctly oriented P waves on the electrocardiogram (ECG). Sinus rhythm is necessary, but not s ...
(NSR).
Normal sinus rhythm produces the prototypical pattern of P wave, QRS complex, and T wave.
Generally, deviation from normal sinus rhythm is considered a cardiac arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adult ...
.
Thus, the first question in interpreting an ECG is whether or not there is a sinus rhythm.
A criterion for sinus rhythm is that P waves and QRS complexes appear 1-to-1, thus implying that the P wave causes the QRS complex.
Once sinus rhythm is established, or not, the second question is the rate.
For a sinus rhythm, this is either the rate of P waves or QRS complexes since they are 1-to-1.
If the rate is too fast, then it is sinus tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia is an elevated sinus rhythm characterized by an increase in the rate of electrical impulses arising from the sinoatrial node. In adults, sinus tachycardia is defined as a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute (bpm). The ...
, and if it is too slow, then it is sinus bradycardia.
If it is not a sinus rhythm, then determining the rhythm is necessary before proceeding with further interpretation.
Some arrhythmias with characteristic findings:
* Absent P waves with "irregularly irregular" QRS complexes is the hallmark of atrial fibrillation.
* A "saw tooth" pattern with QRS complexes is the hallmark of atrial flutter.
* A sine wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in ...
pattern is the hallmark of ventricular flutter.
* Absent P waves with wide QRS complexes and a fast heart rate is ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a fast heart rate arising from the lower chambers of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period ...
.
Determination of rate and rhythm is necessary in order to make sense of further interpretation.
Axis
right axis deviation
The electrical axis of the heart is the net direction in which the wave of depolarization travels. It is measured using an electrocardiogram (ECG). Normally, this begins at the sinoatrial node (SA node); from here the wave of depolarisation travel ...
and beyond −30° is left axis deviation
In electrocardiography, left axis deviation (LAD) is a condition wherein the mean electrical axis of ventricular contraction of the heart lies in a frontal plane direction between −30° and −90°. This is reflected by a QRS complex positive ...
(the third quadrant of −90° to −180° is very rare and is an indeterminate axis).
A shortcut for determining if the QRS axis is normal is if the QRS complex is mostly positive in lead I and lead II (or lead I and aVF if +90° is the upper limit of normal).
The normal QRS axis is generally ''down and to the left'', following the anatomical orientation of the heart within the chest. An abnormal axis suggests a change in the physical shape and orientation of the heart or a defect in its conduction system that causes the ventricles to depolarize in an abnormal way.
The extent of a normal axis can be +90° or 105° depending on the source.
Amplitudes and intervals
 All of the waves on an ECG tracing and the intervals between them have a predictable time duration, a range of acceptable amplitudes (voltages), and a typical morphology. Any deviation from the normal tracing is potentially pathological and therefore of clinical significance.
For ease of measuring the amplitudes and intervals, an ECG is printed on graph paper at a standard scale: each 1 mm (one small box on the standard 25mm/s ECG paper) represents 40 milliseconds of time on the x-axis, and 0.1 millivolts on the y-axis.
All of the waves on an ECG tracing and the intervals between them have a predictable time duration, a range of acceptable amplitudes (voltages), and a typical morphology. Any deviation from the normal tracing is potentially pathological and therefore of clinical significance.
For ease of measuring the amplitudes and intervals, an ECG is printed on graph paper at a standard scale: each 1 mm (one small box on the standard 25mm/s ECG paper) represents 40 milliseconds of time on the x-axis, and 0.1 millivolts on the y-axis.
