|
CLEC5A
C-type lectin domain family 5 member A (CLEC5A), also known as C-type lectin superfamily member 5 (CLECSF5) and myeloid DAP12-associating lectin 1 (MDL-1) is a C-type lectin that in humans is encoded by the ''CLEC5A'' gene. Structurally MDL-1 is a type II transmembrane protein with a short cytoplasmic tail and without signaling motifs, therefore it requires association with the adaptor protein DAP12 to generate signals via Syk pathway. MDL-1 is highly expressed on myeloid lineages like neutrophil, monocyte, macrophage and also osteoclast, microglia and dendritic cells. Activation of MDL-1 induces production of many cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8 and IL-17A) and chemokines ( MIP-1α, RANTES, IP-10, MDC). MDL-1 also amplifies innate immune response. Viral pathology The most known ligand for CLEC5A is dengue virus (DV). Activated CLEC5A by binding to the dengue virion leads to phosphorylation of DAP12 and through Syk pathway are induced proinflammatory cytokines. CLEC5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-type Lectin
A C-type lectin (CLEC) is a type of carbohydrate-binding protein known as a lectin. The C-type designation is from their requirement for calcium for binding. Proteins that contain C-type lectin domains have a diverse range of functions including cell-cell adhesion, immune response to pathogens and apoptosis. Classification Drickamer ''et al.'' classified C-type lectins into 7 subgroups (I to VII) based on the order of the various protein domains in each protein. This classification was subsequently updated in 2002, leading to seven additional groups (VIII to XIV). Most recently, three further subgroups were added (XV to XVII). CLECs include: * CLEC1A, CLEC1B * CLEC2A, CLEC2B, CD69 (CLEC2C), CLEC2D, CLEC2L * CLEC3A, CLEC3B * CLEC4A, CLEC4C, CLEC4D, CLEC4E, CLEC4F, CLEC4G, ASGR1 (CLEC4H1), ASGR2 (CLEC4H2), FCER2 (CLEC4J), CD207 (CLEC4K), CD209 (CLEC4L), CLEC4M * CLEC5A * CLEC6A * CLEC7A * OLR1 (CLEC8A) * CLEC9A * CLEC10A * CLEC11A * CLEC12A, CLEC12B * CD302 (CLEC13A), LY75 (CLEC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 8
Interleukin 8 (IL-8 or chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 8, CXCL8) is a chemokine produced by macrophages and other cell types such as epithelial cells, airway smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Endothelial cells store IL-8 in their storage vesicles, the Weibel–Palade bodies. In humans, the interleukin-8 protein is encoded by the ''CXCL8'' gene. IL-8 is initially produced as a precursor peptide of 99 amino acids which then undergoes cleavage to create several active IL-8 isoforms. In culture, a 72 amino acid peptide is the major form secreted by macrophages. There are many receptors on the surface membrane capable of binding IL-8; the most frequently studied types are the G protein-coupled serpentine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2. Expression and affinity for IL-8 differs between the two receptors (CXCR1 > CXCR2). Through a chain of biochemical reactions, IL-8 is secreted and is an important mediator of the immune reaction in the innate immune system response. Functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza A Virus Subtype H5N1
Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 (A/H5N1) is a subtype of the influenza A virus, which causes the disease avian influenza (often referred to as "bird flu"). It is enzootic (maintained in the population) in many bird populations, and also panzootic (affecting animals of many species over a wide area). A/H5N1 virus can also infect mammals (including humans) that have been exposed to infected birds; in these cases, symptoms are frequently severe or fatal. A/H5N1 virus is shed in the saliva, mucus, and feces of infected birds; other infected animals may shed bird flu viruses in respiratory secretions and other body fluids (such as milk). The virus can spread rapidly through poultry flocks and among wild birds. An estimated half billion farmed birds have been slaughtered in efforts to contain the virus. Symptoms of A/H5N1 influenza vary according to both the strain of virus underlying the infection and on the species of bird or mammal affected. Classification as either Low Pathogeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon Type I
The type-I interferons (IFN) are cytokines which play essential roles in inflammation, immunoregulation, tumor cells recognition, and T-cell responses. In the human genome, a cluster of thirteen functional IFN genes is located at the 9p21.3 cytoband over approximately 400 kb including coding genes for IFNα (''IFNA1, IFNA2, IFNA4, IFNA5, IFNA6, IFNA7, IFNA8, IFNA10, IFNA13, IFNA14, IFNA16, IFNA17'' and ''IFNA21''), IFNω (''IFNW1''), IFNɛ (''IFNE''), IFNк (''IFNK'') and IFNβ (''IFNB1''), plus 11 IFN pseudogenes. Interferons bind to interferon receptors. All type I IFNs bind to a specific cell surface receptor complex known as the IFN-α receptor ( IFNAR) that consists of IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 chains. Type I IFNs are found in all mammals, and homologous (similar) molecules have been found in birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish species. Sources and functions IFN-α and IFN-β are secreted by many cell types including lymphocytes ( NK cells, B-cells and T-cells), macropha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
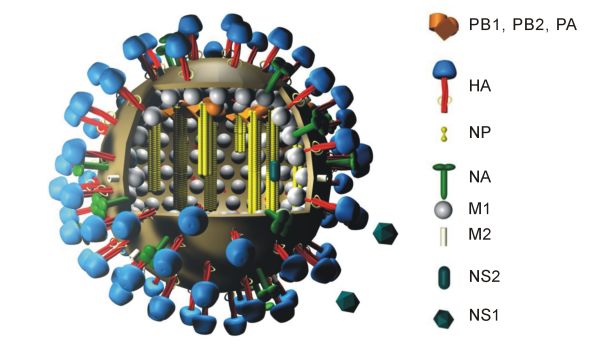
Hemagglutinin (influenza)
Influenza hemagglutinin (HA) or haemagglutinin#Notes, [p] (British English) is a homotrimeric glycoprotein found on the surface of influenza viruses and is integral to its infectivity. Hemagglutinin is a class I fusion protein, having multifunctional activity as both an attachment factor and membrane fusion protein. Therefore, HA is responsible for binding influenza viruses to sialic acid on the Cell membrane, surface of target cells, such as cells in the Respiratory tract, upper respiratory tract or erythrocytes, resulting in the Receptor-mediated endocytosis, internalization of the virus. Additionally, HA is responsible for the fusion of the viral envelope with the late endosome, endosomal membrane once exposed to low pH (5.0–5.5). The name "hemagglutinin" comes from the protein's ability to cause red blood cells (i.e., erythrocytes) to clump together (i.e., Agglutination (biology), agglutinate) ''in vitro''. Subtypes Hemagglutinin (HA) in influenza A virus (IAV) has at lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
