|
Calais Lecordieri
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. The population of the city proper is 72,929; that of the urban area is 149,673 (2018).Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Calais (073), Commune de Calais (62193) INSEE Calais overlooks the , the narrowest point in the |
Subprefectures In France
In France, a subprefecture (french: sous-préfecture) is the commune which is the administrative centre of a departmental arrondissement that does not contain the prefecture for its department. The term also applies to the building that houses the administrative headquarters for an arrondissement. Senate (in French). The civil servant in charge of a subprefecture is the subprefect, assisted by a general secretary. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coquelles
Coquelles (; vls, Kalkwelle, lang) is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department near Calais in northern France. The town comprises a shopping centre, hotels and farm in Vieille Coquelles (old Coquelles), part of the L'Européenne autoroute (A16) and the Channel Tunnel terminal. The Eurotunnel Calais Terminal is located in Coquelles off the A16, exit 42. This is the terminus of shuttle services from the UK, as well as the terminus of the LGV Nord, whereby Eurostar services can travel into the Channel Tunnel. Population See also *Communes of the Pas-de-Calais department The following is a list of the 890 communes of the Pas-de-Calais department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):France–UK border Reference ...
|
Église Notre-Dame De Calais
Église Notre-Dame ("The Church of Our Lady") is a Roman Catholic parish church located on Rue de la Paix, in Calais, department of Pas-de-Calais, in northern France. It dates from the 12th century, and chiefly from the 14th century. Arguably, it is the only church built in the English perpendicular style in all of France. History The church was damaged during the early wars between France and England, especially in 1346-47, after the Battle of Crécy. Many of the kings and queens of France and England prayed here; and John Bourchier, 2nd Baron Berners is buried in the church choir. On 11 July 1469 George Plantagenet, 1st Duke of Clarence, the third surviving son of Richard Plantagenet, 3rd Duke of York, and Cecily Neville, and the brother of English Kings Edward IV and Richard III, was married to Isabel Neville, by Rt. Revd. George Neville, Archbishop of York. The tower of Notre Dame church was used as an observation point for the Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790), which us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways. Lighthouses mark dangerous coastlines, hazardous shoals, reefs, rocks, and safe entries to harbors; they also assist in aerial navigation. Once widely used, the number of operational lighthouses has declined due to the expense of maintenance and has become uneconomical since the advent of much cheaper, more sophisticated and effective electronic navigational systems. History Ancient lighthouses Before the development of clearly defined ports, mariners were guided by fires built on hilltops. Since elevating the fire would improve the visibility, placing the fire on a platform became a practice that led to the development of the lighthouse. In antiquity, the lighthouse functioned more as an entrance marker to ports than as a warning signal for reefs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Island
An artificial island is an island that has been constructed by people rather than formed by natural means. Artificial islands may vary in size from small islets reclaimed solely to support a single pillar of a building or structure to those that support entire communities and cities. Early artificial islands included floating structures in still waters or wooden or megalithic structures erected in shallow waters (e.g. crannógs and Nan Madol discussed below). In modern times artificial islands are usually formed by land reclamation, but some are formed by the incidental isolation of an existing piece of land during canal construction (e.g. Donauinsel, Ko Kret, and much of Door County, Wisconsin), or flooding of valleys resulting in the tops of former knolls getting isolated by water (e.g., Barro Colorado Island). One of the world's largest artificial islands, René-Levasseur Island, was formed by the flooding of two adjacent reservoirs. History Despite a popular image of mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Calais (1940)
The siege of Calais (1940) was a battle for the port of Calais during the Battle of France. The siege was fought at the same time as the Battle of Boulogne, just before Operation Dynamo, the evacuation of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) through Dunkirk. After the Franco-British counter-attack at the Battle of Arras (21 May), German units were held back to be ready to resist a resumption of the counter-attack on 22 May, despite the protests of General Heinz Guderian, the commander of the XIX , who wanted to rush north up the Channel coast to capture Boulogne, Calais and Dunkirk. An attack by part of the XIX was not authorised until on the night of By the time that the 10th Panzer Division was ready to attack Calais, the British 30th Infantry Brigade and 3rd Royal Tank Regiment (3rd RTR) had reinforced the French and British troops in the port. On 22 May, the British troops had established roadblocks outside the town and French rearguards skirmished with German armour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Calais (1558)
The French siege of Calais in early 1558 was part of the Italian War of 1551–1559 between France and England and their respective allies. It resulted in the seizure of the town by France. The Pale of Calais had been ruled by England since 1347, during the Hundred Years' War. By the 1550s, England was ruled by Mary I of England and her husband Philip II of Spain. When the Kingdom of England supported a Spanish invasion of France, Henry II of France sent Francis, Duke of Guise, against English-held Calais, defended by Thomas Wentworth, 2nd Baron Wentworth. Following the failure in mid-1557, a renewed attack captured the outlying forts of Nieullay and Rysbank and Calais was besieged. Background The victory of Louis XI of France over Charles the Bold in 1477 and the annexation of Picardy to the French royal domain marked the end of a status quo over the possession of Calais. For nearly a century the House of Valois had preferred to turn their armies towards Italy, rich and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lace
Lace is a delicate fabric made of yarn or thread in an open weblike pattern, made by machine or by hand. Generally, lace is divided into two main categories, needlelace and bobbin lace, although there are other types of lace, such as knitted or crocheted lace. Other laces such as these are considered as a category of their specific craft. Knitted lace, therefore, is an example of knitting. This article considers both needle lace and bobbin lace. While some experts say both needle lace and bobbin lace began in Italy in the late 1500s, there are some questions regarding its origins. Originally linen, silk, gold, or silver threads were used. Now lace is often made with cotton thread, although linen and silk threads are still available. Manufactured lace may be made of synthetic fiber. A few modern artists make lace with a fine copper or silver wire instead of thread. Etymology The word lace is from Middle English, from Old French ''las'', noose, string, from Vulgar Latin *' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to organolead compounds. Like the lighter members of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
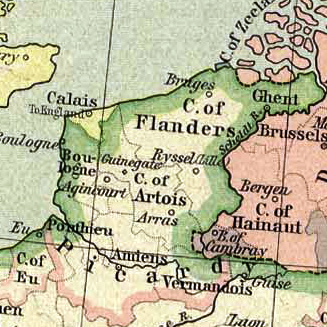
Pale Of Calais
The Pale of Calais was a territory in Northern France ruled by the monarchs of England for more than two hundred years from 1347 to 1558. The area, which was taken following the Battle of Crécy in 1346 and the subsequent Siege of Calais (1346–47), siege of Calais, was confirmed at the Treaty of Brétigny in 1360. It became an important economic centre for England in Europe’s textile trade centred in Flanders. The Pale, which was historically part of Flanders, also provided England with a permanent strategic, defensible outpost from which it could plan and launch military action on the continent. Its position on the English Channel meant it could be reinforced, garrisoned and supplied over the Straits of Dover, short distance by sea. The territory was bilingual with Middle English, English and Flemish commonly spoken. It was democratically represented in the Parliament of England by the Calais constituency. During the reign of Mary I, the Pale was unexpectedly retaken by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Calais (1346–1347)
The siege of Calais (4 September 1346 – 3 August 1347) occurred at the conclusion of the Crécy campaign, when an English army under the command of King Edward III of England successfully besieged the French town of Calais during the Edwardian phase of the Hundred Years' War. The English army of some 10,000 men had landed in northern Normandy on 12 July 1346. They embarked on a large-scale raid, or , devastating large parts of northern France. On 26 August 1346, fighting on ground of their own choosing, the English inflicted a heavy defeat on a large French army led by their king Philip VI at the Battle of Crécy. A week later the English invested the well-fortified port of Calais, which had a strong garrison under the command of Jean de Vienne. Edward made several unsuccessful attempts to breach the walls or to take the town by assault, either from the land or seaward sides. During the winter and spring the French were able to run in supplies and reinforcements by s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |