|
Cannabicitran
Cannabicitran (CBTC) is a phytocannabinoid first isolated in 1974 as a trace component of ''Cannabis sativa'', Structurally related compounds can be found in some other plants. It is not psychoactive, but was found to reduce intraocular pressure in tests on rabbits, which may reflect agonist activity at the NAGly receptor (formally GPR18) that is known to be a target of many structurally related cannabinoids. See also * 9-OH-HHC * Cannabichromene * Cannabicyclol * Cannabidiol dimethyl ether * Cannabielsoin * Cannabigerol * Cannabimovone * Cannabitriol Cannabitriol ((+)-CBT, (''S'',''S'')-9,10-Dihydroxy-Δ6a(10a)-THC) is a phytocannabinoid first isolated in 1966, an oxidation product of tetrahydrocannabinol which has been identified both as a trace component of cannabis and as a metabolite in ... References Benzochromenes Phytocannabinoids Heterocyclic compounds with 4 rings Oxygen heterocycles {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9-OH-HHC
9-Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol (9-OH-HHC) is a semi-synthetic derivative of tetrahydrocannabinol. It is formed as an impurity in the synthesis of Delta-8-THC, and retains activity in animal studies though with only around 1/10 the potency of Δ9-THC, with the 9α- and 9β- enantiomers having around the same potency. See also * 9-Nor-9β-hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol * 11-Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol * 11-Hydroxy-THC * 11-Hydroxy-Delta-8-THC * Cannabicitran * Cannabitriol * Delta-10-THC * Hexahydrocannabinol Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a hydrogenated derivative of tetrahydrocannabinol. It is a naturally occurring phytocannabinoid that has rarely been identified as a trace component in ''Cannabis sativa'', but can also be produced synthetically by hy ... References Cannabinoids Benzochromenes Phenols {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabidiol Dimethyl Ether
Cannabidiol dimethyl ether (CBDD) is a trace component of cannabis which can also be made synthetically. It is a potent and selective inhibitor of the enzyme 15-lipoxygenase and inhibits oxygenation of linoleic acid, a process involved in the development of atherosclerosis. See also * 4'-Fluorocannabidiol * 7-Hydroxycannabidiol * 8,9-Dihydrocannabidiol * Cannabicitran * Delta-6-Cannabidiol * KLS-13019 * O-1918 O-1918 is a synthetic compound related to cannabidiol, which is an antagonist at two former orphan receptors GPR18 and GPR55, that appear to be related to the cannabinoid receptors. O-1918 is used in the study of these receptors, which have been ... References Cannabinoids Methoxy compounds {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabielsoin
Cannabielsoin (CBE) is a metabolite of cannabidiol, one of the major chemical components of cannabis. History Cannabielsoin in scientific journals was first cited in 1973. It was concluded that cannabielsoin was formed from cannabidiol as part of the metabolic process and is non-psychoactive. See also * Cannabicitran * Cannabicyclol * Cannabimovone * Cannabitriol Cannabitriol ((+)-CBT, (''S'',''S'')-9,10-Dihydroxy-Δ6a(10a)-THC) is a phytocannabinoid first isolated in 1966, an oxidation product of tetrahydrocannabinol which has been identified both as a trace component of cannabis and as a metabolite in ... References Cannabis Dibenzofurans Isopropenyl compounds Phenols Tertiary alcohols Human drug metabolites Phytocannabinoids {{Cannabis-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabimovone
Cannabimovone (CBM) is a phytocannabinoid first isolated from a non-psychoactive strain of ''Cannabis sativa'' in 2010, which is thought to be a rearrangement product of cannabidiol. It lacks affinity for cannabinoid receptors, but acts as an agonist at both TRPV1 and PPARγ. See also * Cannabichromene * Cannabicitran * Cannabicyclol * Cannabielsoin * Cannabigerol * Cannabinodiol * Cannabitriol * Delta-6-CBD Delta-6-cannabidiol (∆6-CBD) is a positional isomer of cannabidiol, found in only trace amounts in natural cannabis plants but readily synthesised from cannabidiol by base-catalysed migration of the double bond. See also * 4'-Fluorocannabidio ... References Cannabinoids Ketones Isopropenyl compounds Cyclopentanols Phenols {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabitriol
Cannabitriol ((+)-CBT, (''S'',''S'')-9,10-Dihydroxy-Δ6a(10a)-THC) is a phytocannabinoid first isolated in 1966, an oxidation product of tetrahydrocannabinol which has been identified both as a trace component of cannabis and as a metabolite in cannabis users. Its pharmacology has been little studied, though it has been found to act as an antiestrogen and aromatase inhibitor. See also * 8,11-Dihydroxy-THC * 9-OH-HHC * Cannabicitran (also sometimes called CBT) * Delta-3-THC Delta-3-Tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta-3-THC, Δ3-THC, Δ6a(10a)-THC, EA-1477) is a synthetic isomer of tetrahydrocannabinol, developed during the original research in the 1940s to develop synthetic routes to the natural products Δ8-THC and Δ9-TH ... References External linksCBD Oil & Capsules Cannabinoids Benzochromenes Phenols {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytocannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a major constituent of temperate Cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabis Sativa
''Cannabis sativa'' is an annual Herbaceous plant, herbaceous flowering plant indigenous to East Asia, Eastern Asia, but now of cosmopolitan distribution due to widespread cultivation. It has been cultivated throughout recorded history, used as a source of Hemp#fibre, industrial fiber, Hemp oil, seed oil, Hempnut, food, Cannabis (drug), recreation, entheogenic use of cannabis, religious and spiritual moods and Medical cannabis, medicine. Each part of the plant is harvested differently, depending on the purpose of its use. The species was first classified by Carl Linnaeus in 1753. The word ''Sativum, sativa'' means "things that are cultivated." Plant physiology The flowers of ''Cannabis sativa'' are unisexual and plants are most often either male or female. It is a short-day flowering plant, with staminate (male) plants usually taller and less robust than pistillate (female or male) plants. The flowers of the female plant are arranged in racemes and can produce hundreds of seeds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraocular Pressure
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the fluid pressure inside the eye. Tonometry is the method eye care professionals use to determine this. IOP is an important aspect in the evaluation of patients at risk of glaucoma. Most tonometers are calibrated to measure pressure in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg). Physiology Intraocular pressure is determined by the production and drainage of aqueous humour by the ciliary body and its drainage via the trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral outflow. The reason for this is because the vitreous humour in the posterior segment has a relatively fixed volume and thus does not affect intraocular pressure regulation. An important quantitative relationship (Goldmann's equation) is as follows: :P_o = \frac + P_v Where: * P_o is the IOP in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) * F the rate of aqueous humour formation in microliters per minute (μL/min) * U the resorption of aqueous humour through the uveoscleral route (μL/min) * C is the facility of outflow in micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NAGly Receptor