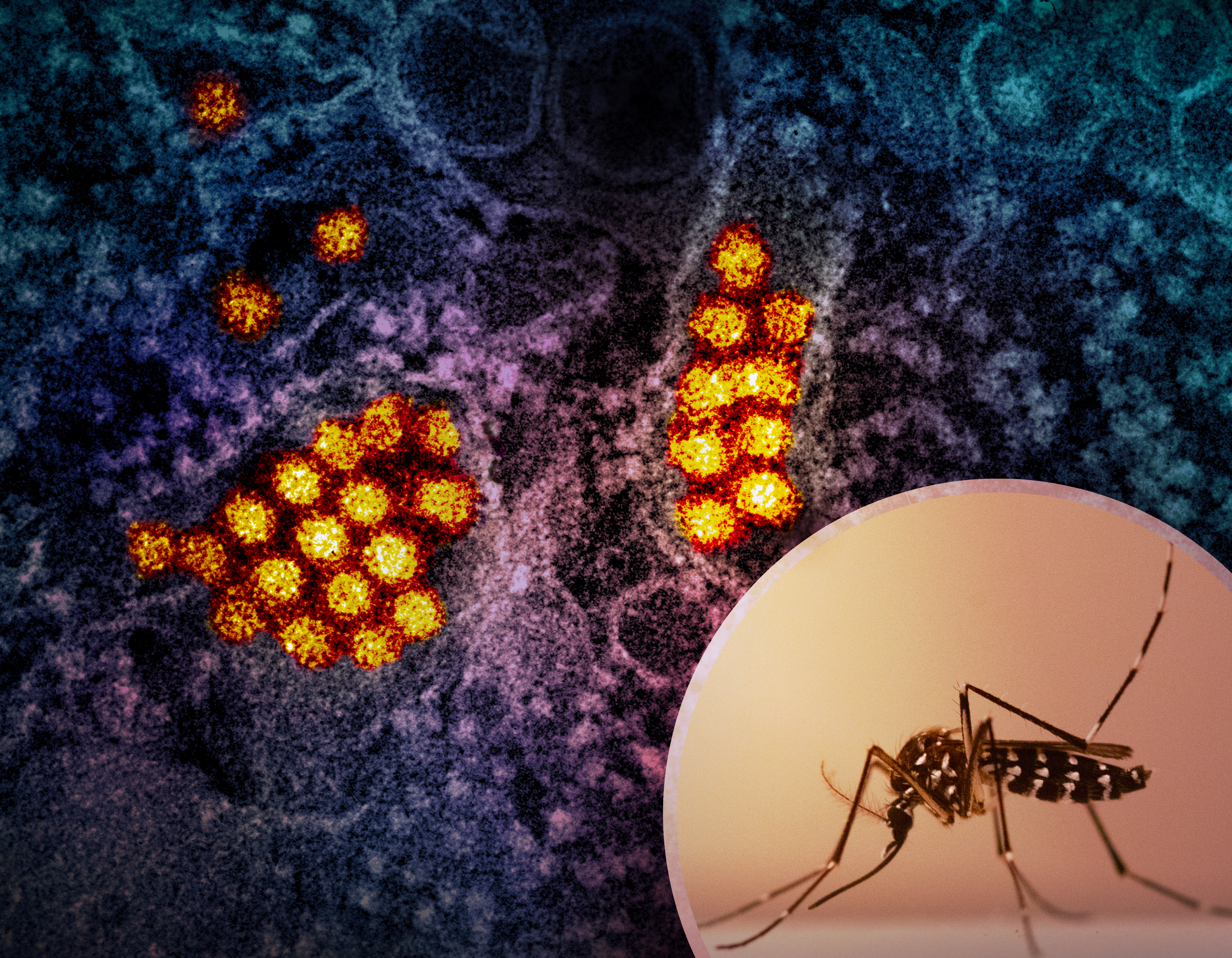
Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue virus, prevalent in tropical and subtropical areas. Asymptomatic infections are uncommon, mild cases happen frequently; if symptoms appear, they typically begin 3 to 14 days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic skin itching and skin rash. Recovery generally takes two to seven days. In a small proportion of cases, the disease develops into severe dengue (previously known as dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome) with bleeding, low levels of blood platelets, blood plasma leakage, and dangerously low blood pressure. Dengue virus has four confirmed serotypes; infection with one type usually gives lifelong immunity to that type, but only short-term immunity to the others. Subsequent infection with a different type increases the risk of severe complications, so-called Antibody-Dependent Enhancement (ADE). The symptoms of dengue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dengue Virus
Dengue virus (DENV) is the cause of dengue fever. It is a mosquito-borne, single positive-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''; genus '' Flavivirus''. Four serotypes of the virus have been found, and a reported fifth has yet to be confirmed,Dwivedi, V. D., Tripathi, I. P., Tripathi, R. C., Bharadwaj, S., & Mishra, S. K. (2017). Genomics, proteomics and evolution of ''Dengue virus''. Briefings in functional genomics.16(4): 217–227, https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/elw040 all of which can cause the full spectrum of disease. Nevertheless, the mainstream scientific community's understanding of dengue virus may be simplistic as, rather than distinct antigenic groups, a continuum appears to exist. This same study identified 47 strains of ''dengue virus''. Additionally, coinfection with and lack of rapid tests for Zika virus and chikungunya complicate matters in real-world infections. ''Dengue virus'' has increased dramatically within the last 20 years, becoming one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CXCL10
C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10) also known as Interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP-10) or small-inducible cytokine B10 is an 8.7 kDa protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CXCL10'' gene. C-X-C motif chemokine 10 is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family. Gene The gene for CXCL10 is located on human chromosome 4 in a cluster among several other CXC chemokines. Function CXCL10 is secreted by several cell types in response to IFN-γ. These cell types include monocytes, endothelial cells and fibroblasts. CXCL10 has been attributed to several roles, such as chemoattraction for monocytes/macrophages, T cells, NK cells, and dendritic cells, promotion of T cell adhesion to endothelial cells, antitumor activity, and inhibition of bone marrow colony formation and angiogenesis. This chemokine elicits its effects by binding to the cell surface chemokine receptor CXCR3. Structure The three-dimensional crystal structure of this chemokine has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCL5