Limb leads and electrical conduction through the heart
 The animation shown to the right illustrates how the path of electrical conduction gives rise to the ECG waves in the limb leads. Recall that a positive current (as created by depolarization of cardiac cells) traveling towards the positive electrode and away from the negative electrode creates a positive deflection on the ECG. Likewise, a positive current traveling away from the positive electrode and towards the negative electrode creates a negative deflection on the ECG. The red arrow represents the overall direction of travel of the depolarization. The magnitude of the red arrow is proportional to the amount of tissue being depolarized at that instance. The red arrow is simultaneously shown on the axis of each of the 3 limb leads. Both the direction and the magnitude of the red arrow's projection onto the axis of each limb lead is shown with blue arrows. Then, the direction and magnitude of the blue arrows are what theoretically determine the deflections on the ECG. For example, as a blue arrow on the axis for Lead I moves from the negative electrode, to the right, towards the positive electrode, the ECG line rises, creating an upward wave. As the blue arrow on the axis for Lead I moves to the left, a downward wave is created. The greater the magnitude of the blue arrow, the greater the deflection on the ECG for that particular limb lead.
Frames 1–3 depict the depolarization being generated in and spreading through the Sinoatrial node. The SA node is too small for its depolarization to be detected on most ECGs. Frames 4–10 depict the depolarization traveling through the atria, towards the Atrioventricular node. During frame 7, the depolarization is traveling through the largest amount of tissue in the atria, which creates the highest point in the P wave. Frames 11–12 depict the depolarization traveling through the AV node. Like the SA node, the AV node is too small for the depolarization of its tissue to be detected on most ECGs. This creates the flat PR segment.
Frame 13 depicts an interesting phenomenon in an over-simplified fashion. It depicts the depolarization as it starts to travel down the interventricular septum, through the Bundle of His and
The animation shown to the right illustrates how the path of electrical conduction gives rise to the ECG waves in the limb leads. Recall that a positive current (as created by depolarization of cardiac cells) traveling towards the positive electrode and away from the negative electrode creates a positive deflection on the ECG. Likewise, a positive current traveling away from the positive electrode and towards the negative electrode creates a negative deflection on the ECG. The red arrow represents the overall direction of travel of the depolarization. The magnitude of the red arrow is proportional to the amount of tissue being depolarized at that instance. The red arrow is simultaneously shown on the axis of each of the 3 limb leads. Both the direction and the magnitude of the red arrow's projection onto the axis of each limb lead is shown with blue arrows. Then, the direction and magnitude of the blue arrows are what theoretically determine the deflections on the ECG. For example, as a blue arrow on the axis for Lead I moves from the negative electrode, to the right, towards the positive electrode, the ECG line rises, creating an upward wave. As the blue arrow on the axis for Lead I moves to the left, a downward wave is created. The greater the magnitude of the blue arrow, the greater the deflection on the ECG for that particular limb lead.
Frames 1–3 depict the depolarization being generated in and spreading through the Sinoatrial node. The SA node is too small for its depolarization to be detected on most ECGs. Frames 4–10 depict the depolarization traveling through the atria, towards the Atrioventricular node. During frame 7, the depolarization is traveling through the largest amount of tissue in the atria, which creates the highest point in the P wave. Frames 11–12 depict the depolarization traveling through the AV node. Like the SA node, the AV node is too small for the depolarization of its tissue to be detected on most ECGs. This creates the flat PR segment.
Frame 13 depicts an interesting phenomenon in an over-simplified fashion. It depicts the depolarization as it starts to travel down the interventricular septum, through the Bundle of His and Bundle branches
The bundle branches, or Tawara branches, are offshoots of the bundle of His in the heart's ventricle. They play an integral role in the electrical conduction system of the heart by transmitting cardiac action potentials from the bundle of His to ...
. After the Bundle of His, the conduction system splits into the left bundle branch and the right bundle branch. Both branches conduct action potentials at about 1 m/s. Interestingly, however, the action potential starts traveling down the left bundle branch about 5 milliseconds before it starts traveling down the right bundle branch, as depicted by frame 13. This causes the depolarization of the interventricular septum tissue to spread from left to right, as depicted by the red arrow in frame 14. In some cases, this gives rise to a negative deflection after the PR interval, creating a Q wave such as the one seen in lead I in the animation to the right. Depending on the mean electrical axis of the heart, this phenomenon can result in a Q wave in lead II as well.