''N''-Arachidonyl glycine receptor (NAGly receptor), also known as G protein-coupled receptor 18 (GPR18), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPR18'' gene. Along with the other previously "orphan" receptors GPR55 and GPR119, GPR18 has been found to be a receptor for endogenous lipid neurotransmitters, several of which also bind to cannabinoid receptors. It has been found to be involved in the regulation of intraocular pressure. Research supports the hypothesis that GPR18 is the abnormal cannabidiol receptor and N-arachidonoyl glycine, the endogenous lipid metabolite of anandamide, initiates directed microglial migration in the CNS through activation of GPR18, though recent evidence demonstrates that NAGly was not shown to be a GPR18 agonist in rat sympathetic neurons. Resolvin D2 (RvD2), a member of the specialized proresolving mediators (SPM) class of polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolites, is an activating ligand for GPR18; RvD2 and its activation of GPR18 contribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
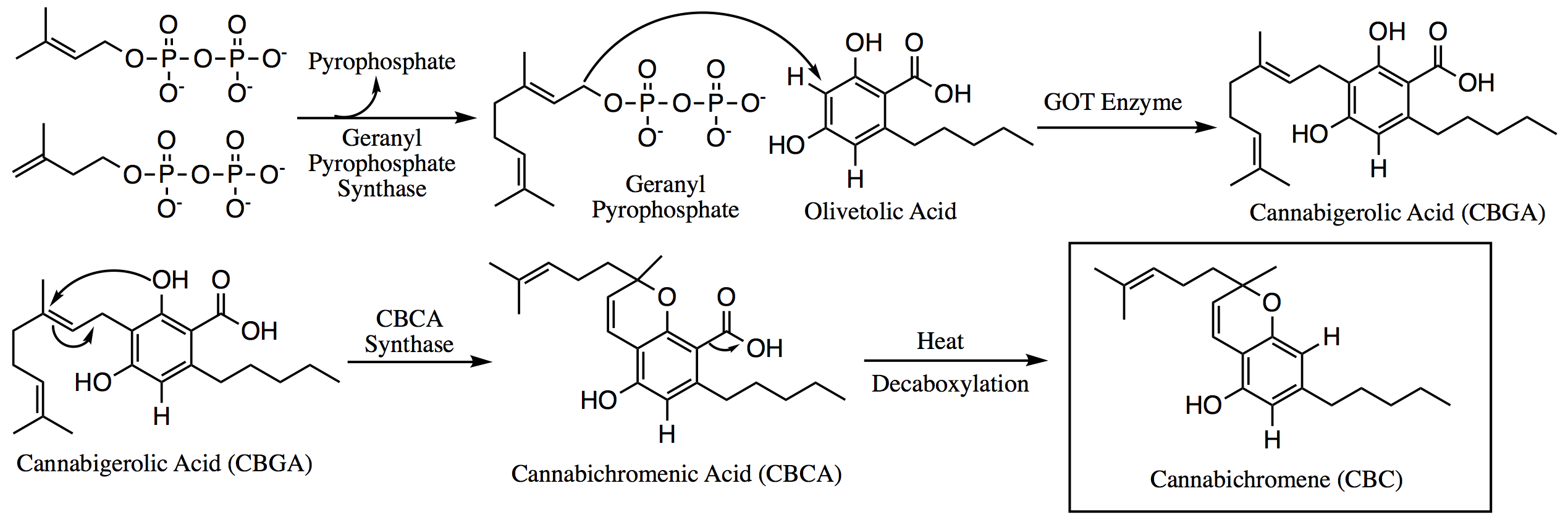
Cannabichromene
Cannabichromene (CBC), also called cannabichrome, cannanbichromene, pentylcannabichromene or cannabinochromene, is an anti-inflammatory which may contribute to the pain-killing effect of cannabis. It is one of the hundreds of cannabinoids found in the ''Cannabis'' plant, and is therefore a phytocannabinoid. It bears structural similarity to the other natural cannabinoids, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), cannabidiol (CBD), and cannabinol (CBN), among others. CBC and its derivatives are as abundant as cannabinols in cannabis. It is not scheduled by the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. It is more common in tropical cannabis varieties. Biosynthesis Within the ''Cannabis'' plant, CBC occurs mainly as cannabichromenic acid (CBCA, 2-COOH-CBC, CBC-COOH). Geranyl pyrophosphate and olivetolic acid combine to produce cannabigerolic acid (CBGA; the sole intermediate for all other phytocannabinoids), which is cyclized by the enzyme CBCA synthas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabicyclol
Cannabicyclol (CBL) is a non- psychoactive cannabinoid found in ''Cannabis''. CBL is a degradative product like cannabinol, with cannabichromene degrading into CBL through natural irradiation or under acid conditions. CBL is not scheduled under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. See also * Cannabis * Medical cannabis References External links CTD's Cannabicyclol pagefrom the Comparative Toxicogenomics Database The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD) is a public website and research tool launched in November 2004 that curates scientific data describing relationships between chemicals/drugs, genes/proteins, diseases, taxa, phenotypes, GO annotations ... Wiley-VCH list of chemicals Phytocannabinoids Phenols Benzopyrans Cyclobutanes Cyclopentanes Heterocyclic compounds with 4 rings {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabigerol
Cannabigerol (CBG) is one of more than 120 identified cannabinoid compounds found in the plant genus ''Cannabis''. Cannabigerol is the decarboxylated form of cannabigerolic acid, the parent molecule from which other cannabinoids are synthesized. Cannabigerol is normally a minor constituent of cannabis. During plant growth, most of the cannabigerol is converted into other cannabinoids, primarily tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or cannabidiol (CBD), leaving about 1% cannabigerol in the plant. Some strains, however, produce larger amounts of cannabigerol and cannabigerolic acid, while having low quantities of other cannabinoids, like THC and CBD. Although cannabigerol is sold as a dietary supplement, its effects and safety for human consumption are undefined. Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of cannabigerol begins by loading hexanoyl-CoA onto a polyketide synthase assembly protein and subsequent condensation with three molecules of malonyl-CoA. This polyketide is cyclized to oliveto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |