|
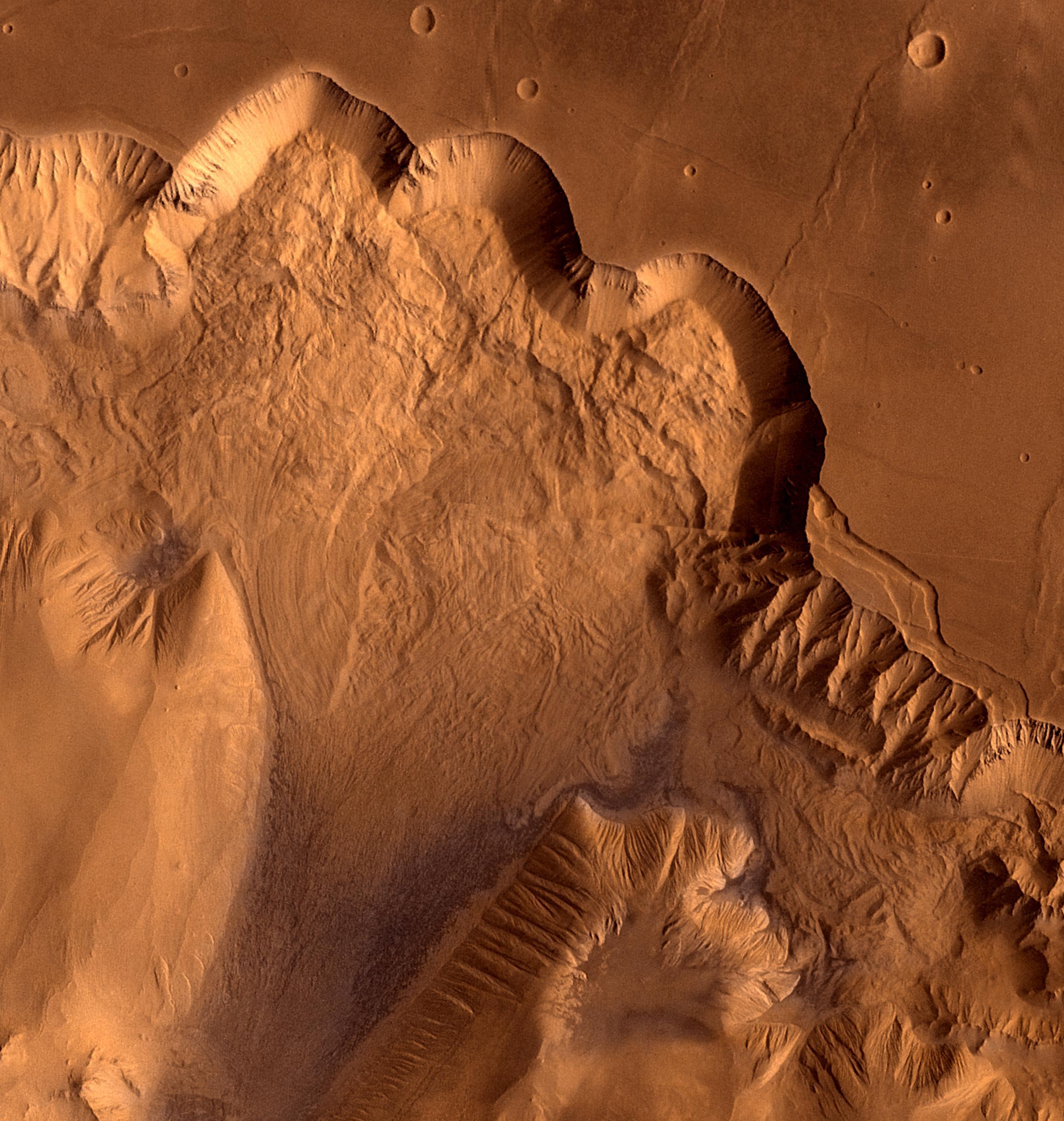
Candor Chasma
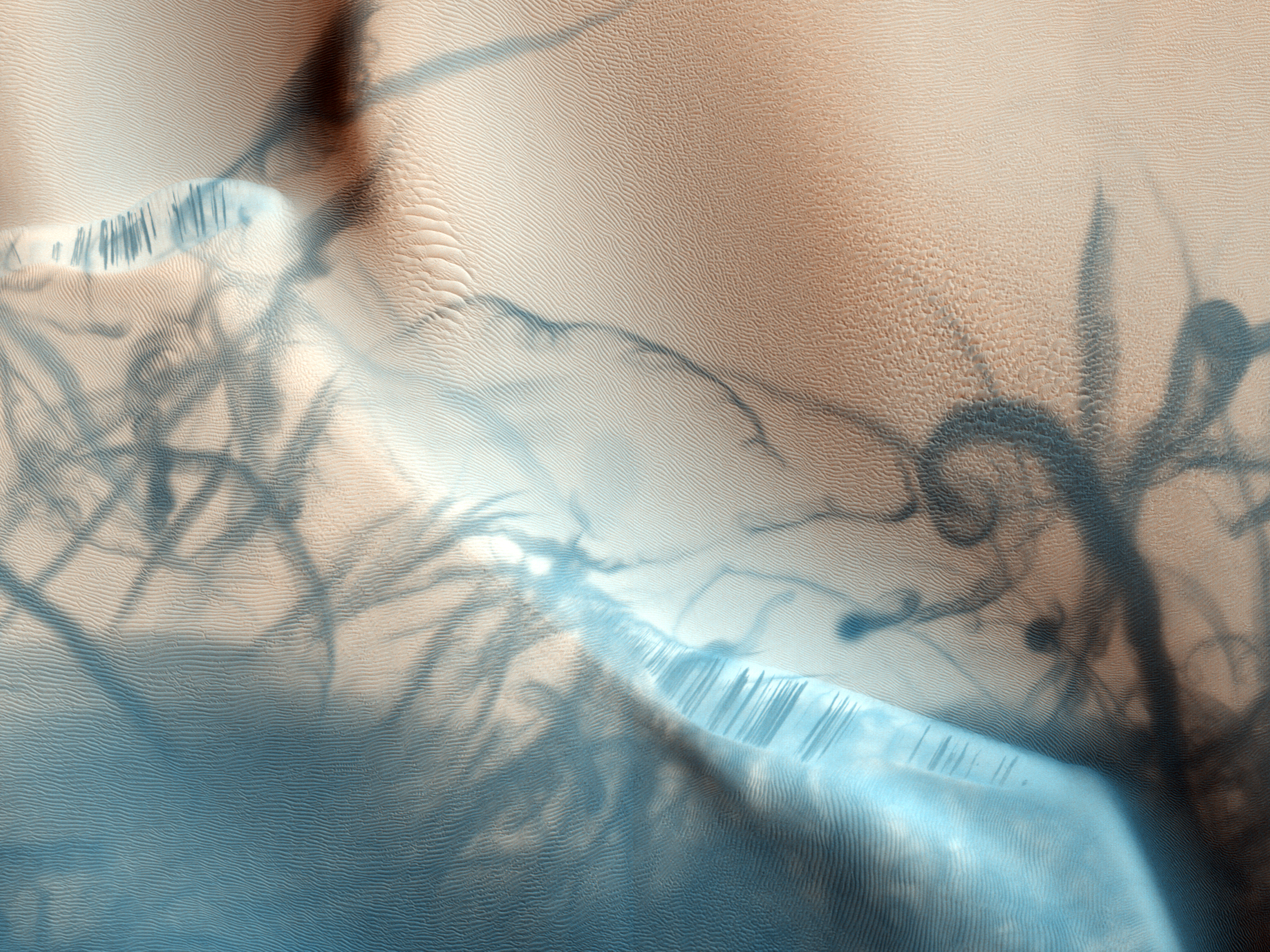
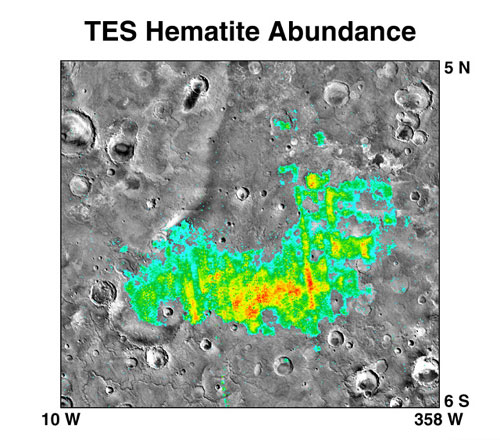
Candor Chasma is one of the largest canyons in the Valles Marineris canyon system on Mars. The feature is geographically divided into two halves: East and West Candor Chasmas, respectively. It is unclear how the canyon originally formed; one theory is that it was expanded and deepened by tectonic processes similar to a graben, while another suggests that it was formed by subsurface water erosion similar to a karst. Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, MRO discovered sulfates, hydrated sulfates, and iron oxides in Candor Chasma. One of the pictures below shows branched channels. Many places on Mars show channels of different sizes. Many of these channels probably carried water, at least for a time. The climate of Mars may have been such in the past that water ran on its surface. It has been known for some time that Mars undergoes many large changes in its tilt or obliquity because its two small moons lack the gravity to stabilize it, as the Moon stabilizes Earth; at times the tilt of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Emission Imaging System
The Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) is a camera on board the 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter. It images Mars in the visible and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum in order to determine the thermal properties of the surface and to refine the distribution of minerals on the surface of Mars as determined by the Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES). Additionally, it helps scientists to understand how the mineralogy of Mars relates to its landforms, and it can be used to search for thermal hotspots in the Martian subsurface. THEMIS is managed from the Mars Space Flight Facility at Arizona State University and was built by the Santa Barbara Remote Sensing division of Raytheon Technologies Corporation, an American multinational conglomerate headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts. The instrument is named after Themis, the goddess of justice in ancient Greek mythology. Infrared camera THEMIS detects thermal infrared energy emitted by the Martian surface at nine di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophir Chasma
Ophir Chasma is a canyon in the Coprates quadrangle of Mars at 4° south latitude and 72.5° west longitude. It is about 317 km long and was named after Ophir, a land mentioned in the Bible. In the Bible it was the land which King Solomon sent an expedition that returned with gold. It is a classical albedo feature name. Valles Marineris canyon system Ophir Chasma is part of the largest canyon system in the solar system; this great canyon would go almost all the way across the United States. The name for the whole system of canyons is Valles Marineris. Starting at the west with Noctis Labyrinthus in the Phoenicis Lacus quadrangle, the canyon system ends in the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle with Capri Chasma and Eos Chasma (in the south). The word ''chasma'' has been designated by the International Astronomical Union to refer to an elongate, steep-sided depression. Valles Marineris was discovered by and named for the Mariner 9 mission. Moving east from Noctis Labyri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melas Chasma
Melas Chasma is a canyon on Mars, the widest segment of the Valles Marineris canyon system, located east of Ius Chasma at 9.8°S, 283.6°E in Coprates quadrangle. It cuts through layered deposits that are thought to be sediments from an old lake that resulted from runoff of the valley networks to the west. Other theories include windblown sediment deposits and volcanic ash. Support for abundant, past Water on Mars, water in Melas Chasma is the discovery by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, MRO of hydrated sulfates. In addition, sulfate and iron oxides were found by the same satellite. Although not chosen as one of the finalists, it was one of eight potential landing sites for the ''Mars 2020'' rover, a mission with a focus on astrobiology. The floor of Melas Chasma is about 70% younger massive material that is thought to be volcanic ash whipped up by the wind into eolian features. It also contains rough floor material from the erosion of the canyon walls. Around the edges of Melas is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juventae Chasma
Juventae Chasma is an enormous box canyon (250 km × 100 km) on Mars which opens to the north and forms the outflow channel Maja Valles. Juventae Chasma is located north of Valles Marineris in the Coprates quadrangle and cuts more than 5 km into the plains of Lunae Planum. Name Juventae was named by Giovanni Schiaparelli after the mythical ''Juventae Fons'', the fountain of youth. Observations The floor of Juventae Chasma is partly covered by sand dunes. There is also a 2.5 km high mountain inside Juventae, 59 km long and 23 km wide, that was confirmed by Mars Express to be composed of sulfate deposits. MRO discovered sulfates, hydrated sulfates, and iron oxides in Juventae Chasma. Juventae Chasma has four bright mounds or light-toned interior layered deposits (IlD's), as they are often called. Researchers have found that monohydrated sulfates were first deposited on the floor. And then polyhydrated sulfates were laid down. Kieserite, a magne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
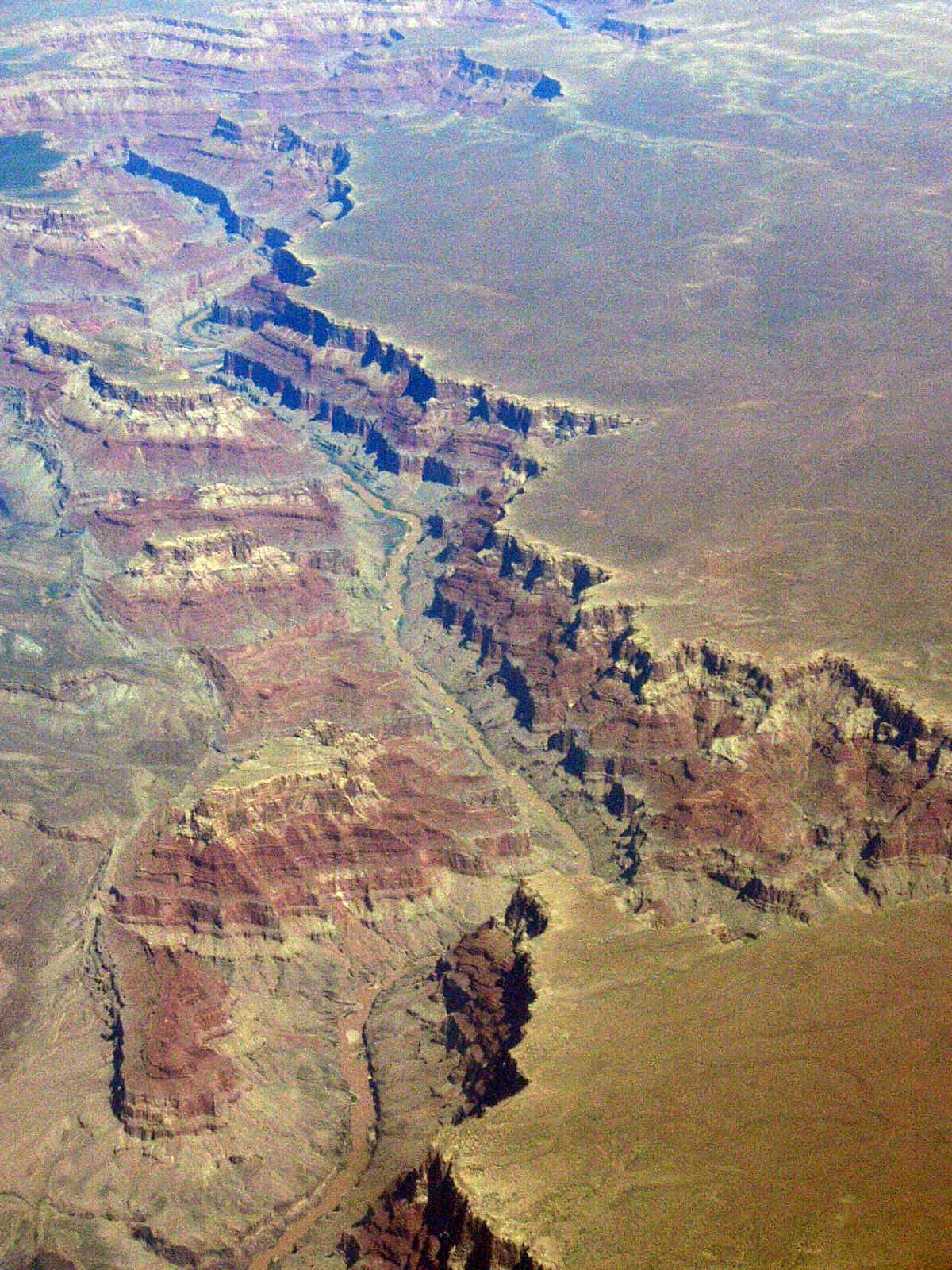
Canyon
A canyon (from ; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), or gorge, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosion, erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tendency to cut through underlying surfaces, eventually wearing away rock layers as sediments are removed downstream. A river bed will gradually reach a baseline elevation, which is the same elevation as the body of water into which the river drains. The processes of weathering and erosion will form canyons when the river's River source, headwaters and estuary are at significantly different elevations, particularly through regions where softer rock layers are intermingled with harder layers more resistant to weathering. A canyon may also refer to a rift between two mountain peaks, such as those in ranges including the Rocky Mountains, the Alps, the Himalayas or the Andes. Usually, a river or stream carves out such splits between mountains. Examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valles Marineris
Valles Marineris (; Latin for ''Mariner program, Mariner Valleys'', named after the ''Mariner 9'' Mars orbiter of 1971–72 which discovered it) is a system of canyons that runs along the Mars, Martian surface east of the Tharsis region. At more than long, wide and up to deep, Valles Marineris is one of the largest List of largest rifts and valleys in the Solar System, canyons of the Solar System, surpassed in length only by the rift valleys of the mid-ocean ridge system of Earth. Valles Marineris is located along the equator of Mars, on the east side of the Tharsis Bulge, and stretches for nearly a quarter of the planet's circumference. The canyon system starts in the west with Noctis Labyrinthus; proceeding to the east are Tithonium Chasma, Tithonium and Ius Chasma, Ius chasmata, then Melas Chasma, Melas, Candor Chasma, Candor and Ophir Chasma, Ophir chasmata, then Coprates Chasma, then Ganges Chasma, Ganges, Capri Chasma, Capri and Eos Chasma, Eos chasmata; finally it emptie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos (moon), Phobos and Deimos (moon), Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and List of tallest mountains in the Solar System, highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The North Polar Basin (Mars), Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults. Etymology ''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic context by Eduard Suess in 1883. The plural form is either ''graben'' or ''grabens''. Formation A graben is a valley with a distinct escarpment on each side caused by the displacement of a block of land downward. Graben often occur side by side with horsts. Horst and graben structures indicate tensional forces and crustal stretching. Graben are produced from parallel normal faults, where the displacement of the hanging wall is downward, while that of the footwall is upward. The faults typically dip toward the center of the graben from both sides. Horsts are parallel blocks that remain between graben; the bounding faults of a horst typically dip away from the center line of the horst. Single or multiple graben can produce a rift valley. Half-g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant rocks, such as quartzite, given the right conditions. Subterranean drainage may limit surface water, with few to no rivers or lakes. However, in regions where the dissolved bedrock is covered (perhaps by debris) or confined by one or more superimposed non-soluble rock strata, distinctive karst features may occur only at subsurface levels and can be totally missing above ground. The study of ''paleokarst'' (buried karst in the stratigraphic column) is important in petroleum geology because as much as 50% of the world's hydrocarbon reserves are hosted in carbonate rock, and much of this is found in porous karst systems. Etymology The English word ''karst'' was borrowed from German in the late 19th century, which entered German much earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, and reached Mars on March 10, 2006. In November 2006, after five months of aerobraking, it entered its final science orbit and began its primary science phase. The cost to develop and operate MRO through the end of its prime mission in 2010 was . The spacecraft continues to operate at Mars, far beyond its intended design life. Due to its critical role as a high-speed data-relay for ground missions, NASA intends to continue the mission as long as possible, at least through the late 2020s. Pre-launch After the twin failures of the ''Mars Climate Orbiter'' and the Mars Polar Lander missions in 1999, NASA reorganized and replanned its Mars Exploration Program. In October 2000, NASA announced its reformulated Mars plans, which reduced the numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coprates Map
The Dez River ( fa, دز), the ancient Coprates (;James Knowles (1835) ''A Pronouncing and Explanatory Dictionary of the English Language'' el, Κοπράτης or Κοπράτας), is a tributary of the Karun River and is 400 km long. It is the site of the Dez Dam ) , image = , image_size = , image_caption = , image_alt = , location_map = Iran , location_map_size = , location_map_caption = , coordinates = , country = I .... References Rivers of Khuzestan Province Landforms of Khuzestan Province {{Iran-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction of the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. It consists of a 0.5m (19.7 in) aperture reflecting telescope, the largest so far of any deep space mission, which allows it to take pictures of Mars with resolutions of 0.3m/pixel (1ft/pixel), resolving objects below a meter across. HiRISE has imaged Mars exploration rovers on the surface, including the ''Opportunity'' rover and the ongoing ''Curiosity'' mission. History In the late 1980s, of Ball Aerospace & Technologies began planning the kind of high-resolution imaging needed to support sample return and surface exploration of Mars. In early 2001 he teamed up with Alfred McEwen of the University of Arizona to propose such a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)