Following depolarization of the interventricular septum, the depolarization travels towards the apex of the heart. This is depicted by frames 15–17 and results in a positive deflection on all three limb leads, which creates the R wave. Frames 18–21 then depict the depolarization as it travels throughout both ventricles from the apex of the heart, following the action potential in the Purkinje fibers. This phenomenon creates a negative deflection in all three limb leads, forming the S wave on the ECG. Repolarization of the atria occurs at the same time as the generation of the QRS complex, but it is not detected by the ECG since the tissue mass of the ventricles is so much larger than that of the atria. Ventricular contraction occurs between ventricular depolarization and repolarization. During this time, there is no movement of charge, so no deflection is created on the ECG. This results in the flat ST segment after the S wave.
Frames 24–28 in the animation depict repolarization of the ventricles. The epicardium is the first layer of the ventricles to repolarize, followed by the myocardium. The endocardium is the last layer to repolarize. The plateau phase of depolarization has been shown to last longer in endocardial cells than in epicardial cells. This causes repolarization to start from the apex of the heart and move upwards. Since repolarization is the spread of negative current as membrane potentials decrease back down to the resting membrane potential, the red arrow in the animation is pointing in the direction opposite of the repolarization. This therefore creates a positive deflection in the ECG, and creates the T wave.
Ischemia and infarction
Ischemia or non-ST elevation myocardial infarctions (non-STEMIs) may manifest as ST depression or inversion ofT wave
In electrocardiography, the T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles. The interval from the beginning of the QRS complex to the apex of the T wave is referred to as the ''absolute refractory period''. The last half of the T wave ...
s. It may also affect the high frequency band of the QRS.
ST elevation myocardial infarctions (STEMIs) have different characteristic ECG findings based on the amount of time elapsed since the MI first occurred. The earliest sign is ''hyperacute T waves,'' peaked T waves due to local hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occa ...
in ischemic myocardium. This then progresses over a period of minutes to elevations of the ST segment by at least 1 mm. Over a period of hours, a pathologic Q wave may appear and the T wave will invert. Over a period of days the ST elevation will resolve. Pathologic Q waves generally will remain permanently.
The coronary artery
The coronary arteries are the arterial blood vessels of coronary circulation, which transport oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The heart requires a continuous supply of oxygen to function and survive, much like any other tissue or organ o ...
that has been occluded can be identified in an STEMI based on the location of ST elevation. The left anterior descending
The left anterior descending artery (also LAD, anterior interventricular branch of left coronary artery, or anterior descending branch) is a branch of the left coronary artery. Blockage of this artery is often called the ''widow-maker infarction' ...
(LAD) artery supplies the anterior wall of the heart, and therefore causes ST elevations in anterior leads (V1 and V2). The LCx supplies the lateral aspect of the heart and therefore causes ST elevations in lateral leads (I, aVL and V6). The right coronary artery (RCA) usually supplies the inferior aspect of the heart, and therefore causes ST elevations in inferior leads (II, III and aVF).
Artifacts
An ECG tracing is affected by patient motion. Some rhythmic motions (such as shivering or tremors) can create the illusion of cardiac arrhythmia. Artifacts are distorted signals caused by a secondary internal or external sources, such as muscle movement or interference from an electrical device. Distortion poses significant challenges to healthcare providers, who employ various techniques and strategies to safely recognize these false signals. Accurately separating the ECG artifact from the true ECG signal can have a significant impact on patient outcomes and legal liabilities. Improper lead placement (for example, reversing two of the limb leads) has been estimated to occur in 0.4% to 4% of all ECG recordings, and has resulted in improper diagnosis and treatment including unnecessary use of thrombolytic therapy.Diagnosis
Numerous diagnoses and findings can be made based upon electrocardiography, and many are discussed above. Overall, the diagnoses are made based on the patterns. For example, an "irregularly irregular" QRS complex without P waves is the hallmark of atrial fibrillation; however, other findings can be present as well, such as a bundle branch block that alters the shape of the QRS complexes. ECGs can be interpreted in isolation but should be applied – like alldiagnostic tests
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic t ...
– in the context of the patient. For example, an observation of peaked T waves is not sufficient to diagnose hyperkalemia; such a diagnosis should be verified by measuring the blood potassium level. Conversely, a discovery of hyperkalemia should be followed by an ECG for manifestations such as peaked T waves, widened QRS complexes, and loss of P waves. The following is an organized list of possible ECG-based diagnoses.
Rhythm disturbances or arrhythmias:
* Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter without rapid ventricular response
* Premature atrial contraction (PACs) and premature ventricular contraction (PVCs)
* Sinus arrhythmia
Sinus arrhythmia is a commonly encountered variation of ''normal'' sinus rhythm. Sinus arrhythmia characteristically presents with an irregular rate in which the variation in the R-R interval vary by more than 0.12 seconds (120 milliseconds). Addit ...
* Sinus bradycardia and sinus tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia is an elevated sinus rhythm characterized by an increase in the rate of electrical impulses arising from the sinoatrial node. In adults, sinus tachycardia is defined as a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute (bpm). The ...
* Sinus pause and sinoatrial arrest
Sinoatrial arrest is a medical condition wherein the sinoatrial node of the heart transiently ceases to generate the electrical impulses that normally stimulate the myocardial tissues to contract and thus the heart to beat. It is defined as lasti ...
* Sinus node dysfunction and bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome
* Supraventricular tachycardia
** Atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response
** Atrial flutter with rapid ventricular response
** AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
** Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia
Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), or atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia, is a type of abnormal fast heart rhythm and is classified as a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). AVRT is most commonly associated with Wolff ...
** Junctional ectopic tachycardia
** Atrial tachycardia
Atrial tachycardia is a type of heart rhythm problem in which the heart's electrical impulse comes from an ectopic pacemaker (that is, an abnormally located cardiac pacemaker) in the upper chambers ( atria) of the heart, rather than from the sin ...
*** Ectopic atrial tachycardia (unicentric)
*** Multifocal atrial tachycardia
*** Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
** Sinoatrial nodal reentrant tachycardia
* Torsades de pointes (polymorphic ventricular tachycardia)
* Wide complex tachycardia
** Ventricular flutter
** Ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and n ...
** Ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a fast heart rate arising from the lower chambers of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period ...
(monomorphic ventricular tachycardia)
* Pre-excitation syndrome
Pre-excitation syndrome is a heart condition in which part of the cardiac ventricles are activated too early. Pre-excitation is caused by an abnormal electrical connection or accessory pathway between or within the cardiac chambers. Pre-excitatio ...
** Lown–Ganong–Levine syndrome
Lown–Ganong–Levine syndrome (LGL) is a pre-excitation syndrome of the heart. Those with LGL syndrome have episodes of abnormal heart racing with a short PR interval and normal QRS complexes seen on their electrocardiogram when in a normal sin ...
** Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
* J wave (Osborn wave)
Heart block and conduction problems:
* Aberration
* Sinoatrial block
A sinoatrial block (also spelled sinuatrial block) is a disorder in the normal rhythm of the heart, known as a heart block, that is initiated in the sinoatrial node. The initial action impulse in a heart is usually formed in the sinoatrial node ...
: first, second, and third-degree
* AV node
** First-degree AV block
** Second-degree AV block (Mobitz enckebachI and II)
** Third-degree AV block or complete AV block
* Right bundle
** Incomplete right bundle branch block (IRBBB)
** Complete right bundle branch block
A right bundle branch block (RBBB) is a heart block in the right bundle branch of the electrical conduction system.
During a right bundle branch block, the right ventricle is not directly activated by impulses travelling through the right bund ...
(RBBB)
* Left bundle
** Incomplete left bundle branch block (ILBBB)
** Complete left bundle branch block (LBBB)
** Left anterior fascicular block (LAFB)
** Left posterior fascicular block (LPFB)
** Bifascicular block
Bifascicular block is a conduction abnormality in the heart where two of the three main fascicles of the His/Purkinje system are blocked.
Most commonly, it refers to a combination of right bundle branch block (RBBB) and either left anterior fa ...
(LAFB plus LPFB)
** Trifascicular block (LAFP plus FPFB plus RBBB)
* QT syndromes
** Brugada syndrome
Brugada syndrome (BrS) is a genetic disorder in which the electrical activity of the heart is abnormal due to channelopathy. It increases the risk of abnormal heart rhythms and sudden cardiac death. Those affected may have episodes of synco ...
** Short QT syndrome
** Long QT syndrome
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a condition affecting repolarization (relaxing) of the heart after a heartbeat, giving rise to an abnormally lengthy QT interval. It results in an increased risk of an irregular heartbeat which can result in fainting, ...
s, genetic and drug-induced
* Right and left atrial abnormality
Electrolytes disturbances and intoxication:
* Digitalis intoxication
* Calcium: hypocalcemia and hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcem ...
* Potassium: hypokalemia and hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occa ...
* Serotonin Toxicity
Ischemia and infarction:
* Wellens' syndrome (LAD occlusion)
* de Winter T waves (LAD occlusion)
* ST elevation and ST depression
* High Frequency QRS changes
* Myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
(heart attack)
** Non-Q wave myocardial infarction
** NSTEMI
** STEMI
** Sgarbossa's criteria for ischemia with a LBBB
Structural:
* Acute pericarditis
* Right
Rights are legal, social, or ethical principles of freedom or entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal system, social convention, or ethical ...
and left ventricular hypertrophy
* Right ventricular strain or S1Q3T3 (can be seen in pulmonary embolism)
History

 * In 1872,
* In 1872, Alexander Muirhead
Alexander Muirhead, FRS, (26 May 1848 – 13 December 1920) born in East Saltoun, East Lothian, Scotland was an electrical engineer specialising in wireless telegraphy.
Biography
Muirhead studied for his Bachelor of Science at University Coll ...
is reported to have attached wires to the wrist of a patient with fever to obtain an electronic record of their heartbeat.
* In 1882, John Burdon-Sanderson
Sir John Scott Burdon-Sanderson, 1st Baronet, FRS, HFRSE D.Sc. (21 December 182823 November 1905) was an English physiologist born near Newcastle upon Tyne, and a member of a well known Northumbrian family.
Biography
He was born at Jesmond ...
working with frogs, was the first to appreciate that the interval between variations in potential was not electrically quiescent and coined the term "isoelectric interval" for this period.
* In 1887, Augustus Waller invented an ECG machine consisting of a Lippmann capillary electrometer fixed to a projector. The trace from the heartbeat was projected onto a photographic plate that was itself fixed to a toy train. This allowed a heartbeat to be recorded in real time.
* In 1895, Willem Einthoven
Willem Einthoven (21 May 1860 – 29 September 1927) was a Dutch doctor and physiologist. He invented the first practical electrocardiograph (ECG or EKG) in 1895 and received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1924 for it ("for the ...
assigned the letters P, Q, R, S, and T to the deflections in the theoretical waveform he created using equations which corrected the actual waveform obtained by the capillary electrometer to compensate for the imprecision of that instrument. Using letters different from A, B, C, and D (the letters used for the capillary electrometer's waveform) facilitated comparison when the uncorrected and corrected lines were drawn on the same graph. Einthoven probably chose the initial letter P to follow the example set by Descartes in geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
. When a more precise waveform was obtained using the string galvanometer, which matched the corrected capillary electrometer waveform, he continued to use the letters P, Q, R, S, and T, and these letters are still in use today. Einthoven also described the electrocardiographic features of a number of cardiovascular disorders.
* In 1897, the string galvanometer was invented by the French engineer Clément Ader
Clément Ader (2 April 1841 – 3 May 1925) was a French inventor and engineer who was born near Toulouse in Muret, Haute-Garonne, and died in Toulouse. He is remembered primarily for his pioneering work in aviation. In 1870 he was also one of ...
.
* In 1901, Einthoven, working in Leiden
Leiden (; in English and archaic Dutch also Leyden) is a city and municipality in the province of South Holland, Netherlands. The municipality of Leiden has a population of 119,713, but the city forms one densely connected agglomeration w ...
, the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, used the string galvanometer: the first practical ECG. This device was much more sensitive than the capillary electrometer Waller used.
* In 1924, Einthoven was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his pioneering work in developing the ECG.
* By 1927, General Electric had developed a portable apparatus that could produce electrocardiograms without the use of the string galvanometer. This device instead combined amplifier tubes similar to those used in a radio with an internal lamp and a moving mirror that directed the tracing of the electric pulses onto film.
* In 1937, Taro Takemi invented a new portable electrocardiograph machine.
* In 1942, Emanuel Goldberger increases the voltage of Wilson's unipolar leads by 50% and creates the augmented limb leads aVR, aVL and aVF. When added to Einthoven's three limb leads and the six chest leads we arrive at the 12-lead electrocardiogram that is used today.
* In the late 1940s Rune Elmqvist
Rune Elmqvist (1906–1996) developed the first implantable pacemaker in 1958, working under the direction of Åke Senning, senior physician and cardiac surgeon at the Karolinska University Hospital in Solna, Sweden.
Elmqvist initially worked as ...
invented an inkjet printer - thin jets of ink deflected by electrical potentials from the heart, with good frequency response and direct recording of ECG on paper - the device, called the Mingograf, was sold by Siemens Elema until the 1990s.
Etymology
The word is derived from the Greek ''electro'', meaning related to electrical activity; ''kardia'', meaning heart; and ''graph'', meaning "to write".See also
*Signal-averaged electrocardiogram
Signal-averaged electrocardiography (SAECG) is a special electrocardiographic technique, in which multiple electric signals from the heart are averaged to remove interference and reveal small variations in the QRS complex, usually the so-called ...
* Electrical conduction system of the heart
* Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocorte ...
* Electrogastrogram
* Electropalatography
Electropalatography (EPG) is a technique used to monitor contacts between the tongue and hard palate, particularly during articulation and speech.
A custom-made artificial palate is moulded to fit against a speaker's hard palate. The artificial p ...
* Electroretinography
* Emergency medicine
Emergency medicine is the Medical specialty, medical speciality concerned with the care of illnesses or Injury, injuries requiring immediate medical attention. Emergency physicians (often called “ER doctors” in the United States) continuous ...
* Forward problem of electrocardiology
The forward problem of electrocardiology is a computational and mathematical approach to study the electrical activity of the heart through the body surface. The principal aim of this study is to computationally reproduce an electrocardiogram (EC ...
* Heart rate
* Heart rate monitor
* KardiaMobile
* Wireless ambulatory ECG
Wireless ambulatory electrocardiography (ECG) is a type of ambulatory electrocardiography with recording devices that use wireless technology, such as Bluetooth and smartphones, for at-home cardiac monitoring (monitoring of heart rhythms). These d ...
Notes
References
External links
The whole ECG course on 1 A4 paper
fro
ECGpedia
a wiki encyclopedia fo
a course on interpretation of ECG
Wave Maven – a large database of practice ECG questions
provided by
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) in Boston, Massachusetts is a teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. It was formed out of the 1996 merger of Beth Israel Hospital (founded in 1916) and New England Deaconess Hospital (founde ...
PysioBank – a free scientific database with physiologic signals (here ecg)
EKG Academy – free EKG lectures, drills and quizzes
ECG Learning Center
created by Eccles Health Sciences Library at
University of Utah
The University of Utah (U of U, UofU, or simply The U) is a public research university in Salt Lake City, Utah. It is the flagship institution of the Utah System of Higher Education. The university was established in 1850 as the University of De ...
{{Authority control
Cardiac electrophysiology
Diagnostic cardiology
Electrodiagnosis
Electrophysiology
Mathematics in medicine
Medical tests
Dutch inventions
Science and technology in the Netherlands
Biology in the Netherlands