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 (also CCL5) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CCL5'' gene. The gene has been discovered in 1990 by ''in situ'' hybridisation and it is localised on 17q11.2-q12 chromosome. It is also known as RANTES (regulated on activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted). RANTES was first described by Dr. Tom Schall who named the protein, the original source of the name Rantes was from the Argentine movie '' Man Facing Southeast'' about an alien who shows up in a mental ward who was named Rantés, the rather clunky acronym was only made to fit the name. Function CCL5 belongs to the CC subfamily of chemokines, due to its adjacent cysteines near N terminus. It is an 8kDa protein acting as a classical chemotactic cytokine or chemokine. It consists of 68 amino acids. CCL5 is proinflammatory chemokine, recruiting leukocytes to the site of inflammation. It is chemotactic for T cells, eosinophils, and basophils, but also for monocytes, natural- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCL3
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 (CCL3) also known as macrophage inflammatory protein 1-alpha (MIP-1-alpha) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCL3'' gene. Function CCL3 is a cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family that is involved in the acute inflammatory state in the recruitment and activation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes through binding to the receptors CCR1, CCR4 and CCR5. Sherry et al. (1988) demonstrated 2 protein components of MIP1, called by them alpha (CCL3, this protein) and beta ( CCL4). CCL3 produces a monophasic fever of rapid onset whose magnitude is equal to or greater than that of fevers produced with either recombinant human tumor necrosis factor or recombinant human interleukin-1. However, in contrast to these two endogenous pyrogens, the fever induced by MIP-1 is not inhibited by the cyclooxygenase inhibitor ibuprofen and CCL3 may participate in the febrile response that is not mediated through prostaglandin synthesis and clinicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 17
Interleukin 17 family (IL17 family) is a family of pro-inflammatory cystine knot cytokines. They are produced by a group of T helper cell known as T helper 17 cell in response to their stimulation with IL-23. Originally, Th17 was identified in 1993 by Rouvier ''et al.'' who isolated IL17A transcript from a rodent T-cell hybridoma. The protein encoded by ''IL17A'' is a founding member of IL-17 family (see below). IL17A protein exhibits a high homology with a viral IL-17-like protein () encoded in the genome of T-lymphotropic rhadinovirus '' Herpesvirus saimiri''. In rodents, IL-17A is often referred to as CTLA8. The biologically active IL-17 interacts with type I cell surface receptor IL-17R. In turn, there are at least three variants of IL-17R referred to as IL17RA, IL17RB, and IL17RC. After binding to the receptor, IL-17 activates several signalling cascades that, in turn, lead to the induction of chemokines. Acting as chemoattractants, these chemokines recruit t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |