|
Cactus Alkaloids
Cactus alkaloids are alkaloids that occur in cactus. Structurally, they are tetrahydroisoquinolines and phenylethylamines. Occurrence and Representatives Cactus alkaloids are found in the cactus family, particularly in the genus ''Lophophora'', which alone contains over 40 known compounds. The alkaloids can be categorized into two groups, derived from phenethylamine and tetrahydroisoquinoline, respectively. The primary alkaloid in ''Lophophora williamsii'' (in terms of quantity) is mescaline, followed by pellotine. In the species ''Lophophora diffusa'' and ''Lophophora fricii'', the primary alkaloid is pellotine, followed by anhalonidine in ''L. fricii'' and anhalamine in ''L. diffusa''. In species outside the genus ''Lophophora'', the content and variety of cactus alkaloids are significantly lower, but some contain compounds such as hordenine, N-methyltyramine, mescaline, or pellotine. File:Lophophora_williamsii_Blüte.JPG, ''Lophophora williamsii'' File:2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloids
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , |
Anhalidine
Anhalidine is a naturally occurring tetrahydroisoquinoline based alkaloid which can be isolated from ''Lophophora williamsii The peyote (; ''Lophophora williamsii'' ) is a small, spineless cactus which contains psychoactive alkaloids, particularly mescaline. ''Peyote'' is a Spanish word derived from the Nahuatl (), meaning "caterpillar cocoon", from a root , "to ...''; it has also been detected other cactii and several species of '' Acacia''. It is part of a family of compounds that are structurally related to mescaline. See also * Pellotine References Lophophora Isoquinoline alkaloids Norsalsolinol ethers {{alkaloid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhalamine
Anhalamine is a naturally occurring alkaloid which can be isolated from ''Lophophora williamsii''. It is structurally related to mescaline. See also * Anhalinine * Anhalonidine * Pellotine Pellotine is an alkaloid found in ''Lophophora'' species. Pellotine is slightly narcotic, and has been used by Native Americans as a constituent of peyote for sacramental purposes. Psychological and physiological effects 8-10 mg of isolated ... References Isoquinoline alkaloids Norsalsolinol ethers {{alkaloid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Group
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. Aromatic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodioxole
1,3-Benzodioxole (1,2-methylenedioxybenzene) is an organic compound with the formula CHOCH. The compound is classified as benzene derivative and a heterocyclic compound containing the methylenedioxy functional group. It is a colorless liquid. Although benzodioxole is not particularly important, many related compounds containing the methylenedioxyphenyl group are bioactive, and thus are found in pesticides and pharmaceuticals. Preparation 1,3-Benzodioxole can be synthesized from catechol with Diiodomethane, disubstituted halomethanes. See also * 1,4-Benzodioxine * MDMA * Methylenedioxy * Safrole * Piperonal References Benzodioxoles, {{heterocyclic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These terms are commonly used in chemistry, biochemistry, soil science, and the biological sciences. In biological systems, methylation is catalyzed by enzymes; such methylation can be involved in modification of heavy metals, regulation of gene expression, regulation of protein function, and RNA processing. In vitro methylation of tissue samples is also one method for reducing certain histological staining artifacts. The reverse of methylation is demethylation. In biology In biological systems, methylation is accomplished by enzymes. Methylation can modify heavy metals, regulate gene expression, RNA processing and protein function. It has been recognized as a key process underlying epigenetics. Methanogenesis Methanogenesis, the process th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor (chemistry), precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is biosynthesis, synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopaminergic pathway, dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward system, reward-motivated behavior. The anticipa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
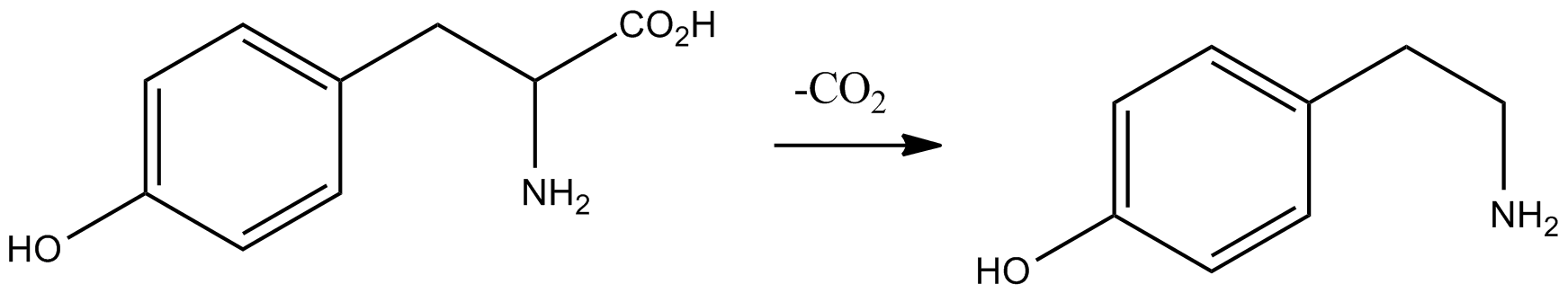
Tyramine
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier, resulting in only non-psychoactive peripheral sympathomimetic effects following ingestion. A hypertensive crisis can result, however, from ingestion of tyramine-rich foods in conjunction with the use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Occurrence Tyramine occurs widely in plants and animals, and is metabolized by various enzymes, including monoamine oxidases. In foods, it often is produced by the decarboxylation of tyrosine during fermentation or decay. Foods that are fermented, cured, pickled, aged, or spoiled have high amounts of tyramine. Tyramine levels go up when foods are at room temperature or go past their freshness date. Specific foods containing considerable amounts of tyramine include: * strong or ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |